RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualizing Solid Shapes Ex 10.3
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualizing Solid Shapes Ex 10.3 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 8 Maths Solutions Chapter 10 Visualizing Solid Shapes Ex 10.3
Question 1.
Can a polyhedron have for its faces
(i) 3 triangles?
(ii) 4 triangles?
(iii) a square and four triangles?
Answer:
We know that polyhedron is a solid, which is bounded by four or more polygonal- faces in such a way that pairs of faces meet along edges and three or more edges meet in each vertex, therefore,
(i) it is not possible that a polyhedron has 3 triangles for its faces.
(ii) 4 triangles can be the faces of a polyhedron.
(iii) A square and 4 triangles can be the faces of a polyhedron.

Question 2.
Is It possible to have a polyhedron with any given number of faces?
Answer:
Yes, it is possible only if the number of faces are greater than or equal to four.
Question 3.
Which are prisms among the following?
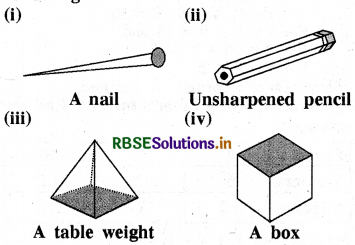
Answer:
We know that a prism is a polyhedron whose base and top are congruent polygons and lateral faces are parallelogram. Therefore,
(i) A nail is not a prism.
(ii) An unsharpened pencil is a prism.
(iii) A tabel weight is not a prism.
(iv) A box is a prism.

Question 4.
(i) How are prisms and cylinders alike?
(ii) How are pyramids and cones alike?
Answer:
(i) A prism becomes a cylinder provided the number of sides of its base becomes large and larger.
(ii) A pyramid becomes a cone provided the number of sides of its base becomes larger and larger.
Question 5.
Is a square prism same as a cube? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, it can be a cube. But it can be a cuboid also.
Question 6.
Verify Euler’s formula for these solids.
(i)
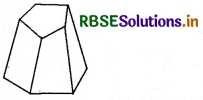
Answer:
In this figure,
F = 7, V = 10, E = 15
∴ F + V = 7 + 10 = 17 and
E + 2 = 15 + 2 = 17
or F + V = E + 2
Hence, Euler's formula is verified.
(ii)
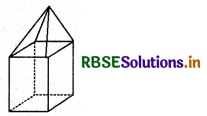
Answer:
In this figure,
F = 9, V = 9, E = 16
∴ F + V = 9 + 9 = 18 and
E + 2 = 16 + 2 = 18
or F + V = E + 2
Hence, Euler's formula is verified.

Question 7.
Using Euler’s formula find the unknown.
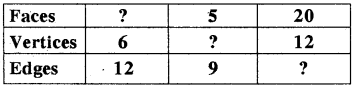
Answer:
∵ F + V - E = 2
(i) F = 2 + E - V
= 2 + 12 - 6
= 14 - 6
= 8
(ii) V = 2 + E - F
= 2 + 9 - 5
= 11 - 5
= 6
(iii) E = V+ F - 2
= 12 + 20 - 2
= 32 - 2
= 30

Question 8.
Can a polyhedron have 10 faces, 20 edges and 15 vertices?
Answer:
Since, F + V = E + 2
(as 10 + 15 ≠ 20 + 2)
∴ A polyhedron cannot have 10 faces, 20 edges and 15 vertices.
