RBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
These comprehensive RBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances and their Surroundings will give a brief overview of all the concepts.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 6. Students can also read RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 6 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Browsing through class 6 science chapter 4 extra questions that includes all questions presented in the textbook.
RBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 10 Notes Motion and Measurement of Distances
→ Invention of the wheel made a great change in modes of transport.
→ The invention of steam led to the development of new means of transport.
→ In ancient times„people used length of a foot, the width of a finger, the distance of a step as units of measurement. This caused confusion and a need to develop a uniform system of measurement arose.
→ The system of units naw used is known as the International System of units (S.I. units).
→ The SI unit of length is metre.


→ Each metre (m) is divided into 100 equal divisions, called centimetre (cm). Each centimetre has 10 equal divisions, called millimetre (mm). Thus,
- 1 m = 100 cm
- 1 cm = 10 mm
→ For measuring large distances, we use the unit kilometre (km).
1 km = 1000 m
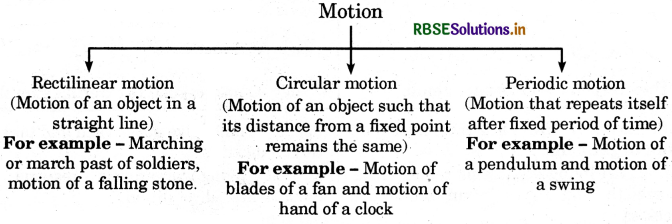
→ Change in the position of an object with time is called motion.
→ Types of motion :

- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 1 भोजन: यह कहाँ से आता है?
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- RBSE Class 6 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 16 Garbage In, Garbage
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Water
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 11 Light, Shadows and Reflections