RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 6. Students can also read RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 6 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Browsing through class 6 science chapter 4 extra questions that includes all questions presented in the textbook.
RBSE Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
RBSE Class 6 Science Getting to Know Plants InText Questions and Answers
Page 54
Question 1.
Paheli wonders what kind of stem - the money plant, beanstalk, gourd plants and grape vines have. Do observe some of these plants. How are these different from a herb, a shrub or a tree? Why do you think some of them need support to climb upwards?
Answer:
The stems of the money plant, beanstalk, gourd plants and grape vines are different from herb, shrub or a tree because their stems are very weak and unable to support the weight of the plant.
As a result they grow horizontally over the ground surface Or climb up with the support of wall or other plant or object. Plants with weak stems that cannot stand upright and spread on the ground are called creepers, while those take support on neighbouring structures and climb up are called climbers.

Page 59
Question 2.
Boojho has a brilliant idea! If he wants to know what kind of roots a plant has, he need not pull it out. He just has to look at its leaves!
Answer:
Yes. This is because the leaf venation and the type of roots in a plant are related in a very interesting way. Plants having parallel venation have fibrous roots, and those with reticulate venation have taproots.
RBSE Class 6 Science Getting to Know Plants Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Correct the following statements and rewrite them in your notebook:
(a) Stem absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
(b) Leaves hold the plant upright.
(c) Roots conduct water to the leaves.
(d) The number of petals and stamens in a flower is always equal.
(e) If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are also joined together.
Answer:
The correct statements of these are:
(a) Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
(b) Stem holds the plant upright.
(c) Stem conducts water to the leaves.
(d) The number of petals and sepals in a flower may not be always equal.
(e) If the sepals of flower are joined together, its petals are separate and not joined together.
(f) If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is not necessarily joined to the petal.
Question 2.
Draw (a) a leaf, (b) a taproot and (c) a flower, you have studied for table 7.3.
Answer:
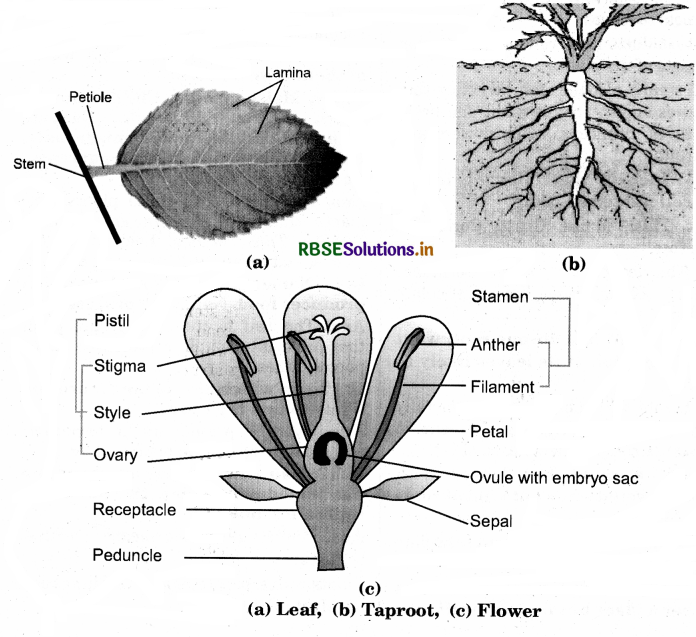
Question 3.
Can you find a plant in your house or in your neighbourhood, which has a long but a weak stem? Write its name. In which category would you classify it?
Answer:
Yes, there are several such plants, one of .which is the lauki (also called bottle gourd) plant. It takes the support of surrounding objects for staying upright, and is called a climber.
Question 4.
What is the function of a stem in a plant?
Answer:
A stem has multiple functions in a plant, and is also compared to a two - way traffic street as:
- It conducts water and minerals from roots to leaves.
- It conducts food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
- A stem is also the main structure that gives support to the plant and bears leaves, branches, buds, flowers and fruits.
Question 5.
Which of the following leaves have reticulate venation?
Wheat, Tulsi, Maize, Grass, Coriander, China rose.
Answer:
The leaves of Tulsi, Coriander (dhania), China rose have reticulate venation.
Question 6.
If a plant has fibrous root, what type of venation of its leaves likely to have?
Answer:
Plants with fibrous roots generally possess parallel venation, i.e., the veins in their leaves run parallel to each other.
Question 7.
If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, what kind of roots will it have?
Answer:
Plants with taproots have a reticulate venation in their leaves.
Question 8.
Is it possible for you to find out whether a plant has taproot or fibrous roots by looking at the impression of its leaf on a sheet of paper?
Answer:
Yes, it is possible to recognise the leaves without seeing them by smelling or touching them Leaves of some plants have aroma which can be recognized by smelling. Another method is by taking an impression of the leaf. Put paper on the leaf.
Hold the pencil tip sideways and rub it on the portion of paper having leaf below. You get impression of leaf with some lines on it. These lines help us to recognise the types of leaf.
Question 9.
Write the name of the parts of flower.
Answer:
The different parts ofa flower are sepals, petals, stamen, pistil. Stamen has two parts: anther and filament and pistil has four parts: stigma, style, ovary and ovule.

Question 10.
From the following plants, which of them have flowers?
Grass, Maize, Wheat, Chilli, Tomato, Tulsi, Peepal, Shisham, Banyan, Mango, Jamun, Guava, Pomegranate, Papaya, Banana, Lemon, Sugarcane, Potato, Groundnut.
Answer:
I have seen all these plants. The plants that have flowers are : Chilli, Tomato, Tulsi, Mango, Lemon, Jamuri, Guava, Pomegranate, Papaya and Banana.
Question 11.
Name the part of the plant which produces food. Name the process.
Answer:
The leaf is the part of the plant that produces food. This process is called photosynthesis.
Question 12.
In which part of flower are you likely to find the ovary?
Answer:
Ovary is present in the lowermost and swollen part of the pistil.
Question 13.
Name two plants in which one has joined sepals and the other has separate sepals.
Answer:
Plants with joined sepals : (i) Rose, (ii) Lotus
Plants with separate sepals: (i) China rose, (ii) Mustard flower.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 1 भोजन: यह कहाँ से आता है?
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- RBSE Class 6 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 16 Garbage In, Garbage
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Water
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 11 Light, Shadows and Reflections