RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 8 Bill of Exchange
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 8 Bill of Exchange Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 8 Bill of Exchange
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State any two essential features of bill of exchange.
Answer:
(a) Unconditional order
(b) must be signed by the drawer
Question 2.
What is meant by maturity of a bill of exchange?
Answer:
It is arrived at by adding three days of grace to the period of the bill.

Question 3.
What is meant by acceptance of a bill of exchange?
Answer:
Acceptance of bill of exchange means the creditor has agreed to pay the amount for the goods bought.
Question 4.
What is noting of a bill of exchange?
Answer:
To prove the dishonour of the bill of exchange, the holder to approach the notary and when he certifies it, it is known as noting of bills of exchange.
Question 5.
What is meant by renewal of a bill of exchange?
Answer:
When the bill is dishonoured, the drawer of the bill requests the drawee to drawer another bill. The amount of the bill is increased with the interest for the extended period.

Question 6.
What is retirement of a bill of exchange?
Answer:
When the bill receivable is honoured by the acceptor before the date of maturity, it is known as retirement of bill at rebate.
Question 7.
What is meant by insolvency?
Answer:
It means the acceptor the bill of exchange has no ability to pay the amount of the bill payable.
Question 8.
Give the meaning of rebate.
Answer:
When the bill receivable is honoured by the acceptor before the date of maturity, it is known as retirement of bill at rebate. Rebate is loss for the holder of the bill and gain for the drawee.
Question 9.
Differentiate between trade bill and accommodation bill.
Answer:
Difference between trade bill and accommodation bill
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate between trade bill and accommodation bill.
Answer:
Difference between trade bill and accommodation bill
|
Basis |
Trade bill |
Accommodation bill |
|
1. Purpose |
It is drawn to meet the financial obligation due to business transaction |
It is drawn to meet financial meet of one or both parties without any business transaction |
|
2. Consideration |
These are drawn against some consideration |
These are drawn without any consideration |
|
3. Evidence |
These are supported by evidence of sale |
These are not supported by any evidence of sale. |

Question 2.
Calculate date of maturity in the following cases:
|
|
Date of bio |
Date of acceptance |
Period |
|
1. |
May 12,2018 |
May 12,2018 |
3 months |
|
2. |
May 31,2018 |
May 31,2018 |
1 month |
|
3. |
November 27,2018 |
November 27,2018 |
3 months |
|
4. |
January 01,2018 |
January 05,2018 |
30 days after acceptance |
|
5. |
January 09,2018 |
January 10,2018 |
60 days after sight |
|
6. |
November 27,2018 |
November 27,2018 |
3 months |
Answer:
1. August 14,2018
2. July 3,2018
3. March 01,2018
4. February 03,2018
5. March 03,2018
6. March 01,2018.

Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
(Based on GST): P of Delhi sold goods to Q of Rajasthan for ₹ 10,000 plus GST @ 12% on January 1,2018 and on the same day draws a bill on Q for the same amount for 3 months. Q accept it and returns it to P, who discounts it on 10th January, 2018 with his bank for ₹ 10,500. The acceptance is dishonoured on the due date and the noting charges were paid by bank being ₹ 50.On 4th April, Q paid ₹ 2,050 (including noting charges) in cash and accepted a new bill at 3 months for the amount due to P together with interest @ 12% per annum. Make Journal Entries in the books of P and Q to record these transactions.
Answer:
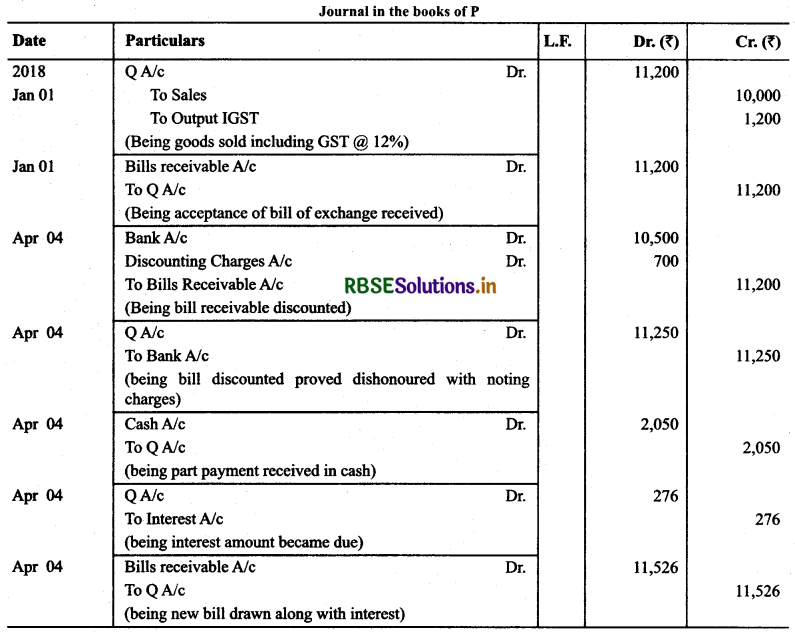
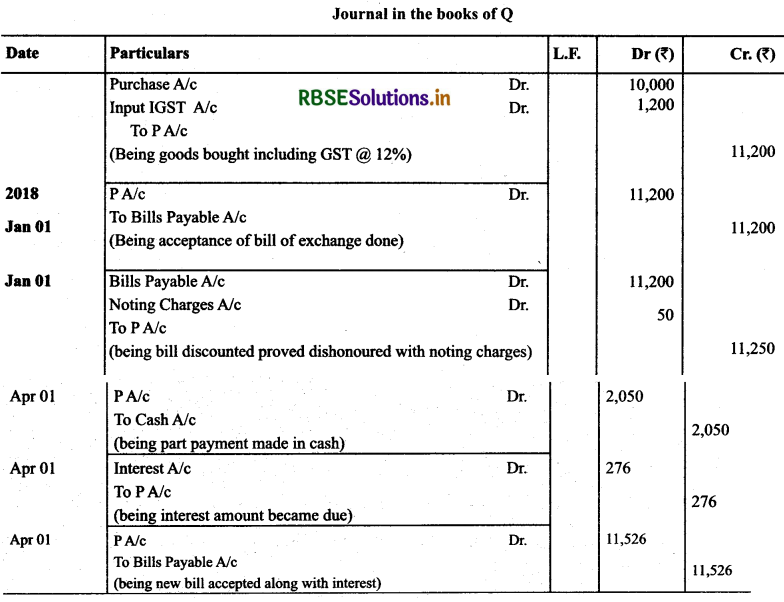
Higher Order Thinking Skills Questions
Question 1.
Briefly explain the purpose and benefits of retiring a bill of exchange to the drawer and the drawee.
Answer:
Benefit to drawer on retiring of bill: Drawer is the person who sells the goods and he gets the payment before the due
date. He can invest such money in the business and earn return on such amount.
Benefit to the drawee on retiring of bill: Drawee is the person who buys the goods and earns the amount of discount as discount received.

Question 2.
A bill of exchange for 15000 is drawn by A on B on 1st April, 2018 for 3 Months. B accepted the bill on 10th April, 2018. Find the DUE DATE and DATE OF MATURITY if
Cash I — The bill is bill after date
Case II — The bill is bill after Sight
Answer:

Question 3.
Geeta sold goods to Shcela for 30,000 at 4th May 2018 @90/. per annum find out:
(i) What would be the discounting charges?
(ii) What amount Geeta would receive?
Answer:
(i) Discounting Charges Amount of Bill Discounted x \(\frac{\text { Rate }}{100}\)x Unexpired Period
(ii) Geeta would receive ₹ 29,500 = 3000 \(\times \frac{9}{100} \times \frac{2}{12}\) = ₹ 450 on discounting the bill.
Question 4.
Ram sold goods to Shyam duly accepted by the later. It was endorsed to Tanin. Who is drawee and payee if the bill is duly honoured?
Answer:
Drawee is shyam and payee is Tanin.

Question 5.
Bills of exchange requires acceptance where promissory note does not require it. Why it so?
Answer:
Bill of exchange requires acceptance as the drawee (buyer) has to make payment whereas in case of promissory note, maker (buyer) promises to make payment instead of giving acceptance.
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which account is credited when the bill receivable is dishonored?
(a) Drawer’s Account
(b) Drawee’s Account
(c) Bank Account
(d) Endorser’s Account
Answer:
(c) Bank Account
Question 2.
A bill of exchange has minimum _____ parties.
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer:
(b) Two
Question 3.
If date of maturity falls on public holiday, the bill becomes due on ...............
(a) One day after the date of maturity
(b) One day before the date of maturity
(c) On date of maturity itself
(d) The request of drawee
Answer:
(b) One day before the date of maturity

Question 4.
If date of maturity is declared as emergency, the bill becomes due on ...............
(a) One day after the date of maturity
(b) One day before the date of maturity
(c) On date of maturity itself
(d) The request of drawee
Answer:
(a) One day after the date of maturity
Question 5.
Nothing charges are initially borne by ...............
(a) The holder of the bill exchange
(b) The payee of the bill of exchange
(c) Notary of the bill of exchange
(d) Endorse of the bill of exchange
Answer:
(a) The holder of the bill exchange
Question 6.
The period of the bill is decided in the number of days, date...............
(a) Will include the date of drawing of bill of exchange
(b) Will exclude the date of drawing of bill of exchange
(c) Not include days of grace
(d) Include one day extra to three days of grace
Answer:
(b) Will exclude the date of drawing of bill of exchange
Question 7.
Noting charges are ultimately borne by ...............
(a) Drawer of the bill of exchange
(b) Drawee of the bill of exchange
(c) Bank of the bill of exchange
(d) Payee of the bill of exchange
Answer:
(b) Drawee of the bill of exchange
Question 8.
Liability of a discounted bill is ...............
(a) An unknown liability
(b) Not a liability
(c) Current liability
(d) A contingent liability
Answer:
(d) A contingent liability
Question 9.
Rebate on the bills exchange means ...............
(a) The bill of exchange has been honoured on the date of maturity
(b) The bill of exchange has been honoured before the date of maturity
(c) The bill of exchange has been honoured after the date of maturity
(d) The bill of exchange has been dishonoured on the date of maturity
Answer:
(b) The bill of exchange has been honoured before the date of maturity
Question 10.
Under which circumstance, the drawer become payee
(a) When the bill of exchange has been retained till the date of maturity
(b) When the bill of exchange has been discounted
(c) When the bill of exchange has been endorsed
(d) When the bill is sent to bank for collection
Answer:
(b) When the bill of exchange has been discounted

Il. State whether the Following True or False.
1. Drawee and acceptor are one and same person.
2. Three days of grace are added to the due date of the bill of exchange.
3. Three days of grace are not added to the bill at sight.
4. There are two parties in case of bill of exchange and three parties in case of promissory note.
5. From the point of view of buyer, the bill of exchange is bills receivable.
6. Rebate is allowed when the acceptor promises to pay the bill the with interest on being dishonor.
7. Noting charges are charged by the bank from the drawee of the bill of exchange.
8. The drawee has nothing to do how the drawer uses the bill of exchange.
9. There are two types of bills, bills at sight (on demand) and bill after date.
Answers:
1. True
2. True
3. True
4. False
5. False
6. False
7. False
8. True
9. True
III. Fill in the blanks with correct answer:
1. A person who prepares the bill of exchange is the _____ of the goods.
2. A person who prepares the promissory note is the _____ of the goods.
3. Due date of the bill of exchange is arrived at by adding _____ days to the _____ of the bill.
4. If date of maturity falls on public holiday, the bills of exchange is honoured one day .
5. If date of maturity is declared as emergency holiday, the bills of exchange is honoured one day _____
6. In the bill _____, no time for payment is mentioned.
Answers:
1. Seller
2. Buyer
3. Three/ period
4. Earlier
5. Later
6. at sight
