RBSE Class 8 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 8 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Social Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 8. Students can also read RBSE Class 8 Social Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 8 Social Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Go through these class 8 history chapter 6 questions and answers in hindi and get deep explanations provided by our experts.
RBSE Class 8 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
What percentage of the earth is covered with land
(a) 20 percent
(b) 30 percent
(c) 40 percent
(d) 50 percent
Answer:
(b) 30 percent
Question 2.
The land is used for which of the following tasks
(a) Agriculture
(b) Forestry
(c) Mining
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above

Question 3.
What is the large movement of rock, debris, soil, etc. downstream called?
(a) Land slide
(b) Earthquake
(c) Soil erosion
(d) Volcano
Answer:
(a) Landslide
Question 4.
Which organization makes the list of trade restrictions on animals and birds?
(a) Red data book
(b) CITES
(c) Wildlife Federation
(d) UNICEF
Answer:
(b) CITES
Question 5.
Land use is determined by which of the following physical factors
(a) Soil
(b) Climate
(c) Water availability
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 6.
The methods used for soil conservation include
(a) Mulching
(b) Terrace farming
(c) Contour plowing
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 7.
Which of the following products do we get in the forest
(a) Wood
(b) Medicine
(c) Gum
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 8.
Which of the following measures has been taken to conserve natural vegetation and wildlife?
(a) Establishment of national parks
(b) Establishment of wildlife sanctuaries.
(c) To put a ban on hunting.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 9.
Which place is known as a ‘water planet’?
(a) Mars
(b) Earth
(c) Saturn
(d) Jupiter
Answer:
(b) Earth
Question 10.
Area with water scarcity is
(a) Most of Africa
(b) Western Asia
(c) Complete Australia
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
When the base ground between plants is covered with a layer of organic matter like straw, then this is called .....................
Answer:
mulching
Question 2.
In the biosphere living beings are interrelated and interdependent on each other for survival, this life-supporting system is known as the .....................
Answer:
ecosystem
Question 3.
Air and water cause erosion of the upper soil which is called soil .....................
Answer:
erosion
Question 4.
It takes ..................... of years to build just 1 cm
of soil.
Answer:
hundreds

State True or False
Question 1.
Natural habitats of plants and animals can be destroyed due to climate change and human interference.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
In India, it is illegal to kill lions, cheetahs, deer, great Indian bustards, and peacocks.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Mosses and lichens are found on places where grasses grow.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
The vulture is not a scavenger because of eating dead organisms.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
A dripping tap wastes 1200 liters of water in a year.
Answer:
True
Match Correctly
|
(a) |
(b) |
|
Terrace farming |
Earth |
|
Water Planet |
Tundra vegetation |
|
Mosses |
Scavenger |
|
Vulture |
Soil conservation |
|
Community land |
Shared property resources |
Answer:
|
(a) |
(b) |
|
Terrace farming |
Soil conservation |
|
Water Planet |
Earth |
|
Mosses |
Tundra vegetation |
|
Vulture |
Scavenger |
|
Community land |
Shared property resources |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is land use?
Answer:
Land is used in various works, such as agriculture, forestry, mining, factory setting, etc., this is called land use.
Question 2.
What is the difference between private land and community land?
Answer:
Private land is owned by individuals while community land is owned by the community.
Question 3.
What are the factors on which land use depends?
Answer:
Land use is determined by physical factors such as topography, soil, climate, minerals, and water availability.
Question 4.
In what ways land resources can be protected? Describe any two ways.
Answer:
- Expansion of forests
- Prohibiting the regulated use of fertilizers and over-exploitation.
Question 5.
What is soil?
Answer:
The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface of the earth is called soil.
Question 6.
What is a landslide?
Answer:
Landslides are simply defined as the mass movement of rock, debris, or earth down a slope.
Question 7.
What is weathering?
Answer:
The breaking up and decay of exposed rocks, to temperature changes, frost action, plants, animals, and human activity.
Question 8.
Where and why terrace farms are made?
Answer:
Broad flat steps or terraces are made on the steep slopes so that flat surfaces are available to grow crops.
Question 9.
What are shelterbelts?
Answer:
In the coastal and dry regions, rows of trees are planted to check the wind movement to protect soil covers.
Question 10.
What is the biosphere?
Answer:
Natural vegetation and wildlife exist only in the narrow zone of contact between the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere, which is called the biosphere.
Question 11.
What does the growth of vegetation depend on?
Answer:
The growth of vegetation mainly depends on temperature and humidity.
Question 12.
What is an ecosystem?
Answer:
In the biosphere living beings are interrelated and interdependent on each other for survival. This life-supporting system is known as an ecosystem.
Question 13.
What are the major groups of different types of vegetation of the world? Write their name.
Answer:
The major vegetation types of the world are grouped as forests, grasslands, scrubs, and tundra.
Question 14.
Write the names of two such animals in India, which are illegal to kill?
Answer:
- Lion
- Peacock.
Question 15.
What do you understand by National Park?
Answer:
A natural area designated to protect the ecological integrity of one or more ecosystems for the present and future generations.
Question 16.
What is rainwater harvesting?
Answer:
Rain water harvesting is the process of collecting rain water from rooftops and directing it to an appropriate location where it is stored for future use.

Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
“The distribution of population is found uneven in different parts of the world.” What is the reason for this?
Answer:
The uneven distribution of population in different parts of the world is mainly due to varied characteristics of land and climate. The rugged topography, steep slopes of the mountains, low-lying areas susceptible to water logging, desert areas, thickly forested areas are normally sparsely populated or uninhabited. Plains and river valleys offer suitable land for agriculture. Hence, these are the densely populated areas of the world.
Question 2.
Write a brief note on land use.
Answer:
Land is an important natural resource. Land is used for different purposes such as agriculture, forestry, mining, building houses, roads and setting up of industries. This is commonly termed as Land use.The use of land is determined by physical factors such as topography, soil, climate, minerals and availability of water. Human factors such as population and technology are also important determinants of land use pattern.
Question 3.
Explain the classification of land on the basis of ownership.
Answer:
On the basis of ownership, land can be classified into two parts:
- Private land: Private land is owned by individuals which they use for private interest.
- Community land: Community land is owned by the community for common uses like a collection of fodder, fruits, nuts, or medicinal herbs. These community lands arc also called common property resources.
Question 4.
What is a landslide? Explain the measures to prevent this.
Answer:
Landslides are simply defined as the mass movement of rock, debris, and earth down a slope They often take place in conjunction with earthquakes, floods, and volcanoes.
Measures to prevent landslides are:
- Hazard mapping to locate areas prone to landslides. Hence, such areas can be avoided for building settlements.
- Construction of retention wall to stop land from slipping.
- Increase in the vegetation cover to arrest landslide.
- The surface drainage control works to control the movement of landslides along with rainwater and spring flows.
Question 5.
Write a brief note on the conservation of land resources.
Answer:
The growing population and their ever-growing demands have led to large-scale destruction of forest cover and arable land and has created a fear of losing this natural resource. Therefore, the present rate of degradation of land must be checked. Afforestation, land reclamation, regulated use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers and checks on overgrazing are some of the common methods used to conserve land resources. Conservation of land resources is essential for the ecosystem.
Question 6.
Draw and illustrate the role of different factors affecting soil formation.
Answer
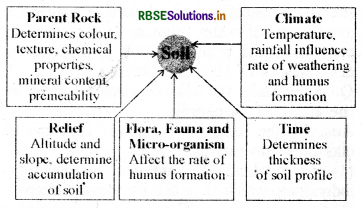
Question 7.
Describe any two methods for preventing soil erosion.
Answer:
(1) Terrace farming:
Broad flat steps of terraces are made on the steep slopes so that flat surfaces are available to grow crops. They reduce surface run-off and soil erosion.
(2) Contour barriers:
Stones, grass, and soil are used to build barriers along contours. Trenches arc made in front of the barriers to collect water.
Question 8.
Why is freshwater the most valuable substance on Earth?
Answer:
The oceans cover two-thirds of the earth's surface and support a rich variety of plant and animal life. The ocean water is however saline and not fit for human consumption. Freshwater accounts for only about 2.7 percent. Nearly 70 percent of this occurs as ice sheets and glaciers in Antarctica, Greenland and mountain regions. Due to their location, they are inaccessible. Only l percent of fresh water is available and fit for human use. It is found as groundwater, as surface water in rivers and lakes and as water vapour in the atmosphere. Freshwater is, therefore, the most precious substance on earth.
Question 9.
Explain the problem of water availability.
Answer:
Freshwater is available in small quantities in the world, so there is a scarcity of water in many regions of the world. Most of Africa, West Asia, South Asia, parts of western USA, north¬west Mexico, part of South America and entire Australia are facing shortages in freshwater supply. Countries located in climatic zones most susceptible to droughts face great problems of water scarcity. Thus, water shortage may be a consequence of variation in seasonal or annual precipitation or the scarcity is caused by overexploitation and contamination of water sources.
Question 10.
Explain the importance of natural vegetation and wildlife.
Answer:
Vegetation and wildlife are valuable resources. Plants provide us with timber, give shelter to animals, produce oxygen we breathe, protect soils so essential for growing crops, act as shelterbelts, help in storage of underground water, and give us fruits, nuts, latex, turpentine oil, gum, medicinal plants and also the paper. Forests attracts rain and protect the soil. Wildlife includes animals, birds, insects as well as aquatic life forms. They provide us milk, meat, hides and wool. Insects like bees provide us honey, help in the pollination of flowers and have an important role to play as decomposers in the ecosystem.

Question 11.
What is the water cycle?
Answer:
Cycling of water through the oceans, the air, the land and back again, through the processes of evaporation, precipitation, and runoff, is referred to as the water cycle.
Question 12.
Write a brief note on C.I.T.E.S.
Answer:
A number of steps have been taken at the international level for the conservation of vegetation and wildlife. For this CITES (The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) has been established that lists several species of animals and birds in which trade is prohibited. CITES is an international agreement between governments that aims at ensuring international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants. It does not threaten their survival.
Question 13.
Explain the causes for forest fire. Write some control measures also.
Answer:
Forest fire mainly occurs due to the following reasons:
- Natural fire due to lightning etc.
- Fire due to heat generated in the litter due to the carelessness of people.
- Fire purposely caused by local inhabitants, mischief-makers, miscreants, etc.
Some Control Measures:
- Prevention of fires through education.
- Prompt detection of fires through a well-coordinated network of observation points, efficient ground patroling and communication network.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the use of land as a natural resource. Explain the need and methods of conservation of land.
Answer:
Land is among the most important natural resources. It covers only about 30 percent of the total area of the earth’s surface. The land is used for different purposes such as agriculture, forest, mining, building houses, roads and setting up of industries.
The use of land is determined by physical factors such as topography, soil, climate, minerals and availability of water. Human factors such as population and technology are also important determinants of land use patterns. Land in the world is used as both private land and community land.
Need for conservation of land:
The availability of land is limited, it cannot be extended. While the world’s population is increasing continuously. For this reason people are destroying forests for housing and agriculture, causing in balance in the ecosystem. Due to urbanization and growing industries, unauthorized interference on community land is continuously increasing.
Today the vast changes in the land use pattern also reflect the cultural changes in our society. Land degradation, landslides, soil erosion, and desertification are the major threats to the environment because of the expansion of agriculture and construction activities. Due to all these reasons conservation of land is necessary.
Conservation of Land Resource:
Growing population and their ever-growing demand has led to large-scale destruction of forest cover and arable land and has created a fear of losing this natural resource. Therefore, the present rate of degradation of land must be checked. Afforestation, land reclamation, regulated use of chemical pesticide and fertilisers and checks on overgrazing are some of the common methods used to conserve land resources.
Question 2.
What is soil? Explain measures to prevent degradation of soil and conservation.
Answer:
Soil:
The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface of the earth is called soil. It is closely linked to land. Landforms determine the type of soil. Soil is made up of organic matter, minerals and weathered rocks found on the earth. This happens through the process of weathering. The right mix of minerals and organic matter make the soil fertile.
Degradation of Soil and Conservation Measures:
Soil erosion and depletion are the major threats to soil as a resource. Both human and natural factors can lead to degradation of soils. Factors which lead to soil degradation are deforestation, overgrazing, overuse of chemical fertilisers or pesticides, rain wash, landslides and floods. Some method of soil conservation are listed below:
- Mulching: The bare-ground between plants is covered with a layer of organic matter like straw. It helps to retain soil moisture.
- Contour barriers: Stones, grass, and soil are used to build barriers along contours. Trenches are made in front of the barriers to collect water.
- Rock dam: Rocks are piled up to slow down the flow of water. This prevents gullies and further soil loss.
- Terrace farming: Broad flat steps or terraces are made on the steep slopes so that flat surfaces are available to grow crops. They reduce surface run-off and soil erosion.
- Intercropping: Different crops are grown in alternate rows and are sown at different times to protect the soil from rain wash.
- Contour plowing: Ploughing parallel to the contours of a hill slope to form a natural barrier for water to flow down the slope.
- Shelterbelts: In the coastal and dry regions, rows of trees are planted to check the wind movement to protect soil cover.
Question 3.
Explain the problem of water availability and clarify the measures to conserve water resources.
Answer:
The problem of water availability:
Water is a vital renewable natural resource. Three-fourths of the earth’s surface is covered with water. The oceans cover two-thirds of the earth’s surface and support a rich variety of plant and animal life. The ocean water is however saline and not fit for human consumption. Freshwater accounts for only about 2.7 percent. Nearly 70 percent of this occurs as ice sheets and glaciers in Antarctica, Greenland and mountain regions. Due to their location, they are inaccessible. Only 1 percent of freshwater is available and fit for human use. But due to excessive use and water pollutants, a water crisis has arisen in many countries.
Increasing population, rising demands for food and cash crops, increasing urbanization and rising standards of living are the major factors leading to shortages in supply of freshwater either due to drying up of water sources or water pollution. Today many regions of the world are facing scarcity of water.
Conservation of water resources:
Access to clean and adequate water sources is a major problem facing the world today. Hence, conservation of water resources is necessary. The following measures can be taken to conserve water resources:
- Discharge of untreated or partially treated sewage, agricultural chemicals and industrial effluents in water bodies are major contaminants. Pure water should be saved from them.
- Polluted water should be treated by various methods and reused.
- Forest and other vegetation cover slow the surface run-off and replenish underground water therefore forests should be expanded.
- The canals used for irrigating field should be properly lined to minimise losses of water seepage.
- Sprinklers effectively irrigate the area by checking water losses through seepage and evaporation.
Question 4.
Describe the distribution of natural vegetation.
OR
Describe the major types of natural vegetation.
Answer:
The distribution of natural vegetation in the world depends on temperature and moisture. The growth of vegetation primarily depends on these factors. On this basis, the major vegetation types of the world are grouped into the following four elapses
(1) Forests:
In areas of heavy rainfall, huge trees may thrive. The forests are thus associated with areas having abundant water supply. As the amount of moisture decreases the size of trees and their density reduces.
(2) Grasslands:
Short stunted trees and grasses grow in the regions of moderate rainfall forming the grasslands of the world.
(3) Scrubs:
Thorny shrubs and scrubs grow in dry areas of low rainfall. In such areas plants have deep roots and leaves with thorny and waxy surfaces that reduce the loss of moisture through transpiration.
(4) Tundra vegetation:
This type of vegetation is found in cold polar regions. Tundra vegetation comprises of mosses and lichens.

Question 5.
Explain the importance of forests and wildlife and also explain the conservation of natural vegetation and wildlife.
Answer:
Importance of vegetation and wildlife:
The importance of vegetation and wildlife can be explained from the following points:
- Forest and wildlife help in maintaining the balance in the ecosystem.
- Forest provides shelter to wildlife.
- Forests provide us with timber, fruits, rubber, paper, gum, etc.
- Many types of raw materials for industries are obtained from forests.
- Forests help in preventing soil erosion.
- Forest attracts rainfall, thereby maintaining the groundwater level.
- We get many types of medicines from forests.
- Wildlife provides us with milk, meat, hides, and wool.
Conservation of natural vegetation and wildlife:
Due to the increasing demand of the population, natural vegetation and wildlife have become a threat. Therefore, many measures have been taken for the protection of natural vegetation and wildlife, which are as follows:
- National parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves are made to protect our natural vegetation and wildlife.
- Hunting of wildlife is banned.
- Efforts have been made to control human activities in the forests.
- Awareness programs should be encouraged at the regional and community level towards the natural vegetation and wildlife.
- A number of national and international organizations have been set up to protect natural vegetation and wildlife.

- RBSE Class 8 Social Science Important Questions History Chapter 3 Ruling the Countryside
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources
- RBSE Class 8 Social Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 8 Social Science Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Social Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 8 Social Science Notes History Chapter 1 How, When and Where
- RBSE Class 8 Social Science Important Questions Civics Chapter 9 जनसुविधाएँ
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Civics Chapter 10 कानून और सामाजिक न्याय
- RBSE Class 8 Social Science Important Questions Civics Chapter 10 कानून और सामाजिक न्याय
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Civics Chapter 9 जनसुविधाएँ
- RBSE Class 8 Social Science Important Questions Civics Chapter 8 हाशियाकरण से निपटना