RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 12 Sound
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 12 Sound Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions Sound
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Note is a sound :
(a) of mixture of several frequencies.
(b) of mixture of two frequencies only.
(c) of a single frequency.
(d) always unpleasant to listen.
Answer:
(c) of a single frequency.
Question 2.
A key of a mechanical piano struck gently and then struck again but much harder this time. In the second case :
(a) sound will be louder but pitch will not be different.
(b) sound will be louder and pitch will also be higher.
(c) sound will be louder but pitch will be lower.
(d) both loudness and pitch will remain unaffected.
Answer:
(a) sound will be louder but pitch will not be different.
Question 3.
In SONAR, we use :
(a) ultrasound waves
(b) infrasonic waves
(c) radio waves
(d) audible sound waves
Answer:
(a) ultrasound waves
Question 4.
Sound travels in air if :
(a) particles of medium travel from one place to another.
(b) there is no moisture in the atmosphere.
(c) disturbance moves.
(d) both particles as well as disturbance travel from one place to another.
Answer:
(c) disturbance moves.

Question 5.
When we change feeble sound to loud sound we increase its :
(a) frequency
(b) amplitude
(c) velocity
(d) wavelength
Answer:
(b) amplitude
Question 6.
In the half curve the wavelength is :
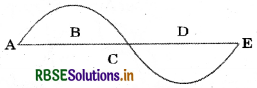
(a) AB
(b) BD
(c) DE
(d) AE
Answer:
(b) BD
Question 7.
Earthquake produces which kind of sound before the main shock wave begins?
(a) Ultrasound
(b) Infrasonic
(c) Audible
(d) Inaudible
Answer:
(b) Infrasonic
Question 8.
Infrasound can be heard by :
(a) Dog
(b) Bat
(c) Rhinoceros
(d) Human being
Answer:
(c) Rhinoceros
Question 9.
Before playing the orchestra in a musical concert, a sitarist tries to adjust the tension and pluck the string suitably. By doing so, he is adjusting :
(a) intensity of sound only.
(b) amplitude of sound only.
(c) frequency of the sitar string with the frequency of other musical instruments.
(d) loudness of sound.
Answer:
(c) frequency of the sitar string with the frequency of other musical instruments.

Question 10.
Speed of sound in a complete rigid rod is :
(a) Zero
(b) infinity
(c) 332 m/s
(d) 664 m/s
Answer:
(b) infinity
Question 11.
Speed of sound is maximum in which of the following :
(a) In water
(b) In iron
(c) In air
(d) In vaccum
Answer:
(b) In iron
Question 12.
Nature of water waves is :
(a) only transverse
(b) only longitudinal
(c) both longitudinal and transverse
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) both longitudinal and transverse
Question 13.
Transverse waves can propagate :
(a) only in metals
(b) only in gases
(c) in both metals and gases
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) only in metals
Question 14.
Frequency of radio station is 30 × 106 Hz. What will be the wavelength of the waves produced by radio station?
(a) 5 m
(b) 10 m
(c) 15 m
(d) 20 m
Answer:
(b) 10 m

Question 15.
Fill in the blanks :
(a) Speed of sound is maximum in ..............
(b) The number of oscillations made by a vibrating body or particles of a medium in 1 second is known as ..............
(c) The audible range of frequency of sound for human ear is ..............
(d) To hear a distinct echo the time interval between the original sound and the reflected one must be at least ..............
(e) Loudness of the sound depends on the .............. of the vibrating body producing the sound.
Answer:
(a) solids
(b) frequency
(c) 20 Hz to 20000 Hz
(d) 0.1 s
(e) amplitude
Question 16.
Match the column (A) with the column (B).
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
(i) Ultrasonic waves |
(a) Frequency 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz |
|
(ii) Infrasonic Waves |
(b) Frequency × Wavelength |
|
(iii) Audible waves |
(c) Frequencies higher than 20 Hz |
|
(iv) Speed of wave |
(d) Frequencies below than 20 Hz |
Answer:
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
(i) Ultrasonic waves |
(c) Frequencies higher than 20 Hz |
|
(ii) Infrasonic Waves |
(d) Frequencies below than 20 Hz |
|
(iii) Audible waves |
(a) Frequency 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz |
|
(iv) Speed of wave |
(b) Frequency × Wavelength |

Question 17.
Read the statements carefully and identify whether they are True or False-
1. Bats can produce and detect ultrasounds.,
2. Pitch of a sound does not depends on its frequency.
3. Infrasonic waves are used in echocardiography.
4. Distance between two consecutive compressions or between two consecutive rarefactions is λ.
5. Sound waves need a material medium for their propagation.
Answer:
1. True
2. False
3. False
4. False
5. True
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by a wave?
Answer:
A wave is a vibratory disturbance in a medium which carries energy from one point to another without being a direct contact between the two points.
Question 2.
What does wave transfer-matter or energy?
Answer:
Energy.
Question 3.
Where is density of air higher at compression or at rarefaction?
Answer:
At compression.
Question 4.
Guess which sound has a higher pitch; guitar or car horn?
Answer:
Guitar has a higher pitch because it has higher frequency.

Question 5.
What is intensity of sound?
Answer:
The amount of sound energy passing through unit area each second is called the intensity of sound.
Question 6.
What is relation between time period and frequency?
Answer:
Frequency = \(\frac{1}{\text { Time period }}\)
Question 7.
Name two animals that communicate using infrasound.
Answer:
Rhinoceroses and whales communicate using infrasound.
Question 8.
Name the waves used by hats while flying in the dark.
Answer:
Bats use ultrasonic waves while flying in the dark.
Question 9.
A Sitarist tries to adjust the tension and pluck the string suitably, before playing the orchestra in a musical concert. By doing so what is he adjusting?
Answer:
He is adjusting frequency if the sitar string with the frequency of the other musical instrument.

Question 10.
If the tension in the wire is increased four times, how will the velocity of wave in a string varies?
Answer:
Velocity of the wave in string is directly proportional to the square root of the tension thus if tension is increased 4 times, the velocity will be doubled.
Question 11.
A girl claps and hears the echo after reflection from cliff which is 660 m away. If the velocity of sound is 330 ms-1, calculate the time taken for hearing the echo.
Answer:
υ × t - 2 d, t = \(\frac{2 \mathrm{~d}}{v}=\frac{2 \times 660}{330}\) = 4s
Question 12.
Explain, how is the principle of echo used by the dolphin to locate small fish as its prey?
Answer:
Dolphins are aquatic animals which send out ultrasonic sound to communicate with each other. They have a sound sensing system which enables them to find animals under water with great accuracy due to the echo of the ultrasonic sound produced by them.
Question 13.
Give two practical applications of the reflection of sound waves.
Answer:
(i) In stethoscope the sound of patient’s heartbeat reaches the doctor’s ears by multiple reflections in the tubes.
(ii) Megaphones are. designed to send sound waves in particular direction are based on the reflection of sound.
Question 14.
Why are longitudinal waves called pressure waves?
Answer:
Sound waves travels in the form of compression and rarefaction, which involve change in pressure, and volume of the air. Thus, they are called pressure waves.

Question 15.
Sound travels faster on a rainy day than on a dry day. Why?
Answer:
Sound travels faster on rainy day because the velocity of sound increases with increase in humidity. On rainy day, humidity is more, thus velocity of sound is also more.
Question 16.
How moths of certain families are able to escape capture?
Answer:
Moths of certain families can hear high frequency sounds (squeaks) of bat as they have sensitive hearing equipment. Thus, they get to know when a bat is near by and hence, able to escape its capture.
Question 17.
What is SONAR?
Answer:
SONAR (Sound Navigation And Ranging) is a technique for determining water depth and locating underwater objects, such as reefs, submarines and schools of fish.
Question 18.
Define one hertz.
Answer:
One hertz is one vibration per second.
Question 19.
Define wavelength.
Answer:
It is the distance between two nearest points in a wave which are in the same phase of vibration.

Question 20.
What is the audible range of the average human ear?
Answer:
An average human ear can hear sound waves between frequencies 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Question 21.
What is sound and how is it produced?
Answer:
Sound is mechanical energy which produces a sensation of hearing. When an object is set into vibrations, sound is produced.
Question 22.
Why is sound wave called as longitudinal wave?
Answer:
Sound wave is called longitudinal wave because the particles of the medium vibrate in the direction of the propagation of wave.
Question 23.
Flash and thunder are produced simultaneously. But, thunder is heard a few seconds after the flash is seen, why?
Answer:
The speed of fight is 3 × 108 ms-1 whereas that of sound is 344 ms-1 in air. Thus, flash of lightning is seen at once, but sound takes few seconds to reach our ears.
Question 24.
The frequency of a source of sound is 100 Hz. How many times does it vibrate in a minute?
Answer:
No. of vibrations produced in 1 s = 100
No. of vibrations produced in 60 (sec) = 1 min = 100 × 60 = 6000.

Question 25.
Name the two types of mechanical waves.
Answer:
The two types of mechanical waves are :
- Transverse wave and
- Longitudinal wave.
Question 26.
What is a wave?
Answer:
A wave is a disturbance that travels in a medium due to repeated periodic motion of particles about their mean position - such that the disturbance is handed over from one particle to the other without the actual motion of the medium.
Question 27.
What is a transverse wave?
Answer:
It is a wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.
Question 28.
What is a longitudinal wave?
Answer:
It is a wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate in the direction of propagation of the wave.
Question 29.
What is a trough?
Answer:
A trough is a depression in a wave, i.e. maximum displacement in the negative direction (below the mean position).
Question 30.
What do you understand by the term infrasonic vibrations?
Answer:
The sounds of frequency lower than 20 Hz are called the infrasonics or subsonics.

Question 31.
Which of the following sound waves we can hear : 10 Hz, 500 Hz, 1500 Hz, 12000 Hz, 25000 Hz?
Answer:
500 Hz, 1500 Hz, 12000 Hz.
Question 32.
What do you understand by the term ultrasonic vibrations?
Answer:
Sounds of frequency higher than 20,000 Hz are called the ultrasonics.
Question 33.
What do you understand by the term echo?
Answer:
The sound heard after reflection from a rigid obstacle is called an echo.
Question 34.
Name the term associated with the travelling disturbance in a medium.
Answer:
Wave.
Question 35.
Do waves transport energy?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 36.
Do waves transport matter?
Answer:
No.

Question 37.
Do the particles of the medium move from one place to another in a medium?
Answer:
No.
Question 38.
Does the velocity of wave motion depend on the nature of the medium?
Answer:
Yes
Question 39.
Does the velocity of wave motion depend on the nature or motion of the source?
Answer:
No.
Question 40.
What is the other name of a long flexible spring?
Answer:
Slinky is the other name of a long flexible spring.
Question 41.
Can you produce both types of waves (Le. longitudinal and transverse) on a slinky?
Answer:
Yes, we can produce both types of waves ti e. longitudinal and transverse) on a slinky.

Question 42.
Where is the density of air higher; at compressions or at rarefactions?
Answer:
At the compressions, the density of air is higher.
Question 43.
Name the quantity that represents the length of one complete wave.
Answer:
Wavelength represents the length of one complete wave.
Question 44.
What is the distance between two consecutive crests in a wave called?
Answer:
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests in a wave.
Question 45.
Is the amplitude of a wave the same, as the amplitude of the vibrating body producing the wave?
Answer:
Yes, the amplitude of a wave is same, as the amplitude of the vibrating body producing the wave.
Question 46.
What is the range of frequencies associated with :
(a) Infrasound
(b) Ultrasound
Answer:
(a) Infrasound: Sound waves between the frequencies 1 to 20 Hz.
(b) Ultrasound: Sound waves of the frequencies above 20,000 Hz.
Question 47.
Give on use of ultrasonography.
Answer:
It is used for the examination of the foetus during pregnancy to detect congenial defects and growth abnormalities.

Question 48.
When a sound is reflected from a distant object, an echo is produced. Let the distance between the reflecting surface and the source of sound production remains the same. Do you hear echo sound on a hotter day?
Answer:
If the temperature rises, the speed of sound will increase. This in turn will increase the minimum distance required for hearing an echo. No echo is heard because the , distance between the source of sound and reflecting body does not increase.
Question 49.
Sound is produced due to a vibratory motion, then why a vibrating pendulum does not produce sound?
Answer:
The frequency of the vibrating pendulum does not lie within the audible range (20 Hz to 20000 Hz) and hence, it does not produce audible sound.
Question 50.
What is the relation between frequency, wavelength and speed of a wave?
Answer:
Speed = Wavelength × frequency
υ = λ × V
Question 51.
Why is the ceiling and wall behind the stage of good conference halls or concert halls made curved?
Answer:
Ceiling and walls are made curved so that sound after, reflection reaches the target audience.
Question 52.
If any explosion takes place at the bottom of a lake, what type of shock waves in water will take place?
Anwer:
Longitudinal waves will take place.

Question 53.
Mention one practical use of echoes.
Answer:
Echoes are used in radars to estimate the distance of flying objects.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Give difference between loudness and intensity of the sound.
Answer:
|
Loudness |
Intensity |
|
1. Loudness is a measure of the response of our ear to the sound. |
1. It is the energy per second per unit area normal to the direction of energy flow. |
|
2. It depends on intensity as well as sensitivity of the ear. Therefore, it is not absolute but relative. |
2. It does not depend upon the sensitivity of the ear. |
|
3. The unit of loudness is decibel. |
3. The unit of intensity is watt/m2. |
Question 2.
How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear?
Answer:
When a vibrating object moves forward, it pushes and compresses the air in front of it creating a region of high pressure called compression. This compression starts to move away from the vibrating object. When vibrating object moves backwards, it creates a region of low pressure called refraction. As the object moves forth and back rapidly, a series of compressions and refractions are created in the air. These produce the sound wave that propagates through the medium. This continues until the sound wave reaches to the ear of the listener.
Question 3.
What are transverse waves? Give two examples.
Answer:
A wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate up and down at right angle to the direction in which the wave is moving.
Example :
- The waves produced by moving one end of a long spring up and down rapidly.
- Ripples formed on the surface of water in a pond.

Question 4.
What are crests and troughs of a wave?
Answer:
The elevation in a transverse wave is called crest. It is that part of transverse wave which s above the line of zero disturbance of the medium. The depression in a transverse wave is called trough. It is that part of the transverse wave which is below the line of zero disturbances.
Question 5.
What is echo? Explain the conditions that have to be satisfied to hear an echo.
Answer:
Reflection of sound wave from a large obstacle is called an echo. The most important condition for hearing an echo is that the reflected sound should reach the ear only after a lapse of at least 0.1 second after the original sound is off and the obstacle is at least at a distance of 17 m.
Question 6.
Why do echoes produced in an empty auditorium usually decrease when it is full of audience?
Answer:
When the hall is empty there are no obstacles in between to reflect the sound other than the walls. When the hall is full of audiences, the sound produced undergoes multiple reflections from the people and so it overlaps with the sound produced. Hence, the listener is not able to distinguish between the original sound and the echo.
Question 7.
Explain, why can echoes not be heard in a small room?
Answer:
For hearing echo, there should be at least a distance of 17 m between the source of sound and the body from which sound is reflected. In small rooms this is not the case, hence, echoes are not heard.
Question 8.
Distinguish between transverse and longitudinal waves (three points).
Answer:
Transverse waves :
- Particles the medium vibrate at right angles.
- Alternate crests and troughs formed.
- Example : Water waves.
Longitudinal waves :
- Particles vibrate parallel to the direction of waves.
- Alternate compressions, rarefactions formed.
- Example : Sound waves.
Question 9.
State three characteristics of a musical sound. On what factors do they depend?
Answer:
Characteristics of musical sound are :
- Loudness- Amplitude affects loudness, more amplitude louder the sound and lesser the amplitude, softer is the sound.
- Pitch - Frequency affects pitch, more frequency more pitch, less frequency less pitch.
- Quality.

Question 10.
How does the sound produced by a musical instrument, reach your ears? Astronauts need radio transmitter to talk to each other on Moon. Why?
Answer:
The sound produced by the musical instrument makes the molecules of air vibrate. These vibrations are carried forward by the other molecules till they reach our ear. These then vibrate our eardrum to produce sound. Since, sound requires a medium to propagate, therefore, sound cannot travel between astronauts on the Moon, hence, they use radio transmitters.
Question 11.
Does sound follow the same laws of reflection as light does? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, sound and light follow the same laws of reflection that are given below :
(a) Angle of incidence at the point of incidence = Angle of reflection, (∠i = ∠r)
(b) At the point of incidence, the incident sound wave, the normal and the reflected sound wave lie in the same plane.
Question 12.
What are longitudinal waves? Give two examples.
Answer:
A wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate back and forth along the same direction, in which the wave is moving, is called a longitudinal wave.
Examples :
- The sound waves in air.
- The waves produced in air when a sitar wire is plucked.
Question 13.
(i) Draw the sound waves for a low pitched and the high pitched sound.
(ii) Which wave property determines pitch?
Answer:
(i) The diagram is as shown :
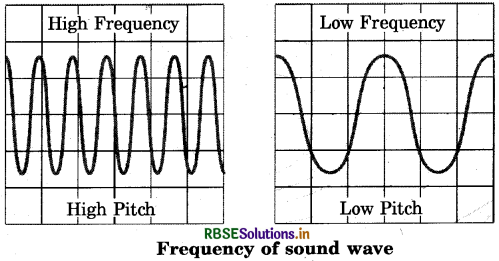
(ii) The pitch depends on frequency.
Question 14.
Write conditions for the production of an echo.
Answer:
Conditions for the production of an echo are :
(i) Time gap between the original sound and the reflected sound.
The echo will be heard if the original sound reflected by an obstacle reaches our ears after 0.1 s.
(ii) Distance between the source of sound and obstacle.
Thus, the minimum distance (in air at 25 °C) between the observer and the obstacle for the echo to be heard clearly should be 17.2 m.
(iii) Nature of the obstacle: For the formation of an echo, the reflecting surface or the obstacle must be rigid such as a building/hill or a diff.
(iv) Size of the obstacle: Echoes can be produced if the size of the obstacle reflecting the sound is quite large.

Question 15.
Distinguish between tone and note.
Answer:
A pitch is a particular frequency of sound. For example : 440 Hz.
A note is a named pitch. For example : Western music generally refers to the 440 Hz pitch as A, specifically A4.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Give uses of multiple reflection of sound.
Answer:
There are several uses of multiple reflection of sound :
(i) Megaphone is a device used to address public meetings. It is horn-shaped.
When we speak through megaphone, sound waves are reflected by the megaphone. These reflected sound waves are directed towards the people (or audience) without much spreading.
(ii) The ceilings of concert halls and auditoriums are made curved. This is done so that the sound reaches all the parts of the hall after reflecting from the ceiling. Moreover, these ceilings are made up of sound absorbing materials to reduce the reverberation.
(iii) Stethoscope is a device used by doctors to listen the sound produced by heart and lungs. The sound produced by heart beat and lungs of a patient reaches the ears of a doctor due to multiple reflections of sound.
(iv) Sound boards are curved surfaces (concave) which are used in a big hall to direct the sound waves towards the people sitting in a hall. The speaker is (i.e. source of sound) placed at the focus of the sound board.
(v) Sound waves from the speaker are reflected by die sound board and these reflected waves are directed towards the people (or audience).
(vi) Hearing aid is used by a person who is hard of hearing. The sound waves falling on hearing aid are concentrated into a narrow beam of sound waves by reflection. This narrow beam of sound waves is made to fall on the diaphragm of the ear. Thus, diaphragm of the ear vibrates with large amplitude. Hence, the hearing power of the person is improved.
Question 2.
Give applications of ultrasound (ultrasonic waves).
Answer:
Ultrasonic waves have number of uses :
- Ultrasonic vibrations are used for homogenising milk. These vibrations break - down the larger particles of the fat present in milk to smaller particles.
- Ultrasonic vibrations are used in dish washing machines. The vibrating detergent particles rub against the dirty utensils and thus, dean them.
- Ultrasonic vibrations produce a sort of depression in rats and cockroaches.
- Ultrasonic vibrations are used to study the growth of foetus in mother’s womb.
- Ultrasonic vibrations are used in relieving pain in joints and muscles.
- Ultrasonic vibrations are used in detecting flaws in articles made from metals. They are also used in finding the thickness of various parts of a metallic component.

Question 3.
Represent graphically by two separate diagrams in each case :
(a) Two sound waves having the same amplitude but different frequencies.
(b) Two sound waves having the same frequency but different amplitudes.
(c) Two sound waves having different amplitudes and also different wavelengths.
Answer:
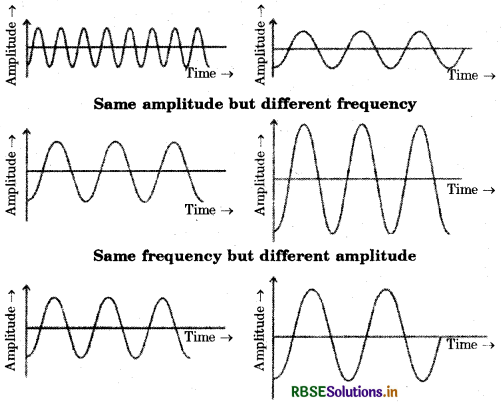
Different amplitude and different wavelengths
Question 4.
Make a table for speed of sound in different mediums at 25° C.
Answer:
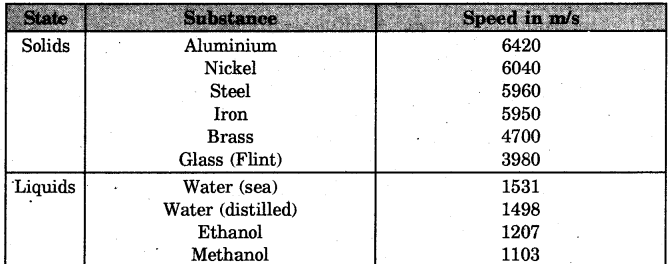
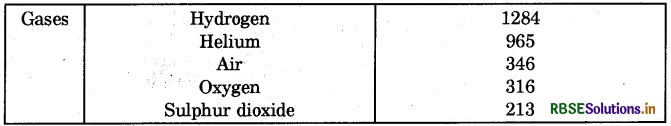

Question 5.
Write about the ultrasound scanner.
Answer:
It is an instrument which uses Ultrasonic waves for getting images of internal organs of the human body. With the help of this instrument, the patient’s organs may image such as liver, gall bladder, kidney, uterus etc. It helps to detect abnormalities, such as stones in gall bladder and kidney or tumours in different organs.
In this technique, ultrasonic waves travel through the tissues of the body and get reflected from a region where there is a change of tissue density. These waves are then converted into electrical signals that are used to generate images of the organ. These images are then displayed on a monitor or printed on film and this process is known as ultrasonography. It is used to examine the foetus during pregnancy to detect growth abnormalities and congenial defects.
Solved Numericals
Question 1.
A particular transmitter of Akashvani broadcasts at 420.5 m wavelength, (given the speed of radio waves 3 × 108 ms-1) Calculate the frequency at which the radio station broadcasts its program.
Answer:
Given
λ = 420.5 m, v = 3 × 108 ms-1
Using the expression v = νλ
ν = \(\frac{v}{\lambda}\)
= \(\frac{3 \times 10^{8}}{420.5}\)
= 7 × 105 Hz
Question 2.
A tuning fork produces 1024 waves in 4 seconds. Calculate the frequency to the tuning fork.
Answer:
As the tuning fork produces 1024 waves in 4 seconds, hence
Frequency of tuning fork, ν = Number of vibration per second
= \(\frac{1024}{4}\) = 256 Hz
Question 3.
A human heart, on an average, is found to beat 75 times a minute. Calculate its frequency.
Answer:
No. of beats of human heart = 75 min-1 = \(\frac{75}{1 \min }=\frac{75}{60 \mathrm{~s}}\) = 1.25 s
So, average frequency of human heartbeat = 1.25 s-1

Question 4.
A boat at anchor is rocked by waves whose consecutive crests are 100 m apart. The wave velocity of the moving crests is 20 m/s. What is the frequency of rocking of the boat?
Answer:
Distance between two consecutive crests = 100 m
Wave velocity v = 20 m/s
The distance between two consecutive crests is equal to the wavelength of the wave. So,
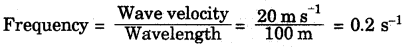
So, the frequency of rocking of the boat is 0.2 s-1.
Question 5.
A longitudinal wave is produced on a toy slinky. The wave travels at a speed of 30 cm/s and the frequency of the wave is 20 Hz. What is the minimum separation between the consecutive compressions of the slinky?
Answer:
Wave speed, v = 30 cm/s
Frequency of the wave, ν = 20 Hz = 20 s-1
The minimum separation between the consecutive compressions is equal to the wavelength. Therefore,
Wavelength = \(\frac{30 \mathrm{cms}^{-1}}{20 \mathrm{~s}^{-1}}\) = 1.5 cm
Thus, the minimum separation between the consecutive compression of the slinky is 1.5 cm.
Question 6.
A bat can hear sound at frequencies up to 120 kHz. Determine the wavelength of sound in the air at this frequency. Take the speed of sound in the air as 344 m/s.
Answer:
Frequency, ν = 120 kHz = 120 × 103 Hz = 120 × 103 s-1
Velocity of sound in the air, v = 344 m/s
Wavelength of the sound wave = λ
We know,
wavelength, λ = \(\frac{\text { wave velocity }}{\text { frequency }}=\frac{344 \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}}{120 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}}\)
= 2.87 × 10-3 m = 0.29 cm
Question 7.
A child hears an echo from a cliff 4 seconds after the sound from a powerful cracker is produced. How far away is the cliff from the child? Velocity of sound in air at 20 °C is 344 m/s.
Answer:
Let the distance between the child and the cliff be d. Then,
Total distance travelled by the sound = 2d
Total time taken by the sound = 4 s
Then, Velocity of sound = 344 m/s = d/2 s
This gives, d = 344 m/s × 2 s = 688 m
Thus, the cliff is at a distance of 688 m from the child.
Question 8.
A ship sends on a high frequency sound wave and receives an echo after 1 second. What is the depth of the sea? Speed of sound in water is 1500 m/s.
Answer:
Let,
Depth of the sea = d
So, total distance travelled by the sound wave = 2d
Time taken by sound to travel both ways = 1 s
As per definition,
Speed of the sound = 1500 ms-1 = 2d/1 s
or d = 1500 ms-1 × \(\frac{1 s}{2}\) = 750 m
Thus, the depth of the sea is 750 metres.

Question 9.
Using the SONAR, sound pulses are emitted at the surface of water. These pulses after being reflected from the bottom are detected. If the time interval from the emission to the detection of the sound pulses is 2 seconds, find the depth of the water. Velocity of sound in water = 1498 m/s.
Answer:
Let, depth of the water from the Earth’s surface be d. Then,
Total distance travelled by the pulse = 2d
Total time taken by the pulse = 2s
As per definition,

So, Velocity of the sound = \(\frac{2 d}{2 s}=\frac{d}{s}\)
1498 m/s = \(\frac{d}{s}\)
This gives, d = 1498 m/s × 1s = 1498 m
Thus, the depth of water is 1498 m.
Question 10.
A stone is dropped into a well 44.1 m deep. The splash is heard 3.13 seconds after the stone is dropped. Find the velocity of sound in air.
Answer:
Stone falling from A to B
u = 0, s = 44.1 m, g = 9.8 ms-2, t = ?
s = ut + \(\frac{1}{2}\)gt2
44.1 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 9.8 × t2
t = 3 s
Sound produced at B, due to sound produced by the stone falling on the surface of water, travels from B to A. The sound moves with constant velocity.

It is given that the total time is 3.13 second.
i.e.,

Question 11.
Calculate (a) the wavelength (b) the time period of a tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz which is set to vibrate. Velocity of sound in air is 320 m/s.
Answer:
Frequency of the tuning fork (ν) = 512 Hz.
Velocity of sound (v) = 320 m/s
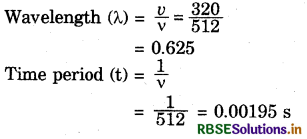
Question 12.
Sound waves travel with a speed of 330 m/s. What is the wavelength of sound, whose frequency is 550 Hz?
Answer:
Speed of the sound wave (v) = 330 m/s
Frequency of the sound wave (ν) = 550 Hz
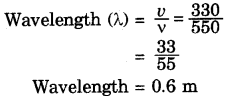

Question 13.
Radiowaves of speed 3 x 108 m s-1 are reflected off the Moon and received hack on Earth. The time elapsed between the sending of the signal and receiving it hack at the Earth station is 2.5 s. What is the distance of the Moon from the Earth?
d = v × \(\frac{t}{2}\)
= \(\frac{3 \times 10^{8} \times 2.5}{2}\)
= \(\frac{7.5 \times 10^{8}}{2}\)
= 3.75 × 108 m
Question 14.
A sound wave of wavelength 0.33 m has a time period of 10-3 s. If the time period is decreased to 10-4 s, calculate the wavelength and frequency of the new wave.
Answer:
λ = 0.33 m
Time taken to travel λ, t = 10-3
velocity = \(\frac{\lambda}{t}=\frac{0.33}{10^{-3}}\) = 330 ms-1
Time period of 2nd wave = 10-4 s
Therefore, wavelength λ = v × t
= 330 × 10-4 = 0.033 m
Frequency = \(\frac{1}{t}=\frac{1}{10^{-3}}\) = 103 Hz
Question 15.
A person standing between two vertical cliffs and 640 m away from the nearest cliff shouted. He heard the 1st echo after 4 seconds and the second echo 3 seconds later. Calculate : (i) the velocity of sound in air and (ii) the distance between the cliff.
Answer:
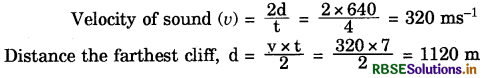
Therefore the distance between the cliffs,
D = 640 + 1120 = 1760 m
Question 16.
A ship on the surface of water sends a signal and receives it hack after 4 seconds from a submarine inside the water. Calculate the distance of the submarine from the ship (the speed of sound in water is 1450 ms-1).
Answer:
v = \(\frac{2 \mathrm{~d}}{\mathrm{t}}\)
d = \(\frac{v \times t}{2}\)
= \(\frac{1450 \times 4}{2}\)
= 2900 m or 2.9 km

Question 17.
A man fires a gun and hears its echo after 5 seconds. The man then moves 310 m towards the hill and fires his gun again. This time he hears the echo after 3 seconds. Calculate the speed of sound.
Answer:
Let d be the distance between the man and the hill in the beginning.
v = \(\frac{2 d}{t}\)
= \(\frac{2 d}{5}\) ............(1)
He moves 310 m towards the hill. Therefore, the distance will be (d - 310) m.
υ = \(\frac{2(d-310)}{3}\) ..............(2)
Since, velocity of sound is same, equating (1) and (2), we get
\(\frac{2 d}{5}=\frac{2(d-310)}{3}\)
3d = 5d - 1550
2d = 1550
d = 775 m
Velocity of sound (v) = \(\frac{2 \times 775}{5}\)
= 310 ms-1
