RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 1 India - Location
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 1 India - Location Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Geography Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 1 India - Location
Multiple Choice Questions
1. In which year did the Suez canal start?
(A) 1849
(B) 1859
(C) 1869
(D) 1879
Answer:
(A) 1849

2. Which is the capital of Sikkim state?
(A) Dispur
(B) Gangtok
(C) Kohima
(D) Shillong
Answer:
(B) Gangtok
3. Where is Lakshadweep located?
(A) Bay of Bengal
(B) Arabian Sea
(C) Indian Ocean
(D) Bay of Khambhat
Answer:
(B) Arabian Sea
4. What is the total land limit of India?
(A) 12200 km
(B) 13202 km
(C) 14200 km
(D) 15200 km
Answer:
(D) 15200 km
5. India has a total geographical area of Lakh km2.
(A) 32.80
(B) 22.80
(C) 42.08
(D) 30.80
Answer:
(A) 32.80
6. Which line of latitude bisects India into two halves?
(A) Equator
(B) Tropic of Cancer
(C) Tropic of Capricorn
(D) Arctic Circle
Answer:
(B) Tropic of Cancer
7. Which is the largest state of India?
(A) Maharashtra
(B) Uttar Pradesh
(C) Rajasthan
(D) Madhya Pradesh
Answer:
(C) Rajasthan
8. India has total number of states.
(A) 18
(B) 24
(C) 28
(D) 30
Answer:
(C) 28
9. Where does India rank in the world?
(A) Fifth
(B) Sixth
(C) Seventh
(D) Eighth
Answer:
(C) Seventh
10. Which is the southernmost point of India?
(A) Kanniyakumari
(B) Indira Point
(C) Rameswaram
(D) Barren Island
Answer:
(B) Indira Point
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which line of latitude passes through the centre of India?
Answer:
Tropic of Cancer 23%° N.
Question 2.
Name the two zones formed by Tropic of Cancer in India.
Answer:
Tropical zone and Temperate zone.
Question 3.
What is the total length of coastline of India?
Answer:
7516.6 km.
Question 4.
Which strait separates India from Sri Lanka?
Answer:
Palk Strait.

Question 5.
Which ocean route links, India with Europe?
Answer:
Suez Canal.
Question 6.
Which is the largest state of India (Area)?
Answer:
Rajasthan.
Question 7.
Which is the smallest state of India?
Answer:
Goa.
Question 8.
Which state of India is surrounded by boundaries of five states?
Answer:
Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka.
Question 9.
How many states are coastal states?
Answer:
Nine states are coastal states: Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Goa, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, West Bengal.
Question 10.
How many islands are there in Andaman and Nicobar Islands?
Answer:
204.
Question 11.
How many islands are there in Lakshadweep Islands?
Answer:
36.
Question 12.
Name a group of Coral islands.
Answer:
Lakshadweep.
Question 13.
What is the total geographical area of India?
Answer:
31,66,414 km2.
Question 14.
What is the East-West and North-South extent of India?
Answer:
East-West extent = 2933 kms. North-South extent = 3214 kms.
Question 15.
Name two towns located on Tropic of Cancer in India.
Answer:
Ahmedabad and Jabalpur.
Question 16.
Which line of longitude passes through the middle of India?
Answer:
\(82 \frac{1^{\circ}}{2}\) E longitude.
Question 17.
Name the states or union territories of India having common frontiers with Pakistan?
Answer:
- Gujarat
- Rajasthan
- Punjab
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Ladakh.
Question 18.
Name the line forming boundary between India and China.
Answer:
McMahon line.
Question 19.
Name the Indian states having common frontiers with Bangladesh.
Answer:
- West Bengal
- Assam
- Meghalaya
- Tripura.
Question 20.
Name the coastal states located on the west coast of India.
Answer:
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
- Goa
- Karnataka
- Kerala.

Question 21.
Name the coastal states located on the east coast of India.
Answer:
- Tamil Nadu
- Andhra Pradesh
- Odisha
- West Bengal.
Question 22.
Which state is called 'the land of dawn'?
Answer:
Arunachal Pradesh.
Question 23.
Where does India rank in the world as regards to area?
Answer:
Seventh.
Question 24.
Where does India rank in the world as regards to population?
Answer:
2nd.
Question 25.
What parallels of latitude mark the northern and southern extent of India?
Answer:
37° N and 8° N.
Question 26.
What is the time lag between the Eastern and Western point of India?
Answer:
About 2 hours.
Question 27.
Name a state which has the longest coastline.
Answer:
Gujarat.
Question 28.
Name a union territory whose area is found on both the eastern coast and western coast.
Answer:
Puducherry.
Question 29.
Name two southern neighbouring countries of India.
Answer:
Sri Lanka and Maldives.
Question 30.
Name an active volcanic island in India.
Answer:
Barren island near Nicobar island.
Question 31.
Which channel separates Andaman Islands from Nicobar Islands?
Answer:
Ten degree channel.
Question 32.
Name the continents bordering Indian Ocean.
Answer:
Africa, Asia, Australia and Antarctica.
Question 33.
Name the Southernmost point of India.
Answer:
Indira Point (Nicobar).
Question 34.
Name the Southernmost point of Indian mainland.
Answer:
Kanniyakumari.
Question 35.
Which are the most thickly populous and least density populated states?
Answer:
Bihar and Arunachal Pradesh.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is a subcontinent? Explain this ijgk with reference to countries lying south of the Himalayan Mountain System in South Central 'Asia.
Answer:
Subcontinent: A sub-continent is a vast independent geographical unit. This land mass is distinctly separated from the main continent. The vastness in size produces a diversity in economic, social and cultural conditions. India is a vast country. It is often described as ‘Indian subcontinent’.
Countries :
The Himalayan mountain system acts as a physical barrier separating the Indian sub-continent from the main land of Asia. India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Bhutan, Maldives, Sri Lanka combine together to form a sub-continent. The great mountain wall isolates these countries from Asia. These are also called ‘SAARC’ countries.
Question 2.
Describe the Westernmost point and Easternmost point of India.
Answer:
East-west extent. India has an east-west extent of about 3,000 kms. Its westernmost point lies on a creek in the salty marshes of the Rann of Kutchh. The Easternmost point lies in the forested hills where the boundaries of Myanmar, China and India meet.

Question 3.
Where does India rank in area among the countries of the world?
Answer:
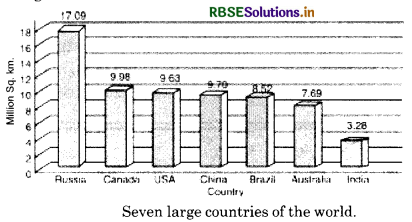
India ranks seventh in area among the countries of the world. India with an area of 3.2 million sQuestion kms. occupies 2.4% of the total world area. Russia, Canada, China, U.S.A., Brazil and Australia are larger in size than India. India almost equals Europe, Russia is seven times as large as India and the U.S.A. is thrice as big.
Question 4.
State the passes in N.W. part of India and explain their importance.
Answer:
The only way people from outside could get into India were the Khyber Pass, near Safed Koh, and the Hindu Kush mountains and the Bolan pass between the Sulaiman and the Kirthar ranges in the north-west that separated the Indian realm from Afghanistan. It is through these routes that earlier central and west Asian tribes came to India, and later armies of Alexander, Afghan and Persians entered India.
Question 5.
Name the important passes across the lofty Himalayan mountains of the Indian sub¬continent.
Answer:
The Himalayas act as a physical barrier in the north. There are many passes to cross these lofty mountains such as :
- Shipkila pass (along Indo-Tibet Road).
- Karakoram pass (Ladakh).
- Nathula pass (Sikkim).
- Jelep-la-pass (Sikkim).
Question 6.
While the Sun rises earlier in the East say Nagaland and also sets earlier. How do the watches at Kohima and New Delhi show the same time?
Answer:
India is a vast and extensive country with an east-west extent of 3000 kms. The east-west extension 1 of India covers almost 30° of longitude which is of the earth’s circumference. Saurashtra lies in the westernmost corner of India while Arunachal being the easternmost part of India. Due to the rotation of the earth from west to east, the eastern parts are ahead in time. The difference in time is 4 minutes for one degree of longitude. Therefore for 30° of longitude, there is a difference of time of 2 hours (30 x 4 = 120 minutes).
When the sun rises in Arunachal, it is still night in Saurashtra. When it is 6 a.m. in Arunachal Pradesh, it is 4 a.m. in Saurashtra. Due to early sunrise, the Arunachal state is rightly called, ‘the land of dawn’. But the Indian standard time, all over the country is according to standard Meridian (821/2°E). SO there is uniformity of time all over India. The watches at all stations show the same time. So vast and extensive is India, that distance has lost its old significance. You can have breakfast in Srinagar and lunch at Thiruvananthapuram. A journey between Jamnagar and Guwahati may be completed within the time taken by a Hindi film show of three hours duration.
Question 7.
Describe the land and water frontiers of India.
Answer:
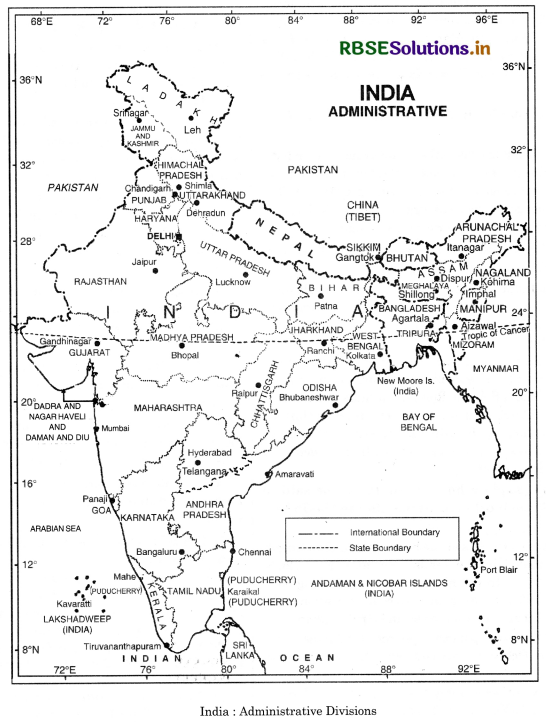
Land and Water Frontiers. India has a land border in the North, North-West and North-East. It is 15,200 kilometres in length. Indian Ocean forms the water frontiers of India. India has a long coastline of 7516 kilometres.
(i) The Northern Border. The great mountain wall in the North is a natural boundary. The high Himalayas form a natural bulwork between China, Tibet and India. These high mountains form the dividing line between India and China. It is known as McMahon line.
(ii) The Western Border. In the west, the border between Pakistan and India runs across Rajasthan (Thar desert) and Punjab Plains along Sutlej and Ravi rivers, J & K, Gujarat and Ladakh.
(iii) The Eastern Border. In the East, a series of mountain ranges separate India from Burma (Myanmar). The Ganges delta forms the boundary between India and Bangladesh. Bangladesh is bounded by India on three sides and Bay of Bengal on the fourth Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and West Bengal are States.
(iv) The Southern Border, Arabian Sea in the west. The Indian ocean in the south, and Bay of Bengal in the east form the water frontiers of India. A narrow stretch of water known as Palk Strait and Gulf of Mannar separate Sri Lanka from India.
Question 8.
Name the five countries whose frontiers meet at the northern apex of India.
Answer:
On the northern side of India, the boundaries of the following five countries meet together- China, Russia, Tajakistan, Afghanistan and Pakistan. These five countries meet at the apex of the north Indian triangle. This apex, Pamir Knot is called the roof of the world.

Question 9.
What is the McMahon Line? What does it signify?
Answer: McMahon line is the dividing line between India and China. It lies to the east of Bhutan. This boundary line runs through a complex mountainous terrain. The crests along this form a natural boundary which acts as a watershed and is historically determined.
Question 10.
Elaborate the statement, “India is neither a pigmy nor a giant.”
Answer:
India is a vast country covering a fairly large area of the globe. India ranks seventh in the world with an area of 3.2 million kms, about 2.4% of the total world area. Many countries are far larger in size than India. Russia is about seven times as large as India and the U.S.A. about thrice as big. Thus India is not a giant country like U.S.A. and Russia. But India is not a small country like Sri Lanka, Japan, etc. India is thirteen times as large as Britain and nine times as large as Japan. Thus it is true to say that India is neither a pigmy nor a giant.
Question 11.
Explain how far India can be said to occupy the most central position in the Indian Ocean.
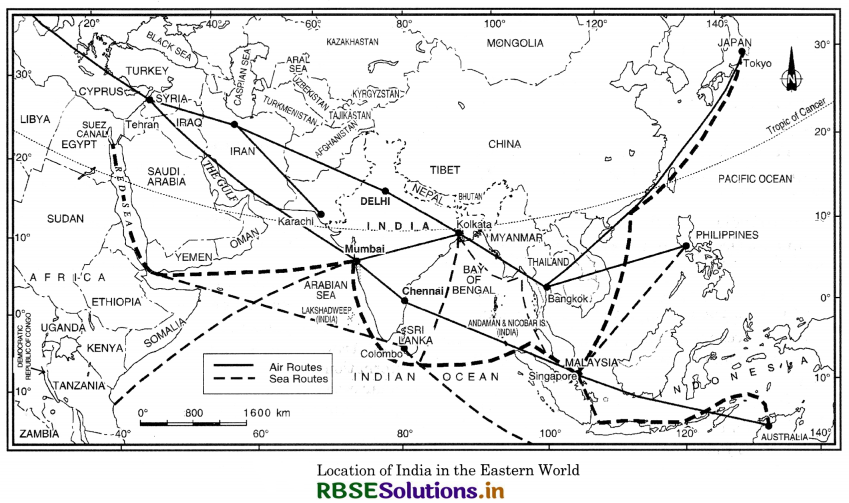
Answer:
(i) India lies at the head of the Indian Ocean. The Indian Ocean extends between 0°E to 120°E longitudes, with Kanniyakumari located along 80°E longitude. Thus India occupies a central position in the Indian Ocean. The Indian Ocean is truly Indian.
(ii) The Deccan peninsula projects itself in the centre of Indian Ocean, in between Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal.
(iii) No other country has such a large coastline along the Indian Ocean. That is why it is named after the country of India.
(iv) India lies on the trade routes of Europe and the far east passing through Indian Ocean.
(v) India occupies a centrally located strategic position in the eastern hemisphere. India is by far the most dominant country surrounding the Indian Ocean.
Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
India is often described as a subcontinent. Justify the statement.
Answer:
A subcontinent is a vast independent geographical unit and distinctly separated from the main continent. In the southern part of Asia, India stands as a subcontinent. Many facts justify this:
(i) The natural frontiers of India provide an isolated character to the vast Indian landmass. The Himalayas in the north, the Indian Ocean in the south, thick and dense forests on the east and Thar desert on the west separate it from the main continent.
(ii) India is surrounded by the major realms of Asia on all sides. The great mountain wall encloses the Indian subcontinent and practically gives it an independent form.
(iii) India covers a fairly large area ranking seventh in the world. India is the second largest populated country of the world. These two elements compare India with a subcontinent.
(iv) India is a land of severe contrasts. But it has a cultural unity behind this diversity.
(v) Monsoon climate determines the life of people and economic development of the country. These are independently and perfectly developed in India. It gives a distinct character of a subcontinent to this landmass.
(vi) The abundant agricultural resources, mineral resources and other natural resources also compare it with a subcontinent.
Question 2.
Explain the importance of Geographical location of India.
Answer:
Importance of Geographical location of India.
- Central Locations. India is centrally located on the Eastern hemisphere. Europe and Western Parts of America are equidistant from India.
- Trade Routes. India is favourably located for international trade. Many trade routes are through Indian ocean.
- Nearness to Tropic of Cancer. The tropic of cancer passes through the centre of India. So India is a tropical country. The long growing season makes India an agricultural country.
- Long Coastline. India has a long coast-line which provides many deep, protected and natural harbours.
- Defence. The natural boundaries are favourably located from defence point of view.
- Effect of Indian Ocean. The Indian ocean leads to the origin of rain giving monsoons.
- Effect of Himalayas. The unbroken chain of Himalayas acts as a climatic barrier. It forces monsoons to give rainfall and protects northern India from cold polar winds.
Source Based Questions
1. Read the following paragraph and answer the questions given below:
India is a vast country extending for about 29° latitudes. India has only one Standard Meridian i.e. 821/2° East. India is located in South Asia. Many countries have more than one Standard Meridian as in Canada and U.S.A. Standard Meridian are generally 15° apart. According to the extent of India, there should be two Standard Meridians -one for the Eastern part and, one for the western part. 75°E and 90°E can be suggested as two Standard MeridiAnswer: With this, time lag of 2 hours can be reduced to one hour between eastern and western parts.

(i) Which of the following latitudinal extent is relevant in context of India?
(a) 68° to 97°E
(b) 69° to 97°E
(c) 67° to 97°E
(d) 69° to 98°E
Answer:
(a) 68° to 97°E
(ii) Which of the following longitudes is the Standard Meridian for India?
(a) 69°30'E
(b) 82°30'E
(c) 75°30'E
(d) 90°30'E
Answer:
(b) 82°30'E
(iii) Which of the following countries has more than one Standard Meridian?
(a) Canada
(b) U.S.A.
(c) India
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
(iv) Which of the following countries has only one Standard Meridian?
(a) Canada
(b) U.S.A.
(c) India
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) India
2. Read the following paragraph and answer the questions given below:
India is a vast and extensive country with an east-west extent of 3000 km. The east-west extension of India covers almost 30° of longitude which is \(\frac{1}{12}\) of the earth’s circumference. India has 28 states. Saurashtra lies in the westernmost corner of India while Arunachal is the easternmost part of India. Due to the rotation of the earth from west to east the eastern parts are ahead in time. The difference in time is 4 minutes for one degree of longitudes. Therefore, for 30° of longitude there is a difference of time of 2 hours. When the sun rises in Arunachal Pradesh, it is 4 a.m. in Saurashtra. Due to early rise, this is called the land of dawn.
(i) How many states are there in India?
(a) 24
(b) 28
(c) 29
(d) 30
Answer:
(b) 28
(ii) What is the east-west extent of India?
(a) 2000 km
(b) 3000 km
(c) 300 km
(d) 2933 km
Answer:
(b) 3000 km
(iii) Which part of the earth is ahead in time due to pattern of rotation?
(a) East
(b) West
(c) South
(d) North
Answer:
(a) East
(iv) Which of the following states is called the ‘land of dawn’?
(a) Saurashtra
(b) Arunachal Pradesh
(c) Assam
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Arunachal Pradesh
HOTS QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Describe how geographical features of the country have fostered unity and homogeneity in the Indian socieity.
Answer:
The vastness of India has produced a diversity in the physical conditions of the country. But there is a fundamental cultural unity behind all this diversity. Indian culture has developed independently. The land frontiers and the water frontiers have given a partially enclosed character to the Indian sub-continent. The following two features have fostered a unique homogeneity in the Indian civilization.
(i) The unbroken chain of lofty mountains in the north has isolated India from the rest of Asia. It has played a great uniflying role in strengthening our people.
(ii) The vast expanse of Indian Ocean has separated India as an independent unit. The Indian Ocean has provided our links with countries of West Asia and South East Asia.

Question 2.
‘India had strong geographical and historical links with her neighbours. Explain by giving examples.
Answer:
India has been linked with S.E. Asia, West Asia, Africa, Central Asia. Indian culture spread to many distant countries such as Indonesia. Bali island, Cambodia and Egypt. These cultures also had an impact on the India culture.
(i) The Indian culture spread to distant lands through ocean routes of the Indian Ocean. The muslin, species, were sent to other countries.
(ii) The mountain passes in the north provided many openings and transport facilities for the outsiders.
(a) The pastoral nomads entered India through the mountain passes of Khyber and Bolan.
(b) The Buddhist Bhikshus crossed into Tibet, China and Japan to carry their message of peace.
(c) Alexander invaded India through these mountain passes and brought Green sculptures, domes, and minerates to India.
(d) Indian merchants has trade links with Central Asia, Afghanistan and Iran through these routes.
(e) The Mongols, Turks, Arabs and Iranians came as conquerors and settled down in India. They took back the Indian numerals, the decimal system and the ideas of the Upanishads to their countries.This give and take and exchange of ideas, goods and art have enriched the Indian culture.
SELF EVALUATION TEST
- What is the total geographical area of India?
- Which is the largest state of India (as regards area)?
- Name a town located on standard meridian of India.
- Name the line forming Boundary between India and China.
- What is a subcontinent?
- Name the islands located in Bay of Bengal.
- Name the states on the Western Border of India.
- Name the passes located in Himalayas.
- Name the countries larger than India.
- What is the importance of geographical location of India?

- RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 भारत - स्थिति
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 3 पृथ्वी की आंतरिक संरचना
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Our Rajasthan Chapter 5 उद्योग
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 2 संरचना तथा भूआकृति विज्ञान
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 भूगोल एक विषय के रूप में
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 7 Natural Hazards and Disasters
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 6 Soils
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 4 Climate