RBSE Class 6 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 2 Globe: Latitudes and Longitudes
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 2 Globe:Latitudes and Longitudes Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 6 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 8 Globe: Latitudes and Longitudes
Multiple Choice Question
Question 1.
Which one of the following statements is false about the globe?
(a) It is a true model of the Earth.
(b) It is the flat representation of the Earth surface.
(c) It shows countries, continents and oceans in their correct size.
(d) It can be rotated the same way as a top spin.
Answer:
(b) It is the flat representation of the Earth surface.
Question 2.
The Earth is tilted on its
(a) Perpendicular
(b) Axis
(c) Orbit
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Axis
Question 3.
The imaginary lines that run vertically from north to south are
(a) Longitudes
(b) Latitudes
(c) Parallels
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(a) Longitudes

Question 4.
How many lines of meridian are in each hemisphere?
(a) 180
(b) 10
(c) 360
(d) 90.
Answer:
(a) 180
Question 5.
The axis of the Earth can be defined as an imaginary line
(a) that runs from west to east
(b) that runs from north to south
(c) around which the earth spins
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(b) that runs from north to south
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
1. As we move away from the equator, the size of the latitudes ..............
2. The poles fall in the ............. zone.
3. To locate a point, we need to know its latitude as well as ...........
4. The British Royal Observatory is located in ...........
5. A hemisphere is one ............. of a sphere.
Answer:
1. decrease
2. Frigid
3. longitude
4. Greenwich
5. half.
True/False
Question 1.
Tropic of Capricorn is in the Southern Hemisphere.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
The distance between the longitudes decreases towards the poles.
Answer:
True

Question 3.
The Arctic circle is located in the Southern Hemisphere.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
The Northern half of the earth is known as the Southern Hemisphere.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
90 degrees north latitude marks the North Pole and 90 degrees south latitude marks the South Pole.
Answer:
True
Match the column
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Equator |
(a) 360° |
|
2. Prime Meridian |
(b) 0° Latitude |
|
3. The earth rotates an axis in about 24 hours |
(c) 0° Longtude |
|
4. Standard meridian of india |
(d) \(23 \frac{1}{2}^{\circ} \mathrm{S}\) |
|
5. Tropic of Capricorn |
(e ) \(82 \frac{1}{2}^{\circ} \mathrm{E}\) |
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Equator |
(b) 0° Latitude |
|
2. Prime Meridian |
(c) 0° Longtude |
|
3. The earth rotates an axis in about 24 hours |
(a) 360° |
|
4. Standard meridian of india |
(e ) \(23 \frac{1}{2}^{\circ} \mathrm{S}\) |
|
5. Tropic of Capricorn |
(d) \(82 \frac{1}{2}^{\circ} \mathrm{E}\) |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the direction of the movement or rotation of the Earth?
Answer:
The Earth rotates from the west to east.
Question 2.
What are the two types of lines needed to locate any point on the Earth’s surface?
Answer:
Latitudes and longitudes are required to locate any point on the Earth’s surface.

Question 3.
What does the time ‘12 noon’ signify at any place?
Answer:
'12 noon’ refers to the time when the Sun is at the highest point in the sky
Question 4.
In which heat zone does the equator lies?
Answer:
The equator lies in the Torrid Zone.
Question 5.
A particular city lies in the time zone (-2). What does this mean?
Answer:
This means that local time of the city is 2 hours behind Greenwich.
Question 6.
What is the latitudinal value of the Standard Meridian for India?
Answer:
The standard meridian for India is 82°30' E.

Question 7.
What is the Equator?
Answer:
An imaginary line running from east to west on the globe that divides it into two equal parts. This line is known as the Equator.
Question 8.
What is Prime Meridian?
Answer:
Prime Meridian is zero degrees longitude, all longitudes are measured relative to it. It passes through Greenwich, England.
Question 9.
What is the Great Circle?
Answer:
The Equator is called the ‘Great Circle’ because it is the longest latitude.
Question 10.
How is the distance between the longitudes measured?
Answer:
The distance between the longitudes are measured in degrees.
Question 11.
How does Prime Meridian divide the Earth?
Answer:
The prime meridian divides the earth into two equal halves, the Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Hemispheres.

Question 12.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a Globe?
Answer:
Advantage: On the globe, countries, continents and oceans are shown in their correct size.
Disadvantage: Globe may be of varying size and type. Big ones, cannot be carried easily.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is a Globe? Name different types of globes.
Answer:
A Globe is a true model of the Earth. The globe is not fixed. It can be rotated the same way as top spins or as a potter’s wheel is rotated.
The different types of globes are:
- Big globes, which are not easy to carry.
- Small pocket globes.
- Globes are like balloons that can be inflated and handy and easy to carry.
Question 2.
Why is it necessary to have a standard time for a country?
Answer:
The local time of places, which are on different meridians are bound to differ. It is, then •tore necessary to adopt the local time of some central meridian of a country as the standard time for the country. For e g., In India, the longitude of East (82°32'E) is treated as the Standard Meridian.

Question 3.
Give some important features of latitudes?
Answer:
Some important features of latitudes are:
- They are drawn between the poles.
- These circles run parallel to the equator and never meet each other.
- 0° Latitude is the equator, which is the longest latitude.
- They are 181 in number.
- Latitudes are not equal in size.
- The value of each latitude is followed by either the word north or south. Generally, the letter ‘N’ or ‘S’ indicates this.
Question 4.
Write a short note on Heat Zones. Draw the diagram.
Answer:
Heat zones are the different zones of the earth, where the Sun’s rays fall differently, thus causing different climate patterns. These are the Torrid Zone, the two Temperate zones, and the two Frigid zones. The Torrid Zone is very hot since the Sun shines, overhead here. The temperate zone maintains a moderate climate, and the frigid zones are extremely cold.
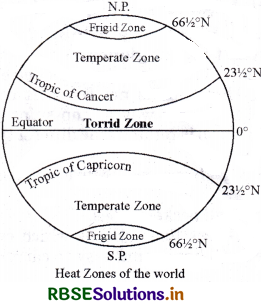
Question 5.
Give the features of longitudes?
Answer:
- They are drawn to join the poles.
- They are semi circles and the distance between them decreases steadily and becomes zero at the poles, where all the meridians meet.
- All meridians are of equal length.
- 0° meridian is called the Prime Meridian.
- They are 360 in number.
- The letter E for the east and W for the west follows the longitude of a place.
Question 6.
Mention the important latitude (parallel) lines and their numerators.
Answer:
Important Parallels of Latitudes:
- Equator (0°)
- Tropic of Cancer \(\left(23 \frac{1}{2}^{\circ} \mathrm{N}\right)\)
- Tropic of Capricorn \(\left(23 \frac{1}{2}^{\circ} \mathrm{S}\right)\)
- Arctic Circle\( \left(66 \frac{1}{2}^{\circ} \mathrm{N}\right)\)
- Antarctic Circle \(\left(66 \frac{1}{2}^{\circ} \mathrm{S}\right)\)
- North Pole (90° E)
- South Pole (90° S)

Question 7.
Draw a diagram and show the important parallels of the latitudes and the Heat Zones.
Answer:
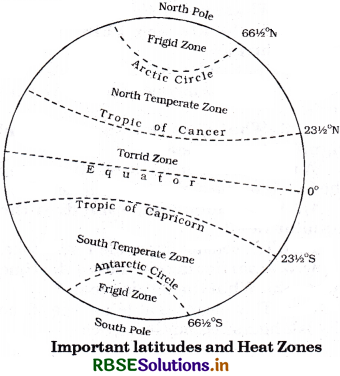
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Earth is divided into how many heat zones? Describe.
Answer:
The Earth is divided into three heat zones. They are as follows -
(1) Torrid Zone:
The Torrid Zone is located between the Tropic of Cancer \(\left(23 \frac{1}{2}^{\circ} \mathrm{N}\right)\) and the Tropic of Capricorn \(\left(23 \frac{1}{2}^{\circ} \mathrm{S}\right)\). The mid-day sun is exactly overhead at least once a year on all latitudes in between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. This area, therefore, receives the maximum heat and is called the Torrid Zone.
(2) Temperate Zone:
In both, Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere the angle of the sun’s rays goes on decreasing towards the poles. As such, the areas bounded by the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle in the Northern Hemisphere, and the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle in the Southern Hemisphere, have moderate temperatures. These are, therefore, called Temperate Zones.

(3) Frigid Zone:
Areas lying between the Arctic Circle and the North Pole in the Northern Hemisphere and the Antarctic Circle and the South Pole in the Southern Hemisphere, are very cold. It is because here the sun does not rise much above the horizon. Therefore, its rays are always slanting and provide less heat. These are, therefore, called Frigid Zones (very cold).
Question 2.
State the main features of latitude and longitude lines.
Or
State the difference between latitude and longitude lines.
Answer:
Difference and features of latitude and longitude lines
Latitude Lines:
- All latitude lines are parallel to each other.
- The latitude lines are from east to west.
- Latitude lines are complete circles.
- Equator divides the earth into two equal parts the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere.
- On both sides of the equator (0°). We calculate 90° S and 90° N latitude.
- Away from the equator, as we move towards the poles, the size of the parallels of latitude decrease.
- The latitudinal lines determine the heat zones.
Longitude Lines:
- Longitudinal lines are not parallel to each other.
- The longitude lines are drawn in a north-south direction joining the South Pole with the North Pole.
- All longitude are semi-circles. But at the distance of 180°, two longitudes make a complete circle.
- The Prime Meridian (0° longitude) and 180° meridian divide the earth into two equal halves, the Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere.
- From the Prime Meridian, we count 180° eastward as well as 180° westward.
- Moving towards the poles, the size of the meridian remains the same, but the distance between them decreases steadily polewards until it becomes zero at the poles.
- Time and dates are determined by longitude lines.

Question 3.
What do you mean by local time? How is it calculated?
Answer:
Local Time:
The time of a particular place is called local time.
Calculation of Local time:
(1) Time is determined on the basis of meridian or longitude. For the calculation of time meridian passing through Greenwich. Greenwich, where the British Royal Observatory is located, has been considered as the Prime meridian. Its name is 0° longitude.
(2) When the Prime Meridian of Greenwich has the sun at the highest point in the sky, all the places along this meridian will have mid-day or noon.
(3) As the earth rotates from west to east, those places east of Greenwich will be ahead of Greenwich time and those to the west will be behind it.
(4) The earth rotates 360° in about 24 hours, which means 15° an hour or 1° in four minutes. Thus, when it is 12 noon at Greenwich, the time at 15° east of Greenwich will be 15 x 4 = 60 minutes, i.e.,1 hour ahead of Greenwich time, which means 1 p.m. But at 15° west of Greenwich, the time will be behind Greenwich time by one hour, i.e., it will be 11.00 a.m.
