RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 16 Biodiversity and Conservation
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 16 Biodiversity and Conservation Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Geography Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Geography Solutions Chapter 16 Biodiversity and Conservation
RBSE Class 11 Geography Biodiversity and Conservation Textbook Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Choose the right answer out of the four alternatives given :
(i) Conservation of biodiversity is important for :
(a) Animals
(b) Animals and plants
(c) Plants
(d) All organisms.
Answer:
(d) All organisms.

(ii) Threatened species are those which :
(a) threaten others
(b) Lion and tiger
(c) are abundant in number
(d) are suffering from the danger of extinction.
Answer:
(d) are suffering from the danger of extinction.
(iii) National parks and sanctuaries are established for the purpose of :
(a) Recreation
(b) Hunting
(c) Pets
(d) Conservation.
Answer:
(d) Conservation.
(iv) Biodiversity is richer in :
(a) Tropical regions
(b) Temperate region
(c) Polar regions
(d) Oceans.
Answer:
(a) Tropical regions.
(v) In which of the following countries, ‘Earth Summit’ was held ?
(a) U.K.
(b) Brazil
(c) Mexico
(d) China.
Answer:
(c) Brazil.
Short Answer Type Questions
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words :
(i) What is biodiversity?
Answer:
Biodiversity itself is a combination of two words, Bio (life) and diversity (variety). In simple terms biodiversity is the number and variety of organisms found within a specified geographical region. It refers to the varieties of plants, animals and micro-organisms, the genes they contain and the ecosystems they form. It relates to the variability among living organisms on the earth.
(ii) What are different levels of Biodiversity?
Answer:
Biodiversity exists at three different levels :
(a) Species Diversity: It is reflected by morphological, physiological and genetic features.
(b) Genetic Diversity: It comprises genetic variations within a species.
(c) Ecosystem Diversity: It is reflected in diverse bio-geographic zones such as lakes, deserts, coasts etc.
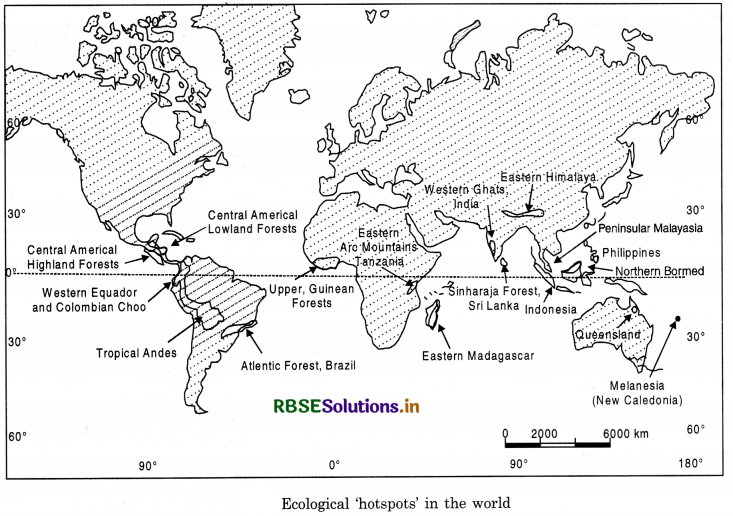
(iii) What do you understand by ‘hotspots’?
Answer:
The diversity of species can be measured through its richness, abundance and types. Some areas are more rich in species than others. Areas rich in species diversity are called hotspots of diversity.
(iv) What is the importance of animals to humankind?
Answer:
Herbivorous and carnivorous animals provide different products. In early history, man was dependent upon cattle rearing. The animals used to eat grass and provide meat and dairy products to feed population.
(v) What do you understand by ‘exotic species ?
Answer:
Species which are not the natural inhabitants of the local habitat but are introduced into the system, are called exotic species. It is not native to a given area. It can be a plant, animal or insect that has been brought to an area, often by immigrants.
3. Answer the following questions in about 150 words :
(i) What are the role played by Biodiversity in shaping the nature?
Answer:
Importance of biodiversity
Biodiversity has contributed in many ways to the development of human culture, and, in turn, human communities have played a major role in shaping the diversity of nature at the genetic, species, and ecological levels. There are four roles-
- ecological,
- economic
- ethical and
- scientific-played by biodiversity which are discussed below :
1. Ecological role of biodiversity Species of many kinds perform some function or the other in an ecosystem. Nothing in an ecosystem evolves and sustains without any reason. That means, every organism besides extracting its needs also contributes something or the other which would be useful to other organisms.

- Species capture and store energy.
- These produce and decompose organic material.
- These help to cycle water and nutrients throughout the ecosystem.
- These fix atmospheric gases and help regulate climate.
These functions are important for ecosystem function and human survival. The more diverse an ecosystem is better are the chances for the species to survive through adversities and attacks and consequently is more productive. Hence, the loss of species would decrease the ability of the system to maintain itself. Just like a species with high genetic diversity, an ecosystem with high biodiversity may have a greater chance of adapting to environmental change. In other words, the more the variety of species in an ecosystem, the more stable the ecosystem is likely to be.
2. Economic role of biodiversity. For all humans, biodiversity is an important resource in their day-to-day life. One important part of biodiversity is ‘crop diversity’, which is also called agro-biodiversity. Biodiversity is seen as a reservoir of resources to be drawn upon for the manufacturer of food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic products. This concept of biological resources is responsible for the deterioration of biodiversity. At the same time, it is also the origin of new conflicts dealing with rules of division and appropriation of natural resources. Some of the important economic commodities that biodiversity supplies to humankind are : food crops, livestock, forestry, fish, medication etc.
3. Scientific role of biodiversity. Biodiversity is important because each species can give us some clue as to how life evolved and will continue to evolve. Biodiversity also helps in understanding how life functions and the role of each species in sustaining ecosystems in which we are also a species. This fact must dawn upon every one of us so that we live and let other species also live their life.
4. Ethical role of biodiversity. It is our ethical responsibility to consider that each and every species along with us have an intrinsic right to exist. Hence, it is morally wrong to voluntarily cause extinction of any species. The level of biodiversity is a good indicator of the state of our relationships with other living species. In fact, the concept of biodiversity is an integral part of many human cultures.
- What are the major factors that are
- responsible for the loss of Biodiversity?
(ii) What steps are needed to prevent them?
Answer:
Loss of Biodiversity
Since last few decades growth in human population has increased the rate of consumption of the natural resources. It has accelerated the loss of species and habitation in different parts of the world. Tropical regions which occupy only about one fourth of the total area of the world, contain about three fourth of the world human population. Over-exploitation of resources and deforestation have become rampant to fulfil the needs of large population. As these tropical rain forests contain fifty per cent of the species on the earth, destruction of natural habitats have proved disastrous for the entire biosphere.
(1) Natural calamities. Natural calamities such as earthquakes, floods, volcanic eruptions, forest fires, droughts etc., cause damage to flora and fauna of the earth, bringing change in the biodiversity of respective affected regions.
(2) Pesticides. Pesticides and other pollutants such as hydrocarbons and toxic heavy metals destroy the weak and sensitive species.
(3) Exotic species. Species which are not natural inhabitants of the local habitat but are introduced into the system, are called ‘exotic species.’ There are many examples when a natural biotic community of the ecosystem suffered extensive damage because of introduction of exotic species.
(4) Illegal hunting. During last few decades some animals like tigers, elephants, rhinoceros, crocodiles, minks and birds are hunted mercilessly by poachers for their horns, tusks, and hides etc. It has resulted in certain types of selected group of organisms as endangered category.
Conservation of Biodiversity:
Biodiversity is important for human existence. All forms of life are so closely interlinked that disturbance in one gives rise to imbalance in the others. If species of plants and animals become endangered they cause degradation in the environment, which may threaten human’s own existence. There is an urgent need to educate people to adopt environment friendly practices and re-orient their activities in such a way that our development is harmonious with other life forms and is sustainable.
There is increasing consciousness of the fact that such conservation with sustainable use is possible only with the involvement and cooperation of local communities and individuals. For this, the development of institutional structures at local levels are necessary. The critical problem is not, merely, the conservation of species or habitat but the continuation of process of conservation.
The Government of India along with 155 other nations have signed the convention of Biodiversity at the Earth Summit held at Rio de Janeiro, Brazil in June 1992. The world conservation strategy has suggested the following steps for biodiversity conservation :
- Efforts should be made to preserve the species that are endangered.
- Prevention of extinction requires round planning and management.
- Varieties of food crop, forage plants, timber trees, livestock, animals and their wild relatives should be preserved.
- Each country should identify habitats of wild relatives and ensure their protection.
- Habitats where species feel, breed, nurse their young and rest should be safeguarded and protected.
- International trade in wild plants and animals be regulated.
To protect, preserve and propagate variety of species within natural boundaries, the Government of India has passed the Wild Life (protection) Act 1972, under which national parks and sanctuaries were established biosphere reserves declared. There are some countries which are situated in the tropical region they possess a large number of the world’s species diversity. They are called ‘megadiversity centres.’ There are 12 such countries namely-Mexico, Columbia, Equador, Peru, Brazil, Zaire, Madagascar, China, India, Malaysia, Indonesia and Australia in which these centres are located. In order to concentrate resources on those areas that are most vulnerable, IUCN has identified certain areas as biodiversity hotspots.

Hotspots are defined according to their vegetation. Plants are important because it what determines the primary productivity of an ecosystem. Most, but not all, of the hotspots rely on species rich ecosystems for food, firewood, cropland and income from timber. In Madagascar, for example, about 85% of the plants and animals are found nowhere else in the world, but its people are also among the world’s poorest and rely on slash and burn agriculture for subsistence farming. Other hotspots in wealthy countries are facing different types of pressures. The islands of Hawaii have many unique plants and animals that are threatened by introduced species and land

- RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 भारत - स्थिति
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 3 पृथ्वी की आंतरिक संरचना
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Our Rajasthan Chapter 5 उद्योग
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 2 संरचना तथा भूआकृति विज्ञान
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 भूगोल एक विषय के रूप में
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 7 Natural Hazards and Disasters
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 6 Soils
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 4 Climate