RBSE Class 11 English Grammar Modals
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 English Grammar Modals Questions and Answers.
The questions presented in the RBSE Solutions for Class 11 English are solved in a detailed manner. Get the accurate RBSE Solutions for Class 11 all subjects will help students to have a deeper understanding of the concepts. Our team has come up with Tenses Class 11 to ensure that students have basic grammatical knowledge.
RBSE Class 11 English Grammar Modals
Modals अर्थात् modal auxiliaries को पूर्ण रूप से समझने से पहले auxiliaries की परिभाषा व इसके महत्व को जानना अति आवश्यक है।
An auxiliary is commonly known as a 'helping verb' which, besides providing a special meaning to a verb (main verb), establishes the identity (tense) of a sentence. Auxiliaries help in formation of different forms of the action or the main verbs in order to cater to the requisites of different kinds of sentences and the tenses.
किसी auxiliary को आमतौर पर एक "सहायक क्रिया" के रूप में जाना जाता है जो किसी क्रिया (मुख्य क्रिया) को एक विशिष्ट अर्थ प्रदान करने के अतिरिक्त, किसी वाक्य की पहचान (काल) स्थापित करती है। सहायक क्रियाएँ मुख्य क्रियाओं के विभिन्न रूपों का निर्माण विभिन्न प्रकार के वाक्यों व कालों की आवश्यकताओं के लिए करती हैं।
Kinds Of Auxiliaries
Auxiliaries दो प्रकार की होती हैं -
(A) Primary Auxiliaries (प्राथमिक सहायक क्रियाएँ)
(B) Modal Auxiliaries (विधिसूचक सहायक क्रियाएँ)
(A) Primary Auxiliaries : इनमें be, have तथा do (मुख्य क्रियाओं) के विभिन्न रूप - is, am, are, Was, Were, has, have, had, do, does, did आदि न केवल मुख्य क्रियाओं बल्कि सहायक क्रियाओं के रूप में भी प्रयुक्त होती है। Auxiliaries के रूप में ये रूप विभिन्न कालों का निर्धारण करती हैं, जबकि मुख्य क्रियाओं के रूप में ये क्रमशः अवस्था (state), निजता (Possession) तथा कार्य (work) का बोध कराती हैं।
उदाहरण:
(1) Hari is reading a novel. हरी एक उपन्यास पढ़ रहा है। (Auxiliary)
(2) Hina was sleeping. हिना सो रही थी। (Auxiliary)
(3) They were going home. वे घर जा रहे थे। (Auxiliary)
(4) I did not know him. मैं उसे नहीं जानता था। (Auxiliary)
(5) Do you like sweets ? क्या आप मिठाइयाँ पसंद करते हैं? (Auxiliary)
(6) Sheela was weeping. शीला रो रही थी। (Auxiliary)
(7) I have done my work. मैंने अपना कार्य कर लिया है। (Auxiliary)
(8) Rani is my best friend. रानी मेरी सबसे अच्छी सखी है। (Main Verb of State)
(9) Rahul has a car. राहुल के पास एक का है। (Main Verb of Possession)
(10) She did a work of praise. उसने प्रशंसा का एक कार्य किया। (Main Verb of Action)

(B) Modal Auxiliaries :
'Modal' शब्द की उत्पत्ति ‘mode' शब्द से हुई है जिसका आशय प्रवृत्ति (nature), व्यवहार (behaviour) या मन:स्थिति (mood) से होता है। कुछ ऐसे शब्द-can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, must, ought to, need, used to, dare - जो Main verbs के साथ मिलकर सामर्थ्य (capacity), योग्यता (ability), शक्ति (power), अनुमति (permission), सम्भावना (possibility), इच्छा (willingness), धमकी (threat), दृढ़-निश्चय (determination), निषेधाज्ञा (prohibition), अनिवार्यता (compulsion), साहस (courage), आवश्यकता (necessity) जैसे भावों को व्यक्त करने में सक्षम हों, modals या modal auxiliaries कहलाते हैं। Modals का प्रयोग केवल सहायक क्रियाओं (helping verbs) के रूप में ही हो सकता है।
Modal Auxiliaries
1. ये हमेशा मुख्य क्रिया के साथ सहायक की भूमिका में ही प्रयुक्त होती हैं । Modals का प्रयोग निम्न नियमों के अनुसार किया जाता है
Active Voice : Subject + Modal + Verb I + Complement.
Passive Voice : Object + Modal + be + Verb III + Complement.
उदाहरण:
(1) He should obey his parents.
(2) It may rain today.
(3) You shall be given the prize.
(4) I will prove my worth.
2. इन पर कर्ता (Subject) के वचन (Number), लिंग (Gender) का कोई प्रभाव नहीं पड़ता ।
उदाहरण:
(1) He can run fast.
(2) She can cook well.
(3) Birds can fly easily.
(4) It can be advantageous for us.
3. इनके बाद not लगाने से Negative तथा Modal को Subject के पहले रखने से वाक्य Interrogative बन
उदाहरण:
(1) He cannot lift this heavy box.
(2) What can you do ?
(3) Would you mind my interrupting you ?
(4) You need not worry about me.
4. एक ही वाक्य में Primary व Modal Auxiliaries का प्रयोग हो सकता है, लेकिन Modal Auxiliary का प्रयोग
Primary Auxiliary के पहले होगा। उदाहरण : I might have gone to the party.
यहाँ might, Modal Auxiliary तथा have Primary Auxiliary है।
5. Modal Auxiliaries की infinitive form (to + modals, e.g. to will, to could) या present participle
(can + ing, could + ing) व past participle नहीं होते।
उदाहरण :
(1) You must take medicine everyday.
(2) Hari can do this work well.
Note : Ought व used के बाद to + V1 (full Infinitive) का प्रयोग किया जाता है ।

6. Negative तथा Negative Questions (नकारात्मक प्रश्न) वाले वाक्यों में अधिकतर Modals के साथ n't का प्रयोग करते हैं।

नोट-
(1) उपर्युक्त संक्षिप्त रूप (Short negative forms या contracted forms) का प्रयोग बोलचाल की भाषा में तथा अनौपचारिक लेखन (informal writing),
जैसे – व्यक्तिगत पत्र या मित्र के लिए लिखे पत्र आदि में करते हैं।
(2) can, may, will तथा shall के past forms - could, might, would तथा should होते हैं लेकिन इन past forms से हमेशा वही भावना व्यक्त नहीं होती है जो इनके present forms से होती है । इनके past forms से अनेक अन्य भावों की भी अभिव्यक्ति होती है ।
1. Uses of can Can का अर्थ है – 'सकना' । इसका प्रयोग Present Tense में निम्न भाव प्रकट करने के लिए होता है -
(A) योग्यता (ability), क्षमता (capacity) या शक्ति (power) का भाव प्रकट करने के लिए :
(to express ability, capacity or power)
1. I can teach mathematics. -- (ability)
मैं गणित पढ़ा सकता हूँ। (मुझमें गणित पढ़ाने की योग्यता है।) -- (योग्यता)
2. A blind man cannot see. एक अंधा आदमी नहीं देख सकता । -- (capacity)
(अन्धे आदमी में देखने की क्षमता नहीं होती, अत: नहीं देख सकता है।) -- (क्षमता)
3. We can climb up this high tree. हम इस ऊँचे पेड़ पर चढ़ सकते हैं । -- (power)
(हममें इस ऊँचे पेड़ पर चढ़ने की शक्ति है ।) -- (शक्ति )
4. I can lift this heavy box. मैं इस भारी बक्से को उठा सकता हूँ। -- (strength)
(मुझमें इस भारी बक्से को उठाने की ताकत है ।) -- (ताकत)
5. I can solve this puzzle. मैं इस पहेली को हल कर सकता हूँ। -- (intelligence)
(मुझमें इस पहेली को हल करने की बुद्धि है ।) -- (बुद्धि)
6. I can befool him. --(cleverness)
मैं उसे मूर्ख बना सकता हूँ। (मुझमें इतनी चतुराई है।)

(3) अनुमति या आदेश देने या लेने का भाव प्रकट करने के लिए :
(be permitted to, be allowed to)
1. You can go now. अब तुम जा सकते हो ।
(order) (आदेश)
2. Can I use your pen ? क्या मैं आपकी कलम प्रयोग कर सकता हूँ ?
(permission) (स्वीकृति लेना)
3. Nobody can roam in this prohibited area.
(order) - कोई इस प्रतिबंधित क्षेत्र में नहीं घूम सकता। (आदेश)
4. Can't she enter without permission ?
(Permission) क्या वह बिना अनुमति प्रवेश नहीं कर सकती है? (अनुमति)
Note : can का प्रयोग अनौपचारिक रूप से permission लेने के लिए किया जाता है ।
(C) सम्भावना या असम्भावना व्यक्त करने के लिए : (to express possibility or impossibility)
1. Accidents can happen everywhere. दुर्घटनाएँ हर स्थान पर हो सकती हैं ।
2. “The Ramayana’ can be found in the household of every Hindu. (Possibility) -- 'रामायण' प्रत्येक हिन्दू के परिवार में पाई जा सकती है । -- (सम्भावना)
नोट – किसी बात की सम्भावना जानने के लिए जब प्रश्न किया जाता है तो can का ही प्रयोग किया जाता है, may का नहीं । जैसे -
1. Can this boy be a thief ? क्या यह लड़का एक चोर हो सकता है?
2. Can a crow be white ? क्या कोई कौवा सफेद हो सकता है?
3. Can the blind see ? क्या नेत्रहीन देख सकता है?
4. Can the lame run ? क्या लंगड़ा दौड़ सकता है?
5. Can God be cruel ? क्या ईश्वर क्रूर हो सकता है?
(D) ज्ञानेन्द्रियों सम्बन्धी उन क्रियाओं के साथ जो continuous tenses में प्रयुक्त नहीं होती। जैसे
1. We can touch the pinnacle of success. हम सफलता के शिखर को छू सकते हैं।
2. Nobody can taste Cyanide. सायनाइड कोई नहीं चख सकता है।
Cannot का प्रयोग वाक्य Negative (नकारात्मक) हो तो can't या cannot का प्रयोग होगा ।
1. I cannot solve this question. (absence of ability)
मैं इस प्रश्न को हल नहीं कर सकता। (योग्यता की कमी)
2. I cannot afford a car. (absence of capability)
मैं कार का खर्च वहन नहीं कर सकता । (क्षमता नहीं, not capable)
3. He cannot lift this box. -- (not strong, no power)
वह इस बक्से को नहीं उठा सकता। -- (शक्ति नहीं)
4. You can't park your car here. -- (not allowed)
तुम अपनी कार को यहाँ खड़ी नहीं कर सकते। -- (अनुमति नहीं)
5. This news cannot be true. --
यह समाचार सत्य नहीं हो सकता। (असम्भावना जब कोई बात तार्किक आधार पर गलत हो) waar

2. Uses Of Could
Could, can का Past है । could का अर्थ है 'सका' या 'सकता था' । इसका प्रयोग Past Tense में योग्यता (ability), क्षमता (capacity या capability), शक्ति (power), चतुराई (cleverness), बुद्धि (intelligence), संभावना (possibility) आदि व्यक्त करने के लिए होता है ।
(A) भूतकाल की योग्यता, क्षमता, शक्ति, ताकत, बुद्धि, चतुराई, अनुमति व सम्भावना व्यक्त करने के लिए अथवा इनका अभाव व्यक्त करने के लिए
(to express ability, capacity, power, strength, intelligence, cleverness, permission and possibility in the past or their absence)
1. I could speak English when I was only five years old. (ability of past)
जब मैं पाँच वर्ष की उम्र का था तब अंग्रेजी बोल सकता था । (भूतकाल की योग्यता)
2. My brother could not send me an M.O. last month. (absence of capacity)
मेरा भाई पिछले माह मुझे मनीऑर्डर नहीं भेज सका । (क्षमता का अभाव)
3. I could run fast when I was young. (power)
जब मैं युवक था तब तेज दौड़ सकता था । (शक्ति )
4. Umesh could go out whenever he wanted. (permission)
उमेश जब चाहता बाहर जा सकता था । (अनुमति)
(उमेश को अनुमति थी कि जब भी वह चाहे बाहर जा सकता था ।)
(B) भतकाल में सम्भावना के लिए (for possibility in the past) I could attend the function.
(possibility) मैं उत्सव में सम्मिलित हो सकता था। (सम्भावना)
(C) वर्तमान काल में विनम्र निवेदन के लिए प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों के साथ (for polite request in the present with interrogative)
1. Could you lend me your pen ? क्या तुम मुझे (इसी समय) अपनी कलम उधार दे सकते हो ?
2. Could you tell me the way to the hotel ? क्या तुम मुझे (इसी समय) होटल का रास्ता बता सकते हो?

(D) बीती हुई घटनाओं के लिए (to express incidents in the past)
1. It was so dark that he could see nothing.
इतना अंधेरा था कि वह कुछ भी नहीं देख सकता था।
2. The fan was so high that Mohan could not touch it.
पंखा इतना ऊँचा था कि मोहन इसे छू नहीं सकता था।
(E) बीते समय की सम्भावना या योग्यता प्रकट करने के लिए (to express past possibility or ability)
कुछ वाक्यों में could + have + Third form of Verb का प्रयोग होता है । इससे यह प्रकट होता है कि काम करने की योग्यता या क्षमता या सम्भावना होते हुए भी भूतकाल में कोई कार्य पूरा न हो सका ।
1. She could have passed the examination. (past ability)
वह परीक्षा में पास हो सकती थी । (पर पास हो न सकी) (योग्यता)
2. He could have caught the train. (past possibility)
वह रेलगाड़ी पकड़ सकता था । (पर पकड़ न सका) (सम्भावना)
(F) काल्पनिक शर्त प्रकट करने के लिए (to express an imaginary condition)
1. If I reached earlier, I could catch the bus. - यदि मैं और जल्दी पहुँच जाऊँ, तो बस पकड़ लूँ।
(परन्तु इस वाक्य में भाव यह है कि मैं जल्दी पहुँचूंगा नहीं और इसलिए बस नहीं पकड़ सकूँगा।)
2. I could buy a scooter if I had money. यदि मेरे पास धन हो तो मैं स्कूटर खरीद लूँ।
(परन्तु वाक्य दर्शाता है कि वक्ता के पास धन नहीं था । वह केवल कल्पना कर रहा है कि यदि धन हो तो स्कू टर खरीद लूँ।)
3. I could solve this problem if I tried. यदि मैं प्रयास करूं तो मैं इस समस्या को हल कर लूँ।
(पुनः भाव यही है कि वक्ता प्रयास नहीं करेगा और समस्या हल भी नहीं कर पाएगा । वह केवल कल्पना मात्र कर रहा है ।)

(G) Indirect में could का प्रयोग (use of 'could' in Indirect)
जब Reporting Verb, Past Tense में हो तो Reported Speech में दिए गए 'can' को 'could' में बदलते हैं, जैसे -
1. She said, “I can sing old melodies excellently."
She said that she could sing old melodies excellently.
2. Ram said, “I can write a thrilling novel.”
Ram said that he could write a thrilling novel.
3. The merchant said to the customers, “You can choose the items you like.”
The merchant told the customers that they could choose the items they liked.
4. The commander said to the tired soldiers, “You can rest for a while.' The commander told the tired soldiers that they could rest for a while.
Could not का प्रयोग भूतकाल की अयोग्यता (inability/disability) को बताने के लिए He was very weak. He could not walk properly. (absence of ability in past)
3.Uses Of Mayana
May का अर्थ भी 'सकना' होता है । इसका प्रयोग Present Tense में अनुमति लेने या देने, संभावना (possibility), शुभकामना या मनोकामना, आशीर्वाद (blessings) या शाप देने (curse) के लिए किया जाता है।
(A) अनुमति लेने अथवा देने के लिए (for giving or asking permission)
1. May I come in, sir ?क्या मैं अन्दर आ सकता हूँ, श्रीमान ? (formal permission)
2. You may go home. तुम घर जा सकते हो। (giving formal permission)
नोट : Permission की अस्वीकृत के लिए may not का प्रयोग नहीं किया जाता है।
1. May I play here ?
No, you can't / mustn't.
2. May I use your mobile phone ?
No, you can't / mustn't.
(3) सम्भावना प्रकट करने के लिए (to express possibility)
1. There are clouds in the sky. It may rain tonight. (possibility)
आकाश में बादल हैं। आज रात वर्षा हो सकती है। (सम्भावना)
2. Today is Sunday. He may go home. (possibility)
आज रविवार है। वह घर जा सकता है। (सम्भावना)
3. The news may be true. (possibility)
समाचार सही हो सकता है। (सम्भावना)
(C) व्यक्तिगत शुभकामना, आशा एवं विश्वास व्यक्त करने के लिए विस्मयादिबोधक वाक्यों के साथ
(to express personal wish, hope or faith)
1. May you live long ! ईश्वर करे तुम चिरंजीवी रहो ! (wish)
2. May he return home safe ! ईश्वर करे वह घर सुरक्षित लौटे ! (hope)
3. May God bless you with strength and wisdom ! (belessing) ईश्वर आपको शक्ति व बुद्धिमत्ता प्रदान करे ! (आशीर्वाद)
4. May all the sinners go to hell ! (curse)
सभी पापी नरक में जायें ! (श्राप)

(D) उद्देश्य प्रकट करने के लिए (to show purpose)
1. Work hard so that you may pass.
कठोर परिश्रम करो ताकि तुम सफल हो सको।
2. We eat so that we may live.
हम भोजन करते हैं ताकि हम जीवित रह सकें।
3. We wear warm clothes in winter so that we may not catch cold.
हम सर्दियों में गर्म कपड़े पहनते हैं ताकि हमें ठंड न लगे।
(E) जब वाक्य में 'भले ही' या 'चाहे' का अर्थ ध्वनित होता हो तो उस स्थिति में may का प्रयोग होता है। जैसे---
1. Whatever place she may visit, she cannot forget her home.
भले ही वह कहीं भी चली जाए, वह अपने घर को नहीं भूल सकती ।
2. Priya may have learnt English for years, her English is still poor.
चाहे प्रिया वर्षों अंग्रेजी सीख चुकी है, उसकी अंग्रेजी फिर भी कमजोर है
Note : नकारात्मक वाक्यों के लिए may not का प्रयोग होगा ।
4. Uses Of 'Might'.
'Might' may का Past Tense Form है । इसका प्रयोग निम्न प्रकार से किया जाता है -
(A) प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में विनम्रतापूर्वक एवं हिचकिचाहटपूर्वक अनुमति माँगने के लिए
1. Might I take your pen ? क्या मैं आपकी कलम ले सकता हूँ?
2. Might we spend some time here ? क्या हम यहाँ कुछ समय व्यतीत कर सकते हैं?
नोट -
(a) यद्यपि अनुमति माँगने के लिए वर्तमान काल के प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में may का प्रयोग होता है पर might से अत्यन्त विनम्रतापूर्वक एवं हिचकिचाहट पूर्ण अनुमति माँगने का भाव प्रकट होता है । इन वाक्यों से संकोच या संदेह का भाव भी प्रकट होता है।
(b) Indirect में 'may' के स्थान पर 'might' के प्रयोग के अतिरिक्त 'might' का प्रयोग अनुमति देने या अनुमति न देने के अर्थ में नहीं किया जाता ।
She said to me, “I may help you.” उसने मुझसे कहा, "मैं तुम्हारी सहायता कर सकती हूँ।"
She told me that she might help me. उसने मुझे बताया कि वह मेरी सहायता कर सकती थी।
(B) बीती हुई संभावना प्रकट करने के लिए (to express past possibility)
1. Your eldest son might have become a doctor.
तुम्हारा सबसे बड़ा लड़का डॉक्टर हो सकता था (पर हुआ नहीं) ।
2. He fell from the roof and broke his leg. He might have been killed.
वह छत से गिर गया और उसकी टाँग टूट गई । वह मर सकता था (पर मरा नहीं) ।
(C) अत्यन्त क्षीण सम्भावना प्रकट करने के लिए (to express remote possibility)
1. Take a taxi. You might catch the train. (remote possibility)
टैक्सी ले लो । तुम्हें गाड़ी मिल सकती है (जिसकी सम्भावना बहुत कम है)।
2. The sky is clear now. It might rain tonight. (remote possibility)
अभी आसमान स्वच्छ है । रात को वर्षा हो सकती है (पर सम्भावना बहुत कम है)।
3. She might reply my letter. (remote possibility)
वह मेरे पत्र का उत्तर दे सकती है (जिसकी सम्भावना बहुत कम है)।
(D) भूतकालीन उद्देश्य प्रकट करने के लिए (to express purpose in the past)
1. He took medicine so that he might get well. उसने दवा ली ताकि वह अच्छा हो सके।
2. The patriots sacrificed their lives so that we might live honourably.
देशभक्तों ने अपना जीवन इसलिए बलिदान किया ताकि हम सम्मानपूर्वक जी सकें ।
Note :
(a) so that के साथ may/might का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
(b) वाक्य नकारात्मक हो तो might not का प्रयोग होगा।

5. Uses Of Will
व्यक्तिगत तौर पर नियन्त्रित किया जा सकने वाला कोई तत्व जब वाक्य में उपस्थित नहीं होता तो वाक्य में will का प्रयोग सिर्फ pure future दर्शाता है, जैसे
1. Tomorrow will be Monday. कल सोमवार होगा।
2. The work will take ten days. इस कार्य में 10 दिन लगेंगे।
(A) सामान्य निर्देश (general instruction)
All the members of this club will attend the meeting.
इस क्लब के सभी सदस्य सभा में शामिल होंगे।
(B) निवेदन (polite request)
Will you please help me ? क्या आप कृपाकर मेरी सहायता करेंगे ?
Will any one lend me some money ? क्या कोई मुझे कुछ धन उधार देगा?
(C) संभावना (possibility)
1. It will be a storm. ऐसी संभावना है कि तूफान आएगा।
2. There will be healthy discussion on this issue. इस मुद्दे पर स्वस्थ विचार-विमर्श होगा।
(D) आदत (habit) या किसी ऐसी बात को दिखाने के लिए जिसकी, बिना किसी परिवर्तन के, सदैव अपेक्षा की जा सकती है।
1. He will talk only nonsense. उसकी बातें बिना अक्ल की ही होंगी।
2. Accidents will happen. दुर्घटनाएँ तो होंगी ही।
(E) Won't you का प्रयोग आमन्त्रण (invitation) के लिए किया जाता है।
1. Won't you stay a little longer? कुछ देर और ठहर जाओ ।
2. Won't you have a cup of coffee. एक कप कॉफी लो । नोट - आधुनिक अंग्रेजी में I तथा we के साथ future time व्यक्त करने के लिए shall के स्थान पर will का भी प्रयोग किया जाने लगा है । पर Interrogative Sentences में | और we के साथ shall का ही प्रयोग होता है, will का नहीं । जैसे --
Shall I go to Agra ? (इस वाक्य में will का प्रयोग नहीं होगा ।) I, We के साथ will का प्रयोग निम्न भाव प्रकट करता है:
(A) वायदा (promise)
1. I will accompany you to Jaipur. -- मैं (वायदा करता हूँ कि) तुम्हारे साथ जयपुर जाऊँगा ।
2. I will try to write better next time. -- मैं (वायदा करता हूँ कि) अगली बार और अच्छा लिखने का प्रयास करूँगा ।
3. We will help you. -- हम (वायदा करते हैं कि) तुम्हारी सहायता करेंगे।

(B) दृढ़ निश्चय (determination)
1. I will prove myself a worthy son of my parents.
मैं (निश्चित रूप से) स्वयं को अपने माता-पिता का योग्य पुत्र साबित करूँगा।
2. We will fight against injustice.
हम (निश्चित रूप से) अन्याय के विरुद्ध लड़ेंगे ।
(C) धमकी (threat) या चेतावनी (warning)
1. I will arrest you. में (धमकी देता हूँ कि) तुम्हें गिरफ्तार कर लूँगा ।
2. I will punish you if you do this work again. यदि तुम इस कार्य को पुनः करते हो तो मैं (चेतावनी देता हूँ कि) तुम्हें दण्ड दूंगा।
(D) इच्छा या सहमति (willingness)
1. I will join the army after two years. (मेरी इच्छा है कि) मैं दो वर्ष बाद सेना में शामिल होऊँगा।
2. We will provide you every possible help. हम आपको हर सम्भव सहायता प्रदान करेंगे।
(E) प्रस्ताव रखना (offer)
I will bring you tea or coffee whichever you like.
Note : वाक्य नकारात्मक (Negative) हो तो will not या won't का प्रयोग होगा ।
6. Uses Of 'Shall'
First Person के Pronouns (I व We) के साथ shall का प्रयोग केवल Simple Future को प्रकट करता है । उस समय shall केवल एक Auxiliary Verb (सहायक क्रिया) का कार्य करता है -
उदाहरण :
I shall be fifty next birthday. अगले जन्मदिन पर मैं पचास का हो जाऊँगा ।
Second Person (you), Third Person (He, She, name, They व It) तथा एकवचन संज्ञाओं के साथ shall लगाने पर यह shall Modal Auxiliary का कार्य करेगा तथा निम्न भावों को प्रकट करेगा -
(A) वायदा (promise)
1. You shall get a prize for your extraordinary bravery. (promise) (वायदा किया जाता है कि) इस असाधारण बहादुरी के लिए तुमको इनाम मिलेगा ।
2. He shall always find me by his side. वह हमेशा ही मुझे अपने साथ पायेगा । (promise)

(B) आज्ञा (command) या धमकी (threat)
1. He shall not attend the class without completing his home work.
वह अपना गृह कार्य पूर्ण किये बिना कक्षा में उपस्थित नहीं होगा ।
(command) (उसको कक्षा में उपस्थित होने की आज्ञा नहीं दी जायेगी ।)
2. He shall be punished if he doesn't behave himself. (threat)
(अगर वह अच्छा व्यवहार नहीं करेगा तो उसे दण्डित किया जाएगा ।)
(C) कानूनी नोटिसों या कार्यालयों की व्यवस्था/अधिनियम व्यक्त करने में
(in legal notices or official regulations)
1. Trespassers shall be punished.
(कानूनी चेतावनी) बिना अनुमति के घुसने वाले दण्डित किये जायेंगे।
2. Members shall elect the chairman from among themselves.
सदस्यगण अपने आप में से अध्यक्ष चुनेंगे। (कार्यालय का अधिनियम)
(D) प्रस्ताव करने अथवा परामर्श/निर्देश प्राप्त करने में
(in offering or seeking advice/instructions)
1. Shall I call in the doctor for you ?
क्या मैं आपके लिए चिकित्सक बुलवाऊँ ? (प्रस्ताव करने हेतु)
2. Where shall I wait for you ?
मैं तुम्हारा इंतजार कहाँ करूँ? (निर्देश प्राप्त करने में)
3. What books shall I consult for the test ?
(सलाह लेने में) मैं परीक्षा के लिए कौन-सी किताबों का अध्ययन करूँ?
(E) पक्का इरादा (determination)
1. You shall help her.
(मैंने इरादा कर लिया है कि मैं तुमसे उसकी मदद करवाऊँगा।)
2. They shall finish the work before the deadline.
(मैंने निश्चय कर लिया है कि उनसे, समय सीमा से पहले ही काम समाप्त करवाऊँगा।)

Note : वाक्य नकारात्मक होने पर shall not या shan't का प्रयोग होगा ।
7. Uses Of 'MUST'
Must का तात्पर्य है 'निश्चित रूप से चाहिये' । इस Modal का प्रयोग अनिवार्यता (compulsion), आवश्यकता (necessity), बाध्यता (persuation), प्रबल सम्भावना (strong possibility), आवश्यक सलाह/परामर्श (strong advice), तर्कसंगत निष्कर्ष (logical inference) आदि को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है ।
(A) अनिवार्यता (compulsion)
1. We must reach school in time to avoid punishment.
हमें सजा से बचने के लिए समय पर विद्यालय पहुंचना चाहिए ।
2. We must enter the office without any noise.
हमें बिना किसी शोर के कार्यालय में प्रवेश करना चाहिए।
(B) प्रबल संभावना (strong possibility)
1. They are in a new dress. They must be going to a party.
वे नये कपड़ों में हैं । वे निश्चित रूप से पार्टी में जा रहे होंगे ।
2. He must be a dacoit.
वह डाकू होना चाहिये (निश्चित रूप से) ।
3. He has three cars. He must be a rich man.
उसके पास तीन कारें हैं । वह धनी व्यक्ति होना चाहिए।
4. He must have been a terrorist.
(निश्चित रूप से) वह एक आतंकवादी रहा होगा ।

(C) आज्ञा व्यक्त करने के लिए (to express command)
1. You must stay where you are.
तुम्हें वहीं रुकना चाहिए जहाँ तुम हो । (आज्ञा)
2. She must attend all her classes.
उसे अपनी सारी कक्षाओं में शामिल होना है।
(D) आवश्यकता व्यक्त करने के लिए (to express necessity)
1. We must work hard to pass.
उत्तीर्ण होने के लिए हमें आवश्यक रूप से कठोर परिश्रम करना चाहिए ।
2. We must have oxygen to save our lives.
हमें अपना जीवन बचाये रखने के लिए ऑक्सीजन अवश्य ग्रहण करनी चाहिए।
(E) आवश्यक परामर्श के लिए (to express strong advice)
1. You are getting late. You must hire a taxi.
तुम्हें देर हो रही है । अतः (परामर्श है कि) तुम्हें टैक्सी किराये पर ले लेनी चाहिए ।
2. You must close all the doors in the night.
तुम्हें (परामर्श दिया जाता है कि) रात्रि में सभी दरवाजे बन्द करने चाहिए।
(F) तर्कसंगत निष्कर्ष के लिए (to express logical inference)
1. Hari is an intelligent boy. He must get first division.
हरी एक बुद्धिमान लड़का है। वह प्रथम श्रेणी अवश्य प्राप्त करेगा।
2. You have been travelling all day. You must be tired.
आप दिन भर से यात्रा कर रहे हैं। आप अवश्य ही थके हुए होंगे।
Use of 'must not'
(A) प्रतिबन्ध (Prohibition) के लिए must not का प्रयोग होता है। जैसे
1. You have T. B. You must not smoke. ...
तुम्हें क्षय रोग है। तुम धूम्रपान नहीं कर सकते।
2. We must not park our vehicles at public places.
हमको सार्वजनिक स्थानों पर अपने वाहन खड़े नहीं करने चाहिए।
(B) आदेश तथा चेतावनी के साथ नकारात्मक सलाह व्यक्त करने के लिए
(to express order, negative advice with warnings)
1. You must not overtake from the left.
2. You must not sit here. आप बायें से दूसरे वाहनों से आगे नहीं निकल सकते। आपको यहाँ नहीं बैठना चाहिए।
8.Uses Of 'HAVE TO'
have to का प्रयोग बाध्यता, व्यक्तिगत भावना इत्यादि को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है । have to form
|
|
Affirmative |
Negative |
Interrogative |
|
Present |
has to |
doesn’t have to / |
Does / Do + Subject + have to? |
|
Past |
had to |
didn’t have to |
Did + subject + have to ...... ? |
|
Future |
will /shall |
won’t / shan’t have to |
Will I Shall + subject + have to ........ ? |

Note-
1. 'has to' का प्रयोग Present Tense में 3rd person, singular number subjects (He, She, It अथवा एक वचन) के साथ करते हैं ।
2. have to का प्रयोग Present Tense में I, You तथा अन्य बहवचन कर्ताओं के साथ किया जाता है ।
3. had to का प्रयोग Past Tense में सभी कर्ताओं के साथ समान रूप से होता है ।
4. will का प्रयोग Future Tense में II व III person pronoun के साथ तथा shall का प्रयोग I person pronouns के साथ किया जाता है। must a have to के प्रयोग में अन्तर Must तथा have to का प्रयोग यह बताने के लिए होता है कि कोई कार्य करना जरूरी है। कभी-कभी तो दोनों में से किसी का भी प्रयोग किया जा सकता है ।
जैसे- Oh, it's earlier than I thought. I must go now. या I have to go now. परन्तु दोनों के प्रयोग में अंतर है जो इस प्रकार से है
|
must |
have to |
|
यह personal होता है तथा इसका प्रयोग तब किया जाता है जब हम अपनी व्यक्तिगत भावना को व्यक्त करें। You must do it. (वक्ता कहता है कि यह करना जरूरी है ।) (i) It's really a nice book. You must read it. (ii) He must stay tonight. I will tell him to do so. (iii) You must go now. I want to go to bed.
|
यह impersonal होता है तथा इसका प्रयोग तथ्यों के साथ किया जाता है न कि व्यक्तिगत भावनाओं के साथ । You have to do it. It is your course book. You have to read it. He has to stay tonight. He can't go back to night. You have to go now. It's time for you to catch the train. You have to call me 'Sir'. It is a rule here. I have to get up early tomorrow. I am going away by 6:30 train. |
नोट - Must का प्रयोग Present व Future के साथ किया जाता है लेकिन Past के साथ नहीं । Must को Past Tense में had to में परिवर्तित कर दिया जाता है जबकि have to का प्रयोग सभी Tenses के साथ किया जा सकता है । जैसे


9. Uses Of Would
Will का Past Tense Form would है । परन्तु इसका प्रयोग polite request (विनम्र निवेदन), past happenings (भूतकालीन घटनाओं), intention (इरादा ज्ञात करने), others' wishes (दूसरों की इच्छाओं) आदि हेतु होता है ।
Note : वाक्य Negative होने पर would not का प्रयोग होगा ।
(A) Will के Past Tense के रूप में (in the past form of 'will')
यदि Reporting Verb Past Tense में हो तो Reported Speech में आये will को Indirect बनाते समय would में बदल देते हैं । जैसे -
1. They said, “The English teacher will not teach on Monday.”
उन्होंने कहा, "अंग्रेजी के अध्यापक सोमवार को नहीं पढ़ायेंगे।"
2. They said that the English teacher would not teach on Monday.
उन्होंने कहा कि अंग्रेजी के अध्यापक सोमवार को नहीं पढ़ायेंगे।
(B) वर्तमान काल में विनम्र निवेदन के रूप में प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों के साथ (for polite request in the present)
1. Would you lend me your pen ?
क्या आप मुझे (इसी समय) अपनी कलम उधार देंगे?
2. Would you tell me the way to the hotel ?
क्या आप मुझे (इसी समय) होटल का रास्ता बतायेंगे ?
3. Would anyone admit the injured in the hospital ?
क्या कोई (आदमी) घायल को अस्पताल में भर्ती करायेगा? नोट-वर्तमान काल में आग्रह करने के लिए will के स्थान पर would के प्रयोग से अधिक नम्रता का भाव प्रदर्शित होता
(C) भूतकाल में होने वाली घटनाओं के लिए या भूतकालिन आदत बताने के लिए (for the happenings in the past or habitual action in the past) :
1. Sometimes my father would get angry with me. कभी-कभी मेरे पिता मुझसे क्रोधित हो जाते थे ।
2. On Saturdays, Sohan would usually run home to his mother. शनिवार को बहुधा सोहन अपनी माँ के पास घर भाग जाता था ।

(D) किसी व्यक्ति की इच्छा या सहमति ज्ञात करने के लिए
1. Would you like to have some tea ?
क्या आप थोड़ी चाय लेना चाहेंगे?
2. Would you share my joys ?
क्या आप मेरे आनन्द बाँटेंगे?
(E) इरादा प्रकट करने के लिए (to express intention)
1. I would obey you even if I die.
मैं आपकी आज्ञा मानूँगा चाहे मैं मर ही जाऊँ ।
2. I would sacrifice my life at the altar of the motherland.
मैं मातृभूमि की बलिवेदी पर अपना जीवन न्यौछावर कर दूंगा।
(F) प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में नम्रतापूर्वक प्रस्ताव, अनुमति तथा इच्छा व्यक्त करने के लिए
(to express polite offer, permission and wish in Interrogatives)
1. Would you like our house ? क्या आप हमारा घर पसंद करेंगे? (polite offer)
2. Would you mind if I smoke ? यदि मैं धूम्रपान करूँ तो क्या आपको बुरा लगेगा ? (permission)
3. Would that I had become a Minister! काश ! मैं मन्त्री बन जाता ।(desire)
(G) बीती सम्भावना प्रकट करने के लिए (to express past possibility)
1. Sheela would be about sixty when she died.
जब शीला की मृत्यु हुई तब वह लगभग साठ वर्ष की रही होगी ।
2. My younger brother would have passed RAS examination when he turned 25.
मेरा छोटा भाई जब 25 वर्ष का हुआ तो वह RAS परीक्षा पास कर चुका होता।

10. Uses Of 'Should'
Should का अर्थ "चाहिये" होता है । इसका प्रयोग advice (सलाह), suggestion (सुझाव), duty (कर्त्तव्य), probability or expectation (अनुमान या सम्भावना), conditional (शर्त वाले वाक्य) में lest (ऐसा न हो कि) के बाद होता है । इसका प्रयोग shall के Past के रूप में भी होता है । सामान्यतः परीक्षा में advice व duty के लिए ही इसे पूछा जाता है।
(A) Shall के Past Tense के रूप में (as the past form of 'shall')
यदि Reporting Verb का कर्ता First Person का है और Reporting Verb, Past Tense में है तो Reported Speech में आये हुए shall को Indirect में परिवर्तित करते हुए should में बदल देते हैं । जैसे -
1. I said, “I shall shine in my life.”
मैंने कहा, "मैं अपने जीवन में असाधारण रूप से सफलता अर्जित करूंगी।"
2. I hoped that I should shine in my life.
मैंने आशा की कि मैं अपने जीवन में असाधारण सफलता अर्जित करूँगी।
(B) सलाह या सुझाव (advice or suggestion)
1. We should take a bath/shower daily.
हमें प्रतिदिन स्नान करना चाहिए । (advice)
2. That is a dangerous place, he should not go there.
वह एक खतरनाक स्थान है, उसे वहाँ नहीं जाना चाहिए । (suggestion)
3. They should sell their house in order to pay their debt.
उन्हें अपना कर्जा चुकाने के लिए अपना मकान बेच देना चाहिये । (advice/suggestion)

(C) कर्त्तव्य (duty)
1. We should obey the elders.
हमें बड़ों की आज्ञा माननी चाहिए ।
2. We should always speak the truth.
हमें सदा सत्य बोलना चाहिए ।
(D) अनुमान या सम्भावना (probability or expectation)
1. She should reach here soon.
(ऐसी संभावना है कि) उसे यहाँ जल्दी ही पहुँचना चाहिए।
2. He should be at the theatre.
(संभावना है या ऐसा अनुमान है कि) वह नाट्यशाला में मौजूद है।
(E) शर्त if के अर्थ में (in the sense of 'if' showing condition)
1. Should it rain, we shall not go home.
(Should it rain = If it rains) यदि वर्षा हुई तो हम घर नहीं जायेंगे।
2. Should it rain, there will be no match.
यदि वर्षा हुई तो मैच नहीं होगा।
(F) Lest के बाद should का प्रयोग (use of 'should' after 'lest')
भविष्य में होने वाली किसी घटना की चिन्ता व्यक्त करने के लिए lest (कहीं ऐसा न हो कि) के साथ should का प्रयोग होता है । जैसे -
1. Walk carefully lest you should fall.
संभलकर चलो कहीं ऐसा न हो कि तुम गिर जाओ ।
2. Work hard lest you should fail.
कठिन परिश्रम करो कहीं ऐसा न हो कि तुम अनुत्तीर्ण हो जाओ।
3. Don't waste your precious time lest you should repent later on.
अपना मूल्यवान समय बर्बाद मत करो ताकि तुम्हें बाद में पछताना न पड़े।

11.Uses Of 'Ought To"
Ought to का प्रयोग कर्ता द्वारा नैतिक कर्त्तव्य (moral obligation) करने या किसी कार्य को करने की उसकी नैतिक बाध्यता को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है । Must में या have to में बाध्यता (obligation) इससे ज्यादा है । Ought to का प्रयोग कर्ता को नैतिक कर्तव्य (moral duty) का बोध कराने, सलाह या सुझाव देने के लिए किया जाता है।
1. She ought to do this work tomorrow.
उसे यह कार्य कल करना चाहिए।
2. You ought to bring that book at once.
आपको वह किताब तुरन्त लानी चाहिए।
संक्षेप में, इससे निम्न बातों का बोध होता है -
(A) नैतिक कर्त्तव्य (moral obligation)
1. You ought to respect your elders.
आपको अपने बड़ों का सम्मान करना चाहिए।
2. We ought to do our duty honestly.
हमें अपने कर्त्तव्य का पालन ईमानदारी से करना चाहिए।
जब भूतकाल के साथ कर्त्तव्य का बोध कराया जाता है, तो ought to have का प्रयोग होता है, जैसे -
1. You ought to have gone to the station.
तुम्हें स्टेशन चले जाना चाहिए था (लेकिन तुम नहीं गये)।
2. She ought to have cleaned her house by then.
उसे तब तक तो अपना घर साफ कर लेना चाहिए था।
नोट - Reported Speech में Past Tense के साथ ought का रूप नहीं बदलता है, जैसे -
They said to him, "He ought to reach the office in time."
They told him that he ought to reach the office in time.

(B) अध्ययन पर आधारित विश्वास या सशक्त सम्भावना व्यक्त करने के लिए
(to express belief based on study or strong probability)
1. She ought to be present here.
(पूरा विश्वास है कि) उसे यहाँ उपस्थित होना चाहिए ।
2. Sheela got good marks. She ought to be a good girl also.
शीला ने अच्छे अंक प्राप्त किये । (निश्चित रूप से) वह एक अच्छी लड़की भी होगी ।
(C) सलाह के लिए (to express advice)
1. You ought to be more careful about your health.
तुम्हें अपने स्वास्थ्य के प्रति अधिक सावधान रहना चाहिए । (सलाह)
2. All of you ought to avoid the company of bad boys.
तुम सबको बुरे लड़कों की संगति से बचना चाहिये । (सलाह)
नोट - (1) Interrogative Sentences में 'ought to' के प्रयोग की अपेक्षा 'should' का प्रयोग अधिक अच्छा माना जाता है।
Ought you to sleep now? ।' इस वाक्य के स्थान पर हमें लिखना चाहिये - Should you sleep now ?
(2) 'ought to' तथा 'must' दोनों ही नैतिक कर्त्तव्य, सलाह, सम्भावना या विश्वास की भावनाओं को व्यक्त करते हैं, पर इन दोनों में 'must' से ये भावनाएँ अधिक जोरदार तरीके से व्यक्त होती हैं।
('must' carries greater force than that conveyed by 'ought to'.)
यही बात oughtn't तथा mustn't पर भी लागू होती है । जैसे -
We oughtn't to laugh at the faults of other people.
We mustn't laugh at the faults of other people.
दोनों वाक्यों का अर्थ है, "हमें दूसरे लोगों की गलतियों पर नहीं हँसना चाहिए।" पर दूसरे वाक्य से यही भाव अपेक्षाकृत अधिक दृढ़तापूर्वक झलक रहा है।
should व ought to के प्रयोग में अन्तर
should aought to के प्रयोग व अर्थ में कोई विशेष अन्तर नहीं है । दोनों में से किसी का भी प्रयोग समान रूप से किया जा सकता है । परन्तु औपचारिक सूचना पट्टों (Notice-Board) पर केवल should का ही प्रयोग किया जाता है ।
जैसे (i) Passengers should not block the passage by their luggage.
यात्रियों को अपने सामान से रास्ता नहीं रोकना चाहिये ।

(ii) On hearing the warning bell, all the staff should come on the duty.
चेतावनी घंटी सुनने पर पूरे स्टाफ को ड्यूटी पर आना है ।
should व ought की must से तुलना
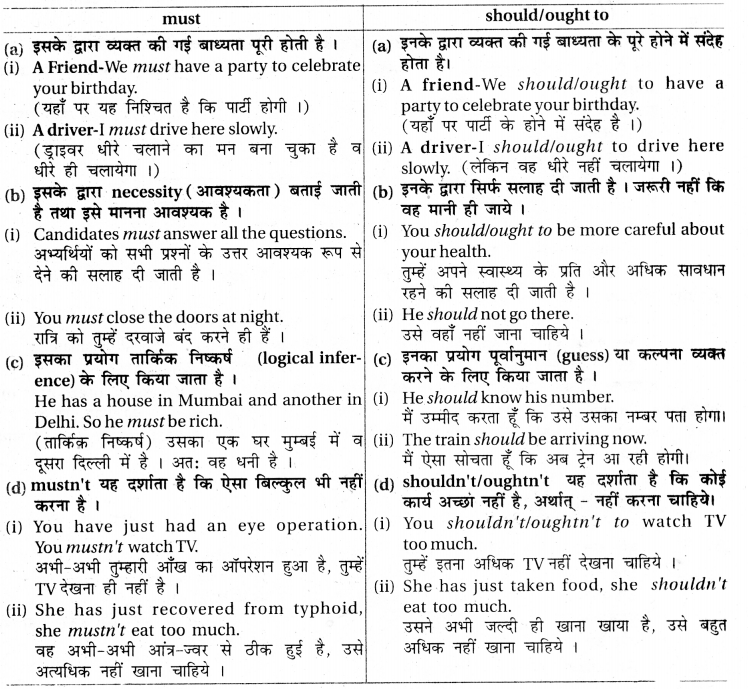
12. Uses Or Used To
Used to एक semi-modal है जिसका प्रयोग भूतकाल की किसी ऐसी आदत या दिनचर्या (habit or routine) को व्यक्त करने के लिए होता है जो कि वर्तमान में मौजूद नहीं है।
अतः इसका प्रयोग वर्तमान काल (Present Tense) में नहीं किया जाता । इसका प्रयोग केवल भूतकाल (Past Tense) में ही होता है। उदाहरण:
(1) I used to go for swimming in my childhood. बचपन में मैं तैरने जाया करता था ।
(2) I used to sing in my school days. स्कूली दिनों में मैं गाया करता था ।
(3) There used to be a garden behind our school. हमारे विद्यालय के पीछे एक बगीचा हुआ करता था ।

13. Uses Of Need
Need, Main Verb के साथ-साथ Semi-modal भी है । Semi-modal के रूप में need का प्रयोग प्रायः नकारात्मक (Negative) तथा प्रश्नवाचक (Interrogative) में होता है किन्तु ऐसा नहीं है कि इसका प्रयोग Affirmative / Assertive / Informative वाक्यों में होता ही नहीं है।
(A) नकारात्मक वाक्यों में यह आवश्यकता, उपयोगिता एवं बाध्यता के अभाव को प्रकट करता है ।
(In Negative Sentences, it is used to express lack of necessity, usefulness and obligation.)
(1) इस प्रकार के वाक्यों से यह बोध होता है कि कर्ता (Subject) के लिए कार्य करना आवश्यक अथवा अनिवार्य नहीं है, जैसे-
1. She needn't work hard.
उसे कठोर श्रम करने की आवश्यकता नहीं है ।
2. You needn't worry about me.
तुम्हें मेरे बारे में चिन्ता करने की आवश्यकता नहीं है ।
3. She needn't go to a doctor.
उसे किसी डॉक्टर के पास जाने की जरूरत नहीं है ।
नोट - इस प्रकार के वाक्यों में Infinitive का प्रयोग बिना to के होता है । (Infinitive without “to’ is used.)
(2) कभी-कभी आवश्यकता, उपयोगिता या बाध्यता के अभाव को need + hardly या scarcely + Infinitive without to' द्वारा भी प्रदर्शित करते हैं, जैसे -
1. He need hardly mention. उसे कहने की जरूरत नहीं है । (needs नहीं)
2. We need scarcely reiterate the fact that Sachin is the all-time greatest batsman.
हमें इस बात को दोहराने की जरूरत नहीं कि सचिन सर्वकालिक महानतम बल्लेबाज है ।
(3) भूतकाल में आवश्यकता/उपयोगिता/बाध्यता के अभाव (absence of necessity, usefulness or obligation in the past) को प्रदर्शित करने के लिए needn't have + Past Participle का प्रयोग होता है । ऐसे वाक्यों से बोध होता है कि भूतकाल में जो कार्य हुआ, उसकी कोई उपयोगिता या आवश्यकता नहीं थी, परन्तु फिर भी कार्य किया गया, जैसे -
1. I needn't have brought my umbrella.
मुझे अपनी छतरी लाने की आवश्यकता नहीं थी (पर ले आया)।
2. You need not have hurried.
तुम्हें जल्दी करने की आवश्यकता नहीं थी (पर तुमने जल्दी कर ही ली) ।
3. She need not have come in person, a letter could have been enough.
उसे व्यक्तिगत रूप से यहाँ आने की आवश्यकता नहीं थी, एक पत्र ही काफी था। परन्तु जब यह भाव प्रदर्शित करना हो कि भूतकाल में किसी विशेष कार्य को करने की जरूरत नहीं थी और उसे किया भी नहीं गया तो ‘didn't need to' का प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे - Ambuja didn't need to buy a new suit.

अम्बुजा को नये कपड़े खरीदने की जरूरत नहीं थी ।
इस वाक्य में यह भाव भी है कि उसने नये कपड़े खरीदे भी नहीं और पुराने कपड़ों से ही काम चला लिया ।
(B) प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में 'need' का प्रयोग आवश्यकता, उपयोगिता या बाध्यता के बारे में पूछने के लिए होता है ।
('needn't in the Interrogative' is used to ask about necessity, usefulness or obligation)
1. Need he beg ?
क्या उसे भीख माँगने की आवश्यकता है?
2. Need she wash clothes ?
क्या उसे कपड़े धोने की जरूरत है?
must, mustn't व needn't में अन्तर
must-बाध्यता (Obligation) को व्यक्त करता है
Obligation - Don't tell it to anybody. You must keep it a secret.
mustn't- व्यक्त करता है कि आप यह काम न करें । ऐसा नहीं करने की बाध्यता है (Negative Obligation) It is a secret. You mustn't disclose it to anybody. (अर्थात् किसी को नहीं कहना है ।) needn't- जब कोई बाध्यता न हो
(absence of obligation or no obligation)
We have got plenty of time. We needn't hurry. (जल्दी करना जरूरी नहीं है
(1) Some More Examples
(i) Doctor to the patient - You needn't go on diet, but you must take food sensibly and you mustn't overeat.
तुम्हें भूखे रहने की जरूरत नहीं है, लेकिन तुम्हें भोजन संयमित मात्रा में करना चाहिये और तुम्हें जरूरत से ज्यादा बिल्कुल भी नहीं खाना है।
(ii) Railway Notice - People must not walk on the railway line.
लोगों को रेलवे लाइन पर बिल्कुल भी नहीं चलना चाहिये।
(iii) You needn't turn on the light. I can see very well.
तुम्हें लाइट चालू करने की आवश्यकता नहीं है। मैं अच्छी तरह से देख सकता हूँ ।
(iv) You mustn't turn on the light. The room is full of gas.
तुम्हें लाइट चालू करना ही नहीं है। कमरा गैस से भरा है।
(v) Teacher - You needn't read all the chapters but you must read the first four.
तुम्हें सारे अध्यायों को पढ़ने की जरूरत नहीं है लेकिन तुम्हें प्रथम चार अध्याय पढ़ने ही हैं।
14. Uses Of Dare (Not)
Dare भी need के समान Main Verb तथा semi-modal है के रूप में इसका प्रयोग प्राय: Negative (नकारात्मक) व Interrogative (प्रश्नवाचक) के रूप में होता है । Dare का अर्थ है – 'साहस होना' । Semi-modal के रूप में इसके प्रयोग में (s. या es) Third Person के साथ या do not/does not का प्रयोग नहीं होता है ।
(A) नकारात्मक वाक्यों में प्रयोग (use in Negative Sentences)
इस प्रकार के वाक्यों से ‘साहस का अभाव' का बोध होता है, जैसे -
1. She daren't ask me any question about this affair. (lack of courage)
इस मामले में मुझसे कोई भी प्रश्न करने का उसमें साहस नहीं है ।
2. He daren't meet the officer.
उसमें अधिकारी से मिलने का साहस नहीं है।
(B) प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में प्रयोग (use in Interrogative Sentences)
इस प्रकार के वाक्यों में dare शब्द का प्रयोग किसी के साहस के बारे में पूछने के लिए किया जाता है ।
(In Interrogative Sentences ‘dare’ is used to ask about such courage.)
1. How dare you say that I copied your notes ?
यह कहने का तुम्हें साहस कैसे होता है कि मैंने तुम्हारे notes की नकल की है ?
2. Dare you tell your teacher about your conduct ?
क्या तुम्हें अपने व्यवहार के विषय में अपने अध्यापक को बताने का साहस है ? 'Dare' का प्रयोग Main Verb के रूप में भी होता है । इस रूप में इसका अर्थ होता है - ‘चुनौती देना' (to challenge)। Main Verb के रूप में कर्त्ता के Number और Person के अनुसार इसका रूप dare या dares हो जाता है । प्रश्नवाचक व नकारात्मक वाक्यों में इसके साथ 'do' या 'does' का प्रयोग होता है, जैसे -
1. I dare you to win the election.
मैं तुम्हें चुनाव जीतने की चुनौती देता हूँ। इसका और अधिक स्वाभाविक अनुवाद है : आप मुझे चुनाव जीतकर तो दिखाओ ।
2. I dare you to say that again.
आप ऐसा फिर से कहो तो जानूँ ।
3. The bowler dared the batsman to hit the ball.
गेंदबाज ने बल्लेबाज को गेंद को सीमा पार भेजने की चुनौती दी, अर्थात गेंदबाज ने कहा कि मेरी गेंद को सीमा पार भेजकर तो दिखाओ
4. Veer Narayan dared his rival to wrestle with him.
वीर नारायण ने अपने प्रतिद्वन्द्वी को कुश्ती लड़ने की चुनौती दी ।

5. Do you dare him to wrestle with you ?
क्या आप उसे अपने साथ कुश्ती लड़ने की चुनौती देते हैं ?
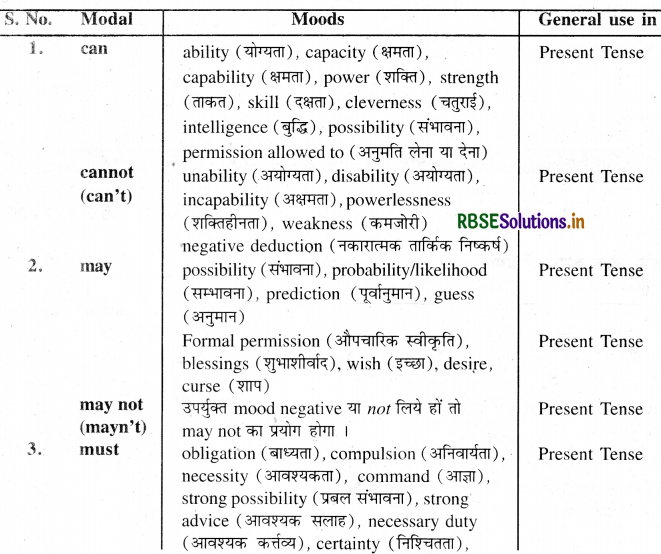
Modal-Mood Chart
निम्न चार्ट के अनुसार Modals को समझने में आसानी रहेगी



Replacement of Modal Phrases with Modals
Modals से सम्बन्धित प्रश्नों में कभी-कभी एक मिला-जुला वाक्य (mixed sentence) दिया हुआ होता है, जिसके एक भाग में दिए गए किसी संकेत के आधार पर दूसरे भाग के modal phrase को हटाकर उसकी जगह निर्दिष्ट Modal का प्रयोग कर पूरा वाक्य पुनः लिखने के लिए कहा जाता है, जैसे
He is able to win the match because he has practised very hard. (Rewrite the sentence using 'can'.) इस वाक्य में 'because he has practised very hard' पूरे वाक्य का एक उपवाक्य है, जो यह संकेत देता है कि उसने चूँकि काफी अभ्यास किया है, इसलिए match जीतने में समर्थ है । अत: दूसरे उपवाक्य से modal phrase is able to' को हटाकर can का प्रयोग करते हुए पूरा वाक्य इस प्रकार लिखा जायेगा He can win the match because he has practised very hard. नीचे दी गई Modal phrases-Modals सारणी की सहायता से यह समझा जा सकता है कि किन शब्दों (modal phrases) को हटाकर उनकी जगह किन Modals का प्रयोग करना है।

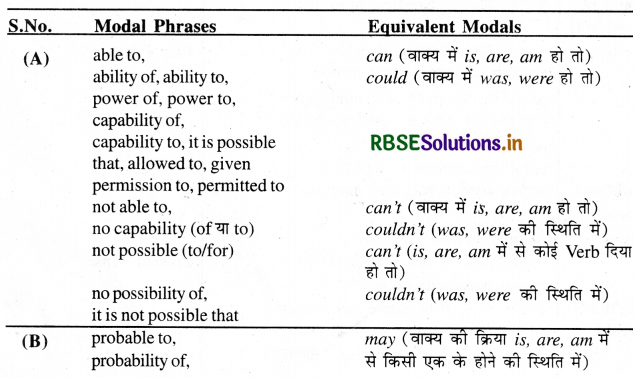




Gap Filling
Exercise
Fill in the gaps with the suitable modals with the help of the words given in the brackets :
1. We...........read only the books we want to read more than once. (advice)
2. I...........behave well to him. (moral obligation)
3. Why.............I spoil it by giving a large part of the profit away ? (questioning a suggestion)
4. My father................read to us the story every night. (habitual action in the past)
5. ................you let me see both the shows everyday ? (request)
6. We............prove that they are false. (ability)
7. Anyone............buy your photograph. (possibility)
8. Chronic stress..........lead to continuously high levels of cortisol. (possibility)
9. The Professor............. correct him publicly. (habitual action in the past)
10. ..............you buy some of them ? (request with insistence)
11. The children .......... go near the cage of the lion. (courage in the past)
12. The atmosphere is all set. It ....... rain any time. (present strong possibility)
13. The naughty monkey ..... leap from one tree to another. (strength in the past)
14. If he commits a crime, he ....... be punished by the law. (threat)
15. He ......... not obey whatever you say. (obstinacy)
Answers:
1. should,
2. ought to,
3. should,
4. used to,
5. Would,
6. can,
7. can,
8. can,
9. would/used to,
10. Won't,
11. dared not,
12. can,
13. could,
14. shall,
15. shall.

Exercise 2.
Fill in the gaps with the suitable modals :
You .....1....... contact 24 x 7 Call Centres any time to know about the company's products. They provide you all information but sometimes you ......2...... find the number busy and you ....3....... have to wait for a while. You .....4..... also lodge a complaint about any of their products. When you talk to them you ........... be decent with them. Usually the Call Centre people are very cool, but if you begin to speak rudely, some of them ........... snap under that pressure.
Answers:
1. can,
2. may,
3. will,
4. can,
5. should,
6. may.
Exercise 3.
Write suitable modals with the help of the words given in the brackets :
1. Being a watchman you..........keep awake on duty. (necessity)
2. If you have completed your work, you.........go home. (permission)
3. I..........do better next time. (promise)
4. Show me your car licence or .......... arrest you. (determination)
5. You..........spend more time in your studies to get first division. (necessity)
6. Being a rich man Mohan......marry off his daughter to an engineer. (capability)
7. Every citizen.........obey the laws of the country. (obligation)
8. As you are a doctor, you..........attend every patient without any distinction. (moral obligation)
9. He.........take such a bold step. (absence of capability)
10. As I was out of station, I..........attend the meeting. (Absence of capability in past)
11. I am not confident, I ....... reach the winning post. (very remote possibility)
12. The censor board ......... impose a ban on the new release for its indecent content. (strong necessity)
13. Children ....... not remain awake till late at night. (normal requirement)
14. ......... you be the king of the world ! (wish)
15. Birds have started to chirp. It ......... be morning now. (conclusion)
Answers:
1. must,
2. may,
3. will,
4. will,
5. must,
6. can,
7. must,
8. ought to,
9. cannot,
10. couldn't,
11. might,
12. must,
13. should,
14. May,
5. must.

Exercise 4.
Write suitable modals with the help of the words given in the brackets :
1. ..........I have a look on the watch you have bought ? (permission)
2. You..........work hard as the examinations are near. (obligation)
3. You..........consult the doctor because you look seriously ill. (necessity)
4. Though the boy ran fast, he..........catch the train. (inability in past)
5. He..........lift this weight as he is a strong man. (capability)
6. We.......... hire a taxi to reach the bus-station. (obligation)
7. You.......... make up for the time as you are getting late. (absence of ability)
8. ..........you send me a calculator from Jaipur ? (request)
9. .........you, please, dial me 2460415 ? (polite request)
10. Ram..........serve his parents. (moral obligation)
11. We ......... not celebrate this holi pompously due to the tragic incident in the neighbourhood. (future plans)
12. Too many problems have crippled her personal life. Somebody ....... come forward to help her. (moral obligation)
13. We .......... abide by the traffic rules to avoid road mishaps. (neccessity)
14. We ........... prefer chocolate to sweets. (perference)
15. Man ......... be merciful to the birds. (Moral duty)
Answers:
1. May,
2. must,
3. must,
4. could not,
5. can,
6. must,
7. cannot,
8. Will,
9. Would,
10. ought to
11. shall,
12. ought to,
13. must,
14. would,
15. should.

Exercise 5.
Write suitable modals with the help of the words given in the brackets :
1. She............become an engineer. (determination)
2. If she is not feeling well, she...........get a good treatment. (strong advice)
3. I have lived in Germany for ten years and I.....Speak German fluently. (ability)
4. ..........you turn down your player ? (polite request)
5. ............help you in your distress. (promise)
6. The examiner ............ not read your illegible hand writing. (possibility)
7. As the train is late, you...........catch it.. (possibility)
8. You............go to the office because it is closed today. (lack of necessity)
9. You............switch on the light. (permission)
10. Major Rajya Verdhan Singh Rathore............win the silver medal in the Olympic Games. (past ability)
11. You ........ view the mountain ranges even from your terrace. (ability)
12. We ........ not make out anything from what he was speaking. (past ability)
13. One of the militants escaped from the police custody, he ....... be anywhere. (future probability)
14. ........ God bless this country with peace and stability! (wish)
15. He suffered all through his life so that his daughters ........ enjoy better future. (past purpose)
Answers:
1. will,
2. must,
3. can,
4. Would,
5. will,
6. may,
7. may,
8. needn't,
9. can,
10. could,
11. can,
12. could,
13. can,
14. May,
15. might.

Sentence Reordering
Exercise 6.
Reorder the following sentences to form meaningful sentences :
1. we/remain/what/cheerful/must/may/come.
2. do/it/can/rains/if/we/What/?
3. at/than/for/rather/I/a walk/go/home/stay/would.
4. carry/suitcase/shall/upstairs/your/the servant/?
5. the needle/you/I/for/thread/shall/ ?
6. that/could/had/wish for/a woman/everything/Ankita.
7. the concert/sing/will/tomorrow/in/you/ ?
8. what/tell/to do/shall/them/I/do/they.
9. the way/the hotel/tell/would/to/me/you/?
10. would/with/sometimes/me/get angry/my father.
11. oxygen/keep alive/to/must have/we.
12. wash/need/she/clothes/?
13. work/Mugdha/so hard/needn't.
14. this club/attend/members/the meeting/will/of/all/the.
15. write/next/try/l/time/better/to/will.
Answers:
1. Come what may we must remain cheerful.
2. What can we do if it rains ?
3. I would rather stay at home than go for a walk.
4. Shall the servant carry your suitcase upstairs ?
5. Shall I thread the needle for you ?
6. Ankita had everything that a woman could wish for.
7. Will you sing in the concert tomorrow ?
8. They shall do what I tell them to do.
9. Would you tell me the way to the hotel?
10. Sometimes my father would get angry with me.
11. We must have oxygen to keep alive.
12. Need she wash clothes ?
13. Mugdha needn't work so hard.
14. All the members of this club will attend the meeting.
15. I will try to write better next time.

Exercise 7.
Choose the correct alternative from the brackets and fill in the blanks :
1. I ......... not accept your challenge, you are too strong. (should/dare)
2. ........ you wait for sometime, please ? (May/Can)
3. ........ you like to accompany us to the Red Fort today? (Would/Will)
4. Oh ! You ....... be Mohan's wife. (must/should)
5. You have been coughing a lot recently. You ........ smoke so much. (shouldn't/mustn't)
6. ......... they return home so early ? (Must/Need)
7. Neha ......... be wishing she'd never taken the job. (might/must)
8. Kashmir daisies ........ be yellow or red. (may/can)
9. Excess of the prescribed dose of medicine ....... cause drowsiness. (may/will)
10. Everyone fully enjoyed her first novel, so the new one ....... be good. (shall/ought to)
11. I am perfectly comfortable. You ...... worry about me. (needn't/mustn't)
12. If I were in your situation, I ...... have ensured that nobody was denied his right. (should/would)
13. Students ....... run, there is ample time for school yet. (shouldn't/needn't)
14. The old sailor ....... sit for hours everyday watching the surging waves of the sea. (should/would)
15. I ........ rather buy a novel than a VCD. (would/will)
Answer:
1. dare,
2. Can,
3. Would,
4. must,
5. mustn't,
6. Need,
7. must,
8. can,
9. may,
10. ought to,
11. needn't,
12. should,
13. needn't,
14. would,
15. would.

Exercise 8. (From Textbook)
Choose the correct alternative from the brackets and fill in the blanks :
1. She ............. never have been pretty; but she was always beautiful. (could/can)
2. This time the village dogs ............. meet us at the temple door. (will/would)
3. When I came back she ............... ask me what the teacher had taught me. (could/would)
4. I ............. hear her reciting her prayers. (could/might)
5. Even before we .............. suspect, her lips stopped moving. (may/could)
6. We aren't afraid of dying if we ............... all be together. (may/can)
7. I knew we ............... have missed the island. (might/must)
8. He ............. see the island at about 5 p.m. (could/would)
9. What more ............... a CT scan reveal of Tut than the X-ray ? (will/would)
10. The father .............. not accept a son-in-law in such a profession. (could/would)
11. This ............. be compared with the yogic practice of pranayama. (may/can)
12. This State .............. endeavour to protect and improve the environment. (should/shall)
13. The constitution says that casteism, untouchability and bonded labour .......... be abolished (may/shall)
14. I .............. be playing golf. (might/must)
15. You .............. know what sadism is. (might/must).
Answers:
1. could,
2. would,
3. would,
4. could,
5. could,
6. can,
7. must,
8. could,
9. would,
10. would,
11.can,
12. shall,
13. shall,
14. might,
15. must.

Exercises 9.
(From Textbook)
Complete the following sentences using suitable modals :
1. At least it ............... show he had some feelings. (would/might)
2. I ............. admit I envy him the effect he seems to have on you boys in the form. (might/must)
3. Now I ............ not remember what the joke was. (can/may)
4. You .............. be good enough to explain it to them. (will/would)
5. He's at the Bursur's and ............... be there quite a time. (must/might)
6. You ............... do a job for him. (can/could)
7. He .............. go to a big library and browse through history books. (should/would)
8. As a historian he felt he ............... have thought of it sooner. (would/should)
9. To find the answer he ............. look for accounts of the battle itself. (might/must)
10. Gangadharpant .............. not help comparing the country he knew with what he was witnessing around him(would/could)
Answers:
1. would,
2. must,
3. can,
4. would,
5. might,
6. can,
7. would,
8. should,
9. must,
10. could.
Dialogue Completion
Exercise 10.
Complete the following dialogue using suitable modals :
Nisha : ....... (1) you mind my opening the window ?
Rajni : ....... (2) you keep it half closed ? I ....... (3) stand the chilly wind.
Nisha : No I ....... (4).
Rajni : Why ....... (5) you try ?
Nisha : 1 ....... (6) because there is no such device in the window.
Rajni : They ....... (7) have provided the window with such a device.
Nisha : Never mind. I....... (8) keep it tightly closed lest you ....... (9) catch cold.
Rajni : Thank you for being so caring. ....... (10) you do me another favour ?
Nisha : I...... (11) love to if I. ....... (12) ..........
Answer:
1. Would,
2. Could,
3. can't,
4. can't,
5. won't,
6. can't,
7. should,
8. will,
9. should,
10. Could,
11. would,
12. can.

Exercise 11.
Complete the following dialogue using suitable modals :
Sindhu : If you help me, we ....... (1) finish by seven.
Shobha : But I ....... (2) stay that long.
Sindhu : ....... (3) you spare a little more time for your sister ?
Shobha: You ....... (4) remind this to me. I know I ......... (5) help you.
Sindhu : As a younger sister I say you .... (6) stay a little longer and help me finish this work.
Shobha : You know my son ....... (7) be getting impatient. I ..........(8) come and help you finish this work tomorrow.
Sindhu : 0.K. ......... (9) I prepare a cup of tea for you?
Shobha : I don't take tea, so you ....... (10) prepare tea for me.
Answers:
1. can,
2. can't,
3. Won't,
4. needn't,
5. must,
6. should,
7. must,
8. will,
9. Shall,
10. needn't.

Exercise 12.
Complete the following dialogues using suitable modals :
(A) Hari : Father;......1.......I go to the market ?
Father : No, you .............. not.
Hari : It is urgent, as I ............... go.
Father : It .......4........ rain so you ................ not go, lest you .............. get wet.
(B) Sarla : Madam, ................ I come in ?
Teacher : Where were you ? You ................ be in the class at the right time.
Sarla : Sorry Madam. I ........3......... not get the direct bus.
Teacher : 0. K. but you .........4........... not come late in future.
Sarla : 1 ................... not repeat the mistake. Kindly pardon me this time.
(C) Old lady : ...................you kindly do me a favour, young boy ?
Young boy : What .................. I do for you?
Old lady : 1 .................. not go across the road. ........4......... you help me in crossing ........... the road ?
Young boy : You are just like my grandmother. I .........5......... gladly help you.
Answers:
(A) 1. may, 2. can, 3. must, 4. might, 5. should, 6. should.
(B) 1. may, 2. must, 3. could, 4. should, 5. will.
(C) 1. Would, 2. can, 3. dare, 4. Would, 5. will.
Sentence Transformation
Exercise 13
Transform the following sentences using the modals given in the brackets :
(A) 1. He is a strong man so he is able to lift this box. (Use : can)
2. There are clouds in the sky so it is likely to rain. (Use may)
3. I request you to tell me the way to the station. (Use : would)
4. Mahesh is advised not to play for a long time. (Use : should)
5. Rita is very weak so she is unable to play for a long time. (Use : can)
6. I request you to lend me your dictionary for a few days. (Use : would)
7. It is not necessary for me to obey you all the time. (Use : need)
8. She was in the habit of spending money on useless things. (Use : used to)
Answers:
1. He is a strong man so he can lift this box.
2. There are clouds in the sky so it may rain.
3. Would you tell me the way to the station ?
4. Mahesh should not play for a long time.
5. Rita is very weak so she cannot play for a long time.
6. Would you lend me your dictionary for a few days?
7. I need not obey you all the time.
8. She used to spend money on useless things.
(B) 1. You are given permission to go home as you have finished your work. (may)
2. You are able to lift this heavy box easily as you are a strong, man. (can)
3. You are not allowed to park your car here as it is a public place. (can)
4. I promise to give you a prize for you have passed the examination with flying colours. (will)
5. It is possible to rain tonight since it is very hot today. (may)
6. You are requested to post the letters which I have written. (will)
7. You are requested to shut the door as it is very cold today. (could)
8. Neeraj is able to speak English fluently as he reads in class XI. (can)
9. Perhaps it will rain today for there are clouds in the sky. (may)
10. You are prohibited to smoke in this office. (must not)
Answers:
1. You may go home as you have finished your work.
2. You can lift this heavy box easily as you are a strong man.
3. You cannot park your car here as it is a public place.
4. I will give you a prize for you have passed the examination with flying colours.
5. It may rain tonight since it is very hot today.
6. Will you post the letters which I have written, please ?
7. Could you shut the door as it is very cold today ?
8. Neeraj can speak English fluently as he reads in class XI.
9. It may rain today for there are clouds in the sky.
10. You must not smoke in this office.

Exercise 14.
Rewrite the following sentences converting modals into modal phrases :
1. Presently, I cannot solve this difficult puzzle.
2. Odds and evens may occur in anybody's life.
3. We ought to take care of the natural gifts.
4. You can beat him.
5. They shall not tease the girls in the street.
6. Nobody must step into the flower beds and pluck flowers.
7. You ought to have abided by the norms of the organisation.
8. He might be busy. 9. Would you inform her relatives ?
10. She must be very angry as somebody has stolen her purse.
Answer:
1. Presently, I am not able to solve this difficult puzzle.
2. Odds and evens are possible in anybody's life.
3. It is moral obligation to take care of the natural gifts.
4. You have the capacity to beat him.
5. They are warned not to tease the girls in the street.
6. Nobody is allowed to step into flower beds and pluck flowers.
7. It was your moral duty to abide by the norms of the organisation.
8. There is a remote possibility that he is busy.
9. We politely request you to inform her relatives.
10. I have reached the conclusion that she is very angry as somebody has stolen her purse.

- The Tale of Melon City Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 8 RBSE Solutions
- Birth Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 7 RBSE Solutions
- The Ghat of the Only World Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 6 RBSE Solutions
- Mother’s Day Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 5 RBSE Solutions
- Albert Einstein at School Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 4 RBSE Solutions
- Ranga’s Marriage Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 3 RBSE Solutions
- The Address Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 2 RBSE Solutions
- The Summer of the Beautiful White Horse Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 1 RBSE Solutions
- Father to Son Question Answer Class 11 English Hornbill Chapter 5 RBSE Solutions
- Childhood Question Answer Class 11 English Hornbill Chapter 4 RBSE Solutions
- The Voice of the Rain Question Answer Class 11 English Hornbill Chapter 3 RBSE Solutions