RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Natural Resources
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Natural Resources Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 9. Students can also read RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 9 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The why do we fall ill important questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Important Questions Natural Resources
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
The atmosphere of the Earth is heated by radiations which are mainly :
(a) radiated by the Sun
(b) re-radiated by land
(c) re-radiated by water
(d) re-radiated by land and water
Answer:
(d) re-radiated by land and water
Question 2.
If there were no atmosphere around the Earth, the temperature of the Earth will :
(a) increase
(b) go on decreasing
(c) increase during day and decrease during night
(d) be unaffected
Answer:
(c) increase during day and decrease during night
Question 3.
One of the following factors does not lead to soil formation in nature :
(a) The Sun
(b) Water
(c) Wind
(d) Polythene bags
Answer:
(d) Polythene bags
Question 4.
The two forms of oxygen found in the atmosphere are :
(a) water and ozone
(b) water and oxygen
(c) ozone and oxygen
(d) water and carbon dioxide
Answer:
(c) ozone and oxygen

Question 5.
The process of nitrogen-fixation by bacteria does not take place in the presence of:
(a) molecular form of hydrogen
(b) elemental form of oxygen
(c) water
(d) elemental form of nitrogen
Answer:
(b) elemental form of oxygen
Question 6.
Rainfall patterns depend on :
(a) the underground water table.
(b) the number of water bodies in an area.
(c) the density pattern of human population in an area.
(d) the prevailing season in an area.
Answer:
(b) the number of water bodies in an area.
Question 7.
Among the given options, which one is not correct for the use of large amount of fertilisers and pesticides?
(a) They are efco-friendly.
(b) They turn the fields barren after some time.
(c) They adversely affect the useful component from the soil.
(d) They destroy the soil fertility.
Answer:
(a) They are efco-friendly.
Question 8.
One of the following processes is not a step involved in the water-cycle operating in nature:
(a) Evaporation
(b) Transpiration
(c) Precipitation
(d) Photosynthesis
Answer:
(d) Photosynthesis

Question 9.
Which of the following is not a greenhouse gas?
(a) Methane
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Carbon monoxide
(d) Ammonia
Answer:
(d) Ammonia
Question 10.
Which step is not involved in the carbon cycle?
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Transpiration
(c) Respiration
(d) Burning of fossil fuels
Answer:
(b) Transpiration
Question 11.
‘Ozone-hole’ means:
(a) A large sized hole in the ozone layer
(b) Thinning of the ozone layer
(c) Small holes scattered in the ozone layer
(d) Thickening of ozone in the ozone layer
Answer:
(b) Thinning of the ozone layer
Question 12.
Ozone-layer is getting depleted because of:
(a) excessive use of automobiles .
(b) excessive formation of industrial units
(c) excessive use of man-made compounds containing both fluorine and chlorine
(d) excessive deforestation.
Answer:
(c) excessive use of man-made compounds containing both fluorine and chlorine
Question 13.
Which of the following is a recently originated problem of environment?
(a) Ozone layer depletion
(b) Greenhouse effect
(c) Global warming
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these

Question 14.
Top-soil contains the following:
(a) Humus and living organisms only
(b) Humus and soil particles only
(c) Humus, living organisms and plants
(d) Humus, living organisms and soil particles.
Answer:
(d) Humus, living organisms and soil particles.
Question 15.
Major source of mineral in soil is the:
(a) parent rock from which soil is formed
(b) plants
(c) animals
(d) bacteria
Answer:
(a) parent rock from which soil is formed
Question 16.
Total Earth’s surface covered by water is:
(a) 75%
(b) 60%
(c) 85%
(d) 50%
Answer:
(a) 75%
Question 17.
Biotic component of biosphere is not constituted by:
(a) producers
(b) consumers
(c) decomposer
(d) air
Answer:
(d) air
Question 18.
An increase in carbon dioxide content in the atmosphere would not cause:
(a) More heat to be retained by the environment
(b) Increase in photosynthesis in plants
(c) Global warming
(d) Abundance of desert plants
Answer:
(d) Abundance of desert plants

Question 19.
Oxygen is returned to the atmosphere mainly by:
(a) burning of fossil fuel
(b) respiration
(c) photosynthesis
(d) fungi
Answer:
(c) photosynthesis
Question 20.
Low visibility during cold weather is due to :
(a) formation of fossil fuel
(b) unburnt carbon particles or hydrocarbons suspended in air
(c) lack of adequate power supply
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) unburnt carbon particles or hydrocarbons suspended in air
Question 21.
Growth of lichens on barren rocks is followed by the growth of:
(a) moss
(b) ferns
(c) gymnosperms
(d) algae
Answer:
(a) moss
Question 22.
Marked temperature changes in aquatic environment can affect:
(a) breeding of animals
(b) more growth of aquatic plants
(c) process of digestion in animals
(d) availability of nutrients
Answer:
(a) breeding of animals
Question 23.
Soil erosion can be prevented by:
(a) raising forests
(b) deforestation
(c) excessive use of fertiliser
(d) overgrasing by animals
Answer:
(a) raising forests

Question 24.
Oxygen is harmful for:
(a) ferns
(b) nitrogen fixing bacteria
(c) chara
(d) mango tree
Answer:
(b) nitrogen fixing bacteria
Question 25.
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Outermost layer of earth is called ...............
(b) Nitrogen fixation process by bacteria doesn't take place in presence of ...............
(c) Above ............... hole in ozone layer is found.
(d) ............... is the main factor in the formation of soil.
(e) Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen combine with water to form ............... and ............... respectively.
Answer:
(a) lithosphere
(b) oxygen
(c) Antartica
(d) Humus
(e) sulphuric acid, nitric add
Question 26.
Match the column (A) with the column (B).
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
Compound |
Main element |
|
(i) Nitrous acid |
(a) Chlorine |
|
(ii) Graphite |
(b) Oxygen |
|
(iii) Ozone |
(c) Nitrogen |
|
(iv) C.F.C. |
(d) Carbon |
Answer:
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
Compound |
Main element |
|
(i) Nitrous acid |
(c) Nitrogen |
|
(ii) Graphite |
(d) Carbon |
|
(iii) Ozone |
(b) Oxygen |
|
(iv) C.F.C. |
(a) Chlorine |

Question 27.
Match the column (A) with the column (B).
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
(i) Combustion |
(a) C.F.C. |
|
(ii) Greenhouse effect |
(b) N2 |
|
(iii) Ozone depletion |
(c) CO2 |
|
(iv) Nitrogen fixation |
(d) O2 |
Answer:
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
(i) Combustion |
(d) O2 |
|
(ii) Greenhouse effect |
(c) CO2 |
|
(iii) Ozone depletion |
(a) C.F.C. |
|
(iv) Nitrogen fixation |
(b) N2 |
Question 28.
Read the statements carefully and identify whether they are True or False-
1. Ozone is more poisonous than oxygen.
2. Temperature on moon surface lies between 110° C and 190° C.
3. Hydrosphere is the outermost layer of the earth.
4. CFC is an inorganic compound formed from chlorine and fluorine.
5. Wind direction in day time is from sea to land.
Answer:
1. True
2. False
3. False
4. False
5. True

Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the three processes which use oxygen.
Answer:
Combustion, respiration and in the formation of oxides of nitrogen.
Question 2.
Give two natural resources available on the Earth.
Answer:
Water and air.
Question 3.
Write one example of biotic component of the biosphere.
Answer:
All animals, plants and microorganisms.
Question 4.
Identify which of the following are not the part of biotic environment : soil, plants, fish, air, insects.
Answer:
Soil, air.
Question 5.
Name two oxides formed by burning of fossil fuels, which are responsible for acid rain.
Answer:
The oxides of nitrogen and sulphur:
- Sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide.
- Nitrous oxide and nitrogen dioxide.

Question 6.
Mention the two forms of precipitation in nature when the temperature of air is very low.
Answer:
(i) Fog and smog, (ii) Hail, (iii) Mist (any two).
Question 7.
Name the factor responsible for change in rainfall patterns in India.
Answer:
Rainfall patterns are decided by the prevailing wind patterns. In large part of India, rains are mostly brought by South-West or North-East monsoons.
Question 8.
Combustion of fossil fuels results in the increase of suspended particles in the air. What are these particles?
Answer:
The suspended particles in the air could be unburnt carbon particles or hydrocarbons which lead to smog.
Question 9.
How the frozen water between cracked rocks causes the cracks to widen?
Answer:
The water inside the cracked rocks expands on freezing. When it expands, its volume increases and it causes the cracks to widen.
Question 10.
Name two gases which cause greenhouse effect.
Answer:
- Carbon dioxide,
- Methane.

Question 11.
Name two biologically important compounds that contain both oxygen and nitrogen.
Answer:
Proteins and nucleic adds (DNA and RNA).
Question 12.
What is the function of humus in soil?
Answer:
Humus causes the soil to become more porous and allows water and air to penetrate deep underground.
Question 13.
Name two essential biological molecules in which oxygen is present.
Answer:
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- Fats aid lipids
- Nucleic adds (any two)
Question 14.
What is the greenhouse effect?
Answer:
Some gases prevent the escape of heat from the Earth. An increase in the percentage of such gases in the atmosphere would cause the average temperatures to increase worldwide and this is called the greenhouse effect.
Question 15.
List any two traditional systems of water harvesting.
Answer:
Two traditional systems of water harvesting are:
Collection of water in ponds and construction of small Earthen dams.

Question 16.
Which cycle is known as the perfect cycle in biosphere? Why?
Answer:
Nitrogen cycle is known as the perfect cycle in biosphere as it maintains the amount of nitrogen in atmosphere, water and soil.
Question 17.
Define weathering.
Answer:
The process of breaking down of rocks into small, fine mineral particles is called weathering.
Question 18.
Write the different means which cause weathering.
Answer:
The weathering may occur due to physical, chemical or biological means.
Question 19.
Write the composition of soil.
Answer:
Soil is a mixture and composed of small particles of rocks of different sizes, humus and various microorganisms.
Question 20.
On what basis is the type of soil decided?
Answer:
The type of soil decided by the average size of particles found in it.

Question 21.
What is soil erosion?
Answer:
The removal of topsoil which is rich in humus and nutrients by flowing water or wind is known as soil erosion. All soil may get eroded if this process continues further. It may lead to the loss of all valuable resources because nothing grows as such on the rocks.
Question 22.
What are the biochemical cycles?
Answer:
The transfer of energy and matter between the biotic components of the biosphere is called biochemical cycle.
Question 23.
What is ozone hole? Where is it found? What is its effect?
Answer:
There is a layer of ozone in the upper regions of the atmosphere which gets depleted due to chlorofluorocarbons and created a hole that is called ozone hole. It is found above North Pole.
Question 24.
Fertile soil has lots of humus. Why?
Answer:
Fertile soils are rich in organisms that decompose dead organic matter forming humus. Humus gives minerals, absorbs water and makes soil porous.
Question 25.
Define paedogenesis.
Answer:
The process of formation of soil is called paedogenesis.

Question 26.
How does ozone affect the environment?
Answer:
Ozone absorbs the harmful radiations from sun and, thereby protects many forms of life from getting damaged.
Question 27.
Define anaerobic degradation.
Answer:
Breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms when oxygen is not present is known as anaerobic degradation.
Question 28.
Lichens are called pioneer colonisers of bare rock. How can they help in formation of soil?
Answer:
Lichens are called pioneer colonisers of bare rock because they release substances which break down the stones resulting in the formation of soil.
Question 29.
Why does Moon have very cold and very hot temperature variations, e.g. from -190°C to 110°C even though it is at the same distance from the Sun as the Earth is?
Answer:
Absence of atmosphere on the Moon.
Question 30.
What is the importance of carbon cycle?
Answer:
It helps to maintain a constant level of CO2 in the Earth’s atmosphere which further help in maintaining Earth’s temperature through greenhouse effect.

Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the two forms of oxygen found in the atmosphere?
Answer:
- Elemental oxygen is normally found in the form of a diatomic molecule (O2) in the lower regions of the atmosphere to the extent of 21%. It is non-poisonous form of oxygen.
- But in the upper part of the atmosphere (stratosphere), it occurs in the form of ozone, containing three atoms of oxygen and having the molecular formula O3. It is the poisonous form of oxygen.
Question 2.
What are the different ways in which water gets polluted? How does it affect the life forms?
Answer:
The addition of undesirable substances like fertilizers and pesticides, mercury salts in water can cause cholera produced by the bacteria.
The removable of desired substances like oxygen from the water adversely affect the aquatic organisms.
A sudden change in temperature in water bodies would be dangerous and affect their breeding. The eggs and larvae are affected by the change in temperature.
Question 3.
List the causes that affect the life forms that are found in water bodies in various ways. Name the element present in coal other than carbon that releases harmful gases during combustion of coal.
Answer:
- Excess of fertilisers and pesticides used in the farms are washed into water bodies.
- Dumping of sewage from dwelling places into water bodies.
- Release of contaminated water from industries.
- Release of water from dams affects the temperature of fiver.
- Sulphur and nitrogen.

Question 4.
What is the main cause of increase in CO2 in atmosphere? Explain the harmful effect of increase in CO2 content in atmosphere.
Answer:
The main cause of increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is industrial revolution. Increase in carbon dioxide gives rise to greenhouse effect and global warming. This causes imbalance in nature, affects monsoons and rainfall.
Question 5.
Name the various organisms involved in nitrogen cycle.
Answer:
- Nitrogen fixing bacteria, e.g. Rhizobium, Azotobacter.
- Bacteria which convert complex nitrogenous organic compounds (proteins) into ammonia, e.g. Actinomyces.
- Nitrifying bacteria that convert ammonia into nitrates, e.g. Nitrosomonas and nitrobactor.
- Denitrifying bacteria, e.g. Pseudomonas.
Question 6.
What are the three ways by which CO2 is returned back into atmosphere?
Answer:
The three ways by which CO2 is returned back into atmosphere are:
- Decomposition of dead organic matter.
- Respiration by both plants and animals.
- Formation of gaseous waste by the combustion of fuels like coal, wood and petrol.
Question 7.
Mention three ways by which atmosphere regulates the average temperature on Earth.
Answer:
- As the air is a bad conductor of heat, therefore, the atmosphere keeps the average temperature of the Earth fairly steady during the day even during the course of the whole year.
- The atmosphere prevents the sudden increase in temperature in daytime.
- It slows down the escape of heat into the outer space.

Question 8.
(a) Explain the formation of acid rain.
(b) What does the presence of smog in an area indicate?
Answer:
(a) Add rain is the rainwater which have excessive amount of acids, i.e. sulphuric acid and nitric acid.
These adds are formed by the reaction of oxides of sulphur and nitrogen with water.
The oxides of sulphur and nitrogen are produced by combustion of fossil fuels in industries, automobiles, thermal power plants and domestic appliances, etc.
The sulphur and nitrogen, present in fossil fuels form these oxides by reacting with oxygen of air by the process of combustion.
(b) The presence of smog in an area indicates the high percentage of smoke released in the air by combustion of fossil fuel in industries or automobiles. It is an indicator of air pollution.
Question 9.
What are the harmful effects of air pollution?
Answer:
- Respiratory problems like sneezing, allergy, asthma or bronchitis in some persons.
- Cause add rain which leads to deterioration of metals and other building material.
- Cause global warming which leads to change in the climate of the Earth.
- Carbon monoxide may lead to many problems of respiratory system.
- Smog, which reduces the visibility as well as causes respiratory ailments.
Question 10.
Mention any three important roles of water required for organisms on the Earth’s surface.
Answer:
- All cellular processes take place in water medium.
- Water regulates body temperature.
- Water is required for transportation of nutrients from one part of the body to the other.
Question 11.
(a) Explain, how soil pollution is caused?
(b) Write three ways to prevent soil pollution.
Answer:
(a) The soil pollution may be caused by throwing the industrial wastes in vacant sites viz., along the roads, railway tracks, etc. The wastes from residences, cattle sheds, industries, agricultural fields, etc. also pollute the soil. The excessive use of fertilisers and pesticides pollutes the soil.
(b) Three ways to prevent soil pollution:
- By judicious use of fertilisers and pesticides.
- By proper management of disposal of household waste.
- Terrace farming should be practiced.

Question 12.
Explain the following terms:
(i) Nitrogen fixation
(ii) Nitrification
(iii) Denitrification.
Answer:
(i) The process in which atmospheric nitrogen is converted into usable forms like ammonia, nitrates, nitrites or NO2, etc. is called nitrogen fixation.
(ii) The process of formation of nitrites and then to nitrates from ammonium compounds is called nitrification.
(iii) The process of conversion of some ammonium compounds, nitrites and nitrates into molecular nitrogen is called denitrification.
Question 13.
In what forms the water is found on the Earth’s surface? Describe in brief.
Answer:
Most of the water on Earth’s surface is found in the form of liquid in seas, oceans, rivers, lakes, ponds, etc. It is found in the form of ice (solid) in the ice-caps on mountain peaks and in Polar Regions. Water is also found in vapour state when it evaporates at the surface of water bodies, as moisture in the atmosphere, air transpired by plants and air exhaled by animals.
Question 14.
‘A change in temperature in the water body affects aquatic organisms.’ Explain in brief.
Answer:
Change in the water temperature can affect the aquatic life in the following ways:
- It can encourage the growth of some life forms and harm some other life forms.
- This affects the balance between various organisms which had been established in that system.
- This can lead to removal of desirable substances like oxygen and other nutrients from water bodies.
- The eggs and larvae of various animals are particularly susceptible to temperature changes.
So such aquatic life forms may become extinct from the related water bodies. Thus, the breeding of aquatic organisms will be affected.
Question 15.
(a) In what ways the water cycle helps the marine organisms?
(b) ‘The biosphere is a dynamic but stable system.’ Justify this statement.
Answer:
(a) (i) Water is capable of dissolving a large number of substances.
(ii) Water flows through rocks containing soluble minerals.
(iii) Some of the minerals get dissolved in the water which is carried by water bodies and made available to aquatic organisms.
(b) (i) There is a constant interaction between the biotic and abiotic components of the biosphere.
(ii) These interactions consist of a transfer of matter and energy between the different components of the biosphere and make it a dynamic but stable system.

Question 16.
Describe how lichens and big trees influence the formation of soil.
Answer:
- Lichens grow on the surface of rocks and release substances that breaks down the rock surface.
- Moss grows on this surface and breaks it further.
- The roots of trees grow into rocks, form cracks and widen them further to form soil.
Question 17.
(a) Explain how forests influence the quality of our air, soil and water resources.
(b) State two ways in which atmospheric carbon dioxide is fixed.
Answer:
(a) Forests influence the quality of our air, soil and water resources in many ways :
- The vegetation/trees in the forest purify the air by the process of photosynthesis.
- The roots of trees and plants bind the soil and prevent the soil erosion as well as floods.
- The roots absorb the water present in the soil as groundwater.
- The water released by the process of transpiration as water vapour becomes a part of atmosphere which helps to bring the rain.
- The forests also help to regulate the temperature of air.
(b) (i) Carbon dioxide is fixed into carbohydrate by the process of photosynthesis.
(ii) The carbon dioxide is fixed in the form of carbonates and bicarbonates; compounds and endoskeletons and exoskeletons of various animals are formed from carbonate salts.
Question 18.
List any four disadvantages of using fossil fuels for the production of energy.
Answer:
Disadvantages:
- Fossil fuels cause pollution.
- They also cause acid rain.
- They disturb ecology.
- They cannot be reused, i.e. they are non-renewable.
Question 19.
Suggest three ways to maintain a balance between environment and development to survive.
Answer:
The three ways to maintain a balance between environment and development to survive are as follows:
- Forest resources should be used in an environment friendly and developmentally sound manner.
- Instead of losing non-renewable natural resources, use of renewable natural resources should be preferred.
- Wastewater generated by industries should be recycled.
- We should use natural resources cautiously so that economic growth and ecological-conservation go hand in hand.

Question 20.
What are the consequences of global warming?
Answer:
- An increase in temperature of Earth even by 1°C may lead to melting of ice on the poles.
- The melting of ice will result in rise of sea level.
- Due to rise in sea level, many coastal cities will be flooded or submerged.
- Increase in temperature of Earth, results the changes in weather and may cause excessive raining or drought or extreme hot or cold weather conditions.
Question 21.
“Burning fossil fuels is a cause of global warming.” Justify this statement.
Answer:
Fossil fuels like coal and petroleum are formed from biomass. In addition to carbon, they contain hydrogen, nitrogen and sulphur. When fossil fuels are burnt, the products are carbon dioxide, water vapour, oxides of nitrogen and oxides of sulphur. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. Increase in the percentage of carbon dioxide increases the temperature on Earth which leads to global warming.
Question 22.
How is reuse better than recycling?
Answer:
‘Sustainable management’ is the management of resources in which development can be maintained for a long time without undue damage to the environment. Recycling needs additional energy to make a usable item. Reuse does not require additional energy and hence, is better than recycle.
Question 23.
List any two causes of our failure to sustain availability of underground water.
Answer:
Two causes of our failure to sustain availability of underground water are :
- Rising population: As the population increases, demand for water increases resulting in depletion of underground water level.
- Industrialisation: Industries need more and more water to manufacture products. With growing industrialisation, demand for water increases which results in reduction in the availability of underground water.

Question 24.
State any four personal choices you would like to make to reduce energy consumption without affecting the quality of life or work explaining how each one of them would help you to do so.
Answer:
- By switching off unnecessary lights and fans. This will reduce consumption of coal in production of electricity.
- By using public transport such as bus, metro, train, etc. as much as possible. This will reduce consumption of petrol and diesel.
- By repairing leaked water taps. We can save water by following this method. This will save energy that is spent during treatment and pumping of water.
- Reusing used paper, envelopes, etc. This will save the trees from which paper is made; it will also save energy spent on making and recycling papers.
Question 25.
Why are forests considered “biodiversity hotspots”? List two ways in which an individual can effectively contribute to the management of forests and wildlife.
Answer:
Biodiversity is measured by the number of different life forms found in an area. In a forest, various species exist which include bacteria, fungi, ferns, plants, nematodes, insects, birds, reptiles and mammals. Forests are, therefore, considered as biodiversity hotspots. An individual can contribute in the management of forests and wildlife by:
- Avoiding cutting down of forests and- killing of wildlife.
- Educating people about the importance of forests and wildlife in our life.
Question 26.
What are the adverse effects of products of combustion of fossil fuels on the environment?
Answer:
When fossil fuels are burnt, carbon dioxide, water, oxides of nitrogen and oxides of sulphur are formed. If the combustion takes place in insufficient air, then carbon monoxide is formed instead of carbon dioxide. Of these products, the oxides of sulphur and nitrogen and carbon monoxide are poisonous gases and carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas.
Question 27.
Write any four advantages of water stored in the ground.
Answer:
Four advantages of storing water in the ground are:
- It does not evaporate.
- It is relatively protected from contamination by human and animal wastes.
- It does not provide breeding ground for mosquitoes.
- It provides moisture for vegetation.

Question 28.
List any four benefit of water harvesting.
Answer:
Benefits of water harvesting are:
- It provides drinking water.
- It provides irrigation water.
- It is responsible for the increase in groundwater level.
- It reduces stormwater discharge, urban flood and overloading of sewage treatment plants.
Question 29.
What is meant by exploitation of resources with short-term aims? List its four advantages.
Answer:
Exploitation of resources with short-term aims means consumption of resources for immediate requirement without their conservation for future. Its four advantages are:
- It fulfils the requirement of mass population.
- It provides industrial growth.
- It provides economic development.
- It makes life comfortable.
Question 30.
Why must we conserve our forests? List any two causes for deforestation to take place.
Answer:
We must conserve our forests as they are of great values. The reasons for conserving forests are:
- Forests help in protection of land and retaining sub-soil water.
- Forests check floods and maintain ecosystem.
Therefore, forests must be conserved for economic and social growth.
Two causes for deforestation taking place are:
- For industrial needs.
- For development projects like building of roads or dams.
Question 31.
Give any four changes that you would like to incorporate in the lifestyle of students of your age to move towards a sustainable use of available resources.
Answer:
- Follow the principle of three ‘R’s - Reduce, Recycle and Reuse.
- Plant more trees.
- Use public transport, school bus and carpools.
- Switch off unnecessary lights and fans, thereby save electricity.

Question 32.
What is meant by sustainable management? The environmentalists are insisting upon “sustainable natural resource management”. State its four advantages.
Answer:
Sustainable management is the management of natural resources which requires a long-term perspective so that they last for generations to come and are not to be exploited by the short-term gains. Its four advantages are as follows :
- Resources last for a longer duration.
- It provides steady economic growth.
- It helps in ecological conservation.
- It reduces pollution.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
(a) Where are ozone layer found?
(b) What is ozone hole and how is it caused?
(c) State the harmful effects of ozone depletion.
Answer:
(a) Ozone layer is found in stratosphere.
(b) Substances such as CFCs lower the ozone layer but do not directly destroy ozone. First they undergo photolysis, forming hydrogen chloride (HCl) or chlorine nitrate (ClNO3), molecules that slowly decompose and give a small number of chlorine atoms (Cl) and chlorine monoxide (ClO) molecules that catalyze the destruction of ozone.
(c) The depletion of ozone layer may cause:
- Skin cancer
- Damage to eyes
- Damage to immune system
- In plants also it may increase the harmful mutations.
Question 2.
List any three human activities which would lead to an increase in the carbon dioxide content of air.
Answer:
Three human activities which would lead to an increase in the CO2 content of air are :
- Respiration: It is the natural process of release of CO2 by both plants and animals.
- Combustion of fuels: The various types of fuels are burnt to provide energy for various, needs like heating, cooking, transportation and industrial fuels.
- Deforestation: Trees help in the conversion of CO2 into organic compounds such as glucose, starch, etc. by the process of photosynthesis but deforestation disturb this process and CO2 level increases in our environment.

Question 3.
How does nitrogen fixation take place during lightning? How do plants make use of the nitrates and nitrites present in soil?
Answer:
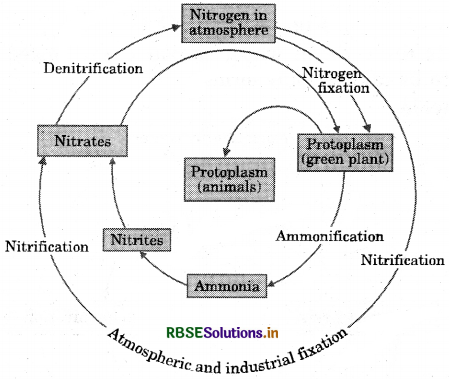
Nitrogen Cycle in Nature
The high temperatures and pressure created in the air convert nitrogen into oxides of nitrogen during lightning. These oxides dissolve in water to give nitrous and nitric adds that fall on land with rain. Nitrogen fixing bacteria which are found in the roots of leguminous plants convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrate (the usable form by plants). The plants use nitrogen in the form of nitrates and nitrites to form amino acids and proteins. The plants are used as food by animals. The bacteria convert these compounds of nitrogen into nitrates and nitrites, after the death of plants and animals. Some other types of bacteria convert nitrites and nitrates into molecular nitrogen, which escapes into atmosphere and becomes a part of it.
Question 4.
Draw labelled diagrams of (a) Carbon cycle (b) Oxygen cycle and briefly explain oxygen cycle.
Answer:
(a) Carbon cycle:
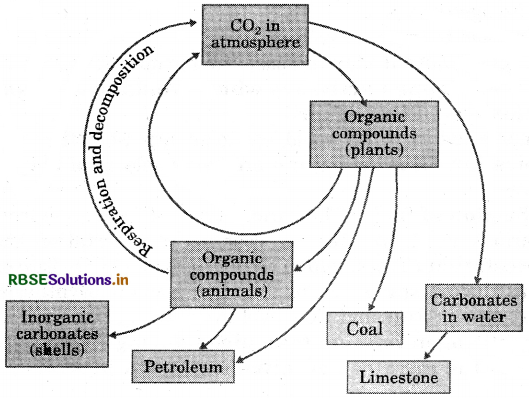
Carbon cycle is the cycle in which carbon is exchanged between the various sphere of Earth by taking many forms.
(b) Oxygen Cycle
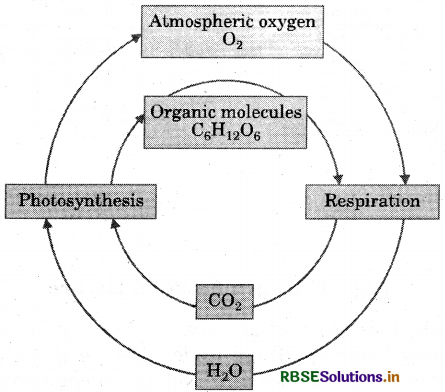
Oxygen cycle: Oxygen from the atmosphere is used up in combustion, respiration and in the formation of oxides of nitrogen. Oxygen is returned to the atmosphere through photosynthesis. This constitutes oxygen cycle in nature.

Question 5.
What are the methods of preventing or reducing soil erosion?
Answer:
The methods of preventing soil erosion are:
- Afforestation: Plants reduce erosion as the roots of plants bind the soil in place.
- Shelterbelts: Trees planted in lines around farmland reduce erosion by reducing the speed of the wind.
- Contour ploughing: Farmers plough land so that furrows he across the natural slope of the land which do not allow it to flow down carrying the topsoil.
- Terrace farming: A terraced hillside is a series of steps formed by horizontal strips supported by walls. It gives the water sufficient time to percolate into the soil and nourish the crop.
- Soil cover: Soil left bare after harvesting a crop is often covered with dried vegetation to prevent erosion.
- Preventing overgrazing: Even a very little grass on a field prevents erosion of soil as the grass has a tendency to bind soil molecules.
Question 6.
Write a note on “how forests influence the quality of our air, soil and water resources”.
Answer:
Forests influence the quality of air, soil and water resources in the following ways:
(i) Influence of forests in controlling the quality of air :
- Forests help in minimising the level of CO2 in the atmosphere which help to reduce greenhouse effect and global warming.
- Forests reduce environmental temperature which increases the rate of photosynthesis in plants in the surrounding regions.
- Some of the trees have the ability to absorb harmful gases present in the atmosphere, e.g. Jamun trees can absorb compounds of lead easily.
(ii) Influence of forests in controlling the quality of soil:
- The roots of trees prevent erosion of topsoil
- Forests also regulate biogeochemical cycles
- Many of the decomposing bacteria and nitrogen-fixing bacteria live in dose association with the roots of the trees.
(iii) Control the quality of water:
- Forests help in returning pure water back to the surface of Earth through rains.
- Forests help in maintaining the water cycle as well as water resources of the Earth.
Question 7.
What are the harmful effects of modern farming practices? Mention any three effects.
Answer:
- Modern farming practices are based on excessive use of fertilisers and pesticides.
- These are used to increase the crop production as well as for pest and weed control.
- From the soil, these chemicals enter the food chain and affect the life of living organisms.
Harmful effects:
- The excessive use of fertilisers and pesticides affects the fertility of soil.
- Harmful non-biodegradable chemicals enter the food chain and adversely affect the health of animals.
- Excessive use of fertilisers and pesticides in the long run reduces the soil fertility.

Question 8.
What is the chemical formula of ozone? What essential function does this gas perform and where it is found? What are CFCs?
Answer:
O3 is the chemical formula of ozone.
Essential function:
- It absorbs the harmful solar UV radiation to prevent various harmful effects on man, animals and plants.
- Ozone is found in the stratosphere, i.e. about 18-50 km above the atmosphere.
- CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons) are synthetic harmful chemicals which are used in refrigerators and air conditioners as coolants, in fire extinguishers, in aerosol sprayers, etc. They are responsible for depletion of ozone layer in the atmosphere.
Question 9.
How is the life of organisms living in water affected when water gets polluted?
Answer:
Almost all types of water pollutants affect the life of organisms living in water.
(i) Eutrophication: The nutrients in fertilizers cause rapid growth of algae, also known as an algal bloom. This process is known as eutrophication. Algal blooms cover the surface of the water so sunlight does not penetrate as far down as it typically would, reducing the ability of underwater plants to perform photosynthesis and produce oxygen. Dying algae feed microorganisms, which deplete more oxygen.
(ii) Thermal wastewater discharge: Pollution can affect the temperature of water bodies, while aquatic animals can manage a little change in temperature only. Heated water decreases the oxygen content of water thereby leading to the death of aquatic organisms. Similarly, cold water affects eggs and larvae and some invertebrates of the aquatic ecosystem.
(iii) Bio-magnification: The increase in concentration of harmful, non- biodegradable chemical substances in the body of living organisms throughout the trophic levels of a food chain is called biological magnification.
Question 10.
All the living organisms are basically made up of C, N, S, P, H and O. How do they enter the living forms? Discuss.
Answer:
The living organisms are basically made up of C, N, S, P, H2 and O2. Most of these elements enter in living forms through plants. Plants take up H2 and C by the process of photosynthesis and the other minerals absorb from the soil. They convert them into food. Consumers take in O2 and H2 during respiration and the rest.of the minerals are taken through the food. The food prepared by plants is consumed by herbivores and then passes through different levels of food chains for utilisation by consumers. At last, the decomposers decompose the dead bodies and the wastes given out by various consumers, thus inorganic nutrient return to the environment.
Decomposition or biodegradation results in the breakdown of complex organic materials to forms of carbon that can be used by other organisms. Through the metabolic processes of fermentation and respiration, organic molecules are eventually broken down to CO2 which is returned to the atmosphere. Some bacteria remove N2 from the atmosphere and converts it to ammonia (NH3) by nitrogen fixation process and by symbiotic associations in plants. Other nitrogen-fixing bacteria are free-living in soil and aquatic habitats. Soil also plays important role in biogeochemical cycle which is a main source of recycling of nutrients from atmosphere to soil and then to water.

Question 11.
There is mass mortality of fishes in a pond. What may be the reasons?
Answer:
The following can the reasons for the mass mortality of fishes in a pond:
- Fertiliser pollution does not make fish grow bigger, for example : fertilisers, whether they are artificial or organic; can cause serious problems if they contaminate-freshwater and marine ecosystems.
- Eutrophication: Eutrophication is the enrichment of a water body with nutrients, usually with an excess amount of nutrients. The nutrients in fertilizers cause rapid growth of algae, also known as an algal bloom. Blooms cover the surface of the water so sunlight does not reach as far down and deplete more oxygen. This leads to the death of most of the water animals as fishes.
- Thermal wastewater discharge: Heated water flowing out of the thermal power plants increase the temperature of the water body. It may also affect the mortality rate of fishes.
- Addition of poisonous compounds in water.
- Domestic Sewage: It mainly contains organic matter, which is biodegradable. Microorganisms involved in their degradation consume a lot of oxygen and the content of oxygen in the water body decreases leading to the death of fishes.
Question 12.
How do fossil fuels cause air pollution?
Answer:
The fossil fuels like coal and petroleum contain small amounts of nitrogen and sulphur. When these fuels are burnt, nitrogen and sulphur too are burnt and this produces different oxides of nitrogen and sulphur. Not only is the inhalation of these gases dangerous, they also dissolve in rain to give rise to acid rain. The combustion of fossil fuels also increases the amount of suspended particles in air. These suspended particles could be unburnt carbon particles or substances called hydrocarbons. Presence of high levels of all these pollutants causes visibility to be lowered, especially in cold weather when water also condenses out of air. This is known as smog and is a visible indication of air pollution.
Question 13.
What are the causes of water pollution? Discuss how you can contribute in reducing water pollution.
Answer:
Cause of Water Pollution: Water pollution can be caused by addition of:
- Undesirable substances - Any poisonous substances like fertilisers and - pesticides,
- Sewage waste.
- Thermal wastewater discharge - The hot water from the power plant that increases the temperature and reduces the dissolved oxygen in water.
- Industrial radioactive substances in water body.
Measures for water pollution:
- By using natural fertilisers and pesticides as far as possible.
- Restrain from throwing litter into any water body.
- Proper sewage drainage system.
- Avoid washing of clothes near water bodies as it adds lot of detergents to it.
- Plantation near water bodies to stop soil erosion.

Question 14.
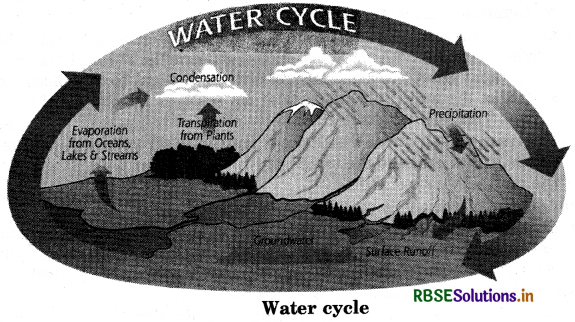
Explain water cycle with diagram.
Answer:
Water cycle: About 97% of total water present on earth is found are saline water in sea, 2% is found in frozen state on poles and mountains. Only 1% remaining water is used by living organisms. Water evaporates from different water bodies found on earth, then condenses and again precipitates as rain, falls on land, flows back in the sea and river. This is called water cycle.

- RBSE Class 9 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 हमारे आस - पास के पदार्थ
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 8 Motion
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 प्राकृतिक सम्पदा
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 10 गुरुत्वाकर्षण
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 8 गति
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 9 बल तथा गति के नियम
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 हम बीमार क्यों होते हैं