RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 3 An Empire Across Three Continents
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 3 An Empire Across Three Continents Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 History in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 History Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 3 An Empire Across Three Continents
Very Short Answer Type Questions
An Empire Across Three Continents Extra Questions 1.
Which city was the capital city of Roman Empire ? When was this city founded?
Answer:
Italy was the capital of Roman Empire. It was (This city was) founded in 1000 BCE and was situated on river Tiber.
An Empire Across Three Continents Important Questions 2.
Name the three important players of the Roman Empire.
Or
What did the political system of Roman Republic consist of?
Answer:
The three important players of the Roman Empire were :
(i) The Emperor
(ii) The Senate
(iii) The Army

An Empire Across Three Continents Important Questions 3.
Who were Plebians ?
Answer:
Plebians were the common people of the Roman Empire (Rome). They were burdened with heavy taxes.
Class 11 History Chapter 3 Extra Questions And Answers Question 4.
Who were known as Patricians ?
Answer:
Roman aristocracy was known as Patricians.The head of Patricians or aristocrate family constituted the senate.
Class 11 History Chapter 3 Extra Questions And Answers Question 5.
Name the sea that seperates the continents of Europe and Africa.
Answer:
The sea that seperates the continents of Europe and Africa is Mediterranean Sea.
Class 11 History Chapter 3 Important Questions And Answers Question 6.
In how many continents did the Roman Empire spread/ Stretched out ? Name them also.
Answer:
The Roman Empire was spread/ stretched out over three continents. These continents were :
(i) Asia
(ii) Europe and
(iii) North Africa.
Important Questions Of An Empire Across Three Continents Question 7.
When did Roman Empire became a Republic ? Till how long it remained a republic ?
Answer:
Roman Empire became a Republic in 509 BCE. It remained republic upto 27 BCE.
Extra Questions Of An Empire Across Three Continents Question 8.
What do you mean by the ‘Augustan Age’ ?
Answer:
The reign of Emperor Augustus from 27 BCE to 14 CE is referred to as the Augustan Age. His reign is remembered for the peace it ushered in after decades of internal strife and centuries of military conquest.

Chapter 3 History Class 11 Extra Questions And Answers Question 9.
What do you mean by concept Late Antiquity ?
Answer:
The period of great crisis from 4th to 7th century history of Roman Empire is known the period of Late Antiquity. During this period Roman rulers (emperors) like Diocletian, Constantine, Theodosius II and Justinian made their best efforts to stem the tide of decay.

An Empire Across Three Continents Class 11 Important Questions 10.
What do you know about Theodosius II?
Answer:
He was the famous ruler of eastern Roman empire, who ruled from 408 to 450 CE. He succeeded in checking the invasion of foreign rulers from the Iran and Germany.
Class 11 History Ch 3 Important Questions 11.
What was the importance of great urban centres in imperial system of Rome ? Name any three largest urban centres of Rome.
Answer:
The great urban centres were the true bedrock of the imperial system in Rome. The government was able to tax the provincial countryside through these cities which generated major portion of the wealth of the empire. Three urban centres were : Antioch, Alexandria and Carthage.
Class 11 History Ch 3 Extra Questions 12.
How is Roman Empire classified ?
Answer:
Roman Empire is broadly classified into two divisions. These divisions are :
(i) Early Roman Empire.
(ii) Later Roman Empire (Late Antiquity)
Important Questions Of Roman Empire Class 11 Question 13.
Who established Principate and when ?
Answer:
Principate means the regime founded by Augustus. It was founded by Augustus replacing Roman Republic in 27 BCE.
An Empire Across Three Continents Class 11 Questions And Answers Question 14.
What was the position of slaves in the Roman society during third century ?
Answer:
Slaves were included in the family.

Roman Empire Class 11 Extra Questions 15.
Write any two important reforms introduced by Augustus in Roman army.
Answer:
(i) Augustus organised army on permanent basis.
(ii) He was the founder of Praetorian guard.
Empire Across Three Continents Extra Questions 16.
Write any two economic reforms done by Augustus.
Answer:
Two economic reforms done by Augustus were :
(i) He encouraged the trade and commerce.
(ii) He patronised agriculture.
(iii) He established trade relations with other countries.
Question 17.
Write any two reasons for the popularity of Marcus Aurelius.
Answer:
(i) Marcus Aurelius introduced many reforms to improve the condition of the poor and the slaves.
(ii) He crushed the invasion of Parthians and the German barbarians.
Question 18.
What is meant by ‘Patrician ?
Answer:
Patrician : This word was used for the aristocratic class of Rome. This class consisted of the rich landlords and industrialists. They were the powerful persons of the Roman Senate.
Question 19.
What does ‘Post Roman’ mean?
Answer:
The general prosperity was especially marked in the East where population was still expanding till the 6th century, despite the impact of plague which affected the Mediterranean in the 540s. In the West, by contrast, the empire fragmented politically as Germanic groups from the North took over all the major provinces and established that are best described as Post-Roman.
Short Answer Type Questions
History Class 11 Chapter 3 Question Answer Question 1.
Write about the geographical situation of Roman Empire.
Answer:
Ancient Roman Empire was very vast. It was spread over three continents namely : Europe, Asia and North Africa. River Euphrates formed the frontier between the Roman Empire and Iran. Rivers Rhine and Danube demarcated its northern frontier while the Sahara desert formed its southern frontier. Thus the Roman Empire dominated the region around the Mediterranean sea.

An Empire Across Three Continents Extra Question Answers Question 2.
Who was Augustus ? Write any three achievements of Augustus.
Answer:
Augustus was the founder of the Roman Empire. He founded the Roman Empire in 27 BCE and ruled till 14 CE. The treatises written by Livy, Virgil and Horace made him more popular. Under him Roman Empire accomplished many walks of the life that is rightly known as the Golden Age of the Roman Empire.
Achievements :
(i) He established peace in Rome.
(ii) He introduced many economic, religious and administrative reforms.
(iii) He introduce military reform to strengthened his empire.
Question 3.
What are various sources available for reconstructing the history of Roman Empire ?
Or
List some major sources of studying Roman history.
Answer:
Major sources of study or reconstructing the history of Roman Empire include :
(i) Ruins of material remains.
(ii) Written accounts of Roman philosophers.
Material remains include a number of buildings, monuments, their ruins, etc. discovered by the archaeologists. Coins, sculpture, pottery etc., also provide valuable information about Roman Empire.
An Empire Across Three Continents Class 11 Extra Questions 4.
Mention any two important works done by the Emperor Constantine.
Answer:
(i) A new denomination called the solidus was introduced by the Emperor Constantine. It was a pure gold coin weighing 4.5 grams this fold coin was minted on a very large scale and millions of these coins were in circulation.
(ii) In the fourth century, he made Christianity the official religion.

Question 5.
Write a short note on the economic reforms introduced by Augustus.
Answer:
Augustus’ reign in history of Roman Empire is known as remarkable progress in the economic sphere. He himself paid personally attention to economic reforms and improved means of transport for the development of trade and commerce within and outside the state. He also took step to improve agriculture and commerce. He did his best to maintain commercial relations between Roman Empire and other countries.
Question 6.
How did the Roman people controlled their workers ?
Answer:
Workers were mainly slaves. Following measures were taken to keep them in control :
(a) Workers were branded so that they could be recognised if and when they run away and try to hide.
(b) Many private employers cast their agreements with workers in the form of debt contracts to be able to claim that their employees were in debt to them and thus ensure tighter control over them.
Question 7.
Write some administrative reforms introduced by Emperor Diocletian.
Answer:
Diocletian ruled from 284 to 305 CE and tried to establish the glory of the Roman Empire. He introduced the following reforms to strengthen his empire :
(i) He abandoned territories which were of less economic or strategic value.
(ii) He fortified the frontiers.
(iii) He reorganised provincial boundaries and seperated civilian from military functions.
(iv) He granted greater autonomy to the military commanders, who now became a more powerful group.

Ch 3 History Class 11 Important Questions 8.
What was amphorae and what were they used for ?
Answer:
Amphorae were a type of containers. They were used in transporting liquids like wine and olive oil. They were made in Mediterranean region.

Question 9.
Give evidence of the Roman’s contribution to law and government.
Answer:
The Roman laws are the basis of the law of many European countries. The Roman Code of Laws was made by emperor Justinian. On this basis, the laws of Germany, France, Italy and Spain were made. England also got great help from this code of laws. The greatest contribution of Roman intelligence is their law. Their law was based on reasoning. At first Kingship was established in Rome. Many centuries later Democratic Government was formed in Rome.
Class 11 An Empire Across Three Continents Important Questions 10.
What do you know about Roman calendar ?
Answer:
The Romans made a calendar on the basis of their knowledge on astronomy. July was named after Julius Ceasar and August was named after the name of Augustus. September, October, November and December were named after Latin language which means 7th, 8th, 9th and 10th.
Question 11.
What were the main social classes in Ancient Roman Civilization ? What was the position of the slaves ?
Answer:
During the ancient Roman civilization the society was divided mainly among three classes :
(i) The Particians or the Rich.
(ii) The Plebians or the Common People.
(iii) The Slaves
In Rome the slaves were employed in agriculture, mining, road construction, workshops and on ships. They were brutally exploited and as a result many used to become cripple in the very young age.

Important Questions Of Chapter An Empire Across Three Continents Question 12.
Give the name of the person and for civilization responsible for the cultural advances as reflected in the following works of literature and art.
Answer:
|
Name of Works |
Name of Person |
Name of Civilization |
|
Iliad |
Andronix |
Roman Civilization |
Question 13.
Describe the main factors which were responsible for the decline of the Roman Civilization.
Answer:
Factors responsible for the decline of Roman Civilization :
(i) Wars and Luxurious Life: Repeated wars and conquests bent and broke the back of democracy. Luxurious and easeful way of living demoralised the ruling class.
(ii) Slave Revolts: The number of slaves out numbered the free men. They grew rebellious and could not be quelled by the ruling class.
(iii) Weakness of Emperors : The Roman emperors being incompetent and weak could not face the invaders.
(iv) Spread of Christianity : The Christian religion gave message of love and equality. It weakened the rule of emperors since it created rebellious feeling among the slaves.
(v) Raids and invasions : Invaders and raiders shattered the Roman Civilization.
Question 14.
What were the systems of Government in ancient Greek and Rome called ? How were they different from the systems of the Government in ancient China or ancient Iran ?
Answer:
Systems of Government in ancient Greek and Rome.
Ancient Greek and Rome had their federal structure of Government. Later on they also had Monarchy and Kingship. The Greeks were successful in their democratic city states. The idea of republicanism was developed by the RomAnswer: There the royal persons used to call themselves as the servants of the people.
It was different from ancient China and Iran :
In ancient China and Iran there was no system of democratic and republican form as in Rome and Greece. China and Iran both had monarchical form of government ruled by the kings/monarch.

Question 15.
What did the Roman political system consist of ? Write in brief.
Or
"The emperor, the aristocracy and the army were the three main players in the political history of the Roman Empire.” Explain.
Answer:
The three main players of the Roman empire were :
(а) The Emperor : He had the overall power over his empire. He had supreme power over his army.
(b) The Senate : It was a body representing the aristocracy. They were mainly landowners and they usually feared the army because of its unpredictable violence.
(c)The Army : They were paid professional army which existed for about 25 years. They were the largest organised body in the empire. They would constantly agitate for more wages and better conditions.
Question 16.
How was Roman society divided ? Describe in short the struggle for tyranny.
Answer:
Roman society was divided into two groups. These groups were :
The Patrician and the Plebians:
The Patrician formed the city’s aristocracy. The head of the Patrician families, made up a group called the senate. While the common Roman people were known as Plebians and force to pay heavy taxes.
Struggle against the Tyranny : The Plebians fought and struggled against the tyranny of the Patrician class and wer^ succeeded in winning their rights to elect tribunes to veto the decision of the councils and the senate.
Question 17.
What was the status of literacy in the Roman Empire ?
Answer:
(i) The rate of literacy varied greatly between different parts of the empire. Literacy was widespread among army officers, estate managers and soldiers.
(ii) Casual literacy existed and it varied from place to place.
(iii) There was a wall in pompeii which carried advertisements and graffiti, which indicates high level of casual literacy.
Question 18.
Describe the position of slaves in ancient Greek and Rome. In what kinds of work were they generally engaged ? What was the impact of slavery on the nature of society ?
Answer:
(i) A large number of people in ancient Greek and Rome were slaves. The prisoners of war and those who could not pay their debts were kept as slaves. Their condition was very bad, they had to work day and night and they were deprived of all the social and political rights.
(ii) All types of works were taken from the slaves. They were employed in agriculture, mining, road building, workshops and on the ships.
(iii) The slave system produced an evil effect both on the Greek and the Roman societies. Continuous exploitation of the slaves often led them to revolt and the State had to strengthen its forces constantly to suppress them.

Question 19.
Compare the social conditions in ancient Greek and Rome.
Answer:
The Greek society was divided into three classes:
(a) Nobles or Upper Class,
(b) Demos or free people,
(c) Slaves.
The Roman society was also divided into three groups :
(а) The Patricians or the Rich
(b) Plebians or the Common People
(c) The Slaves
The upper class in both the countries included rich and the landed aristocracy which led a very luxurious life. The second class was comprised of traders, craftsmen, warriors and the cultivators. These people enjoyed all the civic rights but they had to bear burden of most of the taxes. For this purpose they were against the upper class. The condition of the third class i.e., the slaves was very bad in both the countries. They were bought and sold in the markets. They were treated like animals by their masters.
Question 20.
Compare the achievements of the Roman people with those of the Greeks in any five spheres.
Answer:
(i) By nature the Greeks were ideals while the Romans were the realists.
(ii) The Greeks could raise the small city states while Romans built a big empire.
(iii) The Greeks attached more importance to the democratic form of government in comparison to the RomAnswer:
(iv) The Greeks were expert in the fields of art and literature while the Romans are well known for their laws and administration.
(v) The Greeks emphasized the freedom of thought while the Romans considered discipline and obedience more important.
Question 21.
Mention one of the striking feature of Roman urban life.
Answer:
Public baths were a striking feature of Roman urban life (when one Iranian ruler tried to introduce then into Iran, he encountered the wrath of the clergy there ! Water was a sacred element and to use it for public bathing may have seemed a desecration to them), and urban populations also enjoyed a much higher level of entertainment. For example, one calendar tells us that spectacular (shows) filled no less than 176 days of the year!

Question 22.
Write about the economic life of the people in Roman Civilisation.
Or
Explain any four basic features of Roman Society and economy which made it look quite modern.
Answer:
Basic features of the Roman society were :
(a) There was widespread prevalence of nuclear family. Adult sons did not live with their families and it was exceptional for adult brothers to share a common household. On the other hand, slaves were included in the family. .
(b) The typical form of marriage was one where wife did not transfer to her a husband's authority but retained full rights in the property of her father's family.
(c) Marriages were generally arranged and there is no doubt that women were often subject to domination by their husbands.
(d) Divorce was relatively easy.
Basic features of Economy :
(a) The empire had substantial economic infrastructure of harbours, mines, quarries, brickyards, olive oil factories etc. Wheat, wine and olive oil were traded and consumed in large quantities and they came mainly from Spain, the Gallic provinces, Egypt, North Africa and to a lesser extent, Italy.
(b) Liquids like wine and olive oil were transported in containers called ‘amphorae’. Spanish producers succeeded in capturing markets for olive oil from their Italian counterparts.
(c) There was diversified application of water power around the Mediterranean as well as advances in water-powered milling technology, the use of hydraulic mining techniques in the Spanish gold and silver mines.
(d) The existence of well organized commercial and banking networks and the widespread use of money are all indications of Roman economy.

Question 23.
Why did the monetary system breakdown in the late Roman empire ?
Answer:
The monetary system broke down in the late Roman empire because Spanish silver mines were exhausted and the government ran out of stock of the metal to support a stable coinage in silver. This also led to the introduction of a new denomination in gold, the solidus
Question 24.
How was the vast Roman empire administered ?
Answer:
The vast Roman empire was controlled and administered with the help of urbanisation. All the territories of the empire were organised and were subject to taxation. The great urban centres that lined the shores of the Mediterranean were the foundation of the imperial system. It was through the cities that government was able to tax the provincial countrysides which generated much of the wealth of the empire.
This shows that the local upper class was actively involved with the Roman state in administering their own territories and collecting taxes from them. Throughout the second and the early third century, the provincial upper class provided experienced officers that administered the provinces and commanded the army.
Question 25.
What was the policy of the Roman emperors towards more expansion of the empire in the first two centuries ?
Answer:
Very few efforts were made, in the first two centuries, towards more expansion of the Roman Empire. This empire was inherited by Tiberius from Augustus. It was already so vast that the ruers saw its further expansion as unnecessary. The Augustus regime is known for the peace which came in after several years of internal struggle and centuries of military conquest. The only major campaign of expansion during the early empire was the Trajan’s occupation of territory beyond the river Euphrates and it was fruitless. It took place in the years 113-117 CE. But Trajan’s successors took this expansion as useless. So they abandoned it.
Question 26.
What was a 'city’ in the Roman sense ? Also tell some characteristics of the urban life.
Answer:
In Roman sense, city was an urban centre which had its own magistrate, city council and a definite territory. This territory contained many villages under its jurisdiction. So one city could not be a part of another city. Decision about the status of a city or village was depended upon royality. Villages could be given the status of cities, and vice-versa.
Characteristics of the urban life :
(i) There was no shortage of food in cities,
(ii) Cities had better facilities during famines than the countryside.
(iii) Urban people enjoyed a higher level of entertainment. For example one calendar tells us that spectecula shows filled not less than 176 days of the year.

Question 27.
The traditional religious culture of the Greeks and Romans had been polytheist. Give examples.
Answer:
(i) Both the Greeks and Romans had faith in various cults and ways of worship.
(ii) They worshipped Roman/Italian gods like Jupiter, Juno, Minerva and Mars. Besides, numerous Greek and eastern dieties were also worshipped.
(iii) There were thousands of temples, shrines and sanctuaries throughout the empire. Polytheists had no common name or label to describe themselves.
(iv) Judaism was another great religion of the Roman Empire. There was a too much diversity within the Jewish communities of late antiquity.These examples prove that the traditional religious culture of the Greeks and Romans had been polytheist.
Question 28.
The Roman Empire was culturally much more diverse than that of Iran. Explain.
Answer:
Iran was ruled over by the Parthian and later by Sasanian dynasties. These dynasties ruled over a population which was mainly Iranian. But the Roman Empire was a mixture of cultures and territories which were mainly bound together by a common system of government. A number of languages were spoken in the Empire.
But Latin and Greek languages were used for administrative purposes. The upper classes of the west spoke and wrote in Latin and upper classes of the east spoke and wrote in Greek. All those people who lived in the empire were the subjects of a single ruler means the emperor. It hardly mattered where they lived and what language they spoke.
Long Answer Type Questions:
An Empire Across Three Continents Long Questions 1.
"Roman Civilisation flourished in the Mediterranean region. It had contributed a lot to the world civilisation”. With the help of the example describe the contribution of this civilisation.
Answer:
Roman Civilisation is a great ancient world civilisation. It had largely contributed in the development of other civilisations. Following examples are given to justify this fact:
(i) Law and Government: The Romans were great exponents of law. The Roman law did not make any discrimination among the citizens. Most of the countries of the world owe their present legal systems of the RomAnswer: The Romans were probably the first people who could exercise effective control upon the different dominions of their vast empire. The credit also goes to the Romans for the development of the idea of Republicanism.
(ii) Contribution in field of Language, Philosophy and Literature : Latin, the language of the Romans became the language of all the educated people of Europe. Cicero was a great philosopher of Rome. He stressed upon the natural rights of all the individuals. Ancient Rome also produced the great poets like Virgil and Horace, who spread the glory of Roman Civilisation through their immortal works.
(iii) Art: The Romans were the inventors of the concrete. They could firmly cement the bricks and the pieces to stone together. They were very efficient engineers too. The art of painting murals was highly developed in Rome.
(iv) Science and Technology : The Romans were the first to start the public services. Free medicines were given to the poor. The Roman physicians wrote a book containing information on surgery. They also compiled a medical encyclopaedia. The Roman Calendar,with a few changes is still in practice in the world.
Question 2.
Explain, how the cultural diversity of the Roman Empire was reflected in many ways and at many levels ?
Answer:
Cultural diversity of Roman Empire was reflected in many ways. It was felt in many ways and levels. Many levels of diversity exist in religious cults. Diversity also exist in many forms like in language spoken, dress style, costumes, the food ate, the social organisation (tribal/non tribals), pattern of settlement etc.
Various languages were spoken in different regions. Aramaic was the dominant language group of the Near East (at least west of the Euphrates), Coptic was spoken in Egypt, Punic and Berber in North Africa, Celtic in Spain and the northwest. But many of these linguistic cultures were purely oral, at least until a script was invented for them.
Armenian, for example, only began to be written as late as the fifth century, whereas there was already a Coptic translation of the Bible by the middle of the third century. Elsewhere, the spread of Latin displaced the written form of languages that were otherwise widespread; this happened notably with Celtic, which ceased to be written after the first century.

An Empire Across Three Continents Questions And Answers Question 3.
“The Romans were great law-givers”. Justify the statement.
Answer:
Romans were the greatest law-givers. All were equal before law. Appeals could be made against injustice. According to Prof. John Conard Appel, “Rome commanded leadership because of the jsutice of the Roman law.”
The Romans introduced civil and criminal laws to safeguard their rights. Roman system of law came into being gradually and over a long period. During the days before the
Republic the laws were made and administered by the kings. The Greeks law-maker Draw prescribed death as the penalty for most crimes. After a long struggle the Plebians got victory over the Patricians and the Roman laws were codified in Twelve Tablets. They were placed in the forum (or market place) where all could see and read them.

As life developed and changed, the Romans also revised their laws acording to the new situations. The Roman Senate passed many laws from time to time; later on the emperors issued decrees which became a part of the Roman legal system. The Roman judges made decisions according to laws based on justice and common sense. All these went a long way in the development of legal system of Rome.
The Roman laws lay scattered at various places and courts and did not exist in one written unit. The Roman Emperor Justinian (527-565 A.D.) appointed a commission of ten legal experts to collect and codify all such laws. They arranged the laws in orderly form and prepared a code of laws known as ‘Corpus Juris Civilis of Justinian’. Justinian earned the title of the “The Lawgiver of civilization”. This is the greatest contribution of Rome to the world. This code forms the basis of the legal system of modern civilized nations.
Question 4.
What was the social hierarchy that was prevelant in the early Roman empire ?
Answer:
Tacitus, a historian of the early empire had described the social hierarchy of the empire. According to him,
(а) In the early Roman empire senators were at the top.
(b) Next were the leading members of equestrian class.
(c) Respectable section of all people who were attached to the great houses was next in the social order.
(d) Then was the untidy lower class and slaves came at the bottom.
Question 5.
What do you understand by Late Antiquity ? Explain the religious and administrative changes during this period.
Answer:
The term ‘Late Antiquity 1 is used to describe the final, fascinating period in the evolution and break-up of the Roman Empire and refers broadly to the fourth to seventh centuries. This period was full of many cultural and economic advances. Following religious and administrative changes were made in the Roman empire during this period:
Religious Changes
1. In the 4th century, emperor Constantine made Christianity the official religion.
2. In the 7th century Islam rose.
3. This religion also began to become very popular rapidly.

Administrative Changes : These changes occurred in the time of Diocletian (243-305) and continued till the time of Constantine changes were as follows :
(a) Changes in the time of Diocletian :
1. He abandoned the territories that had less economic or strategic value.
2. He fortified frontiers of the empire.
3. He reorganised the provincial boundaries.
4. He seperated civilian from military functions and granted greater autonomy to the military commanders.
(b) Changes in the time of Constantine :
1. He created Constantinople and made it the second capital. It was surrounded on three sides by the sea.
2. As the new capital required a new senate, there was a rapid expansion of the governing class in the 4th century.
Question 6.
How the third century crisis was different than the first and second centuries a period of peace ?
Answer:
If the first and second centuries were by and large a period of peace, prosperity and economic expansion, the third- century brought the first major signs of internal strain.
(i) From the 230s, the empire found itself fighting on several fronts simultaneously. In Iran a new and more aggressive dynasty emerged in 225 (they called themselves the ‘Sasanians’) and within just 15 years were expanding rapidly in the direction of the Euphrates.
(ii) Meanwhile, a whole series of Germanic tribes or rather tribal confederacies (most notably, the Alamanni, the Franks and the Goths) began to move against the Rhine and Danube frontiers, and the whole period from 233 to 280 saw repeated invasions of a whole line of provinces that stretched from the Black Sea to the Alps and southern Germany.
(iii) The Romans were forced to abandon much of the territory beyond the Danube, while the emperors of this period were constantly in the field against what the Romans called ‘barbarians’.
(iv) The rapid succession of emperors in the third century (25 emperors in 47 years !) is an obvious symptom of the strains faced by the empire in this period.

Question 7.
What was the status of women in the Roman Empire ?
Answer:
(i) The women in the Roman empire enjoyed considerable legal rights in owning and managing property.
(ii) They were married off in the late teens or early twenties.
(iii) Arrange marriage was the general norm and women were often subject to domination by their husbands.
(iv) The typical form of marriage was where the wife did not transfer to her husband's authority but retained her full rights in her natal family.
(v) Under law, a married couple was not one financial entity but two, and the wife enjoyed complete legal independence.
(vi) Divorce was easy to get.
Source Based Questions
1. Read the following passage and answer the questions given below :
The Doctor Galen on how Roman Cities Treated the Countryside
The famine prevalent for many successive years in many provinces has clearly displayed for men of any understanding the effect of malnutrition in generating illness. The city- dwellers, as it was their custom to collect and store enough grain for the whole of the next year immediately after the harvest, carried off all the wheat, barley, beans and lentils, and left to the peasants various kinds of pulse - after taking quite a large proportion of these to the city. After consuming what was left in the course of the winter, the country people had to resort to unhealthy foods in the spring; they ate twigs and shoots of trees and bushes and bulbs and roots of inedible plants... - Galen, On Good and Bad Diet.
Questions :
(i) What is the main value attached to the occurrence of famine in any part of the world ?
Answer:
Food shortage, natural calamity, etc., are the values attached to the occurrence of famine.
(ii) What does this passage depict ?
Answer:
This passage depicts the ill effect of famine. It increased the level of malnutrition in generating illness.
(iii) Discuss the social conditions in ancient Roman society.
Answer:
The Roman society was also divided into the three groups :
1. The Particians or the Rich,
2. Plebeians or the Common People,
3. The Slaves.
The upper class in both the countries included in rich and the landed aristocracy which led a very luxurious life. The second class was comprised of traders, craftsmen, warriors and the cultivators. The people enjoyed all the civic rights but they had to bear burden of most of the taxes. The condition of the third class i.e. the slaves was very bad in both the countries. They were bought and sold in the markets. They were treated like animals by their masters.

2. Read the passage given below and answer the questions which follows :
On the Treatment of Slaves
‘Soon afterwards the City Prefect, Lucius Pedanius Secundus, was murdered by one of his slaves. After the murder, ancient custom required that every slave residing under the same roof must be executed. But a crowd gathered, eager to save so many innocent lives; and rioting began. The senate-house was besieged. Inside, there was feeling against excessive severity, but the majority opposed any change (....) [The senators] favouring execution prevailed. However, great crowds ready with stones and torches prevented the order from being carried out. Nero rebuked the population by edict, and lined with troops the whole route along which those condemned were taken for execution.’ - Tacitus (55-117), historian of the early empire
Questions :
(i) Who murdered his master Lucius Pedanius Secundus ?
Answer:
He was murdered by his slave.
(ii) What was the position of the slave in the society ?
Answer:
The position of the slave was very miserable in the society. They have no rights and privileges.
(iii) Describe the position of Slaves in ancient Greek and Rome. In what kinds of work were they generally engaged ? What was the impact of slavery on the nature of society ?
Answer:
1. A large number of people in ancient Greek and Rome were slaves. The prisoners of war and those who could not pay their debts were kept as slaves. The conditions was very bad, they had to work day and night and they were deprived of all the social and political rights.
2. The slaves system produced an evil effect both on the Greek and the Roman societies. Continuous exploitation of the slaves often led them to revolt and the State had to strengthen its forces constantly to suppress them.

Map Questions
Question 1.
On the map of Europe and North Africa mark and locate some of important towns of Mesopotamian Civilisation.
Answer:
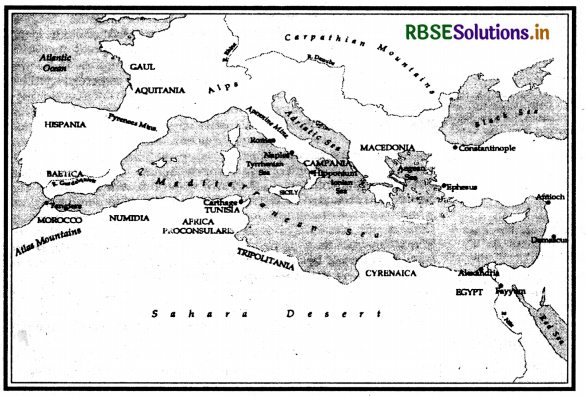
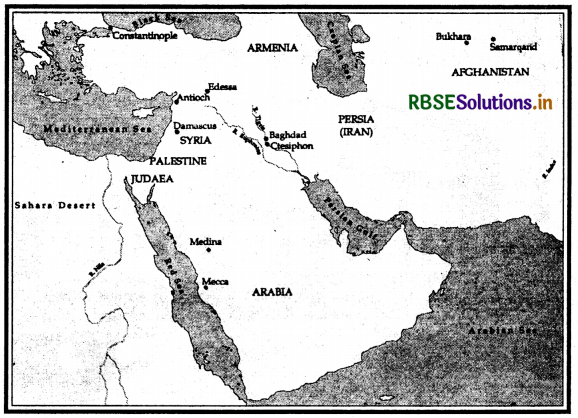
An Empire Across Three Continents Question Answer Question 2.
On the given map mark and locate the following cities/towns:
(i) Mecca
(ii) Medina
(iii) Baghdad
(iv) Ctesiphon
(v) Bukhara
(vi) Samarqand
(vii) Antioch
(viii) Damascus
(ix) Constantinople
(x) Edessa
Answer:

Choose the Correct Option:
Question 1.
In which of these continents Roman Empire had not spread?
(a) America
(b) Africa
(c) Asia
(d) Europe
Answer:
(a) America.
Question 2.
Which of the following languages were used by Roman emperors for administrative purpose?
(i) Latin
(ii) Greek
(iii) Spanish
(iv) Italinn
(v) Dutch
(vi) Flemish
(a) (i), (iii) (iv), (ii) and (vi)
(b) (iii) and (ii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (i), (iii) and (ii)
Answer:
(c) (i) and (ii).

Question 3.
When did Roman Empire became a Republic?
(a) 563 BCE
(b) 563 CE
(e) 509 CE
(d) 509 BCE
Answer:
(d) 509 BCE.
Question 4.
Roman Empire remained the Republic till .............
(a) 27 BCE
(b) 27 CE
(c) 527 BCE
(d) 512 BCE
Answer:
(a) 27BCE.
Question 5.
Which of the following statements regarding Augustus is not true?
(a) He was the adopted son of Julius Caesar
(b) His real name was Octavian.
(e) His empire is known as PrincipaLe.
(d) He adopted the throne after Tiberius
Answer:
(d) He adopted the throne after Tiberius.
Question 6.
When was battle of Actium fought?
(a) 31 CE
(b) 31 BCE
(c) 311CE
(d) 311 BCE
Answer:
(b) 31 BCE.

Question 7.
Which of following titles were given to Octavian?
(a) Pnncep
(b) Impretor
(c) Augustus
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question 8.
‘Princeps’ means .
(a) Most respectable
(b) Most famous
(c) The first citizen
(d) The first group
Answer:
(c) The first citizen.
Question 9.
The army which consist of 9000 men to protect the Roman emperor was called ..............
(a) Infantry
(b) Cavalry
(c) Protector Guard
(d) Practorian Guard
Question 10
A soldier was required to serve atleast for ..............
(a) 15 years
(b) 25 years
(e) 5 years
(d) 3 - 6 years
Answer:
(b)25 years.

Question 11.
Soldiers were paid in ............... during Roman emperor Augustus.
(i) Cash
(ii) Pension
(iii) Regular Salaries
(a) (i) and (iii) (b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) Only (iii) (d) Only (j)
Answer:
(b) (ii) and (iii).
Question 12.
The Roman historian who wrote Roman history in 142 volume was
(a) Livy
(b) Virgil
(e) Ovid
(d) Horace
Answer:
(a) Livy.
Question 13.
Who was Tiberius?
(a) Son of Livia
(b) Son of Caesar from his first wive
(e) Son-in-law of Julia
(d) Son-in-law of Augustus
Answer:
(a) Son of Livia.
Question 14.
When did Nero become the Roman emperor?
(a) 54 BCE
(b) 54 CE
(c) 94CE
(d) 94BCE
Answer:
(b) 54 CE.

Question 15.
The Roman emperor who occupied Dacia was ............
(a) Nero
(b) Augustus
(c) Trajan
(d) Tiberius
Answer:
(c) Trajan.
Question 16.
Who was the sky God of Roman people?
(a) Mars
(b) Juno
(e) isis
(d) Jupiter
Answer:
(d) Jupiter.
Question 17.
Was slavery practised during Roman Empire?
(a) Yes
(b) No
(c) Cannot say
(d) No argument
Answer:
(a)Yes.
Question 18.
The members of consuls were elected for a period of ....
(a) Five years
(b) Two years
(e) Three years
(d) Six years
Answer:
(b) Two years.
Question 19.
Roman laws were inscribed on
(a) 12 tablets
(b) l8tabiets
(c) 19 tableta
(d) 24 tablets
Answer:
(a) 12 tablets,
Question 20
Whose rule in Rome is known as Paz Romana’?
(a) Julius Career’s
(b) Tiberiuss
(c) Mark Antony’s
(d) Octavian Caeser’s
Answer:
(d) Octavian Caeser’s.

Question 21.
Which is not correct about Constantine?
(a) He was the popular ruler of the Roman Empire
(b) He introduced gold currency in 310 CE.
(c) He developed means of mass communication.
(d) He encouraged external trade
Answer:
(c) He developed means of mass communication

- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 1 From the Beginning of Time
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 10 Displacing Indigenous Peoples
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 2 लेखन कला और शहरी जीवन
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 7 Changing Cultural Traditions
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 6 तीन वर्ग
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 6 The Three Orders
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 3 तीन महाद्वीपों में फैला हुआ साम्राज्य
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 History Chapter 1 From the Beginning of Time
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 11 Paths to Modernisation
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 9 The Industrial Revolution