RBSE Class 11 History Notes Chapter 1 From the Beginning of Time
These comprehensive RBSE Class 11 History Notes Chapter 1 From the Beginning of Time will give a brief overview of all the concepts.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 History in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 History Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 History Chapter 1 Notes From the Beginning of Time
→ The origin of human being is a long and a complicated story.
→ There are several stages in the journey of human’s development since his coming into beings. \ → Primates living beings existed in Africa and Asia about 36-24 mya.
→ Primates constituted a sub-group of a large number of mammals.
→ The Hominoids came into existence about 24 mya.
→ Hominoids included apes and had comparatively smaller brain.
→ Hominoids had four legs. They moved on their four paws, but were unable to walk erect.
→ Hominids, evolved from Hominoids. They originated in Africa in about 5.6 mya.
→ The Hominids belong to hominide family.
→ Hominids got divided into several branches known as genus.

→ Homo is a Latin word which means human. It includes both males and females.
→ Homo came into existence app. in 2.5 mya.
→ Homo habilis fossils date back to 2.2 mya to 1.8 mya. They were more intelligent as compared to Australopithecus.
→ Homo erectus knew the art of walking. They could walk erect and could also run.
→ The fossils of Homo erectus have been foun d in many parts of Africa and Asia.
→ Homo sapiens were the wiseman and were also known as modem man.
→ Homo sapiens originated around 0.19 to 0.16 mya.
→ Earlier fossil fuels of Homo-sapiens were found in Omo Kibish, Border Cave, Die Kelders and Dar-es-solten.
→ Homo sapiens used superior intelligence, sophisticated tools and language to exploit the natural world more efficiently than any other species of the earth had been.
→ Homo-neanderthalensis were also called Neanderthal man because their fossils have been found in Neander valley in Germany.
→ Living in huts helped him to practise agriculture.
→ The most important evidence comes from Terra Amata in Southern France. It was made up thatch.
→ Discovery of fire brought many changes in the life of early man.
→ The traces of the use of fire have been discovered at Chesowanja in Kenya and Swartkrans in South Africa.
→ The tools of early man were made of stone.
→ Stone tools were divided into three categories. These are hand axes, choppers and flake tools.
→ The earliest evidence of stone tools are traced from Ethiopia and Kenya.
→ Sewing needle was invented 21,000 years ^ago.
→ The mastery of speech made it possible for man to develop culturally beyond the other primates.
→ The early human painted the picture of flora and fauna, sun, moon, rivers, their daily day-to-day activities etc.
→ The painting was done on the walls and roofs of the caves.
→ The earliest cave paintings of Altamira, Lascaux and Chauvet are very famous.
→ The early human also know the art of sculpture making and made small-sized statues.
→ The Hadza lived around the salty lake, ‘Lake Eyasi’. They were also fond of hunting.
→ The Hadza did not assert their rights over resources.
→ Altamira is in Spain. It is a cave site. The painting of the cave brought into notice by a local landlord and an amateur archaeologist Marcelino Sanz de Sautuala and his daughter Maria.

→ Otduvai came to be identified with Mary and Louis Leakey.
→ Some historians are of the view that Ethnographic data cannot be used for understanding the past society.
→ Ethnography is the analytical study of contemporary ethnic society, which provides information about their livelihood, traditions, social customs, political institution, etc. The early humans was totally dependent on nature and had no knowledge about agriculture. The early human obtained his food through several ways e.g. by gathering seed, nuts, fruit, etc., by fishing, by hunting etc.
→ Early human was food gatherers. He collect eatable goods likes seed, nuts, fruits and tuber for his survival.
→ Early man used hooks for catching smaller fish and harpoons to catch comparatively large fishes. Sometimes he also catch fishes from rivers and ponds with hands.
→ Early man lived on trees, in caves and later on in huts.
→ Early man lived on the trees. It was because most of his food he obtained from the trees and wander from place to place in search of food.
→ About 400,000 years ago early man begin to live in caves.
→ Dwelling him in caves proved very beneficial. The most prominent example of cave dwelling used by early man is Cave Lazaret. It is in Southern France.
→ Early human around 125,000 years began to live in huts.
→ Timeline of The Events:
|
Peopling of the World |
||
|
WHEN |
WHERE |
WHO |
|
5-1 mya |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
Australopithecus, early Homo, Homo erectus |
|
1 mya-40,000 years ago |
Africa, Asia and Europe in mid-latitudes |
Homo erectus, archaic Homo sapiens, Neanderthals, Homo sapiens sapiens / modem humans |
|
45,000 years ago |
Australia |
Modern humans |
|
40,000 years ago to present |
Europe in high-latitudes and Asia-Pacific islands North and South America in deserts, rain forests |
Late Neanderthals, modern humans |
→ The Earliest Fossils of Modern Humans
|
WHERE |
WHEN (years ago) |
|
ETHIOPIA |
195,000-160,000 |
|
SOUTH AFRICA |
120,000-50,000 |
|
MOROCCO |
70,000-50,000 |
|
ISRAEL |
100,000-80,000 |
|
AUSTRALIA |
45,000-35,000 |
|
BORNEO |
40,000 |
|
FRANCE |
35,000 |

→ Timeline - 1(mya)
|
36-24 mya |
Primates; Monkeys in Asia and Africa |
|
24 mya |
(Superfamily) Hominoids; Gibbons, Asian orang-utan and African apes (gorilla, chimpanzee and bonobo or ‘pygmy’ chimpanzee) |
|
6.4 mya |
Branching out of hominoids and hominids |
|
5.6 mya |
Australopithecus |
|
2.6-2.5 |
Earliest stone tools |
|
2.5-2.0 |
Cooling and drying of Africa, resulting in decrease in woodlands and increase in grasslands. |
|
2.5-2.0 mya |
Homo |
|
2.2 mya |
Homo habilis |
|
1.8 mya |
Homo erectus |
|
1.3 mya |
Extinction of Australopithecus |
|
0.8 mya |
‘Archaic’ sapiens, Homo heidelbergensis |
|
0.19-0.16 mya |
Homo sapiens sapiens (modem humans) |
→ Timeline - 2 (years ago)
|
Earliest evidence of burials |
300,000 |
|
Extinction of Homo erectus |
200,000 |
|
Development of voice box |
200,000 |
|
Archaic Homo sapiens skull in the Narmada valley. India |
200,000-130,000 |
|
Emergence of modem humans |
195,000-160,000 |
|
Emergence of Neanderthals |
130,000 |
|
Earliest evidence of hearths |
125,000 |
|
Extinction of Neanderthals |
35,000 |
|
Earliest evidence of figurines made of fired clay |
27,000 |
|
Invention of sewing needles |
21,000 |
→ Recovering Fossils is a painstaking process. The precise location of finds is important for dating.
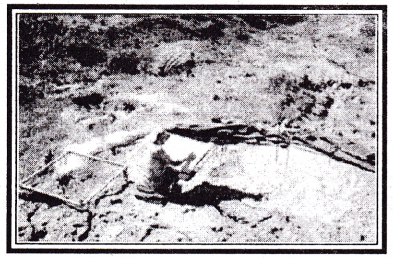
Depicts the equipment used to record the location of finds. The square frame is a grid divided into 10 cm squares each. Placing it over the find spot helps to record the horizontal position of the find. While the triangular apparatus to the right is used to record the vertical position of the object located by archaeologist
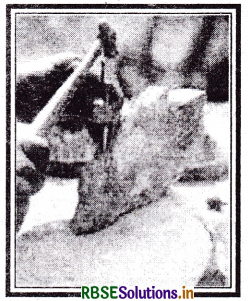
Deptics a fossil fragment recovered from the surrounding stone.

→ Stone Tools: Made of The Punch Blade Technique
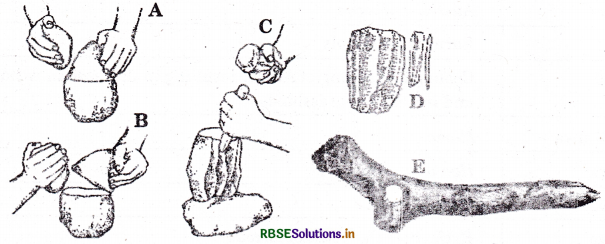
(A) The tap of a large pebble is removed using a hammer stone
(B) This produces a flat surface called the striking platform
(C) This is then struck using a hammer ami a punch, made of bone or antler.
(D) This lehds to the production of blades that casn be used. as knives, or modified to serve as chisels or burins which could be used to engrave bom, antler, ivory or wood.
(E) An example of engraving on bone. Note ike drawings of animals on it.

- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 1 From the Beginning of Time
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 10 Displacing Indigenous Peoples
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 2 लेखन कला और शहरी जीवन
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 7 Changing Cultural Traditions
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 6 तीन वर्ग
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 6 The Three Orders
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 3 तीन महाद्वीपों में फैला हुआ साम्राज्य
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 3 An Empire Across Three Continents
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 History Chapter 1 From the Beginning of Time
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 11 Paths to Modernisation
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium