RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Drainage
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Drainage Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Social Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 9. Students can also read RBSE Class 9 Social Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 9 Social Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The india size and location important questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 9 Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 3 Drainage
RBSE Class 9 Social Science Drainage InText Questions and Answers
Page No. 17
Question 1.
Which river has the largest basin in India?
Answer:
The Ganga river has the largest basin in India.

Page No. 22
Question 2.
The name of the biggest waterfall in India.
Answer:
The Jog Falls is the biggest waterfall in India.
RBSE Class 9 Social Science Drainage Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
(i) In which of the following slates is the Wular lake located?
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Punjab
(d) Jammu and Kashmir
Answer:
(d) Jammu and Kashmir
(ii) The river Narmada has its source at
(a) Satpura
(b) Brahmagiri
(c) Amarkantak
(d) Slopes of the Western ghats
Answer:
(c) Amarkantak
(iii) Which one of the following lakes is a salt water lake?
(a) Sambhar
(b) Dal
(c) Wular
(d) Gobind Sagar
Answer:
(a) Sambhar

(iv) Which one of the following is the longest river of the Peninsular India?
(a) Narmada
(b) Krishna
(c) Godavari
(d) Mahanadi
Answer:
(c) Godavari
(v) Which one amongst the following rivers flows through a rift valley?
(a) Mahanadi
(b) Tungabhadra
(c) Krishna
(d) Tapi
Answer:
(d) Tapi
Question 2.
Answer the following questions briefly :
(i) What is meant by a water divide? Give an example.
Answer:
Any elevated area, such as a mountain or an upland, which separates two drainage basins is known as a water divide.
Example :
Ambala is as a water divide between Indus and Ganga river system.
(ii) Which is the largest river basin in India?
Answer:
The Ganga river basin is the largest river basin in India.
(iii) Where do the rivers Indus and Ganga have their origin?
Answer:
The Indus river has its origin near Lake Mansarowar in Tibet, while the Ganga River originates from the Gangotri Glacier located in the Garhwal Himalayas in the state of Uttarakhand.
(iv) Name the two headstreams of the Ganga. Where do they meet to form the Ganga?
Answer:
Bhagirathi and Alaknanda are the two headstreams of the Ganga. They meet at Devprayag to form the Ganga.
(v) Why does the Brahmaputra in its Tibetan part have less silt, despite a longer course?
Answer:
The Brahmaputra in its Tibetan part has less silt despite a longer course because it is a cold and a dry area.

(vi) Which two peninsular rivers flow through trough?
Answer:
The Narmada and Tapi are the two peninsular rivers that flow through trough.
(vii) State some economic benefits of rivers and lakes.
Answer:
(i) Economic benefits of river - Rivers have been of fundamental importance in human history. It provides water which is basic natural resources and also essential for various human activities. River banks have attracted settlers from ancient times and these settlements have now become big cities. River water are used for irrigation, navigation, hydro-power generation.
(ii) Economic benefits of Lakes - Lakes are of great value to humanbeings. A lake helps to regulate the flow of a river. During heavy rains, it prevents flooding and during the dry season, it helps to maintain an even flow of water. They help hydro-power generation. They moderate the climate of the surroundings; maintain the acquatic ecosystem, enhance natural beauty help develop tourism and provide recreation.
Question 3.
Below are given names of a few lakes of India. Group them under two categories - natural and created by human beings.
(a) Wular
(b) Dal
(c) Nainital
(d) Bhimtal
(e) Gobind Sagar
(f) Loktak
(g) Barapani
(h) Chilika
(i) Sambhar
(j) Rana Pratap Sagar
(k) Nizam Sagar
(l) Pulicat
(m) Nagarjuna Sagar
(n) Hirakud
Answer:
|
Natural Lakes |
Lakes Created by Human Beings |
|
(a) Wular |
(e) Gobind Sagar |
|
(b) Dal |
(j) Rana Pratap Sagar |
|
(c) Nainital |
(k) Nizam Sagar |
|
(d) Bhimtal |
(m) Nagaijuna Sagar |
|
(f) Loktak |
(n) Hirakud |
|
(g) Barapani |
|
|
(h) Chilika |
|
|
(1) Pulicat |
|
|
(i) Sambhar |
|
Question 4.
Discuss the significant difference between the Himalayan and the Peninsular rivers.
Answer:
|
The Himalayan Rivers |
The Peninsular Rivers |
|
1. Most of the Himalayan rivers are perennial because they receive water from rain as well as from melted snow from the lofty mountains. |
1. A large number of Peninsular rivers are seasonal because their flow is dependent on rainfall. |
|
2. These rivers are long, and are joined by many large and important tributories. |
2. Dining the dry season, the large rivers have reduced flow of water in their channels. |
|
3. The Himalayan rivers have long cources fromtheir sources to the sea. |
3. The Peninsular rivers have shorter and shallower cources as compared to Himalayan rivers. |
|
4. Himalayan rivers perform intensive erosional activity in their upper cources and carry huge loads of silt and sand. |
4. These rivers hardly perform any erosional activity. |
|
5. Inthemiddle andthelower cources, these rivers form meanders, oxbow lakes, and many other depositional features in their flood plains. They also have well developed deltas. |
5. Some major Peninsular rivers flow eastwards and drain into the Bay of Bengal and make deltas at their mouths. |
|
6. These rivers have larger drainage basin. |
6. The drainage basins of the Peninsular rivers are smaller in size. |
|
7. Indus, Ganga and Brahmputra are the major Himalayan river. |
7. Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, Narmada and Tapi are the major Peninsular rivers. |
Question 5.
Compare the east-flowing and the west-flowing rivers of the Peninsular plateau.
Answer:
|
The east-flowing rivers of the Peninsular Plateau |
The west-flowing rivers of the Peninsular Plateau |
|
1. These rivers originate from Western Ghats. |
1. These rivers originate in Central India. |
|
2. These rivers flow eastwards and drain into the Bay of Bengal. |
2. These rivers flow westwards and drain into the Arabian Sea. |
|
3. These rivers form deltas. |
3. They form estuaries on the west coast. |
|
4. These rivers are longer and have larger drainage basins. |
4. Most of these rivers are shorter and have smaller drainage basins. |
|
5. These rivers flow through flat area. These rivers have a developed and large tributory system. |
5. They flow through trough and form gorges. These rivers are devoid of any developed tributary system. |
|
6. Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri are the major east flowing rivers of the Peninsular Plateau. |
6. Narmada and Tapi are the major west flowing rivers of the Peninsular Plateau. |
Question 6.
Why are rivers important for the country’s economy?
Answer:
Rivers are important for the country’s economy because of the following reasons :
- Rivers are natural sources of water, essential for various human activities.
- The settlements that grew on the river banks in the ancient times, have now developed into big cities.
- Rivers are used for irrigation, navigation and hydro-power generation. All these are significant particularly to a country like India, where agriculture is the major source of livelihood of the majority of its population.
- They moderate the climate of the surroundings and maintain aquatic ecosystem.
- Rivers also enhance natural beauty, develop tourism and provide recreation.

Map Skills
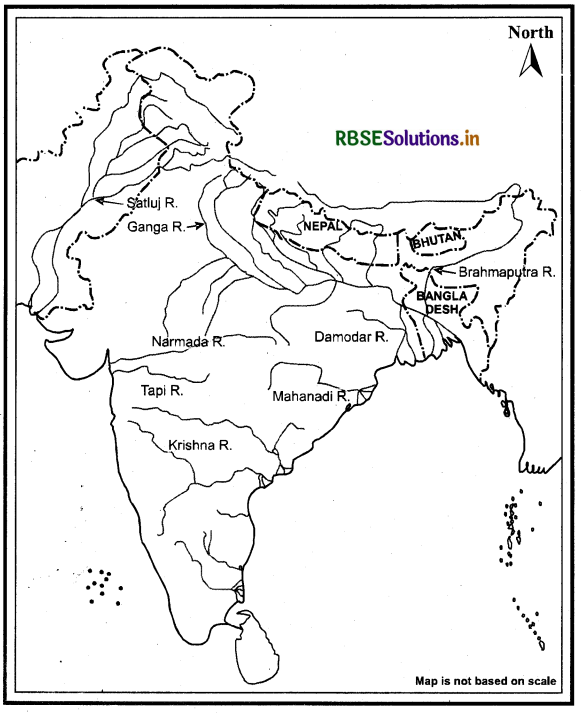
(i) On an outline map of India mark and label the following rivers.
Ganga, Satluj, Damodar, Krishna, Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi, Brahmaputra.
Answer:
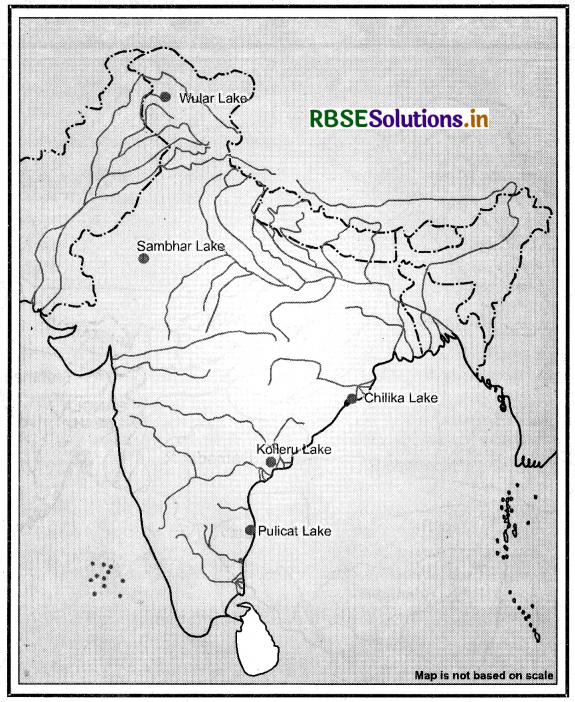
(ii) On an outline map of India, mark and label the following lakes:
Chilika, Sambhar, Wular, Pulicat, Kolleru.
Answer:
Proj ect/Activity
Solve this crossword puzzle with the help of given clues:
Across
1. Nagarjuna Sagar is a river valley project. Name the river.
2. The longest river of India.
3. The river which originates from a place known as Beas Kund.
4. The river which rises in the Betul district of MP and flows westwards.
5. The river which was known as the ‘Sorrow’ of West Bengal.
6. The river on which the reservoir for Indira Gandhi canal has been built.
7. The river whose source lies near Rohtang Pass.
8. The longest river of Peninsular India.

Down
9. A tributary of Indus originating from Himachal Pradesh.
10. The river flowing through fault and drains into the Arabian Sea.
11. A river of south India, which receives rain water both in summer and winter.
12. A river which flows through Ladakh, Gilgit and Pakistan.
13. An important river of the Indian desert.
14. The river which joins Chenab in Pakistan.
15. A river which rises at Yamunotri glacier.
Answer:
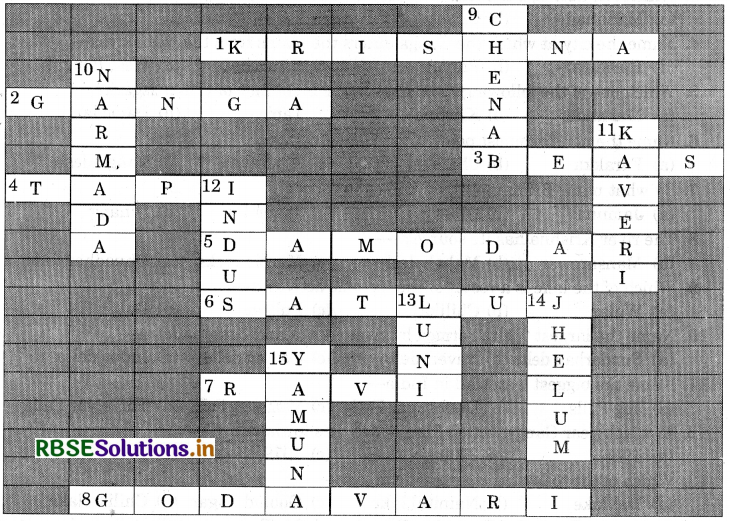
Across
1. Krishna
2. Ganga
3. Beas
4. Tapi
5. Damodar
6. Satluj river
7. Ravi
8. Godavari

Down
9. Chenab
10. Narmada
11. Kaveri
12. Indus
13. Luni
14. Jhelum
15. Yamuna

- RBSE Class 9 Social Science Important Questions Civics Chapter 1 लोकतंत्र क्या? लोकतंत्र क्यों?
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 6 Population
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Social Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 9 Social Science Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Class 9 Social Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions History Chapter 9 क्षेत्रीय संस्कृतियों का निर्माण
- RBSE Class 9 Social Science Important Questions Civics Chapter 1 What is Democracy? Why Democracy?
- RBSE Class 9 Social Science Notes Civics Chapter 4 संस्थाओं का कामकाज
- RBSE Class 9 Social Science Important Questions Economics Chapter 4 भारत में खाद्य सुरक्षा
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Civics Chapter 5 लोकतांत्रिक अधिकार