RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 2 Writing and City Life
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 2 Writing and City Life Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 History in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 History Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 2 Writing and City Life
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Where did urban life begin in the world ? What is its present name ?
Answer:
The urban life began in Mesopotamia. The present name of Mesopotamia is Iraq.
Question 2.
What is the meaning of Mesopotamia ?
Answer:
The word Mesopotamia is made up of two Greek words ‘Mesos’ meaning middle and ‘Potamos’ means the river. Hence the meaning of Mesopotamia is The land between two rivers’. These two rivers were Tigris and Euphrates.

Question 3.
When did excavation begun in Mesopotamia ? Which three types of cities were found (excavated) here ?
Answer:
Excavation work began in Mesopotamia in 1840 C.E. During this excavation work, three kinds of cities were found. These were :
(i) Royal Cities.
(ii) Commercial / Trading Cities
(iii) Religious Cities
Question 4.
Where did towns developed first in world history ? Name any three early developed towns.
Answer:
The towns first developed in Meso-potamia. The three early developed towns were:
(i) Ur,
(ii) Uruk,
(iii) Kish
Question 5.
Write any three causes for the development of urbanisation in Mesopotamia.
Answer:
Causes for the development of urbanisation in Mesopotamia:
(i) Increase in Agricultural Production
(ii) Division of Society
(iii) Expansion of Trade

Question 6.
Which was the oldest Mesopotamian town ? When did it came into existence ?
Answer:
Uruk was the oldest Mesopotamian town. It came into existence around 3000 BC.
Question 7.
Describe in brief the geographical condition of Uruk.
Answer:
The town ‘Uruk’ was situated on the bank of Mesopotamian river Euphrates. It was about 250 km away from the capital city of Iraq, Baghdad.
Question 8.
Name two prominent rulers of Uruk.
Answer:
(i) Enmerkar,
(ii) Gilgamesh.
Question 9.
By whom Uruk was excavated and by when ?
Answer:
Uruk was excavated by Julius Jorbon in 1913 C.E.
Question 10.
From where did the Mesopotamian people procurred necessary metals and other goods ? What did they exported for these goods?
Answer:
It was from Turkey and Iran or across the Gulf, that the Mesopotamian people procurred necessary metals and other goods. They exported cloth and agricultural products for these things.
Question 11.
When and by whom was the city of Ur founded ?
Answer:
The city of Ur was founded by Mesanepada. He founded this city in 2670 BCE and made it the capital of her empire.
Question 12.
What does the excavation reveals regarding Ur ? Write any three.
Answer:
(i) The city was not well designed.
(ii) Streets were narrow and zigzag.
(iii) Mule was carried for carrying load.
(iv) Drainage pattern was not efficient like that of Indus Valley Civilisation in India.

Question 13.
Name the chief deity worshipped in the city of Ur.
Answer:
Mannor (Moon God) was the chief deity worshipped in Ur.
Question 14.
Who was the founder of Babylon ?
Answer:
The city of Babylon was founded by Sargar. This city made remarkable progress under Hammurabi.
Question 15.
Mention any three features of Urban life.
Answer:
Features of urban life are :
(a) Division of Labour,
(b) Social Organisation,
(c) Efficient Transport System.
Question 16.
What do you know about Gilgamesh ?
Answer:
‘Gilgamesh’ is the great epic not in the Sumerian but world literature. This epic was written by great Sumerian ruler Gilgamesh on 12 tablets in 2000 BCE. It narrates the achievements of Gilgamesh.
Question 17.
Why only a few Mesopotamians were able to read and write.
Or
Why was literacy rate so slow in Mesopotamia ?
Answer:
Only a few Mesopotamians were able to read and write because :
(a) There were hundreds of signs to learn.
(b) Many of these signs were complex.

Question 18.
Which was the earliest language known to Mesopotamians ? Which language replaced it and when ?
Answer:
Sumerian was the earliest language known to Mesopotamians. It was replaced by ‘Akkad’ around 2400 BE.
Question 19.
Why was there agricultural crisis in Mesopotamia ?
Answer:
There was often agricultural crisis in Mesopotamia because :
(i) Crops were destroyed by the overflow of water in rivers Tigris and Euphrates.
(ii) People living in higher (upper) reaches, divert the flow of river to secure water supply which causes water scarcity in lower reaches.
Question 20.
Which main crops were known to Mesopotamians ?
Answer:
The main crops known to Mesopotamians were :
(i) Wheat,
(ii) Peas,
(iii) Datepalm,
(iv) Barley.
Question 21.
Write two features of civilisation.
Answer:
(i) A suitable form of writing able to express ideas.
(ii) People should have the knowledge of making tools.
Question 22.
What was the status of women in Mesopotamian society ?
Answer:
Women in Mesopotamian society enjoyed equal status as the man did. They enjoyed equal status in religious as well as social sphere of life. They were also free to set up their trade unit and could keep slaves. They were also allowed to remarry and seek divorce.

Question 23.
Describe the status of slave in short.
Answer:
Slaves constitute the lower status in Mesopotamian society. They had no rights. They can be buy or sold in the market. They were given severe punishment if they disobey their master.
Question 24.
What were the different means of entertainment for the Mesopotamians ?
Answer:
Different means of entertainment for the Mesopotamians include dancing, hunting, watching wrestling, singing, watching animals and birds fight etc.
Question 25.
What were the different types of slaves in Mesopotamian society ?
Answer:
Different types slaves were :
(i) War prisoners.
(ii) Children sold by their parents.
(iii) Those who were unable to pay their debts.
Question 26.
Which type of cities developed in Mesopotamian civilization?
Answer:
Three types of cities developed in
Mesopotamian civilization. These were:
(a) Religious Towns,
(b) Trading Towns,
(c) Imperial Towns.
Question 27.
Who was considered as the theoretical owner of the agricultural fields, the fisheries and the herds In Mesopotamia?
Answer:
God.
Short Answer Type Question :
Question 1.
Name the imports and exports of Mesopotamia.
Answer:
Imports of Mesopotamia included
(a) Agricultural Produce,
(b) Abundant Textiles.
Exports of Mesopotamia included - copper, wood, silver, gold, tin, steel and different types of stones.
Question 2.
Describe the social division of Mesopotamian Civilisation.
Answer:
The Mesopotamian society was mainly divided into three classes :
(i) The Higher Class : This class represented the King and his relations, the priests and the Government officials.
(ii) The Middle Class : This class consisted of the landlords, the merchants, the craftsmen and the shopkeepers.
(iii) The Lower Class: In this class there were the farmers, the labourers, the prisoners of war and the slaves.
Question 3.
What do you know about occupation and crafts of Mesopotamians ?
Answer:
Agriculture was the main occupation of the Mesopotamians.They produce a variety of crops like wheat, barley, pulses, vegetables, fruits etc. They were also skilled in art and crafts. They practised various occupations like Ironsmith, Blacksmith etc.

Question 4.
Describe main features of Hummurabi’s Code of Law.
Answer:
Hummurabi was a great king of the Mesopotamia. He prepared a code of law in 2025 BCE. Some of the key features of these code of laws were :
(i) They were 282 in number.
(ii) They deals with every aspect of life.
(iii) These code recognise the division of - society into three classes.
(iv) The main principles of these code were that the strong shall not injure the weak.
(v) It also includes the rule which deal about family life, trades etc.
Question 5.
What do you know about the Mesopotamian writing system ?
Or
What were the main characteristics of the system of writing of Mesopotamian civilisation ?
Answer:
Mesopotamians were known as the first to develop the art of writing. Their system of writing had following features :
(a) There script was pictographic.
(b) They wrote on tablets with the help of a reed or bone. These tablets contained the signs and symbols of fish, bread, leaves and were written around 3200 BCE.
(c) By 2600 BCE, the letters became cuniform and the language was Sumerian, which was gradually replaced by the Akkadian language.
(d) Writing was now used not only for keeping records, but also for making dictionaries, giving legal validity to land transfers etc.
Question 6.
What is the contribution of the Mesopotamian civilization to world ?
Answer:
(i) The Mesopotamians were the first people to introduce the use of the potter’s wheel to the world.
(ii) They were the first to enter into written trade agreement.
(iii) They also introduced to the world the idea of a written code of law.
(iv) They were the first people to divide a day into 24 hours, an hour into 60 minutes and a minute into 60 seconds.
(v) They were first to develop a script and established the libraries and reading rooms.
Question 7.
Which was the earliest temple town of Egypt ? How did it become reliable ?
Answer:
Uruk was the earliest reliable temple town of Egypt. It became reliable from the depiction of armed heroes and their victims.
Question 8.
Write a short note on the code of Hammurabi.
Answer:
Hummurabi was a famous king of Babylonia. He got prepared the world’s first Code of Laws. He also got it engraved on a veiy big stone shaft in the form of 282 articles. These laws were connected with trade, exchange of money, payment of taxes, theft, murder etc. Most of the laws were based on the principle of “An eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth”.
Question 9.
“Urbanisation first took place in Mesopotamian cities”. Why its so ?
Answer:
Urbanisation first took place in Mesopotamian cities. It was due to following reasons :
(i) Mesopotamian region was very fertile.
(ii) Water was easily available.
(iii) Military power of the rulers.
(iv) Well develop means of transportation.
(v) Division of labour.

Question 10.
Write about the town planning of the Mesopotamian cities.
Answer:
(i) The cities were well designed according to definite plan.
(ii) Special heed was given toward the construction of the towns.
(iii) Baked bricks were used for constructing houses.
(iv) Houses were single storeyed.
(v) There was provision of adequate roads in town and cities.
Question 11.
Write a note on animal herders of Mari.
Answer:
Mari is an important ancient town of Mesopotamia. Most of the people here were agriculturists. They were animal herders and used their animals for barter system. When the people need credit, ornament, metal tools etc., they exchange their young animals in the return of these items.
Question 12.
“Mobile animal herding (rearing) not necessarily a threat to town life.” Why ?
Answer:
Mobile animal herding (rearing) was not a necessarily a threat to town life during the Mesopotamian civilisation because :
(i) Both were carried out close to each other in this region. Some communities in Mari were both farmers and pastoralists but most of the territory was used for pasturing sheep and goats.
(ii) Herders practised barter system to meet their daily needs. Yet at the same time there were also conflicts between the people due to barter system.
(iii) Shepherd may take his flock to water across a sown field, to the ruin of the crops.
(iv) Herdsmen being mobile can raid agricultural villages and seize their store goods.
Question 13.
Write the causes of the increasing activities of the temples.
Answer:
Causes for increasing activities of the temples were:
(i) Temples during the time of harvesting received good donation from peasants.
(ii) Temple records of distribution and allotment were begun to be recorded.
Question 14.
Mention some of the important facts regarding the Mesopotamian seals.
Answer:
(i) In Mesopotamia until the end of the first millennium BCE, cylindrical stone seals, pierced down the centre, were fitted with a stick and rolled over wet clay so that a. continuous picture was created.

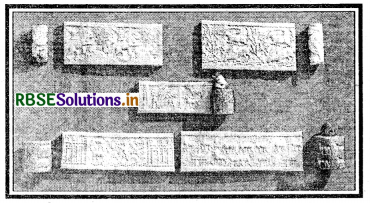
(ii) They were carved by very skilled craftsmen, and sometimes cany writing: the name of the owner, his god, his official position, etc.
(iii) A seal could be rolled on clay covering the string knot of a cloth package or the mouth of a pot keeping the contents safe. When rolled on a letter written on a clay tablet, it became a mark of authenticity. So the seal was the mark of a city dweller’s role in public life.
Question 15.
What do you know about the time division of Mesopotamians ?
Answer:
The division of the year into 12 months according to the revolution of the moon around the earth, the division of the month into four weeks, the day into 24 hours, and the hour into 60 minutes-all that we take for granted in our daily lives has come to us from the Mesopotamians.
These time divisions were adopted by the successors of Alexander and from there transmitted to the Roman world, then to the world of Islam, and then to medieval Europe. Whenever solar and lunar eclipses were observed, their occurrence was noted according to year, month and day. So too there were records about the observed positions of stars and constellations in the night sky.

Question 16.
Describe in brief the importance of writing.
Answer:
(i) Writing helped in the spread of education.
(ii) It helped in the promotion of trade and also about the contemporary condition of the society at that particular time.
Question 17.
Why Mesopotamia is considered important by Europeans ?
Answer:
Mesopotamia is considered important by Europeans because of the following points:
(a) In the old Testament, there are references about it, which refers to ‘Shimar’, meaning the Sumer (the land of brick built cities). It clearly refers to Mesopotamia, because early planned cities existed there.
(b) European scholars and travellers referred to Mesopotamia as their ancestral land.
(c) Archaeological discoveries also depict that Europeans had keen interest in this region.
Question 18.
Division of labour is one of the important features of urban life. Exalain it with example.
Answer:
The meaning of division of labour is to fulfil our needs with each other’s products and services. The division of labour is very much necessary for urban life. The reason is that besides food production, trade, manufactures and several types of services also play an important role in urban economies. But city people are not self-sufficient. They depend on the products and services of other city of village people.
There is continued interaction between urban people and village people. For example the carver of a stone seal need bronze tools which he himself cannot make. He does not even know from where to get coloured stones for the seals. He is specialised in carving, not trading. The bronze tool maker will definitely go out himself to get the metals - tin and copper. All these functions are perfomed with each other’s help.
Question 19.
What is the legacy of Mesopotamia to the world ?
Answer:
The scholary tradition of time reckoning and mathematics is the greatest lagacy of Mesopotamia to the world.
(i) Some tablets have been found which are dated around 1800 BCE. These tablets are the tables of multiplication and division, tables of square and square roots and tables of compound interest. The value of square root of 2 given in them is slightly different from the real value of square root of 2.
(ii) Mesopotamians had divided the year into 12 months according to the revolutions of the moon around the earth. Then they divided a month into four weeks, a day into 24 hours and an hour into 60 minutes. This is one of their greatest contributions to the world.
(iii) Mesopotamian people also noted the occurrence of solar and lunar eclipses.
(iv) They also observed positions of stars and constellations in the night sky and kept their records.

Question 20.
Why do we remember the city of Babylon ?
Answer:
Babylon was the premier city of the wolrld unitl 331 BCE when it was conquered by Alexander. Following were the main features of the city of Babylon :
(i) Its area was more than 850 hectares.
(ii) It had a triple wall.
(iii) Great palaces and temples were situated in it.
(iv) Aziggurat or stepped tower was there in the city.
(v) There was a processional way to the main ritual centre of the city.
(vi) Its trading houses had widespread dealings.
(vii) Its mathematicians and astronomers made some new discoveries.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Estimate the achievements of Mesopotamian King Assurbanipal.
Answer:
(a) King Assurbanipal was the greatest Mesopotamian among all the kings ruled from 668 to 628 B.C.E.
(b) His reign is known as the Golden Age in Assyrian history.
(c) He extended the boundaries of his empire and conquered even southern part of Egypt which could not be conquered by his ancestors.

(d) He was also a great patron of learning. He collected about 22,000 tablets into great library which has been found and preserved in a British museum in London.
(e) They tell us the deeds of kings and heroes, and about the ancient stories and legends of Babylonia. After the death of Assurbanipal the great empire of Assyria fell with a rapid space.
Question 2.
What do you know about the Palace at Mari of King Zimrilim ? Why it was so famous ?
Or
Mention any two special features of the palace of King Zimrilim at Mari.
Answer:
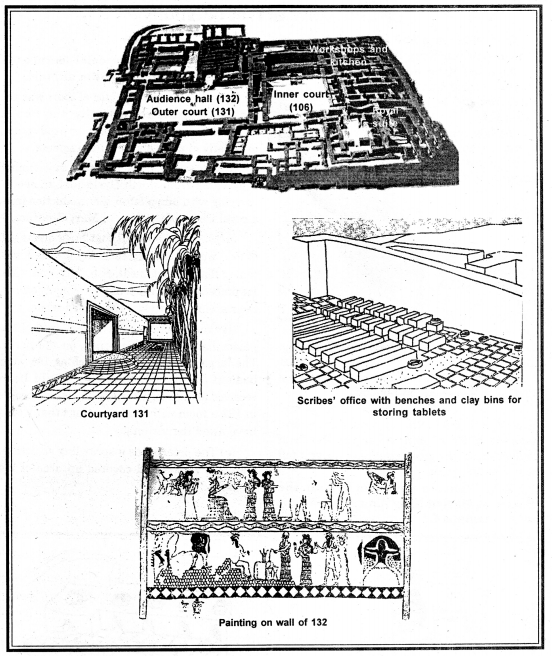
(i) The great palace of Mari was the residence of the royal family, the hub of administration, and a place of production, especially of precious metal ornaments.

(ii) It was so famous in its time that a minor king came from north Syria just to see it, carrying with him a letter of introduction from a royal friend of the king of Mari, Zimrilim.
(iii) Daily lists reveal that huge quantities of food were presented each day for the king’s table : flour, bread, meat, fish, fruit and wine. He probably ate in the company of many others, in or around courtyard 106, paved white.
(iv) You will notice from the plan that the palace had only one entrance, on the north. The large, open courtyards such as 131 were beautifully paved. The king would have received foreign dignitaries and his own people in 132 a room with wall paintings that would have awed the visitors.
(v) The palace was a sprawling structure, with 260 rooms and covered an area of 2.4 hectares.
Question 3.
Explain, how the geographical conditions of Egyptian and Mesopatamian civilisations affect their history.
Answer:
Mesopotamian civilization, flourished on the land lying between the two rivers - The Tigris and Euphrates. This land was very fertile and suitable for agriculture, because water was available in large quantity. Here, the climate was warm and pleasant. These factors combined together gave birth to the civilization of Mesopotamia. Unlike Egypt it was not protected by natural features and was thus exposed to foreign invasions.
Mesopotamia, in fact, served as a reservoir into which constantly poured streams of different people. This very factor gave rise to various civilizations such as the Sumerian civilization, the Babylonian civilization and the Assyrian civilization. Mesopotamia has sometimes been called “The cradle and grave of many civilizations”. The civilization of Mesopotamia was more or less contemporary of the Egyptian civilization.

Question 4.
Mention some of the facts regarding Ur, one of the earliest cities to have been excavated.
Answer:
Ur was a town whose ordinary houses were systematically excavated in the 1930s.
(a) Narrow winding streets indicate that wheeled carts could not have reached many of the houses.
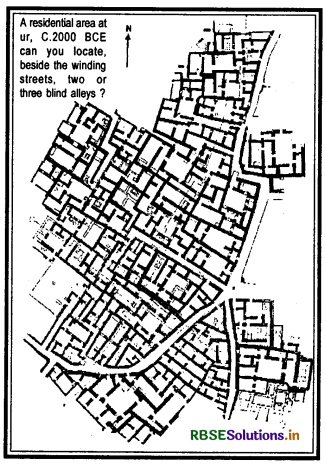
(b) Sacks of grain and firewood would have arrived on donkey-back.
(c) Narrow winding streets and the irregular shapes of house plots also indicate an absence of town planning.
(d) There were no street drains of the kind we find in contemporary Mohenjo-daro.
(e) Drains and clay pipes were instead found in the inner courtyards of the Ur houses and it is thought that house roofs sloped inwards and rainwater was channelled via the drainpipes into sumps in the inner courtyards.
(f) There was a town cemetery at Ur in which the graves of royalty and commoners have been found, but a few individuals were found buried under the floors of ordinary houses.
Question 5.
Give an estimate of the Sumerian Civilisation of Mesopotamia.
Or
Describe in detail the achievements of Mesopotamia Civilisation.
Answer:
The Sumerian Civilization was the first civilization to flourish in Mesopotamia. Some of the main features of this civilisation were the. following :
(i) Political Life : Many city states; priests kings called Patesti; King had to perform many duties; He ruled with the help of officials.
(ii) Economic Life : Their main occupations were agriculture, domestication of animals and trade. They were skilled craftsmen. They were the first to cultivate wheat; Invention of the wheel.
(iii) Art: Introduction of columns, vaults and arch; Ornamentation of temples and buildings; Various crafts.
(iv) Social Life : The Sumerian society was divided into three classes; Slavery prevailed there; Women occupied high position.
(v) Religious Life : Worship of many Gods; Enlil was the chief God, Building of temples called Ziggurats; Belief in life after death; Priests occupied high position in society.
(vi) Literature : Literature consisted of stories, songs, epics, hymns.

(vii) Science : Great progress in mathematics, astronomy, astrology and medicine. Sixty as the unit in their system of numerals; Division of circle in 360°; Calendar; Eclipses.
Question 6.
What do you know about the temples of Mesopotamia ?
Answer:
(a) Early settlers began to build and rebuild temples at selected spots in their villages. The earliest known temple was a small shrine made of unbaked bricks.
(b) Temples were the residences of various gods of the moon God of Ur or of Inanna the Goddess of Love and War.
(c) Constructed in brick, temples became larger over time, with several rooms around open courtyard.
(d) The god was the focus of worship, to him or her people brought grain, curd and fish. The god was also the theoretical owner of the agricultural fields, the fisheries and the herds of the local community.
(e) Organiser of production, employer of merchants, keeper of written records of distributions, allotment of grains, plough animals, bread, beer etc. the temple gradually developed its activities and became the main urban institution.
Question 7.
What were the steps taken by the Mesopotamian king to increase his influence and control ?
Answer:
Following steps were taken by Mesopotamian king to increase his influence and control :
(i) The king himself paid attention toward the well beings of his people.
(ii) To increase his influence he paid special attention toward the community temple and offered preciously booty to the gods.
(iii) He patronised the settlement of new villages close to his empire.
(iv) Local people were not forced to do the work of temple and begar for the king.
(v) For the beautification of the temples he sent men in various directions to collect precious metals and stones. These metals and stones were used by the king to beautify the temples. All of these king's efforts show that he was very kind towards the need of his people. This helped him to increased his influence and control.

Question 8.
Describe the technological advances that took place in Uruk around 3000 BCE.
Answer:
Around 3000 BCE, following technological advances took place in Uruk :
(a) Bronze tools came into use for various crafts.
(b) Architects learnt to construct brick columns.
(c) Hundreds of people were put to work at making and baking clay cones that could be pushed into temple walls, painted in different colours, creating a colourful mosaic.
(d) In sculpture, there were superb achievements, not in easily available clay but in imported stone.
(e) Potter’s wheel was a technological landmark which enabled the Potter’s workshop to ‘mass produce’ dozens of similar pots at a time.
Question 9.
Iraq is a land of geographical diversities. Explain with examples.
Answer:
Iraq is in fact a land of geographical diversities:
(i) Green undulating plains lie in the north east of the country. These plaine gradually rise to tree covered mountain ranges. Clear streams and wild flowers are found here. These plains experience enough rainfall to grow crops.
(ii) There is a stretch of upland in the north which is known as steppe. Here, animal rearing is the main source of livelihood. After the winter rains, goats and sheep feed on the grasses and low shrubs which grow here.
(iii) In the east direction, tributaries of the river Tigris provide routes of communication into the mountains of Iran.
(iv) Southern part of the country is a desert.
Source Based Question
1. Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow :
The Seal-An Urban Artefact
In India, early stone seals were stamped. In Mesopotamia until the end of the first millennium BCE, cylindrical stone seals, pierced down the centre, were fitted with a stick and rolled over wet clay so that a continuous picture was created. They were carved by very skilled craftsmen, and sometimes carry writing : the name of the owner, his god, his official position, etc. A seal could be rolled on clay covering the string knot of a cloth package or the mouth of achievements, not in easily available clay but in imported stone. a pot, keeping the contents safe. When rolled on a letter written on a clay tablet, it became a mark of authenticity. So the seal was the mark of a city dweller’s role in public life.
(i) Who carved the seals during Mesopotamian civilisation ?
Answer:
The skilled crafts persons carved the seals during Mesopotamian civilisation.
(ii) What do you see on each of the seals ?
Answer:
The seal depicts the important work done by Mesopotamians in sphere of literary. They known the art of reading and writing. The developed pictographic script and their language was called cuneiform.
(iii) What does the inscribed sign describe ?
Answer:
They describe the authenticity of the seal.

(iv) Mesopotamians valued city life in which people of many communities and cultures lived side by side. Mention some of the facts regarding this.
Answer:
1. The most poignant reminder to us of the pride Mesopotamians took in their cities comes at the end of the Gilgamesh Epic, which was written on twelve tablets. Gilgamesh is said to have ruled the city or Uruk some time after Enmerkar.
2. After a heroic attempt, Gilgamesh failed, and returned to Uruk. There, he consoled himself by walking along the city wall, back and forth. He admired the foundations made of fired bricks that he had put into place.
2. Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow:
And, an Early Archaeologist !
A man of the southern marshes, Nabopolassar, released Babylonia from Assyrian domination in 625 BCE. His successors increased their territory and organised building projects at Babylon. From that time, even after the Achaemenids of Iran conquered Babylon in 539 BCE and until 331 BCE when Alexander conquered Babylon, Babylon was the premier city of the world, more than 850 hectares, with a triple wall, great palaces and temples, a ziggurat or stepped tower, and a processional way to the ritual centre. Its trading houses had widespread dealings and its mathematicians and astronomers made some new discoveries.
Nabonidus was the last ruler of independent Babylon. He writes that the god of Ur came to him in a dream and ordered him to appoint a priestess to take charge of the cult in that ancient town in the deep south. He writes: ‘Because for a very long time the office of High Priestess had been forgotten, her characteristic features nowhere indicated, I bethought myself day after day ...’
Then, he says, he found the stele of a very early king whom we today date to about 1150 BCE and saw on that stele the carved image of the Priestess. He observed the clothing and the jewellery that was depicted. This is how he was able to dress his daughter for her consecration as Priestess.
On another occasion, Nabonidus’s men brought to him a broken statue inscribed with the name of Sargon, king of Akkad. (We know today that the latter ruled around 2370 BCE.) Nabonidus, and indeed many intellectuals, had heard of this great king of remote times. Nabonidus felt he had to repair the statue. ‘Because of my reverence for the gods and respect for kingship,’ he writes, ‘I summoned skilled craftsmen, and replaced the head.’
(i) Who was Nabopolassar ?
Answer:
Nabopolassar was the conqueror of Babylonia. He released this city from Assyrian domination in 625 BCE.
(ii) Who won Babylonia, the world famous city of time in 539 BCE and 331 BCE respectively ?
Answer:
Achaemenids of Iran and Alexander the Great won Babylon in 539 BCE and 331 BCE respectively.

(iii) Which is correct about Nabonidus ?
(a) He was the last ruler of Babylon.
(b) He was a slave ruler.
(c) He repaired the statue of Sargon the king of Akkad.
Answer:
Statements (a) and (c) are correct about Nabonidus.
Map Questions
Question 1.
On the given map of West Asia mark and locate any five centres related to Mesopotamia civilisation and entire Mountainous region.
Answer:
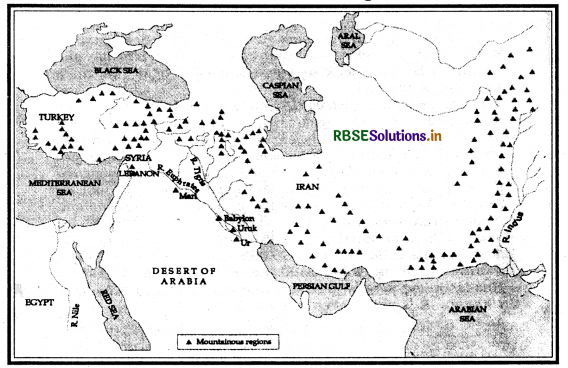

Question 2.
On the map given below mark and locate the following features :
(a) Zone of agricultural productivity
(b) Southern limit of zone of rainfed agriculture
(c) Mountainous Region
Answer:
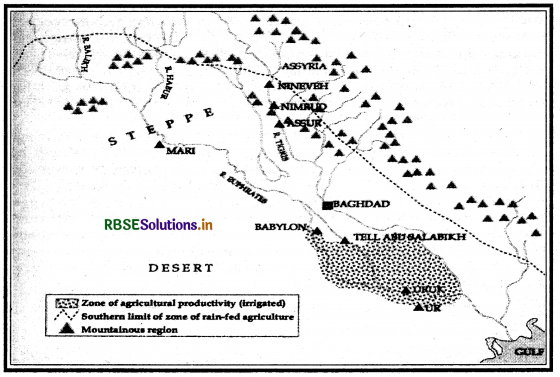
Choose the Correct Option:
Question 1.
Mesopotamia is in modern
(a) Iran
(b) Iraq
(c) Syria
(d) Egypt
Answer:
(b) Iraq.
Question 2.
Mesopotamia means .
(a) Land between two rivers
(b) Land covered by water on three sides
(c) Land covered by water on all sides
(d) Land covered by walls in two sides
Answer:
(a) Land between two rivers.
Question 3.
When was Mesopotamian art of writing begun ?
(a) 3200 CE
(b) 3200 BCE
(c) 2200 CE
(d) 3350 CE
Answer:
(b) 3200 BCE.

Question 4.
What is the meaning of ‘mesos’ ?
(a) The Highland
(b) The Mid Land
(c) The Plateau region
(d) An Island
Answer:
(b) The Mid Land.
Question 5.
‘Potamos’ is a Greek word. It means:
(a) The Sea
(b) Bay
(c) An Ocean
(d) River
Answer:
(d) River.
Question 6.
Cross (x) the incorrect option :
(a)Tigris - Mesopotamian civilisation.
(b) Euphrates - Mesopotamian civilisation.
(c) Indus - Indus Valley civilisation
(d) Hwang-Ho - Mesopotamian civilisation
Answer:
(d) x
Question 7.
Towns first developed in the plains of
(a) Indus
(b) Hwang Ho
(c) Mesopotamia
(d) Nile
Answer:
(c) Mesopotamia.
Question 8.
Mesopotamian society was consist of ............
(a) three classes
(b) four classes
(c) Number of classes
(d) No division of society
Answer:
(a) three classes.
Question 9.
Cuneiform script had ....
(a) 250 signs
(b) 350 signs
(c) 150 signs
(d) 160 signs
Answer:
(b) 350 signs.

Question 10.
Code of law has ............. laws in number.
(a) 182
(b) 382
(c) 282
(d) 82
Answer:
(c) 282.
Question 11.
Where did early city life develop ?
(a) Sumena
(b) Egypt
(c) Banaras
(d) Atlantic
Answer:
(a) Sumena.
Question 12.
Which of the following did not consist of middle class of Mesopotamian society ?
(a) Traders
(b) Merchants
(c) Landlords
(d) The nobles
Answer:
(d) The nobles.

Question 13.
"The strong shall not injure the weak” is the main principle of
(a) The Bible
(b) The Gita
(c) The Islam
(d) Code of Law
Answer:
(d) Code of Law.
Question 14.
The great epic ‘Gilgamesh’ was compiled on how many tablets ?
(а) 12
(b)13
(c) 18
(d) 36
Answer:
(a) 12.
Question 15.
Which of the Mesopotamian river was known as a world trade route?
(a) Tigris
(b) Euphrates
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Euphrates.
Question 16.
When was cuneiform script deciphered ?
(a) 1860s
(b) 1880s
(c) 1960s
(d) 1850s
Answer:
(d) 1850s.
Question 17.
Which material did Mesopotamians use for writing ?
(а) Cloth
(b) Clay
(c) Skin of Animals
(d) Paper
Answer:
(b) City.

Question 18.
Mesopotamian Civilisation is also known as ..............
(a) Egyptian Civilisation
(b) Gift of Nile
(c) Sumerian Civilisation
(d) Euphrates Civilisation
Answer:
(c) Sumerian Civilisation.

- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 1 From the Beginning of Time
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 10 Displacing Indigenous Peoples
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 2 लेखन कला और शहरी जीवन
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 7 Changing Cultural Traditions
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 6 तीन वर्ग
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 6 The Three Orders
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 3 तीन महाद्वीपों में फैला हुआ साम्राज्य
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 3 An Empire Across Three Continents
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 History Chapter 1 From the Beginning of Time
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 11 Paths to Modernisation
- RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium