RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 7 Natural Hazards and Disasters
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 6 Soils Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Geography Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 6 Soils
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which change happens at a faster rate?
(A) Crack
(B) Folding
(C) Earthquake
(D) Surface heating
Answer:
(C) Earthquake
2. Which disaster is related to human activities?
(A) Earthquakes
(B) Volcanoes
(C) Environmental Pollution
(D) Tornadoes
Answer:
(C) Environmental Pollution
3. First earth summit was held in:-
(A) 1974
(B) 1984
(c)994
(D) 1998
Answer:
(c)994
4. Where was first earth summit held?
(A) Rio de Janeiro
(B) Tokyo
(C) New York
(D) London
Answer:
(A) Rio de Janeiro
5. When did Tsunami occur?
(A) 2001
(B) 2002
(C) 2003
(D) 2004
Answer:
(D) 2004
6. Of which type is landslide a disaster?
(A) Atmospheric
(B) Geomorphologic
(C) Hydro
(D) Organic
Answer:
(B) Geomorphologic
7. At which rate is Indian plate drifting?
(A) 1 cm
(B) 2 cm
(C) 3 cm
(D) 4 cm
Answer:
(A) 1 cm
8. When was the disaster management rule made in India?
(A) 2001
(B) 2002
(C) 2005
(D) 2006
Answer:
(C) 2005
9. How much area is flood affected in India?
(A) 1 crore hectare
(B) 2 crore hectare
(C) 3 crore hectare
(D) 4 crore hectare
Answer:
(D) 4 crore hectare
10. How much of the total area of India is dry?
(A) 9 %
(B) 12 %
(C) 19%
(D) 25%
Answer:
(C) 19%
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the different Natural Disasters occurring in India.
Answer:
Floods, Droughts, Cyclones, Landslides and Earthquakes.
Question 2.
What is the main cause of Natural disasters?
Answer:
Sudden tectonic movements.
Question 3.
Name the recent devastating Earthquake which occurred in India.
Answer:
Bhuj (Gujarat) -26 January 2001.
Question 4.
Name the different Earthquake waves.
Answer:
P-Waves, S-Waves, L-Waves.
Question 5.
Which instrument measures the seismic waves?
Answer:
Seismograph.
Question 6.
On which scale, is the intensity of Earthquakes measured?
Answer:
Richter Scale.
Question 7.
What was the main cause of lattur Earthquakes?
Answer:
Northward drifting of Indian Plate.
Question 8.
What was the cause of Koyna Earthquake?
Answer:
Hydraulic Pressure in Koyna reservoir.
Question 9.
What is a drought?
Answer:
Drought means widespread and extreme scarcity of food.
Question 10.
How much area is affected by droughts and floods?
Answer:
10% by droughts and 12% by floods.
Question 11.
What is the cause of floods?
Answer:
Heavy rainfall and cyclones.
Question 12.
Why do major floods not occur in Southern Peninsula?
Answer:
The rivers are seasonal.
Question 13.
Name different units of Landslides. Answer: Slumps, Rockslides, Rockfall.
Question 14.
Name three states which are affected by cyclones.
Answer:
Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the major natural hazards; occurring in India?i
Answer:
Natural disasters or Hazards are the result of sudden earth movements which change the face of earth in a short period causing a lot of loss of life and property. Droughts, Floods, Cyclones, Landslides, and Earthquakes and some of the major hazards.
Question 2.
What are Landslides? Explain their effects. :
Answer:
Landslides. Groundwater increases the weight of the rock or the soil which contains it. Sometimes a mass of earth saturated with water slides down a hill slope causing landslides. There are many varieties of landslides depending on the mass slided and the distance traversed. Those which move only through short distances are called slumps. When millions of cubic feet of material moves through thousands of feet distance they are known as rockslides (debris slides). When under gravity rock material falls down a high cliff debris fall or rockfall occurs.
Causes. One or more causes such as lubrication by rains or melting snow, steep slopes and unusual structures, earthquakes, removal of support or gravity may produce landslides. Lubrication of rocks takes place by means of rains or melting snows as in many parts of Himalayas. Rocks become slippery and slide down. Steep slopes may be caused by sliding of rock strata through faulting or by quarries made by man. The sides of these may collapse on account of other factors. These include unusual structures in which
beds of rocks may have steep slopes. Earthquakes cause earth shaking which makes the rock mass of the roofs of mines and caverns unstable causing land slips. Volcanic explosions also are the causes of the tremors. Removal of support takes place in this way. Effects of Landslides. Landslides produce great scares, on the sides of mountains, and sometimes give a rippled shape to the hill-side on account of mixed rock slumps on back slopes. These may form backward rotation when their base slips thus creating a terrace¬like structure. Landshdes and rock shdes are of frequent occurrence in many mountains. In 1957, such a huge land slides came down in Kashmir. It washed out the National highway. The traffic was suspended. Recently a land slide in Tehri-Garhwal region occurred due to cloud burst.
Question 3.
Write a note on Tropical cyclones in India.
Answer:
Tropical cyclones originate in Bay of Bengal and Arabian Seas during the season of retreating monsoons. These mostly occur in the months of October-November. Their direction is variable. These move in a west or North-West and North-East direction. These effect the coastal areas of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha. Most of these cyclones recurve in North East direction.
These cyclones bring strong winds, dense clouds, and heavy rainfall. On an average, 50 cms. of rainfall occurs in a day. These cyclones cause a large scale damage and destruction to lives and property. The low pressure of N.W. India shifts to Bay of Bengal. It results in the occurrence of Cyclones over Bay of Bengal. These manage to cross the southern Peninsula and cause heavy rains and arid destructive. The deltas of Godawari, Krishna and Cauvery are the main targets. Sunderbans Delta and Bangladesh also suffer from these cyclones.
Question 4.
What are Natural Hazards and Disasters?
Answer:
Due to tectonic movements, the earth is undergoing various types of changes—slow and catastrophic changes that affect humans adversely are called natural hazards. Sometimes natural hazards are called disasters (French word des meaning Bad and aster meaning 'Star'). Disaster is a calamity or tragedy or a consequence of a hazard that causes great loss to human life and Economy.
Question 5.
Name the important disasters which occurred during last 60 years.
Answer:
12 serious disasters occurred during last 60 years. It has resulted in loss of life and property. UNO organised a disaster management conference in 1994 at Yokohama (Japan).
Table: 12 Natural disasters after 1948
|
Year |
Place |
Type |
Deaths |
|
1948 |
C.I.S. |
Earthquakes |
1,10,000 |
|
1949 |
China |
Flood |
57,000 |
|
1954 |
China |
Flood |
30,000 |
|
1965 |
Bangladesh |
Cyclones |
36,000 |
|
1968 |
Iran |
Earthquakes |
30,000 |
|
1970 |
Peru |
Earthquakes |
66,794 |
|
1970 |
Bangladesh |
Cyclone |
5,00,000 |
|
1971 |
India |
Cyclone |
30,000 |
|
1976 |
China |
Earthquakes |
3,00,000 |
|
1990 |
Iran |
Earthquakes |
50,000 |
|
2004 |
Indonesia to India |
Tsunami |
5,00,000 |
|
2005 |
India-Pakistan |
Earthquakes |
70,000 |
Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Discuss the Twin problem of Drought and floods.
Answer:
Drought. Drought is a natural hazard. Drought may be defined as wide spread and extreme scarcity of food. Due to droughts, lakhs of people die. In 1943, a drought in Bengal caused 15 lakh people to die. India is a vast country. The average rainfall is 117 cms per annum. Due to variability of rainfall, one part or the other suffer from drought. On an average one year in every five years is a drought year. About 12% of the country's area receives less than 61 cm. of rainfall on average, and only 8% receives more than 250 cm. The erractic nature of the Indian monsoon with long dry spells accompanied by high temperature is responsible for creating drought conditions
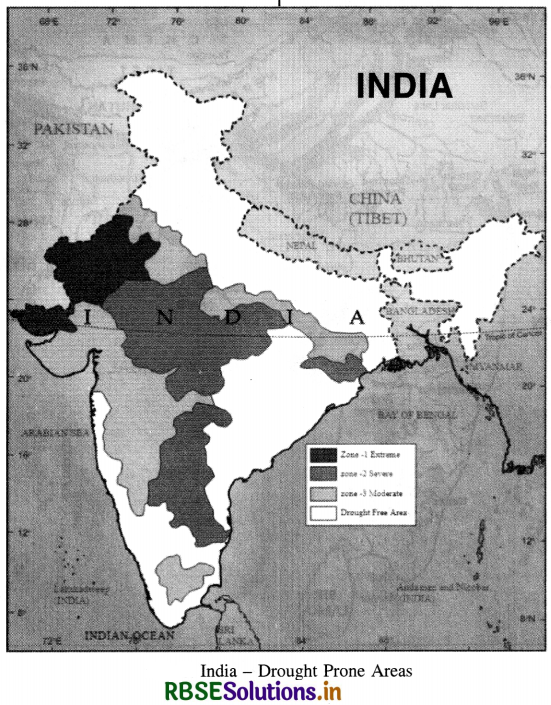
In India, there are certain well-defined tracts of drought. These are :
(a) The desert and the semi-arid regions, with approximately 0.6 million sq. km, from a rectangle from Ahmedabad to Kanpur on one side and Kanpur to Jalandhar on the other. The rainfall in this region is less than 7.5 cm., and at places less than 4 cm. Some of the areas, where irrigation is not provided, are among the worst famine tracts of the country.
(b) Regions lying east of the Western Ghats, up to a width of 300 km. The region extends all along the Krishna river almost to within 80 kms. from the coast. The area of this region is 0.37 million sQuestion km.
(c) Other pockets of drought lie in several parts of India, such as
- Tirunelveli district, south of Vaigai river,
- Coimbatore area,
- Saurashtra and Kutchh regions,
- Mirzapur plateau and Palamau regions,
- Purulia district of West Bengal and
- Kalahandi region of Odisha. These scattered pockets total to 0-1 million sq. km.
Causes of Droughts
- Weak monsoons.
- Areas of Low rainfall (less than 50 cm.)
- Inadequate means of irrigation.
- Variability of rainfall.
- Absence of rivers.
- Long dry spells with high temperalines.
Effects of Drought
- Production of food grains is affected.
- Agricultural labour starve due to un¬employment.
- Low production of Kharif crops.
- There is absence of fodder for cattle.
- There is shortage of water.
Floods :
Floods are another natural hazard. Floods occur in India widely every year. Sometimes it is drought in one part, and Floods occur in other part. It is a seasonal
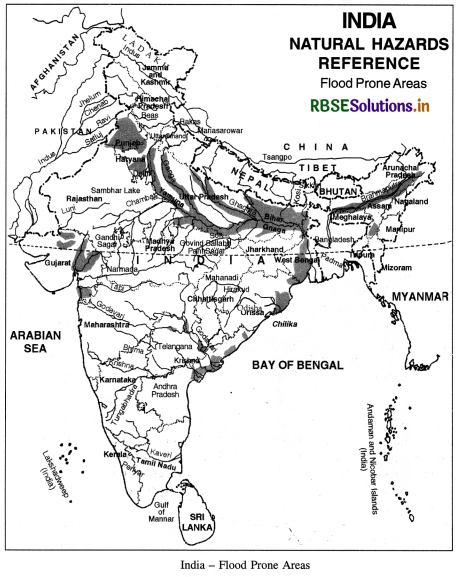
problem due to heavy monsoonal rainfall. Floods occur due to early start or late ending of monsoons. Rivers of northern India are generally in floods in summer. Flash floods occur in Narmada River. Recently a tropical cyclone burst caused heavy floods in Andhra Pradesh.
Causes of Floods:
India has the worst distinction of being one of the worst affected tropical countries. Floods are usually the result of:
- heavy precipitation (i.e., 15 cm. or more in a single day);
- cyclones accompanied by strong winds, tide bores, indiscriminate deforestation in the catchments and the upper reaches of the river basins;
- spilling of rivers over natural banks and the rising of the river beds;
- (iv) inadequate drainage arran-gements in intensely cultivated and irrigated areas; and
- (v) changes in river courses through the formation and inundation of river meanders.
Flood affected areas
Flood occurrence in India is associated with the river system of the country.
1. The basin of the Himalayan rivers (covering a part of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Delhi, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal). The worst offenders are Kosi and Damodar, which have been notorious for devastating large areas. Brahmaputra basin is also subject to earthquakes and landslides which obstruct the free flow of water. In the Brahmaputra basin, floods are almost an annual feature and cause heavy damage by inundation and erosion. Assam valley is considered to be one of the worst flood affected areas of India. Floods occur here mostly due to heavy rains during the rainy seasons, and silting of tributaries like Dihang and Luhit.
2. The North-western river basin covering Jammu and Kashmir, parts of Punjab, Haryana, West U.P. and Himachal Pradesh, the Jhelum, the Sutlej, the Beas, the Ravi and the Chenab. In the Kashmir valley, the Jhelum is unable to carry the flood discharge. In Punjab and Haryana plain the problem is mainly due to lack of adequate drainage.
3. The Central India and Peninsular river basins, covering Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra, contain the Tapi, the Narmada and the Chambal. In their basins, at times the rainfall is excessive, causing floods in some of the rivers, but such floods do not occur every year, and when they do occur they are not of long duration. Heavy floods occur in the Godavari, the Krishna, the Pennar and the Cauvery at long intervals and the flood problem is said to be not generally serious.
Effects of Floods.
Floods damage crops, houses, means of transport. Many epidemics break out. About 2 million Hectare land is flood affected. About 500 persons die every year due to floods. A damage of? 1500 crores is suffered. Flood Control Programmes.
The National Flood Control Policy comprises three phases:
(1) Immediate phase, extending over a period of 2 years and comprising collection of basic hydrologic data, construction of embankments, urgent spurs, rivetments, improvement of river channels, and raising of villages above flood level.
(2) Short-term phase, covering next 4 to 5 years, consists of improvement of surface drainage, establishment of proper flood warning systems, shifting or raising of villages over flood level, construction of building channel diversions, more embankments and construction of raised platforms to be used during times of flood emergency.
(3) Long-term phase, which envisages schemes such as construction of dams or storage reservoirs for flood protection and soil conservation in the catchment of various river, detention basins, and digging larger channel diversions.
Question 2.
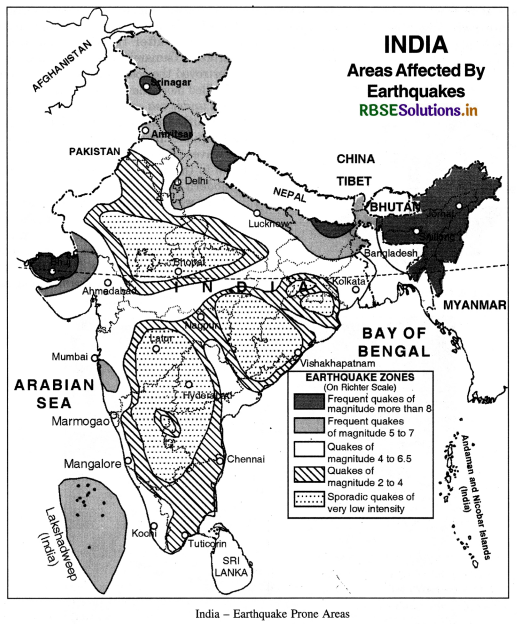
Define an earthquake. Describe the distribution of earthquakes in India.
Answer:
An earthquake is a sudden movement of the crust of the earth. It is a sudden shaking of the crust which results in tremors and vibrations. The earthquake proceeds in the form of waves in all directions from the origin or focus. There are three types of waves ‘P’ waves, ‘S’ waves and ‘L’ waves. The general causes of earthquakes are volcanic eruptions, tectonic causes, elasticity of rocks and local causes. But now-a-days, earthquakes are related to tectonic water.
In India, the Indian plate and Eurasian plate collide with each other. These plates underthrust each other. In Himalayan earthquakes are related to folds and faults, but in the rigid Deccan shield earthquakes are not common. The intensity of earthquakes is measured by a scale devised by C.F. Richter in 1935. It has nine divisions from 1 to 9. Major earthquakes of higher intensity are destructive. The following zones are seismological zones of India :
1. The Himalayan Zone :
It is a zone of active Earthquakes. Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttrakhand, and North-Eastern states suffer great losses due to Earthquakes. These earthquakes are due to the collision of Eurasian plate and Indian plate (which is pushing in the North and North-East direction at an annual rate of 5 cms.) These areas suffered earthquakes in 2005 in Kashmir, in 1936 in Quetta, in 1905 at Kangra and in 1950 in Assam.
2. The Indo-Gangetic Zone : This zone has moderate intensity Earthquakes with 6 to 6.5 on Richter Scale. But these Earthquakes are very harmful as it is a densely populated area.
3. The Peninsular Zone : The Peninsular Region is a stable and rigid zone. But despite its stable rocks, serious Earthquakes occurred in Koyna (1967), Latur (1993) and Bhuj (2001). Koyna Earthquake occurred due to excessive Hydraulic pressure in the reservoir formed by Koyna Dam. But recent Earthquakes are result of Northward drift of Indian plate.
Some other important Seismic zones are:
(a) North-eastern India (Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Shillong)
(b) Bihar-Nepal Zone
(c) North-Western Himalayas
(d) Gujarat Region
(e) Koyna Region
Some important Earthquakes in India
|
Area/Kegion |
Intensities (Richter Scale) |
Year |
|
1. Kuchh |
8.0 |
1819 |
|
2. Kachar |
7.5 |
1869 |
|
3. Meghalaya |
8.7 |
1885 |
|
4. Bengal |
8.5 |
1885 |
|
5. Assam |
8.0 |
1897 |
|
6. Kangra |
8.0 |
1905 |
|
7. Assam |
8.7 |
1950 |
|
8. Koyna |
6.3 |
1967 |
|
9. Himachal Pradesh |
7.5 |
1975 |
|
10. Latour |
6.0 |
1993 |
|
11. Bhuj |
8.0 |
2001 |
Question 3.
What are Cyclones? Explain the damage caused by it.
Answer:
CYCLONES
Cyclones of a diameter of 600 km or more is one of the most destructive and dangerous atmospheric storms on the earth. With about 6 per cent of the worldwide cyclones, the Indian subcontinent is the worst cyclone-affected area.
Origin :
A tropical cyclone can form when the horizontal temperature gradients are exeedingly high around a weakly developed area of low pressure. The cyclone is the heat engine whose heater is the oceanic surface. The released heat after condensation converts it into kinetic energy for the cyclone. The following are the stages in the formation of a cyclone :
(a) Temperature of the oceanic surface over 26°C.
(b) Appearance of a closed isobar.
(c) Low pressure dropping below 1000 mb.
(d) Areas of circular movement, first spreading to a radius of 30-50 km then increasing gradually to 100-200 km and even to 1000 km, and
(e) Vertically the wind speed first rising to a height of 6 km, then much higher.
Structure of Tropical Cyclone.
1. Tropical cyclones have large pressure gradients 14-17 mb/100 km; in some cyclones it is as high as 60 mb/100 km.
2. The wind belt can spread to a distance of 10 to 150 km from the centre and at times even further.
3. The tropical cyclones have a warm core. In the centre of the cyclone there is generally a cloudless spot known as the eye of the storm. The eye is encircled by a cloud of great vertical extent.
4. The average rainfall in a tropical cyclone amounts to over 50 cm. some time rising to over 100 cm.
5. The cyclone moves forward at an average speed of about 20 km per hour. As soon as the cyclone moves over the land, its energy, because of the absence of sea water, starts decreasing. This leads to the death of the cyclone. The cyclone lasts for five to seven days.
Damage by Cyclones.
The damaging impact of a tropical storm is due to winds of hurricane force, hurricane waves and floods caused by heavy showers. The majority of the storms inflict heavy losses because of either strong wind or storm waves. In mountainous areas, heavy damages are caused by powerful surface run offs smashing everything on their way. Intensity of storm waves depends on wind speed, pressure gradient, topography of sea bottom and profile of coastline. Tropical cyclones entail casualties and losses to life and property in spite of warning system introduced in several areas.
Area. We find that the number of storms in the Bay of Bengal is much greater than in the Arabian sea. The maximum number of storms both in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian sea occur in the months of October and November. Also, early part of the monsoon season is favourable for the formation of tropical storms in both the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian sea. Most of the cyclones have their origin between 10°N and 15°N during the monsoon season. Almost all storms in the Bay of
Bengal have their genesis between 16°N and 21°N and west of 92°E in June. By July, the Bay storms form north of 18°N and west of 90°E. It is also noteworthy that most July storms move along a westerly track. They are generally confined to the region between 20°N and 25°N and recurvature to the Himalayan foothills is comparatively rare. Reducing Impact of Damage : Most damage from cyclones is caused by the strong winds, torrential rain and high storm tides. Floods generated by cyclonic rainfall are more destructive than the winds. Today adequate warning system has been developed. Other measures are constitution of cyclone shelter, embankments, dykes, reservoir, and coastal afforestation.
Question 4.
What is a Tsunami? How is it caused? Describe the destruction caused by Tsunami Disaster of 26th December 2004.
Answer:
Tsunami. Tsunami is a Japanese word meaning ‘Harbour wave’. ‘TSU’ means Harbour and ‘sami’ means a ‘wave’. It is often referred as Tidal wave or a Seismic wave. A Tsunami wave rises unexpectedly as destructive high wave. It moves deep waters. It is several metres high wave. Tsunamis are large waves that are generated when the sea floor is deformed by seismic activity vertically displacing the overlying water in the ocean.
Tsunamis are relatively rare in Indian Ocean. Most Tsunamis occur in Pacific Ocean. Origin of Tsunami. The earth is internally an active planet. Most of earth quakes occur at plate boundaries. Tsunamis are caused by sub-marine earth quakes. Tsunamis are caused by Subduction zone earth quakes. It is a zone where two of the earth’s rigid tectonic plates are converging. One heavier plate drives beneath the lighter plate. Sea-floor is displaced. It is a shallow thrust type earthquake.
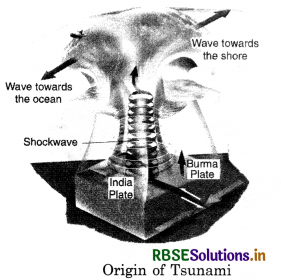
It was 7:58 a.m. on ‘black Sunday’on 26th December, 2004, a day after the Christmas when a massive, destructive Tsunami hit the coastal areas of Indian ocean. It destroyed the coastal areas from Indonesia to India, and killed more than 3 lakh people in these areas. An under sea earthquake that had its epicentre 25 kms South East of Sumatra Island (Indonesia). The earth quake measured 8.9 on the Richter Scale.
The sea waves rose to form a gaint wall of water. It will go down in the as one of the greatest natural calamities of modern times. This was the Fourth largest earth-quake in the world since 1900. This earth quake producted the Tsunami that unleashed energy millions of times greater than the Hiroshima Bomb. It is called an earth quake driven Killer wave. It occured at the interface between the Indian and Burmese plates. About 1000 km., long plate boundary slipped.
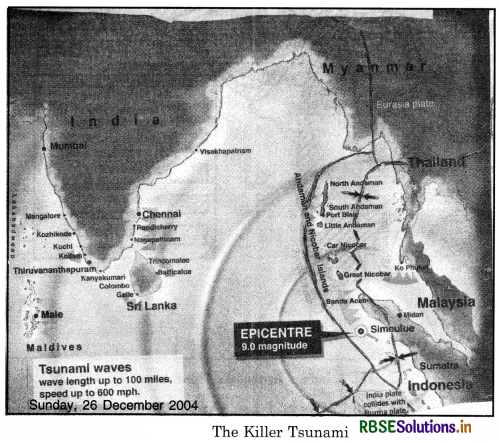
This resulted in the ocean bed rising more than 10 metres and displaced hundreds of cubic kilometers overlying water, travelling at a speed of 700 kms per hour. It covered the distance from epicentre and the Indian coastal regions in about 2 hours. The black Sunday changed the history and Geography of these coastal areas tb a certain extent. Effects of the Tsunami Disaster The coastal countries of Indian ocean like, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Myanmar, India, Sri Lanka and Maldives were badly affected. The worst affected areas in India were Tamil Nadu, Puducherry,
Andhra Pradesh, Kerala. The islands of Andaman and Nicobar were badly mauled by demon waves. About 1 lakh persons in Indonesia, 10,000 in Thailand, 30,000 in Sri Lanka and 15,000 in India were killed. In India, in Tamil Nadu, Nagapattinam district was the main ©victim area of Tsunami waves. Water entered 1.5 km. inside the town. Communcation and electric supply were cutt off in affected areas. Many pilgrims were swept away on the beach near the Church of our lady of health at Velankanni. Holiday makers were swept away at the 3 km long Marina beach at Chennai. This is the longest beach in Asia.
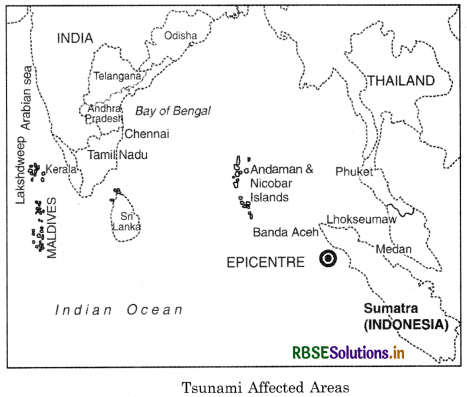
Powerful waves swept into nearly Kalpakkam Nucelar power station. The reactors were shut down. Gigantic waves surged into world famous temple at Mamallpuram. The Andaman-Nicobar island, took the largest death toll. Great Nicobar, the Southern most island was only 150 km. away from the epicentre so it was the worst affected area. A wall of water travelled 2000 km. from the epicentre, and slammed into India. In Car Nicobar, an Indian air force base was wiped out by the Tsunami. It is feared that a large area of the islands might have been eaten into by the sea. Thus Tsunami has changed the Geography of this group of islands and maps of these are to be redrawn.
Source Based Questions
1. Read the following paragraph and answer the questions given below:
Indian agriculture has been heavily dependent on the monsoon rainfall. Droughts and floods are the two accompanying features of Indian climate. According to some estimates, nearly 19 per cent of the total geographical area of the country and 12 per cent of its total population suffer due to drought every year. About 30 per cent of the country’s total area is identified as drought prone, affecting around 50 million people.
It is a common experience that while some parts of the country reel under floods, there are regions that face severe drought during the same period. Moreover, it is also a common sight to witness that one region suffers due to floods in one season and experiences drought in the other. This is mainly because of the large-scale variations and unpredictability in the behaviour of the monsoon in India. Thus, droughts are widespread and common phenomena in most parts of the country, but these are the most recurrent and severe in some and not so in others.
(i) How much of the total area of India is dry?
(a) 9%
(b) 12%
(c) 19%
(d) 25%
Answer:
(c) 19%
(ii) Which sector of India is primarily dependent on monsoon?
(a) Industry
(b) Agriculture
(c) Services
(d) Manufacturing
Answer:
(b) Agriculture
(iii) How much area of the country is identified as a drought-prone area?
(a) 10%
(b) 20%
(c) 30%
(d) 40%
Answer:
(c) 30%
2. Read the following paragraph and answer the questions given below:
Natural forces are not the only causes of disasters. Disasters are also caused by some human activities. There are some activities carried by human beings that are directly responsible for disasters. Bhopal Gas tragedy, Chernobyl nuclear disaster, wars, release of CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons) and increase of greenhouse gases, environmental pollution like noise, air, water and soil are some of the disasters which are caused directly by human actions. There are some other activities of human beings that accelerate or intensify disasters indirectly.
Landslides and floods due to deforestation, unscientific land use and construction activities in fragile areas are some of the disasters that are the results of indirect human actions. It is a common experience that human-made disasters have increased both in numbers and magnitudes over the years and concerted efforts are on at various levels to prevent and minimise their occurrences. Establishment of National Institute of Disaster Management, India, Earth Summit at Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1993 and the World Conference on Disaster Management in May 1994 at Yokohama, Japan, etc. are some of the concrete steps towards this direction initiated at different levels.
(i) Which of the following is a cause of a disaster?
(a) Natural
(b) Human made
HOTS QUESTIONS
Question 1
Write a note on Disaster Management.
Answer:
The Term disaster management includes all aspects of preventive and protective measures, preparedness, and organisation of relief operations for mitigating the impact of disaster on human being and socio-economic aspects of the diaster on human being and socio-economic aspects of the disaster prone areas. The whole process of disaster management can be divided into three phases : impact phase, rehabilitation and reconstruction phase and integrated long term development and preparedness phase.
(i) Impact phase contains three components :
(1) forecasting of disaster
(2) close monitoring of agents
(c) Animals
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
(ii) Which of the following is a reason of increase in Greenhouse gas?
(a) Wars
(b) Release of CFCs
(c) Chernobyl nuclear
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
(iii) In which of the following countries, ‘Earth Summit’ was held?
(a) U.K
(b) Brazil
(c) Mexico
(d) China
Answer:
(c) Mexico
causing disasters and (3) management activites after the disaster has occured. Flood forecasting can be done by studying rainfall in the catchment area. Approach of cyclones can be tracked and monitored by satellites, based on these details, early warning and evacuation efforts may be made. Close monitoring of agents responsible for disaster can help development of terms to help evacuation and supply of food, clothing and drinking water. Disaster leaves a trail of death and destruction. This will require medical care and help of various kinds to the affected people. Under long term development phase preventive and precautionary measures of various kinds should be chalked out.
SELF EVALUATION TEST
- What is a natural disaster?
- Name the different types of earthquake waves.
- What is a landslide?
- What is a drought?
- Name the major natural hazards.
- What are tropical cyclones?
- What are disasters?
- What are the causes of floods?
- Describe the flood control programmes.
- Describe the disaster of tsunami which occurred on 26th December 2004.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 भारत - स्थिति
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 3 पृथ्वी की आंतरिक संरचना
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Our Rajasthan Chapter 5 उद्योग
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 2 संरचना तथा भूआकृति विज्ञान
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 भूगोल एक विषय के रूप में
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 6 Soils
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 4 Climate
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 3 Drainage System