RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 5 Water
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 5 Water Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 5 Water
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1
These are the best fishing ground in the - world:
(a) Seas in Japan
(b) Seas around the eastern coast of North America
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)

Question 2.
During low tides:
(a) Water recedes from the shore
(b) Water covers much of the shore
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Water level increases
Answer:
(a) Water recedes from the shore
Question 3.
World water day is celebrated on:
(a) April 22
(b) March 22
(c) February 22
(d) January 22
Answer:
(b) March 22
Question 4.
The loss of moisture from the plants into the atmosphere is called:
(a) Evaporation
(c) Transpiration
(c) Percolation
(d) Interception
Answer:
(d) Interception
Question 5.
Fisherman can catch fish easily on
(a) Full moon day
(b) Half moon day
(c) Waxing crescent
(d) Waning crescent
Answer:
(a) Full moon day
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
The periodic rise and fall in water in the seas and oceans is called ...............
Answer:
tide
Question 2
............... is the amount of salt in grams present in 1000 grams of water.
Answer:
Salinity
Question 3.
An ............... , a ............... or ............... can shift large amounts of ocean water.
Answer:
earthquake, volcanic eruption, underwater landslides
Question 4.
The ............... tides helps the ships to arrive at the harbour more easily.
Answer:
high
Question 5.
...............sea is the largest lake.
Answer:
Caspian

True/False
Question 1.
Ocean water is still and calm.
Answer:
Fhlse
Question 2.
Tsunami can be caused by underwater landslides.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
Mediterranean sea lies between Europe and Africa.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
Cold currents carry water from lower latitudes to poles.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Tides -help removing silt from the harbors.
Answer:
True.
Match the column
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
1. Spring tides |
(a) Between Europland and Africa |
|
2. Gulf stream |
(b) Cold current |
|
3. Labrador current |
(C) Low tide |
|
4. Neap tides |
(d) High tide |
|
5. Mediterranean sea |
(e) Warm current |
Answer:
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
1. Spring tides |
(d) High tide |
|
2. Gulf stream |
(e) Warm current |
|
3. Labrador current |
(b) Cold current |
|
4. Neap tides |
(C) Low tide |
|
5. Mediterranean sea |
(a) Between Europland and Africa |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why is our earth like a terrarium?
Answer:
Our earth is like a terrarium as the water which existed centuries ago still exists.

Question 2.
Where do puddles of water vanish after rains?
Answer:
Most of the water percolates into the ground. The sun’s heat evaporates the water vapors.
Question 3.
What do you mean by salinity?
Answer:
Salinity is the amount of salt in grams present in 1000 grams of water.
Question 4.
What is average salinity of the ocean?
Answer:
The average, salinity of oceans is 35 parts per 1000.
Question 5.
What is the salinity of the Dead Sea?
Answer:
The salinity of the Dead Sea is 45 parts per 1000.
Question 6.
Which are the largest water bodies on earth? How much water do they contain?
Answer:
Oceans are the largest water bodies on the earth; they contain about 90% of water of the planet.
Question 7.
What is the effect of currents on surrounding regions?
Answer:
The currents modify the climate and agriculture and other economic activities of coastal areas.
Question 8.
What is the effect of warm current in polar regions?
Answer:
Warm currents keep the parts of Polar Regions free from ice during winter.
Question 9.
Why do ships prefer to sail along the ocean currents?
Answer:
A ship sailing in the direction of ocean current moves faster, saves fuel and time also.
Question 10.
Why does new found land have thick fog all the year?
Answer:
The mixing of warm and cold current produces very thick fog near the region of new found land. Warm Gulf Stream meets the cold Labrador Current.
Question 11.
Why are rich fishing grounds found in the areas where cold and warm current mix?
Answer:
The mixing of cold and warm current helps in production of plankton (food for fish) hence these areas support fish in large number
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How are tides formed? How are high tides important?
Answer:
Tides are periodic rise and fall in the level of water in seas and ocean caused by the attraction of the moon and the sun. Twice a day, about every 12 hours and 26 minutes, the sea level rise and falls. Importance:
- They help in navigation by raising the water level close to the shores.
- Many more fishes come closer to the shore during high tide.
- The rise and fall of water is used to generate electricity.
Question 2.
Differentiate between tide and wave.
Answer:
|
S. No. |
Tide |
Wave |
|
1. |
The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice a day is known as tides. |
Waves are the rise and fall of water on the surface of ocean. |
|
2. |
Tides are formed due to the gravitational pull exerted by the sun and moon on the earth’s surface. |
Waves are formed when wind scrapes across the ocean surface. |
|
3. |
There are two types of tides; spring tide and neap tide. |
Waves depend upon the speed of wind. The stronger waves are formed when speed of wind is high and vice-versa. |
|
4. |
High tide or spring tide is beneficial in many ways. Example : navigation, generation of electricity, importance for fisherman. |
Huge waves like tsunami are disastrous. They can cause heavy damage to life and property. |
Question 3.
Explain water cycle with a neat and labelled diagram.
Answer:
Water present in the water bodies like oceans, seas, lakes etc. converts into water vapour due to the heat of sun, this process is called evaporation. The evaporated water rises up in the atmosphere and condenses into tiny crystals of ice or droplets of water forming clouds, this process is called condensation. When the condensed ice crystals or water droplets become too heavy to float in air, they come down in form of rain, snow, sleet etc. this process is called as precipitation. This process never stops and is known as water cycle.
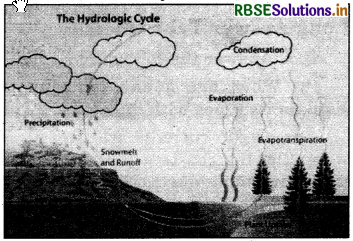
Question 4.
Differentiate between spring tide and neap tide?
Or
How are spring and neap tides formed?
Answer:
|
S. No |
Spring |
Neap Tide |
|
1. |
During the full moon and new moon days, the sun, moon and. earth are in the same line and tides are highest. These tides are called spring tide spring tide occurs. |
This happens when Moon is in its first and last quarter the ocean water get drawn in diagonally opposite directions by the gravitational pull of sun and moon resulting low tides. These tides are called neap tides. |
|
2. |
The attraction of the moon and the sun help each other and exert great gravitational pull which creates stronger and higher tides known as spring tides. |
The attraction of the sun and the moon neutralise each other which exerts lesser gravitational pull and thus tides are weaker which are known as neap tides. |
|
3. |
Spring tides hold lot of importance. For example, in generation of electricity, etc. |
Neap tides do not have much importance. |
Question 5.
Our unique planet earth is covered by different categories of water. Give the distribution of water in percentage.
Answer:
We all know that three fourth of the earth’s surface is covered by water. Water plays a major role on the earth surface for the survival of different modes of life. The different categories of the water according to their catchment area are—Ocean 97%, ice caps 02.0%, ground water 0.68%, fresh water 0.009%, Inland seas and salt lakes 0.009%, atmosphere 0.0019%, rivers 0.0001%.

Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Answer the following:
(a) What are ocean currents? Explain its types with examples.
Answer:
Ocean currents are streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in definite directions. There are two types of ocean currents:
(i) Warm ocean currents: Warm ocean currents flow from equatorial regions towards Polar Regions. As they are warm, they bring warm temperature over land surface, for example Gulf Stream.
(ii) Cold ocean currents: Cold ocean currents flow from polar regions or higher latitudes towards lower latitudes. As they are cold they lack moisture, for example, Labrador Ocean current.
(b) How are tsunamis formed? How do they cause destruction?
Answer:
Tsunami is a Japanese word meaning harbor waves. Wind blowing at high speed during a storm form huge waves. An earthquake, volcanic eruption or underwater landslide can shift large amount of ocean water. These tidal waves are called tsunami. Their height may be as high as 15m. It travels at a speed of more than 700 km/hr. The areas near the coast get submerged and lead to earthquake also.
