RBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 15 Our Environment
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 15 Our Environment Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 10. Students can also read RBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 10 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Browsing through class 10 science chapter 12 question answer in hindi that includes all questions presented in the textbook.
RBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Important Questions Our Environment
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
How much percentage of sunlight is received in converting the food material in a terrestrial ecosystem by the leaves of green plants?
(a) 1 percent
(b) 2 percent
(c) 3 percent
(d) 4 percent.
Answer:
(a) 1 percent

Question 2.
From the following in which year , the amount of ozone in the atmosphere began to drop sharply -
(a) 1978
(b) 1979
(c) 1980
(d) 1981
Answer:
(c) 1980
Question 3.
The function of decomposers is -
(a) Synthesis of food
(b) Purify the air
(c) Impure the air
(d) Cycling of materials
Answer:
(d) Cycling of materials
Question 4.
Substance which develops biological magnification is -
(a) pesticides
(b) D.D.T.
(c) herbicides
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
Question 5.
Energy flow is in food web -
(a) unidirectional
(b) bidirectional
(c) quadridirectional
(d) bidirectional
Answer:
(a) unidirectional
Question 6.
If CO2 is removed from; biosphere at first, which organisms will have harmful (negative) effect?
(a) decomposer
(b) primary consumer
(c) secondary consumer
(d) tertiary consumer
Answer:
(b) primary consumer
Question 7.
The known causes of depletion of ozone sphere, the most responsible cause is -
(a) Chlorofluro carbon
(b) El Nino effect
(c) PAN
(d) Green house effect
Answer:
(a) Chlorofluro carbon

Question 8.
If decomposers are completely removed from any ecosystem, opposite effect would be on the function of ecosystem, it will be because -
(a) herbivores will not receive solar energy
(b) the decomposition rate of other elements will be very high
(c) mineral flow will stop
(d) energy flow will stop.
Answer:
(c) mineral flow will stop
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
The ozone layer of the sun, protect us from which radiations?
Answer:
The ozone layer protect us from ultraviolet rays.
Question 2.
Who are ‘producers’?
Answer:
All green plants and blue-green algae which can prepare their food through photosynthesis are called producers.
Question 3.
How do producers prepare food?
Answer:
Producers make organic compounds like sugar and starch from inorganic substances using the radiant energy of the sun in the presence of chlorophyll.
Question 4.
Write the full form of UNEP.
Answer:
UNEP stands for United Nations Environment Programme.
Question 5.
Name any two abiotic components of environment.
Answer:
- Climatic factor: light, temperature, rain etc.
- Inorganic factor: nitrogen, bromine etc.

Question 6.
What is biodegradable?
Answer:
Substances that are broken down by biological processes are said to be biodegradable.
Question 7.
Give example of any man made (artificial) ecosystem.
Answer:
Garden and agriculture field is the man made (artificial) ecosystem.
Question 8.
How many categories of organism have been divided according to the manner in which they obtain their substance from the environment?
Answer:
The organism can be grouped as producers, consumers and decomposers according to the manner in which they obtain their substances from the environment.
Question 9.
How can kulhads for drinking tea affect the ecosystem?
Answer:
Making these kulhads on large scale would result in the loss of the fertile top-soil, which will affect the productivity of ecosystem producers.
Question 10.
How many categories of consumers have been divided?
Answer:
Consumers are mainly divided into herbivorous, carnivorous, omnivorous and parasite.
Question 11.
Autotrophs on receiving the energy present in sunlight convert in which energy?
Answer:
Autotrophs on receiving the energy present in sunlight convert it into chemical energy.

Question 12.
How is the ozone formed from oxygen?
Answer:
On higher level of atmosphere by the effect of ultraviolet radiation Ozone (O3) is formed by the molecule of oxygen (O2).
Question 13.
Write the name of chemical used as coolants in refrigerators and fire extinguishers.
Answer:
The name of the chemical which is used in fire extinguishers and coolants in refrigerators is the chloroflurocarbons (CFCs).
Question 14.
On the basis of nutrition what type of organisms is the insect?
Answer:
On the basis of nutrition the insect is the primary consumer.
Question 15.
When will the food chain be more long?
Answer:
More diversity in the food habit of the organism, food chain will also be long.

Question 16.
What is the ecosystem?
Answer:
The community of the living organisms and the non - living part of the environment in a habitat together make up an ecosystem.
Question 17.
What is ecological pyramid?
Answer:
The relation of trophic level of different biotic components of a ecosystem represents by triangular pyramid, is called ecological pyramid.
Question 18.
When we go from one trophic level to other trophic level, what will happen about energy?
Answer:
When we go from one trophic level to other trophic level, there will be a loss of energy.
Question 19.
In which programme an agreement was made to freeze CFC production on 1986 levels.
Answer:
In 1987, the united nations environment programme (UNEP) succeeded in forging an agreement to freeze CFC production at 1986 levels.
Question 20.
Write the main speciality of pyramid of energy.
Answer:
Pyramid of energy always remains upright.
Question 21.
Write the name of any three natural ecosystem.
Answer:
- Pond
- Lake
- Forest.
Question 22.
How much of the amount of food taken converts into approximate percent part of biomass.
Answer:
Approximately 10 percent part of the taken food convert into biomass.
Question 23.
By what changes in our attitude there is the sufficient increase in the non - biodegradable materials?
Answer:
Changes in packaging have resulted in much of our waste becoming non - biodegradable.

Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the benefits of using disposable paper cups compared to disposable plastic cups ?
Answer:
Disposable paper cups are disposed off easily and can be recycled and used. They are also beneficial for the environment.
Question 2.
Why is the restriction essential on the use of polythene bags?
Answer:
Polythene is a non - biodegradable material, which can not be decomposed. It is prepared by different type of chemical material in the industry. After use they are thrown.
They cause very serious problems such as -
- As they are non - biodegradable they cannot be decomposed due to which their quantity increases, making them difficult to decompose.
- They are eaten by stray animals along with food items but as they cannot be digested, they get accumulated in the food pipe of animals and cause their death.
Therefore, it is essential to restrict the use of polythene bags.
Question 3.
How is more use of pesticides chemical developing the problem of bio - logical magnification?
Answer:
Non - toxic pollutants enter into food chain and maximum concentration of these pollutants remain in top level of the food chain is called ‘biological magnification’. Because pesticides are non - biodegradable material so they can not be decomposed. These chemicals are either washed down into the soil or into the water bodies. From the soil, these are absorbed by the plants alongwith water and minerals, and from the water bodies these are taken up by aquatic plants and animals.
This is one of the ways in which they enter the food chain. As these chemicals are not degradable, they get accumulated progressively at each trophic level. As human occupy the top level in any food chain, the maximum concentration of these chemicals get accumulated in our bodies, which create the problem of biological magnification.
Question 4.
Who are the consumers in the ecosystem ? In which categories are they divided ? Give example of each.
Answer:
Those organisms that directly or indirectly depend on the food produced by the producers are called consumers. They are mainly divided into the following four categories -
|
Consumer Category |
Example |
|
1. Herbivores |
Goat, Rabbit |
|
2. Carnivores |
Snake, Lion |
|
3. Omnivores |
Humans, Cockroach |
|
4. Parasites |
Lice, Cuscuta reflexa (Amarbel) |
Question 5.
Clearly give the causes of following -
(i) Any ecosystem is not functional in non - availabiltiy of CO2.
(ii) It is essential to have decomposers in ecosystem.
(iii) What will hapeen if all producers are removed from ecosystem?
Answer:
(i) Green plants in presence of sunlight produce their food material by using CO2. If CO2 is not available, food will not be synthesized.
(ii) They break down the dead remains and waste products of organisms. They break-down the complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances that go into the soil and are used up once more by the plants so that they can again form the new protoplasm.
(iii) Organisms depend on the producers either directly or indirectly for their substance, if all prdoucers were removed from the ecosystem, all the consumers would die.
Question 6.
Below there is the list of organisms -
grass, lion, snake, frog, maize, grasshopper, cat, rat, squirrel, spider, lizard, moth, wheat, fruit, rabbit, peacock.
(i) From, this list make two food chain.
(ii) Make a list of all primary consumers.
(iii) Write the name of any two tertiary consumers.
Answer:
(i)
(a) Grass → grasshopper →Hizard
(b) Maize → rat → snake → peacock.
(ii) Moth, squirrel, rabbit, rat, grass-hopper.
(iii) Lion, peacock.

Question 7.
What are decomposers ? Why is their role important in ecosystem?
Answer:
Microorganisms like bacteria and fungi that break - down the dead remains and waste products of organisms are called decomposers. Decomposers are very important for any ecosystem because they break-down the complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances that go into the soil and are used up once more by the plants.
Question 8.
What are the main characteristics of energy flow in an ecosystem?
Answer:
In an ecosystem, the main characteristics of energy flow are as follows -
- The flow of energy is unidirection. The energy that is captured by autotrophs does not revert back to the solar input and the energy which passes to the herbivores does not come back to autotrophs. As it moves progressively through the various trophic levels it is no longer available to the previous level.
- The energy available at each trophic level gets diminished progressively due to loss of energy at each level.
Question 9.
Why is there an energy - loss when it goes from lower trophic level to upper trophic level of food chain?
Or
What is the rule of ten percent?
Answer:
In a food chain when energy goes from one trophic level to next higher trophic level, energy is lost. Because the amount of food taken, its only 10% converts into biomass and the rest available to ,the consumer of next trophic level, 90% lost in the atmosphere by radiation. It is called the rule of 10%. Therefore, 10% can be taken as the average value for the amount of organic matter that is present in each step and reaches the next level of consumers.
Question 10.
Write the differences between producers and decomposers.
Answer:
Differences between producers and decomposers
|
Producers |
Decomposers |
|
1. They are the green plants. |
They are micro- organisms. |
|
2. The nature of producers and autotrophic i.e., they are autotrophs. |
Their nature is heterotrophic i.e., they are heterotrophs. |
|
3. They need inorganic nutrients. |
They produce inorganic nutrients. |
|
4. They provide food to all organisms. |
They develop raw materials and provide the place for new generation. |
|
5. They remain in first trophic level. |
They come in last trophic level. |
Question 11.
Why man - made materials such as plastic can not be decomposed by bacteria and other living organisms ?
Answer:
The food we eat is digested by various enzymes in our body. Enzymes are specific in their action, specific enzymes are needed for the break - down of a particular substance. Enzymes are found in organisms for digestion/decomposition of natural food items but no enzymes are found for the decomposition of man - made substances such as plastics. Therefore, plastic decomposition can not be caused by bacteria and other living organisms.

Question 12.
If plant gets 20,000 joule energy from sun then in following food chain how much energy will be available to lion? Calculate.
Plant → Deer → Lion
Answer:
According to 10% law of energy flow, only 10% energy of a trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level. So the obtained energy of plants, out of this deer
will get 200 joule and lion will get from deer only 20 joule of energy.
Plant → Deer →Lion
20,000 J → 200 J → 20 J
Question 13.
What is trophic level and food chain?
Ans. In the ecosystem every organism is dependent for food on other organism. The sequence for getting food will be in the following sequence :
Producer → Primary → Secondary →Consumer Consumer Tertiary → Top Consumer Consumer
In this way a chain or a sequence of eating and being eaten is formed. This is called a food chain. The various steps of a food chain are known as trophic level.
Question 14.
How is the ozone formed in atmosphere? Explain.
Answer:
In the higher levels of atmosphere by the action of ultraviolet radiation ozone is formed from oxygen molecule. The higher energy ultraviolet radiations split into molecular oxygen (O2) into free oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms are then combined with the molecular oxygen to form Ozone
\(O2\begin{aligned} &\frac{\text { Ultraviolet(UV) }}{\mathrm{O}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow \mathrm{O}_{3}}\\ &\text { (Ozone) } \end{aligned} O + O\)
Question 15.
Clearly differentiate in biodegradable wastage and non - biodegradable wastage.
Answer:
Differences between Biodegradable and non - biodegradable wastage -
|
Biodegradable wastage |
Non - biodegradable wastage |
|
1. Those substances that are broken down by biological processes are called biodegradable. |
Substances that are not broken down |
|
2. Their orgin is biological. |
They are formed by human. |
|
3. These substances are never accumulated in nature. |
They accumulate in nature. |
|
4. Biodegradable wastes never show biomagnification. |
Soluble non- biodegradable substances enter into food chain i.e., show the biomagnification. |
|
5. Example: Ex - creta, paper, herb, fruit, cloth etc. |
Example - Plastic, D.D.T., canes |
Question 16.
In general, why the food chain consists of maximum fourth tropic levels in the ecosystem?
Answer:
In ecosystem, 10 percent is taken as the average value for the amount of organic matter that is present at each step and reaches the next level of consumers. Since, so little energy is available for the next level of consumers, food chain consists of maximum fourth tropic levels. The loss of energy at each step is so great that very little usable energy remains after four tropic levels.

Question 17.
What do you mean by environment? Explain.
Answer:
Environment: The surroundings of an organism which directly or indirectly effect him, is called environment. For getting the basic need of life there is an interaction which takes place between organism and environment. Organisms depend for many things on environment - like energy, water, oxygen, food and shelter.
Actually there are two components of environment -
- living i.e. biotic component, in which all organism come (microorganisms, plants and animals)
- Non - living i.e. abiotic componentns (also called physical environment). It includes soil, earth or water, light, temperature, humidity and rain of that area etc. in which that organism resides.
So the environment of an organism consists of all living and non - living things, which are in surroundings.
Question 18.
Describe in brief, giving the examples of natural ecosystems.
Answer:
Some examples of natural ecosystems -
Aquatic ecosystem -
1. Pond:Pond is an ecosystem, in which green plants (large, small and also microscopic) are producers. Herbivore fishes and insects are the primary consumers, which eat the plants. Big size fishes, frogs, toads etc. are the secondary consumers.
2. Sea is also an ecosystem, in which green algae are present in upper layers, which produce the food on first level. Herbivore fishes, snails and other different animals are the consumers, large fishes are secondary consumers and in this way series is continue.
3. Terrestrial ecosystem:Forest is a terrestrial ecosystem, in which green trees, green bushes and green grass are the producers. Deer, rabbit, rats and squirrels are the primary consumers and lion, wolf, fox, owl etc. are the secondary consumers.
Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
(a) What is food chain?
(b) Explain the food chain in grassland with example.
(c) Explain energy flow in an eco - system with diagram.
Answer:
(a) Food chain: In the ecosystem every organism depend on other organisms for food. Their order is as follows -
Producer - Primary
consumer - Secondary
consumer - Tertiary
consumer - Highest consumer.
The chain of organism that eat or being eaten in this way is called food chain.
(b) Food chain in grassland - The food chain in grassland can be understood by the following example -
\(\frac{\text { Grass }}{\text { Producer }} \rightarrow \frac{\text { Moth }}{\begin{array}{c} \text { Primary } \\ \text { Consumer } \end{array}} \rightarrow \frac{\text { Frog }}{\begin{array}{c} \text { Secondary } \\ \text { Consumer } \end{array}} \rightarrow\)\(\frac{\text { Snake }}{\text { Tertiary }} \rightarrow \frac{\text { Eagle }}{\text { Consumer }} \text { Courth }\)
In grassland, grass act as a producer which is eaten as food by the primary consumer or herbivores. Herbivores like moth are eaten by secondary consumer or eaten by carnivores like frog. Frog is eaten by tertiary consumer or eaten as food by secondary carnivores like snake. Snake is eaten by the fourth or the top carnivore like eagle. In this way, grassland forms the food chain.
(c) Energy flow in ecosystem -
The interaction among various components of the environment involves flow of energy from one component of the system to another. The autotrophs capture the energy present in sunlight and convert it into chemical energy. This energy supports all the activities of the living world. From autotrophs, the energy goes to the heterotrophs and decomposers. When one form of energy is changed to another, some energy is lost to the environment in the forms which cannot be used again. We can understand this as follows -
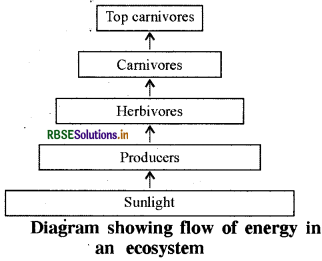
Question 2.
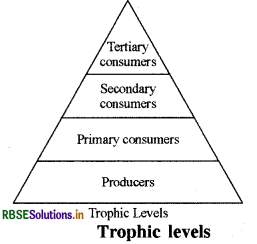
What do you understand by ‘trophic level’? Represent the trophic level in the ecosystem in diagram.
Answer:
A series of organisms feeding on one another. This series or organisms taking part at various biotic levels form a food chain. Each step or level of the food chain forms a trophic level. The autotrophs or the producers are at the first trophic level. They fix up the solar energy and make it available for heterotrophs or the consumers. The herbivores or the primary consumers come at the second, small carnivores or the secondary consumers at the third and larger carnivores or the tertiary consumers form the fourth trophic level.
Question 3.
What is ecosystem? Describe and draw diagram of an artificial ecosystem.
Or
Acquarium is a balanced ecosystem. Explain.
Answer:
Ecosystem:
The community of living organisms and the non-living part of the environment in a habitat together make up an ecosystem. An ecosystem is self supporting and fairly stable.
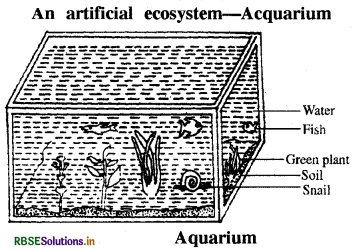
ecosystem. Aquarium is a water container which is a rectangular glass box. Inside there is soil, on which some aquatic plants are kept, by which it becomes a self sufficient system. Inside some fishes move freely in water and food chains are established. CO2 released by fishes are used by plants in making food and oxygen released by paints are used by fishes in respiration. Excreta of fishes becomes the nutrient for plants. Some decomposers (bacteria) can be present in soil which decompose the dead living part (for example broken and dead leaves). In this way aquarium is the balanced ecosystem.

Question 4.
Define ecosystem. Describe its different components.
Answer:
Ecosystem:
All living and non-living components of environment make a total balanced unit, called ecosystem i.e. interrelation between the organism and environment is called ecosystem. Its component in ecosystem remains together in a dynamic balance.
Components of ecosystem:
Mainly ecosystem consists of two components -
(a) Abiotic component
(b) Biotic component.
(a) Abiotic/non-living component -
It includes the following -
- Inorganic material: Nitrogen, phos-phorus, oxygen, hydrogen, sulpher etc. quantity remain in definite condition in the environment by recycling.
- Organic material: Carbohydrates, protein, fat etc. cycle takes place in biotic and abiotic environment. Green plants and decomposers maintain this cycle.
- Climatic factor: It includes physical, factor like temperature, rain, air, soil, water etc.
(b) Biotic components -
It includes the following components:
(i) Producer:
They are autotrophs i.e. green plants and blue green algae, which by photosynthesis manufacture organic food material. They convert light energy into chemical energy and store it in organic material.
(ii) Consumer:
They direclty or indirectly depend on producer for food. They are mainly divided into herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and parasites. Usually they are divided in the following classes:
1. Primary consumers: They get food directly from producers. They are herbivorous animals, like - cow, rabbit, rat etc.
2. Secondary consumers: They are carnivorous and eat the herbivorous animals, like - snake, frog etc.
3. Tertiary consumers: They are also carnivorous and for food depend on the secondary consumers.
There may be some top level consumers. In the end omnivorous comes, which obtain the food from both types i.e. carnivorous and herbivorous.
(iii) Decomposers: fungi and some bacteria live on dead or decay plant or animal bodies and act as saprophytic and decompose them into simple substances. These substances reach in the environment and are again obtained by green plants. Such organisms are called decomposers.
Question 5.
Describe with example the food chain and food web.
Answer:
1. Food chain:
In an ecosystem the chain of organisms taking part at different biotic levels is called food chain. Its every step or link makes one trophic level. First trophic level is of autotrophs or producers, which fixes the solar radiation and gets available to heterotrophs or consumers. Herbivorous (primary consumers) second trophic level, small carnivorous (secondary consumers) third trophic level and large carnivores organism (tertiary consumers) forms the fourth trophic level.
Together interactions of different component of environment there is a flow of energy from one component to other component. In this way food chain shows the flow of food and energy in the eco - system.
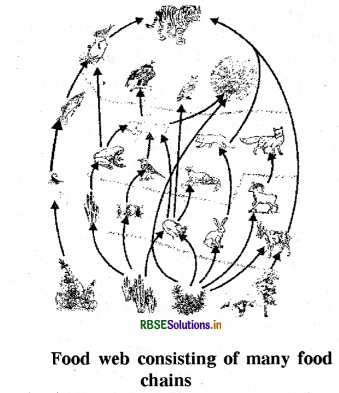
Food chain usually consists of only three or four steps. The loss of energy at each step is so great that very little usable energy remains after four trophic levels.
Some food chains are as follows:
(i) Tree →Deer →Lion
(ii) Grass → Grasshopper →Frog → Snake →Hawk
(iii) Algae → Insect →Fish →Crane
(ii) Food web: Length and complexity of different food chain have too much difference. Usually each organism is eaten by two or more type of organisms, which himself becomes the food for various types of organisms. Food chains are not found in isolation in nature. They exist in the form of a network of food chains. This network of food chains is called food web.
In this way the food web is very complex and large, in which the flow of energy is multidirectional. Trophic level in ecosystem shows the natural balance.

Question 6.
What are the major things that are found when a detailed study of the flow of energy between various components of the environment is done?
Answer:
When a detailed study of the flow of energy between various components of the environment is done following major thing can be known -
1. The green plants in the terrestrial ecosystem capture about 1% of the energy of sunlight that falls on their leaves and convert it into the food energy.
2. When green plants are eaten by primary consumers, a great deal of energy is lost as heat to the environment, some amount goes into digestion and in doing work and the rest goes towards growth and reproduction. An average of 10% of the food eaten is turned into its own body and made available for the next level of consumers.
3.Therefore, 10% can be taken as the average value for the amount of organic matter that is present at each step and reaches the text level of consumers.
4.Since so little energy is available for the next level of consumers, food chains generally consists of only three or four steps. The loss of energy at each step is so great that very little usable energy remains after four trophic levels.
5.There are generally greater number of individuals at the lower trophic levels of an ecosystem, the greatest number is of the producers
6.The length and complexicity of food chains vary greatly. Each organism is generally eaten by two or more other kinds of organisms which in turn are eaten by several other organisms. So instead of a straight line food chain, the relationship can be shown as a series of branching lines called a food web.
Question 7.
In present time what are the two stressful events related to pollution?
Answer:
In the present time the two main stressful events related to pollution are as follows -
(i) Depletion of ozone layer.
(ii) Garbage management.
(i) Depletion of Ozone Layer -
Ozone O3 is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen. While O2 which we normally refer to as oxygen, is essential for all aerobic forms of life. Ozone, is a poison gas. It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun. This radiation is highly damaging to organisms, for example, it is known to cause skin cancer in human beings.
Ozone at the higher levels of the atmosphere is a product of UV radiation acting on oxygen (O2) molecule. The higher energy UV radiations split apart some molecular oxygen (O2) into free oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms then combine with the molecular oxygen to form ozone as shown -
\(\begin{aligned} &\mathrm{O}_{2} \stackrel{\text { Ultraviolet(UV) }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{O}\\ &\mathrm{O}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow \mathrm{O}_{3}\\ &\text { (Ozone) } \end{aligned}\)
The amount of ozone in the atmosphere began to drop sharply in the 1980s. This decrease has been linked to synthetic chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) which are used as refrigerants and in fire extinguishers. In 1987, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) succeeded in forging an agreement to freeze CFC production at 1986 levels.
(ii) Garbage management: Presently if you go to any town or city, and we are sure to find heaps of garbage all over the place. Improvements in our life-style have resulted in greater amounts of waste material generation. Changes in attitude also have a role to play with more and more things we use becoming disposable. Changes in packaging have resulted in much of our waste becoming non-biodegradable.
For example before few years tea in trains was served in plastic glasses which had to be returned to the vendor. The introduction of disposable cups was hailed as a step forward for reasons of hygiene. No one at that time perhaps thought about the impact caused by the disposal of millions of these cups on a daily basis.
Presently due to more use there is an increase of these non - biodegradable articles or garbage, which create the negative effect on our environment. In this way disposal of garbage developed by us is a serious environmental problem.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 विद्युत
- RBSE Class 10 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 16 प्राकृतिक संसाधनों का संपोषित प्रबंधन
- RBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 विद्युत धारा का चुम्बकीय प्रभाव
- RBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 10 प्रकाश - परावर्तन तथा अपवर्तन
- RBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 11 मानव नेत्र एवं रंगबिरंगा संसार
- RBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 12 विद्युत
- RBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 उर्जा के स्रोत
- RBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 15 हमारा पर्यावरण