RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Intext Questions
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Rational Numbers Intext Questions Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Integers Intext Questions
(Try These Page No: 2)
Question 1.
A number line representing integers is given below:
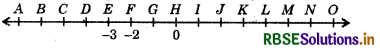
- 3 and - 2 are marked by E and F respectively. Which integers are marked by B, D, H, J, M and O?
Answer:
B = - 6, D = - 4, H = 0, J = 2, M = 5, O = 7
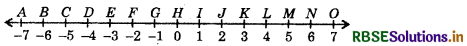

Question 2.
Arrange 7, - 5, 4, 0 and - 4 in ascending order and then mark them on a number line to check your answer.
Answer:
Since,
(i) Every positive integer is greater than 0.
(ii) Every negative integer is less than 0.
- 5 < - 4 < 0 < 4 < 7

(Try These Page No: 3)
Question 1.
We have done various patterns with numbers in our previous class. Can you find a pattern for each of the following? If yes, complete them :
(a) 7, 3, - 1, - 5, ______, ______, ______
Answer:
7, 3, - 1, - 5, - 9, - 13, - 17
(Decreasing each number by 4)
(b) - 2, - 4, -6, -8, ______, ______, ______
Answer:
- 2, - 4, - 6, - 8, - 10, - 12, - 14
(Decreasing each number by 2)
(c) 15, 10, 5, 0, ______, ______, ______
Answer:
15, 10, 5, 0, - 5, - 10, - 15
(Decreasing each number by 5)
(d) -11, -8, -5, -2, ______, ______, ______
Answer:
- 11, - 8, - 5, - 2, 1, 4, 1
(Increasing each number by 3)
(Try These Page No: 8)
Question 1.
Write a pair of integers whose sum gives:
(a) a negative integer
(b) zero
(c) an integer smaller than both the integers.
(d) an integer smaller than only one of the integers.
(e) an integer greater than both the integers.
Answer:
(a) (- 5) + 3 = - 2
(b) (2) + (- 2) = 0
(c) (- 2) + (- 5) = (- 7)
(d) (- 5) + 3 = - 2
(e) 5 + 2 = 7

Question 2.
Write a pair of integers whose difference gives:
(a) a negative integer
Answer:
4 and 9
Difference: 4 - 9 = - 5
(negative integer)
(b) zero
Answer:
- 6 and - 6
Difference : - 6 - (- 6) = 0
(c) an integer smaller than both the integers.
Answer:
8 and 5
Difference : 8 - 5 = 3
(3 is smaller than 8 as well as 5)
(d) an integer greater than only one of the integers.
Answer:
13 and 4
Difference : 13 - 4 = 9
(9 is greater than 4)
(e) an integer greater than both the integers.
Answer:
11 and - 7
Difference : 11 - (- 7) = 18
(18 is greater than 11 as well as - 7)
(Try These Page No: 10)
Question 1.
Find:
(i) 4 × (- 8), using number line.
Answer:
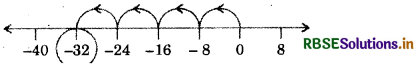
So, 4 × (- 8) = (- 32)

(ii) 8 × (- 2),
Answer:
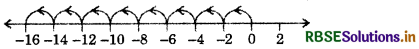
So, 8 × (- 2) = (- 16)
(iii) 3 × (- 7),
Answer:
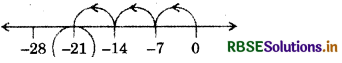
So, 3 × (- 7) = (- 21)
(iv) 10 × (-1)
Answer:
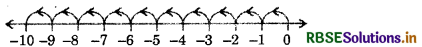
So, 10 × (- 1) = (- 10)
(Try These Page No: 10)
Question 1.
Find:
(i) 6 × (- 19)
(ii) 12 × ( - 32)
(iii) 7 × (- 22)
Answer:
(i) 6 × (- 19) = - (6 × 19) = - 114
(ii) 12 × ( - 32) = - (12 × 32) = - 384
(iii) 7 × (- 22) = - (7 × 22) = - 154
(Try These Page No: 11)
Question 1.
(a) 15 × (- 16)
(b) 21 × (- 32)
(c) (- 42) × 12
(d) - 55 × 15
Answer:
Since - a × b = - (a × b) = a × - b
(a) - (15 × 16) = - 240
(c) - (42 × 12) = - 504
(b) - (21 × 32) = - 672
(d) - (55 × 15) = - 825

Question 2.
Check if (a) 25 × (- 21) = (- 25) × 21
(b) (- 23) × 20 = 23 × (- 20)
Write five more such examples.
Answer:
(a) LHS = 25 × (- 21)
= - (25 × 21) = - 525
RHS = - 25 × 21
= -(25 × 21) = - 525
LHS = RHS
Hence verified,
(b) LHS = (- 23) × 20
= - (23 × 20) = - 460
RHS = (23) × (- 20)
= - (23 × 20) = - 460
LHS = RHS
Hence verified.
Five more examples are:
(i) 15 × (- 16) = (- 15) × 16
(ii) (-24) × 22 = 24 × (-22)
(iii) (- 19) × 17 = 19 × (- 17)
(iv) 20 × (- 10) = (- 20) × 10
(v) 17 × (- 12) = (- 17) × 12
(Try These Page No: 12)
Question 1.
(i) Starting from (- 5) × 4, find (- 5) × (- 6).
Answer:
- 5 × 4 = - 20
- 5 × 3 = - 15 = (- 20) - (- 5)
- 5 × 2 = - 10 = (- 15) - (-5)
- 5 × 1 = - 5 = (- 10) - (- 5)
- 5 × 0 = 0 = - 5 - (- 5)
(- 5) × (-1) = 5 = 0 - (- 5)
(- 5) × (- 2) = 10 = 5 - (- 5)
(- 5) × (- 3) = 15 = + 10 - (- 5)
(- 5) × (- 4) = 20 = 15 - (- 5)
(- 5) × (- 5) = 25 = 20 - (- 5)
(- 5) × (- 6) = 30 = 15 - (- 15)

(ii) Starting from (- 6) × 3, find (- 6) × (- 7)
Answer:
- 6 × 3 = - 18
- 6 × 2 = - 12 = (- 18) - (-6)
- 6 × 1 = - 6 = (- 12) - (- 6)
- 6 × 0 = 0 = - 6 - (- 6)
(- 6) × (- 1) = 6 = 0 - (- 6)
(- 6) × (- 2) = 12 = 6 - (- 6)
(- 6) × (- 3) = 18 = 12 - (- 6)
(- 6) × (- 4) = 24 = 18 - (- 6)
(- 6) × (- 5) = 30 = 24 - (- 6)
(- 6) × (- 6) = 36 = 30 - (- 6)
(- 6) × (- 7) = 42 = 36 - (- 6)
(Try These Page No: 12)
Question 1.
Find:
(i) (- 31) × (- 100)
(ii) (- 25) × (- 72)
(iii) (- 83) × (- 28)
Answer:
Since (- a) × (- b) = a × b
(i) 31 × 100 = 3100
(ii) 25 × 72 = 1800
(iii) 83 × 28 = 2324
(Think, Discuss and Write Page No: 14-15)
Question 1.
The product (- 9) × (- 5) × (- 6) × (- 3) is positive whereas the product (- 9) × (- 5) × 6 × (- 3) is negative. Why?
Answer:
Since the number of negative integers in the first product is 4 (even) so it will be positive and the number of negative integers in the second product is 3 (odd), therefore, it will be negative.

Question 2.
What will be the sign of the product if we multiply together:
(a) 8 negative integers and 3 positive integers?
(b) 5 negative integers and 4 positive integers?
(c) (- 1), twelve times?
(d) (- 1), 2m times, m is a natural number?
Answer:
(a) Positive, as the number of negative integers in the product is 8 (even).
(b) Negative, as the number of negative integers in the product is 5 (odd).
(c) Positive, as (- 1) is multiplied 12 (even) number of times.
(d) Positive, as (- 1) is multiplied 2m (even) number of times.
(Try These Page No: 18)
Question 1.
(i) Is 10 × [6 + (- 2)] = 10 × 6 + 10 × (- 2)?
Answer:
(i) LHS = 10 × [6 + (- 2)]
= 10 × 4 = 40
RHS = 10 × 6 + 10 × (- 2)
= 60 + (- 20) = 40
∴ 10 × [6 + (- 2)] = 10 × 6 + 10 × (- 2)
(ii) Is (- 15) × [(- 7) + (- 1)] = (- 15) × (- 7) + (- 15) × (- 1)?
Answer:
LHS = (-15) × [(-7) + (-1)1 = - 15 × (- 8) = 120
RHS = (- 15) × (- 7) + (- 15) × (- 1) = 105 + 15 = 120
∴ - 15 × [(- 7) + (- 1)] = (- 15) × (- 7) + (- 15) × (- 1)
Question 2.
(i) Is 10 × [6 - (- 2)] = 10 × 6 - 10 × (-2)?
Answer:
LHS = 10 × [6 - (- 2)]
= 10 × [6 + 2] = 10 × 8 - 80
RHS = 10 × 6 - 10 × (- 2)
= 60 - (- 20) = 60 + 20 = 80
∴ 10 × [6 - (- 2)] = 10 × 6 - 10(- 2)
(ii) Is (- 15) × [(- 7), (- 1)] = (- 15) × (- 7) - (- 15) × (- 1)?
Answer:
LHS =(-15) × [(-7)-(-1)]
= (- 15) × (- 7 + 1)
= (- 15) × - 6 = 90
RHS = (- 15) × (- 7) - (- 15) × (- 1)
= 105 - (15) = 90
∴ (- 15) × [(- 7) - (- 1)] = [(- 15) × (- 7)] - [(- 15) × (- 1)]

(Try These Page No: 19)
Question 1.
Find: (i) (- 49) × 18,
(ii) (- 25) × (- 31)
(iii) 70 × (- 19) + (- 1) × 70 using distributive property.
Answer:
(i) - 49 × 18 = - 49 × (20 - 2)
= (- 49 × 20) - (- 49) × 2
(By distributive property)
= - 980 - (- 98) = - 980 + 98 = - 882
(ii) (- 25) × (- 31) = - 25 × (- 30 - 1)
= (- 25 × - 30) - (- 25 × 1)
(By distributive property)
= 750 - (- 25) = 750 + 25 = 775
(iii) 70 × (- 19) + (- 1) × 70 = 70 × [(- 19) + (- 1)3
(By distributive property)
= 70 × (- 20) = - 1400
(Try These Page No: 22)
Question 1.
Find:
(a) (- 100) ÷ 5
(b) (- 81) ÷ 9
(c) (- 75) ÷ 5
(d) (- 32) ÷ 2
Answer:
Since, (- a) ÷ b = - (a ÷ b)
(a) (- 100) ÷ 5 = - (100 ÷ 5) = - 20
(b) (- 81) ÷ 9 = - (81 ÷ 9) = - 9
(c) (- 75) ÷ 5 = - (75 ÷ 5) = - 15
(d) (- 32) ÷ 2 = - (32 ÷ 2) = - 16

(Try These Page No: 23)
Question 1.
Find:
(a) 125 ÷ (-25)
(b) 80 ÷ (- 5)
(c) 64 ÷ (- 16)
Answer:
Since a ÷ (- b) = - (a ÷ b)
(a) 125 ÷ (- 25) = - (125 ÷ 25) = - 5
(b) 80 ÷ (- 5) = - (80 ÷ 5) = - 16
(c) 64 ÷ (- 16) = - (64 ÷ 16) = - 4
Question 2.
Find:
(a) (- 36) ÷ (- 4)
(b) (- 201) ÷ (- 3)
(c) (- 325) ÷ (- 13)
Answer:
Since (- a) ÷ (- b) = a ÷ b
(a) (- 36) ÷ (- 4) = (36 ÷ 4) = 9
(b) (- 201) ÷ (- 3) = (201 ÷ 3) = 67
(c) (- 325) ÷ (- 13) = (325 ÷ 13) = 25
(Try These Page No: 24)
Question 1.
Is (i) 1 ÷ a = 1?
(ii) a ÷ (- 1) = - a?
For any integer a. Take different values of ‘a’ and check.
Answer:
(i) 1 ÷ a = 1 only if a = 1
(ii) Yes, a ÷ (- 1) = - a, for all values of a.
Example: (i) If a = - 5, then
a ÷ (- 1) = (- 5) ÷ (- 1) = 5
(ii) If a = 12, then a ÷ (- 1) = 12 ÷ (-1) = - 12
(iii) If a = - 2, then a ÷ (-1) = (- 2) ÷ (- 1) = 2
