RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 6. Students can also read RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 6 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Browsing through class 6 science chapter 4 extra questions that includes all questions presented in the textbook.
RBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Important Questions Getting to Know Plants
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following forms the female part of the flower?
(a) Sepal, petal and stamen
(b) Stigma, style and ovary
(c) Ovary, stamen and stigma
(d) Ovary, style and stamen
Answer:
(b) Stigma, style and ovary

Question 2.
Which of the following has taproot?
(a) Grass
(b) Wheat
(c) Maize
(d) Carrot
Answer:
(d) Carrot
Question 3.
Which part of onion shows modification for food storage
(a) Flower
(b) Stem
(c)Root
(d) Fruit
Answer:
(b) Stem
Question 4.
Which among, the following is a modified stem?
(a) Carrot
(b) Radish
(c) Potato
(d) Turnip
Answer:
(c) Potato
Question 5.
The region off attachment of the leaf with the stem is called:
(a) petiole
(b) lamina
(c) leaf margin .
(d) leaf base
Answer:
(a) petiole
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1.
The process of leaves absorbing water and carbon dioxide from the air to produce food is called .................
Answer:
photosynthesis
Question 2.
The food prepared by leaves is stored as .................
Answer:
starch
Question 3.
................. is the female reproductive organ of a flower.
Answer:
Pistil
Question 4.
The root system consisting of a main root from which lateral roots develop is called .................
Answer:
taproot system
Question 5.
The plants with weak stems that cannot stand upright and spread on ground are called .................
Answer:
creepers
State whether True or False
Question 1.
The water and minerals go to all parts of plant through narrow tubes ijiside stem.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Sunlight, carbon dioxide, chlorophyll and water are necessary for photosynthesis.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Money plant and pea are examples of creepers, and pumpkin and watermelon are examples of climbers.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the stamen may or may not be joined to the petal.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Leaves are attached to the stem at places called nodes.
Answer:
True

Match the followings
|
column I |
column II |
|
1. Polyandrous |
(a) rice |
|
2. Pistil |
(b) tulsi |
|
3. Reticulate venation |
(c) flower |
|
4. Anchorage |
(d) root |
|
5. Photosynthesis |
(e) stigma |
|
6. Modified shoot |
(f) transpiration |
|
7. Shrub |
(g) rose |
|
8. Herb |
(h) leaf blade |
|
9. Stomata |
(i) taproot |
|
10. Adventitious roots |
(j) multiple stamens |
Answer:
|
column I |
column II |
|
1. Polyandrous |
(i) taproot |
|
2. Pistil |
(e) stigma |
|
3. Reticulate venation |
(i) taproot |
|
4. Anchorage |
(d) root |
|
5. Photosynthesis |
(h) leaf blade |
|
6. Modified shoot |
(c) flower |
|
7. Shrub |
(g) rose |
|
8. Herb |
(b) tulsi |
|
9. Stomata |
(f) transpiration |
|
10. Adventitious roots |
(a) rice |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the components of the shoot system?
Answer:
The shoot system consists of the leaves, buds, stems, flowers and fruits.
Question 2.
Which category of plants are used generally for the purpose of decoration?
Answer:
Shrubs are generally used for decoration purposes.
Question 3.
What is a trunk?
Answer:
The thick, brown and woody stems of tr^es are called trunk.
Question 4.
What are banyan, neem, coconut and mango examples of?
Answer:
These are examples of trees.
Question 5.
Give some examples of under¬ground stems.
Answer:
Potato, onion, radish, carrot etc.
Question 6..
What is a petiole?
Answer:
The part of the plant that joins a leaf to a stem is called petiole.
Question 7.
What is the advantage of waxy coated leaves?
Answer:
Some leaves have waxy coatings that protect them against water loss, rain, and leaf infections.
Question 8.
Define photosynthesis.
Answer:
Photosynthesis is the process by which plant makes its own food using sunlight, water and soil.

Question 9.
Name the different parts of a root.
Answer:
Parts of a root are:
- Radical
- Primary and secondary roots
- Root hair
- Root cap.
Question 10.
What type of root is present in coffee, cocoa, carrot and papaya plant?
Answer:
These plants have taproots.
Question 11.
What is flower?
Answer:
Flower is an attractive, a colourful and a sweet smelling structure of flowering plant. It is the reproductive structure of a plant.
Question 12.
What is the stalk of a flower called?
Answer:
The stalk of the flower is called a pedicel.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are weeds?
Answer:
Weeds are the unwanted plants that grow with the useful crops and share water, sunlight, space and other resources with them, due to which crop production gets affected.
Question 2.
What is a leaf?
Answer:
A leaf is a part of a plant having blade-like structure. It is attached to a stem directly or through stalk. It is flat, thin, and absorbs the light, which is used by chloroplasts during photosynthesis.
Question 3.
Why do leaves have different col-ours?
Answer:
The different colours of the leaves is due to pigments.. Chlorophyll pigment is always green. Plant .leaves and stems have many pigments other than chlorophyll that are not always green. Pigments absorb specific colours of, light and reflect other colours, depending, on their chemical structure.
Question 4.
What do you mean by venation? Describe its subtypes with examples.
Answer: The arrangement of veins in a leaf is called the venation, pattern. It is of two types:
- Parallel venation: Some plants have parallel venation in which the veins run in straight lines across the length of the leaf. For example, wheat.
- Reticulate venation: Other plants
have reticulate venation in which the veins of the leaf have a het-like appearance. For example, gram
Question 5.
Where is the root located?
Answer:
The root is located below the surface of the soil and grows'downward. In some plants, they grow above the ground or especially above water.
Question 6.
What is the difference between taproot and lateral root?
Answer:
Taproot: A primary root that grows vertically downward and forming the centre from which subsidiary rootlets originate is called taproot. For example, Radish, carrot, pea, mango, marigold, mustard. Lateral root: The small roots that extend horizontally from the primary root and support the plant to hold the soil. For example, Ferns.
Question 7.
Describe the main functions of a root.
Answer:
The main functions of a root are:
- The root is the organ of a plant that helps in holding the plant firmly to the soil.
- Roots absorb water and dissolved minerals from the soil and transfer to other parts of the plant.
- Roots store food. For example, Vegetables like carrots, radish, beetroot, etc are few roots where plants store their food and nutrients.
Question 8.
Write short notes on fibrous roots.
Answer:
In fibrous roots, there is no single main root. All roots are small, thin, having the same length, the same thickness and the same shape, i.e. they seem similar. These roots grow as a tuft of hair. For example, Onion, rice, millet, maize.
Question 9.
Why is a flower important to the plant?
Answer:
A flower is important because it performs the following two functions:
- Reproduction: Flowers have male and female reproductive parts, hence help in reproduction of plants.
- Pollination: Flowers being colourful, sweet smelling and attractive, help in attracting bees and other insects to help in pollination.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Plants are essential for life. Explain.
Answer:
Plants are essential for life because:
- Plants provide food for nearly all the terrestrial organisms, including humAnswer: We eat either plants or other organisms that eat plants.
- Hants produce oxygen during photosynthesis and oxygen is essential for all living organisms.
- Plants absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis which reduces the greenhouse effect and global warming.

Question 2.
Can plants be classified on tbe basis of their stem properties?
Answer:
Yes, plants can be classified on the basis of their stems properties:
- Creepers s They are plants with weak stems that cannot stand upright and hence, spread on the ground. For example, Pumpkin.
- Climbers: These are plants with weak stems that take the support of neighbouring structures like - wall, tree, fence and climb up with the help of tendrils. For example, Grapevine.
Question 3.
What is so special about the stem of a cactus plant?
Answer:
In a cactus plant, photosynthesis occurs in the stem, whereas in other plants, it occurs in leaves. It has spines in the place of leaves. The sharp spines protect them from animals and birds. These spines do not allow stored water of cactus to escape in air. Cactus can survive in a hot and dry climate. Its stem contains chlorophyll, which prepare food for its survival.
Question 4.
Describe the structure of a leaf.
Answer:
The leaf structure generally consists of the following parts:
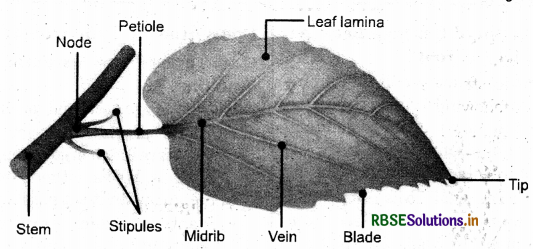
- Lamina: The broad green part of the leaf.
- Margin: The edge of the leaf is called the margin.
- Petiole: The part of the leaf that joins a leaf to a stem is called petiole.
- Midrib: The thick vein in the middle of the leaf is called midrib.
- Leaf venation: The design made by veins in a leaf is called leaf venation.
- Venation pattern: The arrangement of veins in a leaf is called the venation pattern.
- Parallel venation: In the leaves of grass, the veins are parallel to one another. This design is called parallel venation.
- Reticulate venation: Some plants have reticulate venation in which the veins of the leaf have a net-like appearance. .
Question 5.
List 4 uses of leaves.
Answer:
Uses of leaves:
- Photosynthesis: The primary function of the leaf is the conversion of carbon dioxide, water and sunlight into sugar.
- Storage: Leaves are the primary site of water and food storage to be used later.
- Gas exchange: Leaves take up carbon dioxide and release oxygen into the atmosphere. .
- Transpiration: It the process in which leaves lose water in the form of vapour in the atmosphere.
Question 6.
How are roots different from stems?
Answer:
Differences between Roots and Stems
|
Roots |
Stems |
|
1.Roots are generally whitish in colour. |
1. Stems are usually green in colour. |
|
2. Roots do not bear leaves, fruits, branches, buds. |
2. Stems bear leaves, fruits, branches, buds. |
|
3. Roots grow in irregular fashion. |
3. Branches grow in regular fashion. |
|
4. They absorb minerals, water and other nutrients from the soil. |
4. They absorb carbon dioxide and oxygen present on the surface of the leaf. |
|
5. Roots cannot make food. |
5. tems can make food through photosynthesis. |
Question 7.
Describe the basic structure of a flower in brief.
Answer:
The basic structure of a flower is comprised the following:
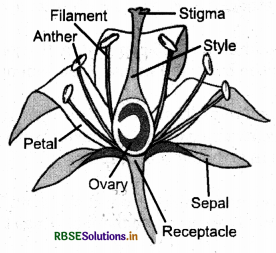
- Petals: Petals, are the main part of flower. They are the coloured leaf like structure of a flower.
- Sepals: Sepals are found below the petals. They are the outer green leafy structure of a plant.
- Stamen: The stamen is a male reproductive organ of a flower. It is surrounded at the centre of the flower. It produces pollen. It consists of a green stalk called filament. The swollen part at the top of the filament is called anther. The stamen has two parts: anther and stalk.
- Pistil: It is the innermost part of the flower. It consists of three parts:
- Ovary: It is lowermost swollen part of the pistil. The ovary contains ovules, which develop into seeds.
- Style: It is a narrow middle part of the pistil.
- Stigma: It is the sticky end at the top of the style.

Question 8.
Describe the parts of a stamen.
Answer:
Each stamen is made up of the following parts:
1. Filament: It is a long slender tube-like structure that holds the anther at the top of it.
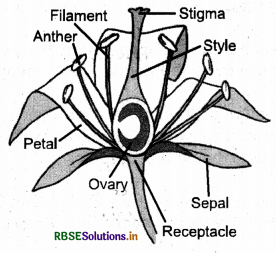
2. Anther: is the pollen producing part of the plant

- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 1 भोजन: यह कहाँ से आता है?
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- RBSE Class 6 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 16 Garbage In, Garbage
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Water
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 11 Light, Shadows and Reflections