RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 4 Distribution of Oceans and Continents
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 4 Distribution of Oceans and Continents Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 4 Distribution of Oceans and Continents
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which is the centre of water Hemisphere?
(A) Near Japan
(B) Near New Zealand
(C) Near Sri Lanka
(D) Near England.
Answers:
(B) Near New Zealand

2. Who presented Continental Drift- Theory?
(A) Holms
(B) Wegner
(C) Taylor
(D) Kant.
Answers:
(B) Wegner
3. Initially all the continents which were together to form a land mass called.
(A) Gondwana Land
(B) Laurasia
(C) Pangea
(D) Panthalasa.
Answers:
(C) Pangea
4. How many years ago was tertiary period?
(A) 700 crore
(B) 70 crore
(C) 3 crore
(D) 7 crore.
Answers:
(D) 7 crore.
5. Which plate is located in S.E. of Pacific Ocean?
(A) Cocos
(B) Nazca
(C) Indian
(D) Phillipine.
Answers:
(B) Nazca
6. When did Wegner presented Drift- Theory?
(A) 1911
(B) 1912
(C) 1913
(D) 1914.
Answers:
(B) 1912
7. Which continent is not a part of Gondwana land?
(A) Africa
(B) Australia
(C) Antarctica
(D) Asia.
Answers:
(D) Asia.
8. Who introduced the concept of convection currents?
(A) Wegner
(B) Homes
(C) Taylore
(D) Trivartha.
Answers:
(B) Homes
9. At what level do the ground plates slide in the opposite direction?
(A) Convergence area
(B) Divergence zone
(C) Transversal zone
(D) Volcanic zone.
Answers:
(C) Transversal zone
10. Where are the gold deposits found in the alluvium?
(A) Ghana Coast
(B) Australia Coast
(C) Chilli Coast
(D) Guiana Coast.
Answers:
(A) Ghana Coast
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Who and when proposed the continental drift theory?
Answer:
Alfred Wegner in 1912.
Question 2.
Name the original supercontinent. When was it formed?
Answer:
Pangea, 280 million years ago. (Carboniferous period)
Question 3.
Name the Northern Continent split from Pangea.
Answer:
Laurasia (Angara Land)
Question 4.
Name the Southern Continent split from Pangea.
Answer:
Gondwana Land.

Question 5.
Name the landmasses included in the Gondwanaland.
Answer:
South America, Africa, Australia and Antarctica.
Question 6.
Name the plant whose fossils are widely found.
Answer:
Glossopteris.
Question 7.
Name the gold-bearing areas of Africa and South America.
Answer:
Ghana coast and Brazil.
Question 8.
What do you mean by Polar Wandering?
Answer:
Changing position of Poles in different periods.
Question 9.
What do you mean by sea-floor spreading?
Answer:
The spreading of crust from oceanic ridges and widening of seafloor.
Question 10.
What is the cause of plate movement?
Answer:
Thermal convection moves the sub-crustal plates.
Question 11.
Who proposed that convection currents are the cause of plate movement?
Answer:
Arthur Holmes in 1928.
Question 12.
How many major plates are there on the earth’s crust?
Answer:
Seven.
Question 13.
Which is the largest tectonic plate?
Answer:
Pacific plate.
Question 14.
Name two volcanic tracts of hot spots in Indian Ocean.
Answer:
90° East ridge and Chagos-Lakshadweep ridge.
Question 15.
What was the cause of formation of Himalayas?
Answer:
The collision between Indian plate and Eurasian plate.
Question 16.
How much time has been taken to separate South America and South Africa.
Answer:
200 million years.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by Tillite? Where are these found?
Answer:
Tillite :
Tillite are the sedimentary rocks formed out of deposits of glaciers. The Gondawana system of sediments from India is known to have its counter parts in six different landmasses of Southern Hemisphere such as Africa, Falkland Island, Madagascar, Antarctica and Australia. At the base the system has thick tillite indicating extensive and prolonged glaciation. The counter parts of this succession are found in Africa, Falkland Island, Madagascar, Antarctica and Australia. Overall resemblance of the Gondawana type sediments clearly demonstrate that these landmasses had remarkably similar histories. The glacial tillites provide unambiguous evidence of palaeoclimates and also of drifting of continents.
Question 2.
Where are Placer deposits found?
Answer:
Placer deposits. The occurrence of rich placer deposits of gold in Ghana coast and absolute absence of source rock in the region is an amazing fact. The gold bearing veins are in Brazil and it is obvious that the gold deposits of Ghana are derived from the Brazil plateau when the two continents lay side by side.
Question 3.
What do you mean by Lemuria?
Answer:
When identical species of plant and animal adapted to living on land or in fresh water are found on either sides of marine barriers a problem arises to account for such distribution. The observation that Lemurs occur in India, Madagascar and Africa, led some consider a contiguous landmass ‘Lemuria’ linking these three landmasses.

Question 4.
Describe the two main types of plates.
Answer:
Plates are of two types
(1) oceanic
(2) continental. It can be named according to the fact that it is connected with oceans or continents. Pacific plate is an oceanic plate, while Eurasian plate is a continental plate. The lithosphere is divided into seven major plates. Young fold mountains, Trenches and faults mark their boundaries.
Question 5.
What do you mean by convergence of plates?
Answer:
When a plate pushes beneath the other plate, it is called converging plate. It is called a subduction zone. This is caused in three ways :
- Between a continental and oceanic plate.
- Between two oceanic plates.
- Between two continental plates.
Question 6.
What is Pangea?
Answer:
About 280 million years ago, all the land masses of the world formed one super continent called Pangea. It evolved in carboniferous period.
Question 7.
What is meant by sea floor spreading?
Answer:
The mid-oceanic ridges are cracks on the floor of ocean. There emits lava actively. Molten matter forms a new crust. The crust spreads away from the ridges. Thus the ocean basin widens. This is called sea floor spreading. In 1961, Atlas proposed a hypothesis known as sea floor spreading. According to this, volcanic erruption bring about huge amounts of lava to the surface though faults.
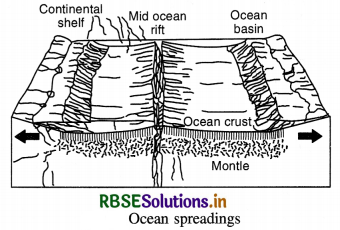
Question 8.
Name the major plates of the earth.
Answer:
There are seven major plates :
- Pacific Plate
- Eurasian Plate
- Indo-Australian Plate
- African Plate
- North American Plate
- South American Plate
- Antarctic Plate.
Question 9.
What is Pangea? When was it evolved? Name the landmasses constituting it. Describe the breaking up of Pangea.
Answer:
Alfred Wegner, in 1912, proposed that all land masses of the world had formed from one supercontinent, called Pangea. The supercontinent, Pangea had evolved some 280 million years ago, at the end of the Carboniferous Period and by mid-Jurassic, 150 million years ago, Pangea had split into a northern continent called Laurasia, and a southern continent called Gondwana land. About 65 million years ago, i.e. at the end of Cretaceous, Gondwana land further broke up to give rise to several other continents such as South America, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica. India broke apart and followed an independent route moving towards northeast.
Question 10.
What do you mean by Jig-Saw-fit? Describe the similarities found on the east and west coasts of Atlantic Ocean. What do these suggest?
Answer:
Jig-Saw-fit means that the land masses on the East and West coast of Atlantic Ocean can be fitted together. Many similarities are found on the two coasts.
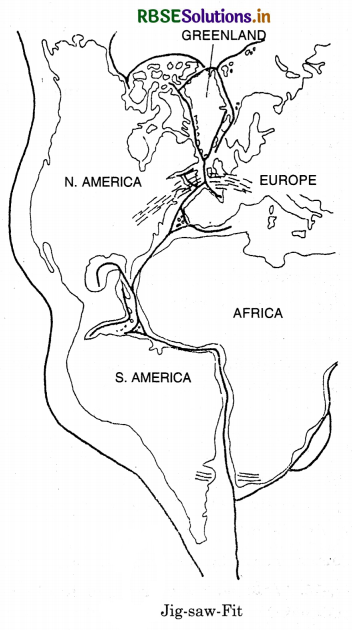
(i) The Gulf of Guinea can be fitted into cape-San- Roque of Brazil. The shoulder of Africa can befitted into Gulf of Mexico. Western Europe and Eastern coast of N. America alongwith Greenland can be fitted together.
(ii) Gold deposits are found in Ghana on the East and in Brazil on the West.
(iii) The glacial deposits are found in all land masses of Gondwana land. All these similarities suggest that these continents were together in the geological past.

Question 11.
What is meant by Polar Wandering?
Answer:
Polar Wandering. One of the strongest lines of evidence that the continents were formely united in the Pangea came from palaeomagnetism. There has been periodic change in the position of magnetic pole that is recorded in rocks by way of permanent magnetism. Unraveling the signatures of such changes in the geologically old rocks by scientific methods provides the changing position of poles in geological time scale. This is known as polar wandering. The polar wandering clearly demonstrates that the continents have frequently moved and changed directions of their motion from time to time.
Question 12.
Name the three kinds of Plate boundaries.
Answer:
Plate boundaries are also called Marginal zones. These are recognised as :
- Zones of Divergence of spreading.
- Zones of Convergence
- Fraction Zones or Transform faults.
Question 13.
What do you mean by Plate Tectonics?
Answer:
Since the advent of the concept of sea floor spreading the interest of scholars was revived in the problem of distributions of Oceans and Continents. It was in 1967, McKenzie and Parker and also Morgan indpendently collected the available ideas and come out with another concept as plate tectonics. Plate Tectonic. A Plate is a portion of the Earth’s lithosphere, which moves horizontally over the Asthenosphere as an intrinsically rigid unit.
The term tectonics means study of structural feature of the crust and their origin. The lithosphere- Asthenosphere layering of the Earth used in plate tectonics is different from the traditional and familiar crustmantle-core layering. The former is based on rigidity, the latter on seismicity and the nature of constituents. The lithosphere includes the crust and top mantle with its thickness range varying between 5-100 km in oceans and about 200 km in the continents.
Essay Type Questions
Answer:
According to global plate tectonic theory, the lithosphere is broken into a number of moderately rigid plates, The plates move continually and have relative direction of motion.
Types of Plate Boundaries. Based on the relative motion of plates, three kinds of plate boundaries or marginal zones are recognised-
(i) zones or margins of divergence or spreading,
(ii) zones or margins of convergence; and
(iii) fracture zones or transform faults.
(i) Zones of divergence. These are boundaries along which plates separate and in this process of separation molten material upwells. This is commonly observed along linear ocean ridges where new lithosphere is created in the form of new ocean floors. Active volcanism and shallow focus earthquakes mark such boundaries.
(ii) Zones of convergence. These are boundaries along which the edge of one plate overrides the other. The overrridden plate slips down into the mantle and is absorbed. This process is known as subduction. Besides volcanism and shallow to deep focus earthquakes, these boundaries also produce deep trenches basins and folded mountain chains.
(iii) Fracture Zones. There is neither creation not destruction along the transform fault. The lithospheric plates slide past each other.
Causes of Plate Movement (Mechanism)
1. Thermal Convection. Arthur Holmes, in 1928, proposed that subcrustal convection currents invoke the mechanism of thermal convection. It acts as driving force for the movement of plates.
2. Movement of currents. Hot currents rise, then cool as they reach the surface. At the same time, cooler currents sink down. This convectional movement moves the crustal plates.
3. Floating of Plates. Owing to current movements, the rigid plates of the lithosphere, which ‘float’ on more mobile asthenosphere, are in constant motion.
4. Hot spots of Volcanic activity. However, small centres of past volcanic activity are often located far from any active plate boundary suggest the effect of convection currents on the lithosphere. These centres of volcanic activity are called the hot spot.
5. Volcanoes. W. Jason Morgan proposed the hypothesis of hot spot in 1971. According to him, the source of magma in the mantle remains fixed in position while the lithospheric plate above it moves steadily. In this way, volcanoes are fomed over a hot spot but then move away from the magma source and become extinct. These extinct volcanoes form a chain that is record of the plate motion.

Plate Boundaries:
Plate boundaries are the most significant structural features of the earth.
Plate boundaries are not difficult to identify ; they are marked by major topographic features.
The lithosphere-is divided into a mosaic of seven major plates and a number of smaller sub-plates. The major plates are outlined by young mountain
systems, oceanic ridges and trenches. These include :
- Pacific Plate
- Eurasian Plate
- Indo-Australian Plate
- African Plate
- North American Plate
- South American Plate
- Antarctic Plate.
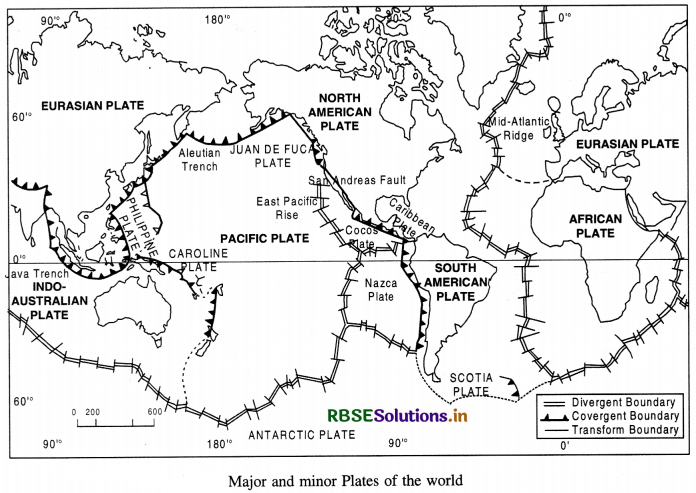
Main Features
- The Pacific Plate which is composed of oceanic crust almost entirely and covers about 20 per cent of the earth’s surface.
- No plate consists of only continental crust.
- Plates range in thickness from about 70 km. beneath oceanic areas to 150 km. beneath continents.
- Plates are not permanent features. They change in size and shape and the ones which do not contain continental crust can become victims of subduction.
- A plate can split or weld with another adjoining plate.
- Each tectonic plate is rigid and moves as a single unit.
- Nearly all major tectonic activity occurs along the plate boundaries and that is why geologists and geographers focus their attention on the plate boundaries.
Question 2.
Describe the main characteristics of Indian Plate.
Answer:
Movement of the Indian Plate.
Boundaries. The Indian plate includes Peninsular India and Australian continental portions. The northern plate boundary is marked by the subduction zone along Himalayas (continent-continent convergence) and it extends through Arakanyoma of Myanmar towards the island arc along Java Trench. The eastern margin is a spreading site lying to the east of Australia in the form of oceanic ridge in SW Pacific. The Western margin follows Kirtar Mountain of Pakistan and extending through Makrana coast coincides with the spreading site extending from Red seas rift southeastward along Chagos Archipelago. The boundary between India and Antarctic plate is also marked by
oceanic ridge running in roughly W-E direction and merging into the spreading site little south of New Zealand. Position of Indian Sub-continent. It is now a well established fact that indian subcontinent, or to be precise the Peninsular India, formed a part of Gondawana land, the southern protocontinent. This includes South America, Africa-India, Antarctica and Australia. The assembly of these continents as suggested by Smith and Hallam (1970) has received wider acceptance. India is the northern most member of this southern configuration and thus is supposed to have undergone maximum amount of northward drift. The Tethys lying in the north of this assembly appears not as a major ocean but a narrow sea.
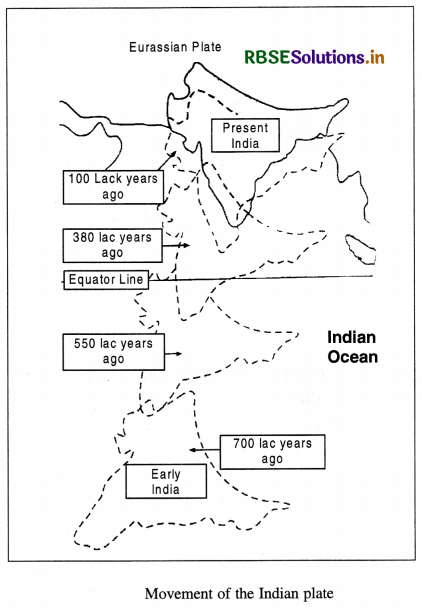
It is assumed that 20 crore years ago, when Pangea was sub-divided, Indian plate started drifting northward. About 4-5 crore years ago, Indian plate collided with Eurasian plate and Himalayas were uplifted out of the Tethys. About 14 crore years ago, Indian subcontinent was located at 50° south latitudes. Tethys separated two plates. Tibetan block was nearer to Asian land mass. An import even took place during drifting of Indian plate. Deccan trap was formed out of lava. It started about 6 crore years ago and continued for a long time. About 4 crore years ago Himalayas were formed and the process is still going on. The Himalayas are still rising.
Source Based Questions
1. Read the following paragraph and answer the questions given below:
Divergent plate boundaries are where new crust is generated as the plates pull away from each other. The sites where plates move away from one another are known as spreading sites. The best example of divergent boundaries is the Mid-Atlantic-Ridge. The American plates also separated from the Eurasian and African plates. Convergent boundaries are where the crust is destroyed as one plate dived under another. Location where sinking of a plate occurs is known as subduction zone. Convergence can occur in three ways-between an oceanic and continental plate, between two oceanic plates and between two continental plates.

(i) The place where new crust is generated as the plates pull away from each other is called
(a) Divergent plate
(b) Convergent plate
(c) Transform Boundary
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Divergent plate
(ii) Mid-Atlantic Ridge is the example of which of the following?
(a) Convergent plate
(b) Divergent plate
(c) Transform boundary
(d) Subduction Zone
Answer:
(b) Divergent plate
(iii) Which of the following is a way in which convergence can occur?
(a) Between oceanic of continental plate
(b) Between two oceanic plates
(c) Between two continental plates
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
2. Read the following paragraph and answer the questions given below:
When Wegener proposed his theory of continental drift, most scientists believed that earth was a solid, motionless body. However, the sea floor spreading concept and unified theory of plate tectonics have stressed that both the surface of the earth and the interior are not static and motionless but are dynamic. Now the fact the plates move is a well-accepted fact.
It is believed that the mobile rocks beneath the tight plates move in a circular manner. Heated material rises to the surface spreads and begins to cool, and then sinks back into deeper depths. To generate a convection cell, this cycle is repeated over and over. Heat within the earth comes from two sources-radioactive decay and residual heat. Arthur Holmes considered this idea in 1930, which later influenced Harry Hess’ thinking about sea floor spreading.
(i) Who proposed the continental drift theory?
(a) Harry Hess
(b) Wegener
(c) Arthur
(d) Holmes
Answer:
(b) Wegener
(ii) According to continental drift theory,
where does the heated material rise?
(a) To the surface
(b) To the sea
(c) To the plains
(d) To the deeper depths
Answer:
(a) To the surface
(iii) Who first considered the idea of radioactive decay and residual heat?
(a) Harry Hess
(b) Wegener
(c) Arthur Holmes
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Arthur Holmes
(iv) In which year was the idea of residual heat proposed?
(a) 1910
(b) 1920
(c) 1930
(d) 1940
Answer:
(c) 1930
HOTS QUESTIONS

Question 1
What were the forces suggested by Wegner for the movement of continents?
Answer:
Force for Drifting. Wegner suggested that the movement-drifting of continents was caused by
(1) pole fleeing force and
(2) tidal force. Wegner believed that these forces would become effective when applied over many million years. However, most of the scholars considered these forces to be totally inadequate. The shape of the earth is not a perfect sphere. It is bulging on equator. This is due to rotation of earth. Tidal force is related with sun and the Moon which cause Tides in oceAnswer:
SELF EVALUATION TEST
- Who first proposed Continental Draft Theory?
- Name the southern continent in Pangea.
- How many major plates are there on the
- earth’s crust?
- Which is the largest tectonic plate?
- What is convergence plate?
- What is Pangea?
- What is Jig-Saw-fit?
- What is plate tectonic?
- What is meant by polar wandering?
- Explain a floor spreading.
