RBSE Class 11 English Grammar Determiners
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 English Grammar Determiners Exercise Questions and Answers.
The questions presented in the RBSE Solutions for Class 11 English are solved in a detailed manner. Get the accurate RBSE Solutions for Class 11 all subjects will help students to have a deeper understanding of the concepts. Our team has come up with Tenses Class 11 to ensure that students have basic grammatical knowledge.
RBSE Class 11 English Grammar Determiners
What is a Determiner ?
Determiners वे शब्द हैं जो किसी Noun के पूर्व आकर उस Noun की पहचान सुनिश्चित करते हैं। Determiner के प्रयोग के तुरन्त बाद Noun का प्रयोग आवश्यक हो जाता है । कभी-कभी Determiner तथा Noun के बीच कोई qualifying word भी आ सकता है ।।

Determiners की परिभाषा के अनुसार चूँकि ये शब्द Noun से पूर्व प्रयुक्त होकर उसकी विशेषता बताते हैं अथवा उसका सुनिश्चयन करते हैं । अतः इनका सही प्रयोग करने के लिए Noun के विषय में निम्नलिखित बातों का ज्ञान होना आवश्यक है -
(i) वाक्य में दिया गया Noun Countable है या Uncountable.
(ii) यदि दिया गया Noun Countable है तो वह Singular Number है अथवा Plural Number.
गिनती की दृष्टि से Nouns दो प्रकार के होते हैं -
(i) Countable Nouns तथा
(ii) Uncountable Nouns

(i) Countable Noun
जिस Noun (संज्ञा) को गिना जा सके उसे Countable Noun कहते हैं, जैसे - apple, bag, boy, chair, dog, goat, horse, school, आदि । इन्हें भी Number (वचन) की दृष्टि से (A) Singular Countable Nouns तथा (B) Plural Countable Nouns में विभाजित किया जा सकता है।
(A) Singular Nouns (एकवचन संज्ञा) - ये Nouns एक व्यक्ति, वस्तु अथवा स्थान के लिए प्रयुक्त होते हैं ।
(B) Plural Nouns (बहुवचन संज्ञा) - ये Nouns एक से अधिक व्यक्तियों, वस्तुओं अथवा स्थानों के लिए प्रयुक्त होते हैं, जैसे -
Singular Number -- Plural Number
apple -- apples
dog -- dogs
bag -- bags
boy -- boys
(ii) Uncountable Noun
जिन Nouns को गिना नहीं जा सके अथवा जिनको गिना जाना सामान्य परिस्थितियों में अत्यन्त कठिन एवं कष्टसाध्य हो, उन्हें Uncountable Nouns कहते हैं , जैसे -milk, sugar, tea, oil, air, wind, fire, आदि। Uncountable Nouns का Plural नहीं होता है ।।
Countable तथा Uncountable Nouns के कुछ उदाहरण नीचे दिये जा रहे हैं, जिससे कि आप इनके पूर्व उचित Determiners का प्रयोग कर सकें।
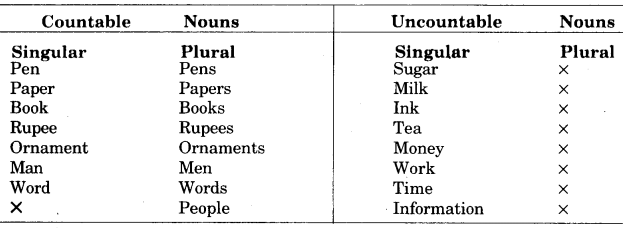
प्रमुख Determiners हैं - a, an, the, some, any, little, a little, the little, few, a few, the few. many, much, each, every, none, no/not any, this, that, these, there, both, all, either, neither. various, several, such, such a, less, fewer, enough, not enough, lots of, a lot of, a great, a great deal of, plenty of, a large number of.

1. Use of 'A' and 'An'. Indefinite Articles
'A' तथा 'An' का प्रयोग मूलतः शब्दों के उच्चारण के समय होने वाली ध्वनियों (sounds) से सम्वन्ध रखता :
'A' का प्रयोग ऐसे शब्दों के पूर्व होता है, जिनका उच्चारण करते समय प्रारम्भ में व्यंजन-ध्वनि
(Consonant soura निकलती हो, चाहे शब्द का प्रथम अक्षर Vowel (स्वर) हो या Consonant (व्यञ्जन); जैसे -
a man a boy a university a European
a pen a dog a useful thing a one-eyed man
(a) 'University' (यूनिवर्सिटि) में U का उच्चारण 'यू' की तरह है और 'यू' की ध्वनि Consonant (व्यञ्जन।' जैसी है । इसलिए इसके पहले a लगेगा । यदि U का उच्चारण 'अ' हो, जैसे- umbrella (अम्ब्रेला), umpire (अम्पायर : हो तो an का प्रयोग होगा ।
An का प्रयोग ऐसे शब्दों के पूर्व होता है, जिनका उच्चारण करते समय प्रारम्भ में स्वर-ध्वनि (Vowel sounts. निकलती हो, भले ही उस शब्द का प्रथम अक्षर Vowel हो या Consonant हो; जैसे

(b) 'Hour' में 'h' silent है । उसके बाद ‘o' आता है जो Vowel (स्वर) की ध्वनि देता है इसलिए इस .. के पहले ‘an' लगेगा ।
Note : a तथा an अंग्रेजी के 'one' शब्द के कमजोर रूप (weak forms) हैं । इनका प्रयोग Countaht Singular Nouns (गिनने योग्य एकवचन संज्ञाओं) के पहले किया जाता है । बहुवचन संज्ञाओं (Plural Nouns) नः अगणनीय संज्ञाओं (Uncountable Nouns) के पहले इनका प्रयोग नहीं होता है । पदार्थवाचक एवं भाववाचक संज्ञा (Material Nouns and Abstract Nouns) अगणनीय संज्ञाओं (Uncountable Nouns) में ही गिनी जाती हैं । इ...' पहले तब तक a या an प्रयुक्त नहीं होता है, जब तक वे Countable Nouns के रूप में प्रयुक्त नहीं होते ।।

A तथा An का प्रयोग निम्नलिखित विन्दुओं के आधार पर समझा एवं उनका प्रयोग किया जा सकता है :
(1) प्रथम बार प्रयुक्त होने वाले Singular Countable Nouns (एकवचन गिनने योग्य संज्ञाओं) पहले :
- I have a book.
- She lives in a hut.
- He saw an old man.
- Mr Sharma is an umpire in this match.
(2) ऐसी एकवचन पूरक संज्ञाओं (Noun Complements) से पूर्व जो किसी पेशे या व्यवसाय (profession) : सम्बन्धित हों :
- She is a nurse.
- He is an engineer.
- Neeraj is a doctor.
- She is an actress.
(3) Adjective + Noun की स्थिति में a अथवा an का प्रयोग Adjective (विशेषण) से पूर्व उसकी प्रारम्भिक ध्व के अनुसार होता है ।।
- a big elephant.
- an old woman.
- an ugly child.
- a useful book.
(4) ऐसी अभिव्यक्तियों के लिए जो मूल्य, गति, अनुपात आदि का बोध कराती हों :
two rupees a kilo, six times a day, eighty rupees a dozen, 20 km an hour, ten rupees; meter इत्यादि।
(5) संख्यात्मक/मात्रात्मक अभिव्यक्तियों से पूर्व :
a pair, a couple, a dozen, half a dozen, a hundred, a thousand, a lot, a great deal, a great man, a quarter, a million इत्यादि ।
(6) few और little के साथ :
- He borrowed a few books from the library.
- Please take a little more tea.
Note -
(i) a few का अर्थ a small number (थोड़ी संख्या) से होता है, जितने से वक्ता का तात्पर्य हो । इसी प्रकार, a little का अर्थ a small amount (थोड़ी मात्रा) से होता है ।
(ii) few और little का प्रयोग बिना a के भी होता है, लेकिन ये ‘लगभग नहीं' का अर्थ ले लेते हैं, जैसेः

1. Few people know this fact. (The fact is almost unknown.)
2. She had little time to attend the meeting. (She had almost no time .............)
(7) विभिन्न भावों को व्यक्त करने वाले Exclamatory Sentences में एकवचन संज्ञा (Singular Noun) के पहले आने वाले विशेषण-शब्द (Adjective) के पूर्व :
- What a beautiful flower !
- What a pretty colour !
- What an old fellow !
- What a cold day !
(8) Such का प्रयोग किसी Countable Noun के साथ होने पर Such के बाद a अथवा an का प्रयोग किया जाता है :
- It was such a good deed.
- He was such a helpful friend.
- It was such an interesting story.
(9) विभिन्न उपाधियों या पदों (degrees or posts) के संक्षिप्त रूपों (abbreviated forms) के पहले निम्न प्रकार से a अथवा an का प्रयोग होता है ।
उदाहरण : an M.A., an M.Sc., an M. Com., an S.P., an S. D. M., an L. L. B., a U. D. C., an L.D.C इत्यादि ।
(10) 'a' तथा 'an' का प्रयोग ‘एक-से' (the same) के अर्थ में भी होता है :
- Birds of a feather flock together.
- These are but two sides of a coin.
- Men of a mind always group together.
- Take two at a time.

(11) Mr / Mrs / Miss + surname के पहले वक्ता से उनका परिचय न होने का भाव दर्शाने के लिए a का प्रयोग होता है :
a Mr Sharma, a Mrs Mathur, a Miss Gupta इत्यादि ।।
(a Mr Sharma से आशय ऐसे व्यक्ति से है, जो Mr Sharma के नाम से पुकारा जाता है परन्तु वक्ता से अपरिचित है; परिचित अवस्था में केवल Mr Sharma या Mrs Mathur ..... लिखते हैं ।)
Exercise 1.
Fill in the following blanks with 'a' or 'an':
1. He was...............wise teacher.
2. The meeting was held in...............big hall.
3. ............... burnt child dreads the fire.
4. She spent...............few months in Mumbai last year.
5. Now cricket has become...............international game.
6. They will be back in...............week.
7. I will finish this work within...............hour.
Answers:
1. a
2. a
3. A
4. a
5. an
6. a
7. an.

Exercise 2.
Fill in the blanks in the following sentences with 'a' or 'an':
1. He is ............... honest man of our city.
2. Let us rest here for ............... while.
3. Can you give ............... example of a cruel king ?
4. We shall go for ............... walk now.
5. She often tells ............... lie.
6. Certainly, it is ............... very interesting story.
7. She bought ............... electric iron for ₹ 350.
Answers:
1. an
2. a
3. an
4. a
5. a
6. a
7. an.
2. Use of 'the' -- Definite Article.
The एक definite article है और इसका प्रयोग Singular व Plural Nouns के पूर्व निम्नलिखित स्थितियों में किया जाता है
(1) ऐसे Noun के पहले जिसका पूर्व में उल्लेख किया जा चुका हो :
- I saw a lion. The lion was sleeping under a tree.
पहले वाक्य में मैंने एक शेर देखा । (दूसरे वाक्य में वही) शेर पेड़ के नीचे सो रहा था । - 2. We heard a noise. The noise came from a neighbour's house.
- 3. I have lost the pen which I bought yesterday.
(2) Adjectives की Superlative Degree के पहले :
- Ravi is the best singer in the school.
- My uncle is the richest man in the town.
अपवाद : किसी सम्वन्धवाचक विशेषण (Possessive Adjective) जैसे : my, his, her, their, your, our के वाद Adjective को Superlative Degree का प्रयोग होने पर the का प्रयोग नहीं होता, जैसे :
- He is my best friend.
- Mr Dixit is our best teacher.

(3) किसी शब्द-समूह (Phrase) या उपवाक्य (Clause) से सुनिश्चित होने वाले Noun के पहले :
- The girl in the blue skirt is my sister.
- The man with a little nose is our Principal.
- The cars made in our factory are the strongest ones.
- The book on the table belongs to the library.
- The man who went out is an excellent singer.
(4) ऐसे singular noun के पहले जो अपनी सम्पूर्ण जाति (the whole class or race) का बोध कराता है :
- The dog is a faithful animal. (यहाँ अर्थ 'समस्त कुत्ता जाति') से है।
- The elephant has a long trunk.
- The cat likes milk.
(5) नदियों, सागरों, महासागरों, खाड़ियों, मरुस्थलों, द्वीप-समूहों, पर्वत-शृंखलाओं, नहरों, जंगलों तथा छोटे-छोटे देशों से मिलकर बने (संयुक्त) देशों के बहुवचनीय नामों के साथः
- The Ganga, The Yamuna (rivers)
- The Bay of Bengal (बंगाल की खाड़ी),
- The Arabian Sea (अरब सागर)
- The Gulf of Maxico (मेक्सिको की खाड़ी),
- The Thar, The Sahara (सहारा मरुस्थल)
- The Himalayas, The UK (इंग्लैण्ड का नाम),
- The West Indies, The USA (संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका)
Note : झीलों के नाम के पूर्व Lake, पर्वत या चोटी के नाम के पूर्व Mount व किसी अन्तरीप के नाम से पूर्व Cape
शब्द का प्रयोग होने की स्थिति में The का प्रयोग नहीं होता है, जैसे :
Cape Camorin, Mount Everest, Lake Mansarovar इत्यादि ।
(6) संज्ञा (Noun) की तरह प्रयुक्त होने वाले विशेषण (Adjective) शब्दों के पूर्व the का प्रयोग होता है :
- The brave always rule over the earth. (बहादुर लोग)
- The rich should help the poor. (अमीर लोग)
- The weak can never do anything. (कमजोर लोग)
7. विश्व में अपने ढंग की अनोखी अथवा एकमात्र वस्तुओं के लिए :
The sun, the moon, the sky, the earth, the world, the Taj, the wall of China.
8. दिशाओं के नाम के पहले :
The east, the west, the south, the north.
9. ऐसे नामों के पहले जो Adjective + Noun या adjective + of + noun रूप में हों :
The National Highway, the New South Coast, the Gold Coast, the Bay of Bengal.
(10) धार्मिक पुस्तकों, वाद्य-यन्त्रों एवं निश्चित संख्याओं (ordinals) से पूर्व :
The Geeta, the Bible, the Quran, the Ramayana, the violin, the flute, the first, the fourth, the eleventh, the last, the next इत्यादि ।
(11) एक ही वाक्य में Comparative Degree के दो बार प्रयोग होने की स्थिति में :
- The more you have, the more you want.
- The sooner, the better.
- The higher you go, the cooler you feel.
- The better I know her, the more I admire her.
(12) जब किसी Proper Noun (व्यक्तिवाचक संज्ञा) की तुलना किसी अन्य प्रसिद्ध व्यक्ति, स्थान या वस्तु से की जाती _है : (जातिवाचक संज्ञा की तरह से प्रयुक्त होने पर)
- Kalidas is the Shakespeare of India.
- Kashmir is the Switzerland of India.
(13) धर्म, समुदाय, जाति, राष्ट्रीयता, राजनीतिक दलों, जहाजों, रेलगाड़ियों, हवाई जहाजों, जलपोतों आदि के
नाम के पहले : The Hindus, the Sikhs, the Jats, the Sanatanees, the Vaishnavas, the English, the Indians, the Americans, the Congress, the B.J.P., the Nilgiri, the Kanishka, the Vikrant, the Chetak Express.
(14) Plural Surnames के पहले जब वे पूरे परिवार का अर्थ देते हैं :
The Guptas, the Sharmas, the Mathurs (माथुर परिवार) इत्यादि ।।
(15) शरीर के अंगों के नाम के पहले जब इनके पूर्व कोई possessive न दिया हो :
- He caught her by the hair.
- She grabbed him by the neck.

(16) तारीखों एवं राष्ट्रीय महत्व के दिनों के पहले :
The 25th July, the 15th August, the 26th January, the Independence Day, the Republic Day इत्यादि ।
(17) Same, only, opposite, front, end, beginning जैसे शब्दों के पूर्व :
The same scene, the only son, the opposite party, the front page, the end of the play, the beginning of the story.
(18) All, some of ........... (Plural Noun), one of ............ (Plural Noun), each of ...............
(Plural Noun) के साथ : All the boys, some of the students, one of the girls, each of the winners.
The Omission of the Definite Article 'the'
निम्नलिखित स्थितियों में Definite Article 'the' का प्रयोग नहीं होता है :
(1) Proper Noun (व्यक्तिवाचक संज्ञा), Material Noun (पदार्थवाचक संज्ञा) तथा Abstract Noun (भाववाचक संज्ञा) के पूर्व :
- Arjun was a great archer.
- Gold is more costly than silver.
- Wisdom is greater than wealth.
(2) जब किसी Common Noun का व्यापक अर्थ में प्रयोग होता हो :
- Man is mortal.
- Man is a social animal.
(3) भाषाओं, अध्ययन के विषयों, सार्वजनिक स्थलों, खेलों, बीमारियों तथा निश्चित समय पर किये जाने वाले साधारण भोजनों के नाम के पहले :
- I am learning French.
- She doesn't like physics.
- We go to hospital when we are ill.
- They go to school regularly.
- We play hockey every day.
- I have lunch at noon.
- She is suffering from pneumonia. (निमोनिया)
- He goes to temple daily.
(4) राष्ट्रों, रंगों, त्यौहारों के नाम के पहले :
- India has a very old and rich culture.
- The leaves of this plant have turned yellow.
- Diwali is celebrated with pomp and show.
(5) महीनों, दिनों तथा ऋतुओं के नाम के पहले :
- January is the first month of the year.
- Sunday comes before Monday.
- Spring is the first season of the year. (also The spring)
(6) God शब्द के पहले इसका प्रयोग नहीं होता (जब 'G' बड़े अक्षर में लिखा गया हो और इसका अर्थ 'ईश्वर' हो):
- He prayed to God for help.
- God is everywhere and within every soul.

(7) 'kind of' तथा 'sort of' के बाद Definite Article नहीं आता, जैसे :
- What kind of man is he?
- He is a right sort of man.
(8) Church, market, school, college, hospital, prison, bed के पूर्व DefiniteArticle नहीं लगाते, यदि इनका प्रयोग उनके मुख्य कार्यों के लिए किया गया हो । Church में प्रार्थना के लिए जाते हैं; market में खरीदारी करने के लिए जाते हैं; school, college में पढ़ने के लिए जाते हैं; hospital में इलाज के लिए; prison में सजा भोगने के लिए तथा bed पर सोने के लिए जाते हैं-अतः यदि इसी अर्थ में इन शब्दों का प्रयोग होता है, तो इन शब्दों के पूर्व Definite Article नहीं लगता, जैसे :
1. My son goes to school. (पढ़ने के लिए)
2. Father is going to hospital. (इलाज के लिए)
3. The thief has been sent to prison. (सजा काटने के लिए)
4. You will have to go to court. (वाद-विवाद या झगड़ा निबटाने के लिए)
5. I go to bed late at night. (सोने के लिए)
6. He goes to church every Sunday. (प्रार्थना के लिए)
लेकिन यदि इनका प्रयोग दूसरे रूप में हो तो Definite Article लगाते हैं, जैसे :
1. I am going to the school to enquire about the progress of my son.
2. Father is going to the hospital to see his friend.
3. Shall we go to the prison to know the prisoner's condition ?
4. I am going to the court to see the dacoits.
5. The school is at the next crossing.
6. The market is closed today.
7. The church of Ajmer is very grand. Proper Noun + s + Noun से पहले Definite Article नहीं आता, जैसे :
This is Mohan's house. (यहाँ the Mohan's house नहीं लिखना चाहिए
8. This is Hari's book. (यहाँ the Hari's book नहीं लिखना चाहिए
9. परन्तु यदि Common Noun के साथ 's आता है, तो इसके पहले Article लगाते हैं, जैसे -
(a) That is an old man's room.
(b) This is a priest's hut.
(10) Possessive Adjective के बाद Definite Article नहीं लगेगा, जैसे : This is my house. I know his address.
(11) शरीर के अंगों के पूर्व कोई Article नहीं लगाते जब उनके पूर्व Possessive Adjective/Noun दिया हो, जैसे : his right hand. her left eye.

Exercise 3.
Fill in the following blanks with 'a', 'an' or 'the' and cross (x) where none of them is needed
1. We study in .............. same school.
2. We shall be in Delhi on .............. Republic Day this year.
3. He has suffered .............. lot.
4. ............... Chetak Express is late today.
5. Somu is .............. tallest boy in his class.
6. A fox is cleverer than .............. crow. condition of the boy is serious,
Answers:
1. the
2. the
3. a
4. The
5. the
6. a
7. The.
Exercise 4.
Use 'a', 'an' or 'the' in the following blanks and put cross (x) where none of them is needed:
1. He should set .............. example before others.
2. The Himalayas lie in .............. north of our country.
3. She is in .............. hurry.
4. He needs an hour and .............. half to complete this work.
5. The police have arrested .............. thief.
6. What kind of .............. man you are !
Answers:
1. an
2. the
3. a
4. a
5. the
6. a.
3. Some का प्रयोग
Some का अर्थ है- 'कुछ' (an unknown and indefinite number or quantity) अर्थात् अज्ञात या अनिश्चित संख्या या मात्रा ।
Some का प्रयोग Uncountable (न गिनने योग्य) तथा Countable (गिनने योग्य) दोनों ही Nouns के पूर्व होता है । इसका प्रयोग Singular (एकवचन) तथा Plural (बहुवचन) दोनों ही प्रकार की संज्ञाओं से पूर्व किया जा सकता है ।
(A) Some का प्रयोग Affirmative sentences ( सकारात्मक वाक्यों) में किया जाता है। जैसे -
1. There is some milk in the pot. (Uncountable Noun - 'milk')
2. There is some one on the road. (Singular Countable Noun - 'one')
3. Some boys are playing there. (Plural Countable Noun - 'boys')
नोट : उपरोक्त तीनों वाक्य Affirmative (सकारात्मक) हैं ।।
(B) Some का प्रयोग Request (निवेदन) में भी किया जाता है । जैसे -
1. Will you please lend me some money ? (Don't use ‘any' here.)
क्या आप मुझे कुछ धन देने की कृपा करेंगे ?
2. Will you spare some time for me ? (Don't use 'any' here.)
क्या आप मेरे लिए कुछ समय निकालेंगे ?
नोट : उपरोक्त दोनों वाक्य Request (निवेदन) का बोध कराते हैं । अतः इन वाक्यों के अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न (?) होने के बावजूद भी इनमें some का ही प्रयोग होगा ।
(C) Some का प्रयोग Command (आदेश) बोधक वाक्यों में भी किया जाता है । जैसे
1. Why don't you give him some oranges ? (Don't use ‘any' here.)
आप उसे कुछ सन्तरे क्यों नहीं देते ?
2. Why don't you help someone in trouble ? (Don't use ‘any' here.)
आप किसी की कठिनाई में सहायता क्यों नहीं करते ?
नोट : उपरोक्त दोनों वाक्य Command (आदेश) का बोध कराते हैं । अतः इनके अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न (?) होने के बावजूद इन वाक्यों में some का प्रयोग होगा ।
(D) Some का प्रयोग उन प्रश्नों में भी किया जा सकता है जो Invitation (निमन्त्रण) का बोध कराते हैं ।
जैसे - Will you please visit us some day? क्या आप किसी दिन हमारे यहाँ पधारेंगे ?
नोट : उपरोक्त वाक्य Invitation (निमन्त्रण) का बोध कराता है ।
अतः अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न होने के बावजूद इस वाक्य में some का प्रयोग हुआ है

4. Any का प्रयोग
Any का अर्थ है – 'कुछ' या 'कोई' (an indefinite number or quantity) - अनिश्चित संख्या या मात्रा)। Any का प्रयोग भी Uncountable (नहीं गिनने योग्य) तथा Countable (गिनने योग्य) दोनों ही Nouns के पूर्व होता है । इसका प्रयोग भी Singular (एकवचन) तथा Plural (बहुवचन) दोनों ही प्रकार की संज्ञाओं के पूर्व किया जा सकता है ।
(A) Any का प्रयोग Negative ( नकारात्मक) तथा Interrogative (प्रश्नवाचक) वाक्यों में किया जाता है । जैसे -
- He did not do any work. (Uncountable Noun 'work')
- I don't want any money. (Uncountable Noun ‘money)
- Have you any book ? (Singular Countable Noun 'book')
- Are there any pens in the drawer ? (Plural Countable Noun 'pens')
(B) dick a if, whether, hardly, scarcely, never, rarely, seldom, deny, fail, forbid, prohibit, impossible, unlikely तथा barely के पश्चात् any का प्रयोग होता है, चाहे वाक्य Affirmative ही क्यों न हो । जैसे --
- He has hardly any money.
- There is scarcely any garden in a desert.
- The teacher asked if we had any questions.
- I wonder whether there is any milk in this jug.
(C) Any का प्रयोग 'one of a number of things or people' ( वस्तुओं या व्यक्तियों में से कोई एक') के अर्थ में Affirmative Sentences में किया जाता है । जैसे -
- Take any book you like. (पुस्तकों में से कोई 'एक')
- Any policeman will tell you the way. (सिपाहियों में से कोई 'एक')
- Any colour will do. (रंगों में से कोई 'एक') -
SOME और ANY में अन्तर Some का प्रयोग अक्सर Affirmative Sentences में तथा any का प्रयोग Negative तथा Interrogative Sentences में होता है । यह मुख्य अन्तर हमेशा याद रखें ।
Exercise 5.
Fill in the blanks with 'Some' or 'Any' as required -
आवश्यकतानुसार 'some' अथवा 'any' से रिक्त स्थान भरिये --
1. There are .............. trees behind our school.
2. Is there .............. letter for me ?
3. There is .............. sugar in this pot.
4. Take .............. book you need.
5. There are .............. monkeys on the roof.
6. There was .............. petrol in my bike but there isn't ..............now.
7. I bought .............. vegetables but I didn't buy .............. fruits.
Answers:
1. some
2. any
3. some
4. any
5. some
6. some, any
7. some, any.
5. Many/Much का प्रयोग
1. Many : Many से संख्या (number) का बोध होता है । अत: इसका प्रयोग सदा ही बहुवचन गिनने योग्य संज्ञाओं (Plural Countable Nouns) के पूर्व होता है ।
उदाहरण :
1. Hari has many story books.
2. I have many friends.
3. I don't have many cars.
2. Much : Much से मात्रा (quantity) का बोध होता है । अतः इसका प्रयोग एकवचन न गिनने योग्य संज्ञाओं (Singular Uncountable Nouns) के पूर्व किया जाता है ।
उदाहरण :
1. He has not much gold and silver.
2. I don't have much milk.
3. Did you buy much food ?
Many/Much से सम्बन्धित कुछ नियम नियम
1. much/many का प्रयोग object के रूप में केवल interrogative/negative sentences के साथ ही होता है । इनका प्रयोग affirmative sentence में object के रूप में नहीं किया जा सकता है। जैसे - Negative:

A - Negative :
1. Mohan hasn't much money.
2. I haven't many friends.
3. They haven't got much luggage.
4. I don't know many people.
5. I don't drink much coffee.
6. I didn't take many photographs.
Interrogative:
1. Did she buy much sugar ?
2. Did she buy many books ?
3. How much money do you want?
4. How many photographs did you take ?
5. Do you drink much tea?
6. Did you teach many boys in the class ?
नियम 2. much/many का प्रयोग affirmative sentences में subject के साथ बहुत / कई के अर्थ
1. Many men attended the function.
2. Much money was wasted to improve the condition of the poor.
नियम 3. much/many का प्रयोग subject/object दोनों ही रूपों में affirmative sentences के साथ सम्भव है यदि इनके साथ solas/too का प्रयोग किया जाये । जैसे -
1. There are too many cars on the road.
2. I have got so much work to do.
3. He had so much money as you.
नियम 4. केवल many का प्रयोग एक affirmative sentence में subject/object के साथ किया जा सकता है यदि इसके पहले a good a great शब्द दिया हो तो । जैसे
Her son made a good many friends in the village.

Method

Exercise 6.
Fill in the blanks with ‘many' or 'much':
1. She hasn't learnt.............lessons yet.
2. How.............friends are coming to the party?
3. How.............milk do you want in your tea ?
4. Did you like.............sugar in coffee ?
5. .............students attended the function.
6. There are not.............temples in our town
7. I haven't got............. petrol in my motorcycle.
8. Hurry up ! We haven't.............time.
9. Not ............. trees were planted.
10. It is not good to take ............ tea.
Answers:
1. many
2. many
3. much
4.much
5. Many
6. many
7. much
8. much
9. many
10. much.

6. Little, A little तथा The little का प्रयोग
1. Little का प्रयोग
Little का अर्थ है - 'अत्यल्प', 'कुछ नहीं' या 'न के बराबर' (hardly any or not much)
'Little' का प्रयोग Uncountable Nouns (न गिनने योग्य संज्ञाओं) से पूर्व होता है । यह Negative meaning प्रदान करता है । जैसे -
1. I am very busy. I have little time for playing.
मेरे पास खेलने के लिए समय ‘बहुत कम' है अर्थात् समय नहीं है ।
2. He has little money. He is very poor.
उसके पास धन 'जरा भी नहीं' है ।
3. There is little milk in the jug. It is nearly empty.
जग में 'जरा भी दूध नहीं' है ।
4. He is very serious. There is little hope of his recovery.
उसके ठीक होने की आशा 'नहीं' (न के बराबर) है ।
2. A littie का प्रयोग
A little का अर्थ है - 'अल्प', 'थोड़ा' (Some quantity though not much)
A little का प्रयोग भी Uncountable Nouns (नहीं गिनने योग्य संज्ञाओं) से पूर्व होता है । यह Positive meaning प्रदान करता है । जैसे -
1. A little knowledge is a dangerous thing.
'थोड़ा' ज्ञान खतरनाक होता है ।
2. There is a little milk in the jug.
जग में 'थोडा-सा' दूध है ।
3. He has a little money.
उसके पास 'थोड़ा' धन है ।
4. I took a little food in the morning.
मैंने सुबह 'थोड़ा' भोजन किया ।
3. The little का प्रयोग
The little का अर्थ है –'जो भी थोड़ा-सा' 'कुछ किन्तु सब' (not much, but all that is)
The little का प्रयोग भी Uncountable Nouns (न गिनने योग्य संज्ञाओं ) से पूर्व होता है । यह समग्रता (all that is) का बोध कराता है, जैसे -
1. He wasted the little time he had.
उसके पास 'जो थोड़ा-सा' समय था उसने उसे बर्बाद कर दिया ।
2. I gave the beggar the little money I had.
मेरे पास 'जो थोड़ा-सा' धन था वह मैंने एक भिखारी को दे दिया ।
3. I ate the little food you gave me.
तुमने मुझे 'जो थोड़ा-सा' भोजन दिया वह मैंने खा लिया ।
4. Do not waste the little energy you possess.
तुम्हारे पास 'जो थोड़ी-सी' ऊर्जा है उसे बर्बाद मत करो ।
नोट - इसमें Noun की मात्रा को बताने के लिए Noun के ठीक बाद एक Clause दिया रहता है ।

Little, A little तथा The little का तुलनात्मक विवरण
Little = Hardly any or not much. (न के बराबर) (Negative)
A Little = Some quantity though not much. (Positive)
The Little = Not much but all that is. (कुछ किन्तु सब) (Positive)
There is little milk in the glass. गिलास में न के बराबर दूध है।
There is a little milk in the glass.
गिलास में थोड़ा दूध है ।
He drank the little milk that was in the glass.
गिलास में 'जितना भी थोड़ा-सा' दूध था वह सब उसने पी लिया ।
7. Few, A few तथा The few का प्रयोग
1. Few का प्रयोग
Few का अर्थ है 'नगण्य' 'न के बराबर' (not many, hardly any) 'मुश्किल से कोई या कुछ'। Few का प्रयोग Plural Countable Nouns (बहुवचन गिनने योग्य संज्ञाओं) से पूर्व किया जाता है । यह Negative meaning प्रदान करता है । जैसे -
1. There were few people at the meeting. सभा में बहुत कम' लोग थे । (अर्थात् 'न के बराबर')
2. He has read few books. उसने ‘बहुत कम' पुस्तकें पढ़ीं हैं । (अर्थात् 'न के बराबर')
3. He has few friends so he often feels lonely. (अर्थात् 'न के बराबर')
उसके 'मुश्किल से कुछ ही' मित्र हैं इसलिए वह अक्सर अकेलापन महसूस करता है ।
2. A few का प्रयोग
A few का अर्थ है – 'कुछ' या 'कम से कम कुछ' । (some; if not many or some at least.)
A few का प्रयोग Plural Countable Nouns (बहुवचन गिनने योग्य संज्ञाओं) से पूर्व किया जाता है । यह Positive meaning प्रदान करता है । जैसे
1. We received a few letters today.
हमने आज 'कुछ' पत्र प्राप्त किये । (Positive)
2. Only a few boys passed in English.
(Positive) अंग्रेजी में केवल 'कुछ ही' छात्र उत्तीर्ण हुए ।
3. A few persons were invited to tea. (Positive)
'कुछ' व्यक्ति ही चाय पर आमन्त्रित किये गये ।
3. The few का प्रयोग
The few का अर्थ है - “जो भी थोड़े' या 'कुछ किन्तु जो भी हों सब' । (not many but all that are)
The few का प्रयोग Plural Countable Nouns (बहुवचन, गिनने योग्य संज्ञाओं) से पूर्व होता है । यह Positive meaning प्रदान करता है । जैसे -
1. The few friends he had deserted him when he was in trouble.
'जो भी थोड़े-से' उसके मित्र थे वे उसे विपत्ति में छोड़कर चले गये ।
2. The few oranges which were lying in the basket were rotten.
'जो भी थोड़े-से' सन्तरे टोकरी में पड़े थे वे सबके सब सड़े हुए थे ।
3. I have already read the few books I had.
मेरे पास ‘जो भी थोड़ी-सी' पुस्तकें थीं वे सब मैंने पहले ही पढ़ ली हैं ।
4. I gave the beggar the few rupees I had.
'जो भी थोड़े-से' रुपये मेरे पास थे वे सब मैंने भिखारी को दे दिये ।
नोट - इसमें Noun की संख्या को बताने के लिए Noun Clause के बाद एक Clause दिया रहता है ।

Few, A few तथा The few का तुलनात्मक विवरण
Few = not many (नगण्य) (Negative)
A few = some (कुछ) (Positive)
The few = not many but all that are (जो भी थोड़े वे सब) (Positive)
1. I have few books on English. (पुस्तकें 'नहीं के बराबर ही' हैं ।)
2. I have a few books on English. ('कुछ' पुस्तकें हैं ।)
3. I have read the few books I have on English. ('जो भी कुछ' पुस्तकें हैं वे 'सब')
Few तथा Little में अन्तर
|
Few, a few, the few |
Little, a little, the little 1. Uncountable Nouns से पूर्व आते हैं। |
Exercise 7.
Fill in the blanks with little.
a little, the little, few, a few or the few :
1. There is ........... food in the fridge. It is nearly empty.
2. Last night I sent ........... messages to my friends.
3. Can I have ........... sugar in my milk, please ?
4. I can't tell you at this time. I need ........... time.
5. There was ........... traffic so we didn't get late.
6. Bus service in our area is not very good. There are ........... buses after 10. p.m.
7. "Would you like ........... biscuits ?" "Yes,please."
8. ........... people live upto 100 years.
9. They still have ........... money left in the bank.
10. ........... milk which was in the pot turned sour.
Answers:
1. little,
2. a few,
3. a little,
4. a little,
5. little,
6. few,
7. a few,
8. Few,
9. a little,
10. The little.

Exercise 8.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate determiner
much, many, some, any, a little, the little:
1. Mary hasn't got.............work to do.
2. She did not invite ............ people to the party.
3. She wasted.............money she had.
4. I haven't got.............money.
5. He hasn't drunk.............wine.
6. I haven't met her.............times.
7. How .............soldiers were killed during the war ?
8. Don't eat.............more snacks. Leave.............snacks for your sister.
9. Please pay.............attention to what your teacher says.
10. .............people are very kind and helpful.
Answers:
1. any,
2. many,
3. the little,
4. any,
5. much,
6. many,
7. many,
8. any, some,
9. a little,
10. A few.
8. Use of Each, Every
Each का प्रयोग दो या दो से अधिक व्यक्तियों या वस्तुओं के समूह में से प्रत्येक इकाई के लिए किया जाता है जब आप उनके बारे में अलग-अलग सोच रहे होते हैं जबकि Every का प्रयोग वस्तुओं अथवा व्यक्तियों के समूह में से प्रत्येक के लिए बिना अलग-अलग सोचे किया जाता है, जैसे
1. Each of the two girls was present.
2. My father will punish each of you.
3. Every word of this letter is correct.
4. He knows every boy of the class.
5. Each question carries equal marks.
6. Each student was given a paper sheet.
7. Every student is supposed to work hard.
सामान्यतया कम संख्या के साथ each व अधिक के साथ every का प्रयोग किया जाता है ।

9.Use of None
None का तात्पर्य है व्यक्तियों या वस्तुओं के समूह में से कोई नहीं'। None का प्रयोग Affirmative Sentence में किया जाता है। इसके पश्चात् noun का प्रयोग नहीं किया जाता है । यह अकेला ही आता है । सिवाय none + of + noun/pronoun के, जैसे
None was sleeping in the room.
2. None of the girls failed in the school.
3. We visited several places but none fascinated us.
10. Use of No/Not any
No का प्रयोग Adjective की तरह किसी Noun के पहले किया जाता है। इसका प्रयोग not any के स्थान पर भी कर सकते हैं ।
No......... = not any or not + a; जैसे
1. I have no work these days. Or I have not any work these days.
2. She has no children. Or She has not any children.
3. There is no garden Or There isn't a garden.
11. Use of This, That, These, Those
This तथा That का प्रयोग Singular Countable Noun (एक वस्तु, स्थान या प्राणी) के पहले होता है ।
These तथा Those का प्रयोग Plural Countable Noun (एक से अधिक वस्तु, स्थान या प्राणी) के पहले होता है।
This तथा These का प्रयोग नजदीक में स्थित Noun के लिए होता है और That तथा Those का प्रयोग दूर स्थित Nouns के लिए होता है, जैसे
1. This student is my brother.
3. These books are ours.
2. That cow is mine.
4. Those flowers are beautiful.
नोट - This का प्रयोग दो बार नहीं किया जाता है । अतः What is this ? का उत्तर That / It is ........ ही होगा । What is this ? It/That is a pen.
That का प्रयोग किसी घटना के लिये भी होता है । यह किसी व्यक्ति द्वारा कही गई बात को भी व्यक्त करता है ।
(i) A : I'm sorry, I am late.
(ii) A : You are lazy.
B : That's all right.
B : That's true !

12. Use of Both, Ali, Most.
Both का प्रयोग of + Noun/Pronoun के पहले होता है। Both संख्या में दो होने का बोध कराता है। All का तात्पर्य 'सभी' (वस्तु, स्थान या प्राणी) से है । Most का प्रयोग अधिकांश के अर्थ में होता है । जैसे
1. Both of them were wise.
2. All of us were tired.
3. Most children like playing.
4. All countries have a national flag.
5. All the students were watching the match.
13. Use of Either, Neither
Either का अर्थ होता है 'दोनों में से कोई एक' । इसी प्रकार neither का अर्थ है 'दोनों में से कोई नहीं' । दोनों के साथ ही Singular noun का प्रयोग होता है । जैसे
1. Either room is good.
2. Either road leads to Jaipur.
3. My brother lost either his purse or pen.
4. Either you or Ram was sleeping on the bench.
5. Neither fan is satisfactory.
6. Neither hotel is very good.
7. You can keep either of these books.
नोट -
(1) All/most/some/any/none/both/either/neither के ठीक बाद of का प्रयोग होता है, यदि इनके पश्चात् Objective Pronoun दिया हो, जैसे
(i) Most of them like playing.
(ii) All of us are going out tonight.
(2) Both/either/neither के बाद of का प्रयोग होता है यदि इनके बाद आने वाले nouns के पूर्व कोई determiner दिया हो । यदि कोई determiner नहीं दिया हो तो of का प्रयोग नहीं होगा, जैसे
(i) Neither boy was present.
(ii) Neither of the boys was present.
14. Use of Various, Several
Various विभिन्न वर्ग के काफी व्यक्तियों । वस्तुओं के संदर्भ में प्रयुक्त होता है।
Various के बाद सदा Plural noun का प्रयोग होता है, जैसे
Various books were lying on the table. अनेक विषयों की अनेक पुस्तकें टेबिल पर पड़ी थीं।
Several के बाद सदा Plural noun का प्रयोग होता है।
1. He sold serveral fans.
2. Several girls are playing in the field.
3. Several books were lying on the table.
एक ही विषय की अनेक पुस्तकें टेबिल पर पड़ी थीं । Comparative use of many, various, several Many एक ही श्रेणी की ढेर सारी मात्रा को तथा Several एक ही श्रेणी की संतुलित मात्रा को प्रदर्शित करता है।

15. Use of Such, Such
a Such या Such a का तात्पर्य होता है ‘ऐसा' ।
Such के बाद Plural countable noun या uncountable noun का प्रयोग होता है जबकि Such a के साथ Singular countable noun का प्रयोग होता है ।
1. He does not like such things. वह ऐसी चीजें पसन्द नहीं करता है ।
2. Such a girl is not fit for the role. ऐसी लड़की उस भूमिका के लिए उपयुक्त नहीं है ।
16. Use of Less, Fewer
Less शब्द मात्रासूचक है । इसका प्रयोग Uncountable noun से पूर्व होता है। Fewer संख्यासूचक है। इसका प्रयोग Plural noun से पूर्व होता है ।
1. We have less time for this work.(मात्रासूचक)
2. We have fewer books to read. (संख्यासूचक)
3. She has less money today. (मात्रासूचक)
4. She had fewer lessons to do. (संख्यासूचक)
17. Use of Enough, Not enough
Enough का अर्थ है 'पर्याप्त'। इससे किसी चीज की मात्रा और संख्या की जानकारी होती है। इसके पश्चात् Uncountable noun या Plural countable noun का प्रयोग होता है। 'Not enough' का अर्थ होता है 'पर्याप्त मात्रा का अभाव'।
1. I have enough money.
2. She has enough books on English grammar.
3. She does not have enough money.

18. Use of Lots of, A great deal of, A good deal of, Plenty of,
A large number of
इन सभी का अर्थ होता है- 'बहुत' । इनका प्रयोग समान रूप से Singular uncountable nouns व Plural countable nouns के पूर्व किया जा सकता है, जैसे -
1. I have a lot of friends.
2. There are a good deal of students in the class.
3. Sita does not take lots of milk.
4. Ravi puts a great deal of sugar in milk.
5. Plenty of people are coming to attend the function.
6. A large number of students were present on the annual day.
Exercise 9.
Fill in the blanks with no, any or none.
1. There is ........... milk in this tea.
2. I haven't got ........... money. Will you lend me some ?
3. It is a public holiday, so there are ........... offices open.
4. There aren't ........... furniture in the hall.
5. How much money have you got ?' ' ...........
6. 'How much money have you got ?' ' I haven't got ...........'
7. 'Do you know this person' 'No. I haven't got ........... idea.'
8. I'm afraid there's ........... milk. Would you like some juice ?'
9. I couldn't make tea because there wasn't ........... milk.
10. I couldn't make tea because there was ........... milk.
Answers:
1. no
2. any
3. no
4. any
5. None
6. any
7. any
8. any
9. any
10 no.
Exercise 10.
Fill in the blanks with each every.
1. The Olympic games are held ........... four years.
2. In a game of tennis there are two or four players. .......... player has a racket.
3. Sheetal plays volleyball ........... Thursday morning.
4. I tried to phone her two or three times, but ........... time there was no reply.
5. Katerina has read ........... book in the library.
6. Our football team is playing well. We've won ........... game this season.
7. There are six apartments in this building. ........... one has a balcony.
Answers:
1. every
2. Each
3.every
4. each
5. every
6. every
7. Each.

Exercise 11.
Fill in the blanks with suitable determiner given in the brackets :
1. I have three winter coats, but ........ of them is new. (neither, none)
2. There are two umbrellas here, but .......... of them is mine. (neither, none)
3. He owns twelve cows. ........... of them are Jerseys. (All,Both)
4. She has painted dozens of pictures. Have you seen ........... of them ? (any, either)
5. Any and Beth are twins. They ........... play the guitar. (all, both)
6. My wife and I ........... enjoy classical music. (all, both)
7. I found all of the questions difficult. Did you answer .... of them correctly ? (any, either)
Answers:
1. none
2. neither
3. All
4. any
5. both
6. both
7. any.
Exercise 12.
Fill in the blanks with both (of) leither (of) / neither (of):
1. Last year I went to Paris and Rome. I liked...........cities very much.
2. There were two pictures on the wall. I didn't like ...........them.
3. It was a good football match. .......... the teams played well.
4. It wasn't a good football match. ........... team played well.
5. Which jacket do you prefer, this one or that one ? I don't like ...........them.
6. 'Is your friend Algerian or English ?''.......... them.'
7. Amina has got two sisters and a brother. ........... sisters are married.
Answers:
1. both
2. either of
3. Both
4. Neither
5. either of
6. Neither of
7. Both.
Exercise 13
Reordering Of Sentences
Look at the sentences given below in a disorderly form. Reorder them to form meaningful sentences:
1. thing/ a / knowledge / a little / dangerous /is.
2. for / a little / tea/ sugar /I / want.
3. days / at / rest / patient / more / keep/the / please / a / few
4. sour / has / jug / in / left / milk / the / gone / little / the
5. entertainment / money / to / on / spend / has / Rakhi/ hardly / any
6. you / to / more / tea / would / like / take / some ?
7. help / needed / he / their / when / selfish / who / him / left / friends / Ravi / some / had.
Answers:
1. A little knowledge is a dangerous thing.
2. I want a little sugar for tea.
3. Please keep the patient at rest a few days more.
4. The little milk left in the jug has gone sour.
5. Rakhi has hardly any money to spend on entertainment.
6. Would you like to take some more tea ?
7. Ravi had some selfish friends who left him when he needed their help.

Exercise 14.
Dialogue Completion
Read the dialogue and fill in the blanks by using words which will help to make the meaning clear.
A. (1) two chairs look so shabby. Don't you think we need to get a set of new ones?
B. We'll talk about it a (2) ..........later, I have (3) ..........important piece of work to complete tonight. I can't spare (4) .......... time right now.
A. I saw (5).......... exquisite chairs at 'WOODCRAFT'. I think they would fit beautifully in (6) .......... drawing-room.
B. WOODCRAFT! It is (7) ..........most expensive show-room in town.
A. But they have authentic teak furniture, or we could choose (8) ..........set of chairs in rosewood; (9) .......... idea may be to buy some cane chairs.
B I guess it would be useful to spend a (10) .......... more on furniture which would last for (11) .......... years.
A. So, when can you spare a (12) .......... hours to visit WOODCRAFT with me?
B. We could go next Saturday or Sunday
Answer:
1. These
2. little
3. an
4. any
5. some
6. the
7. the
8. a
9. the
10. little
11. many
12. few

Exercise 15.
Choose the appropriate option from the brackets to complete the given sentences.
1. I have been to .......... (a / the) doctor, whose name appeared in the New York Times.
2. Is there .......... (the / a) fitness centre near your house?
3. (one / few / an) example helps understand concepts better.
4. That house at the corner of the street belongs to .......... (many / those) people who are standing near its gate.
5. He has hardly read .......... (many / any) book.
6. He drove with .......... (much / little) care and hence was fined by the traffic police.
7. .............. (little / a little) milk is required for a cup of tea.
8. ............... (few / some) of the mango trees in their garden bear fruit twice a year.
9. ............. (any / each) student of this class is a scholar badge holder
10. I spent .......... (the little / a little) money I had.
11. You may have. ......... (either / any) of the four watches.
Answers:
1. the
2. a
3. An
4. those
5. any
6. little
7. A little
8. Some
9. Each
10. the little
11. any

- The Tale of Melon City Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 8 RBSE Solutions
- Birth Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 7 RBSE Solutions
- The Ghat of the Only World Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 6 RBSE Solutions
- Mother’s Day Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 5 RBSE Solutions
- Albert Einstein at School Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 4 RBSE Solutions
- Ranga’s Marriage Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 3 RBSE Solutions
- The Address Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 2 RBSE Solutions
- The Summer of the Beautiful White Horse Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 1 RBSE Solutions
- Father to Son Question Answer Class 11 English Hornbill Chapter 5 RBSE Solutions
- Childhood Question Answer Class 11 English Hornbill Chapter 4 RBSE Solutions
- The Voice of the Rain Question Answer Class 11 English Hornbill Chapter 3 RBSE Solutions