RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Exercise
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Exercise Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Maths Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Maths Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Exercise
Question 1.
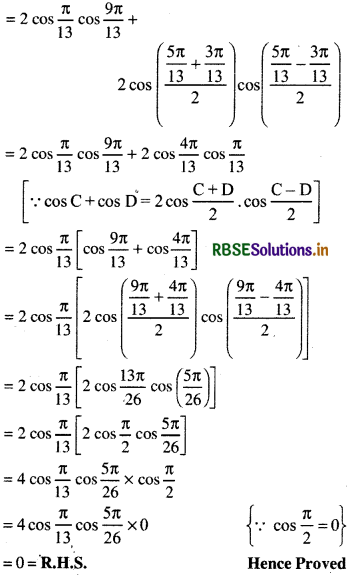
Prove that 2cos\(\frac{\pi}{13}\)cos\(\frac{9 \pi}{13}\) + cos\(\frac{3 \pi}{13}\) + cos\(\frac{5 \pi}{13}\) = 0.
Answer:
L.H.S = 2cos\(\frac{\pi}{13}\)cos\(\frac{9 \pi}{13}\) + cos\(\frac{3 \pi}{13}\) + cos\(\frac{5 \pi}{13}\)
Question 2.
Prove that:
(sin 3x + sin x)sin x + (cos 3x - cos x) cos x = 0
Answer:
L.H.S. = (sin 3x + sin x) sin x +(cos 3x - cos x) cos x
= sin 3x sin x + sin2 x + cos3x cosx - cos2 x
= cos 3x cos x + sin 3x sin x + sin2x - cos2 x
= cos(3x - x) - (cos2 x - sin2 x)
=cos2x - cos2x
(Using formula cos 2A = cos2A - sin2A)
= O = R.H.S. Hence Proved
Question 3.
Prove that:
(cos x + cos y)2 + (sin x - sin y)2 = 4cos2\(\frac{x+y}{2}\)
L,H.S. = (cos x + cos y)2 +(sin x - sin y)2
= cos2 x + cos2 y + 2cosxcosy + sin2x + sin2y - 2sinxsiny
= (cos2x + sin2x) + (cos2y + sin2y) + 2cos x cos y - 2sinx siny
= 1 + 1 + 2(cos x cosy - sin x sin y) {∵ cos2θ + sin2θ = 1)
= 2 + 2cos (x + y)
= 2[1 + cos(x + y)]
= 2[1 + 2cos2\(\left(\frac{x+y}{2}\right)\) - 1]
[Using formula cos x = 2 cos2\(\frac{x}{2}\) - 1]
= 2 × 2 cos2\(\frac{x+y}{2}\)
= 4 cos2\(\frac{x+y}{2}\)
= R.H.S
Hence Proved
Question 4.
Prove that
(cos x - cos y)2 + (sin x - sin y)2 = 4sin2
Answer:
L.H.S. = (cos x - cos y)2 ± (sin x - sin y)2
= cos x + cos y - 2cosx cos y + sin2x + sin2y - 2sinx siny
=(cos2x + sin2x) + (cos2y + sin2y) - 2cosx cosy - 2sinx sin y
= 1 + 1 - 2[cosx cosv+ sin x sin y] {From cos2θ + sin2θ = 1)
= 2 - 2 [cos (x - y)]
= 2[1 - cos(x - y)]
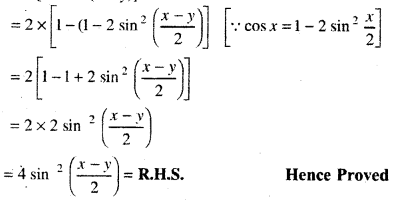

Question 5.
Prove that
sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x + sin 7x = 4 cos x cos 2x sin 4x
Answer:
L.H.S = sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x + sin 7x
= (sin 7x + sin x) + (sin 5x + sin 3x)
= 2sin\(\frac{7 x+x}{2}\)cos\(\frac{7 x-x}{2}\) + 2sin\(\frac{5 x+3x}{2}\)cos\(\frac{5 x-3x}{2}\)
[Using formula sin A + sin B = 2 sin\(\frac{A+B}{2}\)cos\(\frac{A-B}{2}\)]
= 2sin\(\frac{8 x}{2}\)cos\(\frac{6 x}{2}\) + 2sin\(\frac{8 x}{2}\)cos\(\frac{2 x}{2}\)
= 2sin 4x.cos 3x + 2sin 4x cos x
= 2sin 4x[cos 3x + cos x]
= 2sin 4x[2 cos\(\frac{3 x+x}{2}\)cos\(\frac{3 x+x}{2}\)]
[Using formula cosx + cosy = 2cos\(\frac{x+y}{2}\)cos\(\frac{x-y}{2}\)]
= 2sin 4x[2 cos\(\frac{4 x}{2}\)cos\(\frac{2 x}{2}\)]
= 4sin 4x cos 2x cos x
= 4 cos x cos 2x sin 4x
= R.H.S
Hence Proved.
Question 6.
Prove that:
\(\frac{(\sin 7 x+\sin 5 x)+(\sin 9 x+\sin 3 x)}{(\cos 7 x+\cos 5 x)+(\cos 9 x+\cos 3 x)}\) = tan 6x
Answer:
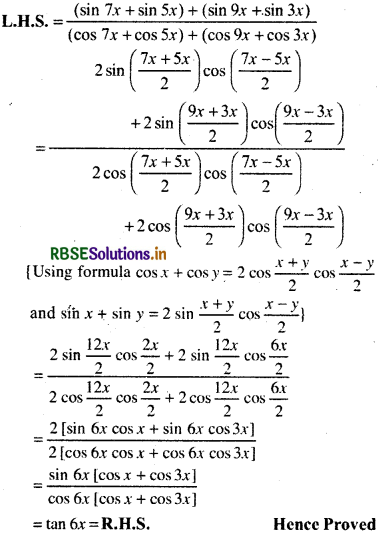
Question 7.
Prove that:
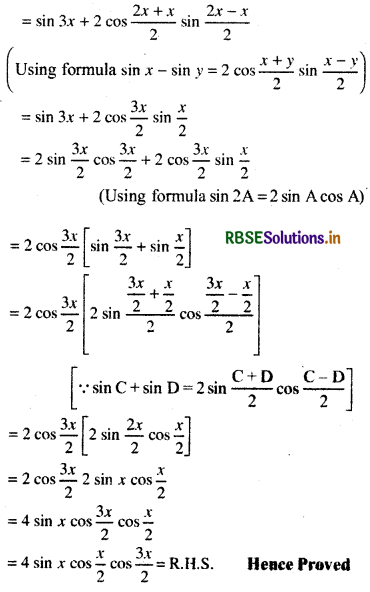
sin 3x + sin 2x - sin x = 4sin x cos \(\frac{x}{2}\) cos \(\frac{3x}{2}\)
Answer:
L.H.S = sin 3x + sin 2x - sin x
Find sin\(\frac{x}{2}\), cos\(\frac{x}{2}\) and tan\(\frac{x}{2}\) in each of the following question.
Question 8.
tan x = -\(\frac{4}{3}\), x is second quadrant.
Answer:
tan x = -\(\frac{4}{3}\), x lies second quadrant.
90° < x < 180° ⇒ 45° < \(\frac{x}{2}\) < 90°
Thus, \(\frac{x}{2}\) will lies in first quadrant so, all trigonometric ratios of \(\frac{x}{2}\) will be positive.
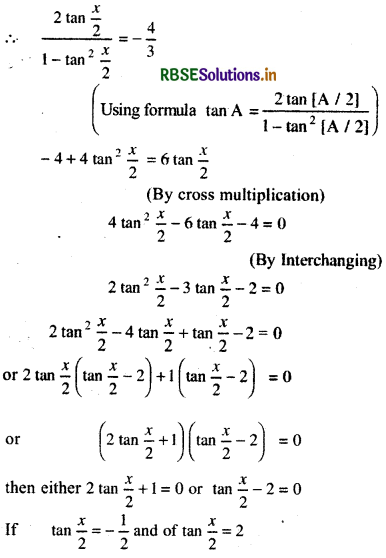
Thus required value of tan\(\frac{x}{2}\) will be 2, since \(\frac{x}{2}\) will lie in first quadrant in which all trigonometric ratios are positive so tan \(\frac{x}{2}=-\frac{1}{2}\) is negligible.
Required value of = 2
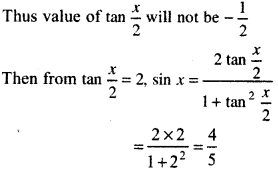
Thus, sin x = \(\frac{4}{2}\) which is positive since. It is given that x lies in second quadrant in which sin x is positive.
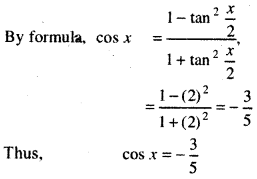
(Since, x lies in second quadrant in which cos x is negative)
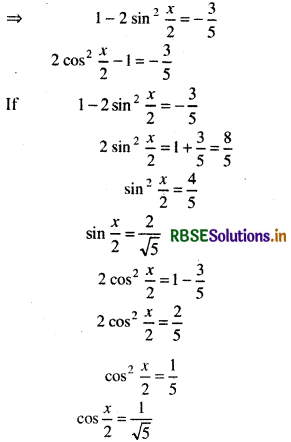
Only positive value will be considered since \(\frac{x}{2}\) lies in first quadrant.
Thus, sin \(\frac{x}{2}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\), cos \(\frac{x}{2}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\) and tan \(\frac{x}{2}\) = 2 are required values.
Question 9.
cos x = -\(\frac{1}{3}\), x in third quadrant.
Answer:
cos x = -\(\frac{1}{3}\)
180° < x < 270°
[∵ given that x lies in third quadrant. In this will be positive.]
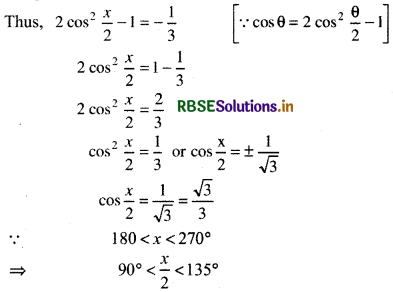
Thus, \(\frac{x}{2}\) will be in second quadrant is negligible since \(\frac{x}{2}\) lies in second quadrant so cos \(\frac{x}{2}\) will be negative.
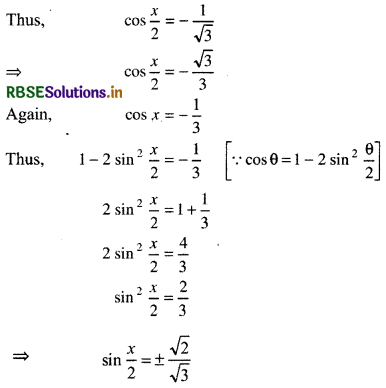
[Since \(\frac{x}{2}\) lies in second quadrant so sin \(\frac{x}{2}\) will be positive]
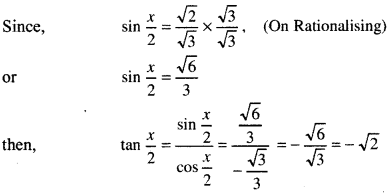
Since, x lies in third quadrant so value of x lies between π and \(\frac{3 \pi}{2}\).
i.e., π < x < \(\frac{3 \pi}{2}\)
Then, value of \(\frac{x}{2}\) will be between \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) and \(\frac{3 \pi}{2}\).
i.e \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)< \(\frac{x}{2}\) <\(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\)
Thus, will lies in second quadrant so that sin will be +ve and cos\(\frac{x}{2}\). and tan \(\frac{x}{2}\) will be negative.
then sin \(\frac{x}{2}=\frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}\), and cos \(\frac{x}{2}=-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\)
and tan\(\frac{x}{2}\) = -√2
Thus,sin \(\frac{x}{2}=\frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}\), cos \(\frac{x}{2}=-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\) and tan \(\frac{x}{2}\) = -√2

Question 10.
sin x = \(\frac{1}{4}\), x in second quadrant.
Answer:
sin x = \(\frac{1}{4}\), [Using formula sin2x + cos2x = 1]
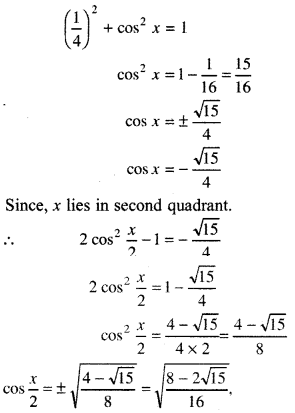
Since \(\frac{x}{2}\) will lie in first quadrant.
Since, x lie is second quadrant.
Thus \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) < x < π
\(\frac{\pi}{4}<\frac{x}{2}<\frac{\pi}{2}\)
\(\frac{x}{2}\) will lie in first quadrant then all trigonometric ratio will be always positive.
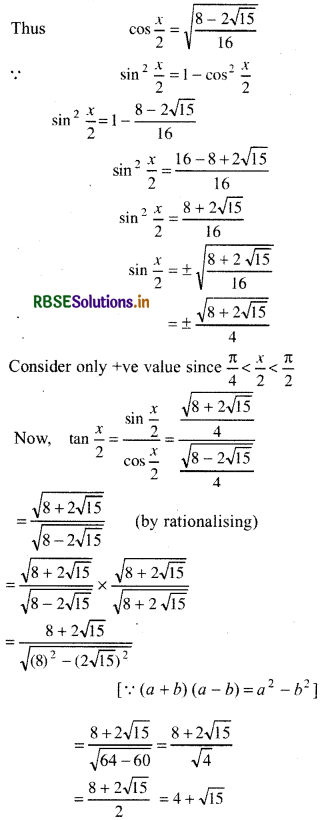
Thus, sin\(\frac{x}{2}=\frac{\sqrt{8+2 \sqrt{15}}}{4}\), cos\(\frac{x}{2}=\frac{\sqrt{8-2 \sqrt{15}}}{4}\) and tan\(\frac{x}{2}=4+\sqrt{15}\) are required values.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 त्रिकोणमितीय फलन Ex 3.1
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 2 संबंध एवं फलन विविध प्रश्नावली
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 2 संबंध एवं फलन Ex 2.3
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 2 संबंध एवं फलन Ex 2.2
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 2 संबंध एवं फलन Ex 2.1
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 समुच्चय विविध प्रश्नावली
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 समुच्चय Ex 1.6
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 समुच्चय Ex 1.5
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 समुच्चय Ex 1.4
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 समुच्चय Ex 1.3
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 समुच्चय Ex 1.2