RBSE Class 11 English Grammar Clauses
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 English Grammar Clauses Exercise Questions and Answers.
The questions presented in the RBSE Solutions for Class 11 English are solved in a detailed manner. Get the accurate RBSE Solutions for Class 11 all subjects will help students to have a deeper understanding of the concepts. Our team has come up with Tenses Class 11 to ensure that students have basic grammatical knowledge.
RBSE Class 11 English Grammar Clauses
Simple Sentence तथा Complex Sentence में अन्तर
(1) I gave him a book.
(2) She was playing football.
(3) They will help us.
उपरोक्त तीनों ही वाक्य Simple Sentences हैं क्योंकि तीनों ही वाक्यों में केवल एक-एक ही finite verbgave, playing a help दी हुई है।
परिभाषा के अनुसार -
A simple sentence is a sentence which has only one finite verb, and may have a subject and a predicate. एक साधारण वाक्य वह वाक्य होता है जिसमें केवल एक ही नियंत्रित क्रिया (finite verb) होती है व एक ही कर्ता व विधेय (predicate) हो सकता है ।
ऊपर दिये गए तीनों वाक्य Clause कहलाते हैं क्योंकि एक Simple Sentence में केवल एक ही Clause प्रयुक्त होता है।

अब पुनः इन वाक्यों को देखिये
(1) I told him then.
(2) He was reading in the room.
इन दोनों ही वाक्यों को जोड़कर एक वाक्य एक प्रकार से बनाया जा सकता है ।
I told him when he was reading in the room.
उक्त वाक्य एक Complex Sentence कहलाता है क्योंकि
A complex sentence is a sentence which consists of two or more clauses.
एक जटिल वाक्य या मिश्रित वाक्य (Complex Sentence) वह होता है जिसमें दो या दो से अधिक | उपवाक्य (Clauses) हों ।
और यहाँ पर वाक्य He was reading in the room को then के स्थान पर when लगाकर जोड़ा गया है । चूँकि then एक adverb है, अतः यहाँ पर जोड़ा गया when he was reading in the room एक adverbial clause है । इस प्रकार से एक Complex Sentence में दो या दो से अधिक Subject-Predicate Structures हो सकते हैं । दूसरे शब्दों में,
A complex sentence is one that contains one main clause (Principal Clause) and one or more subordinate clauses. एक Complex Sentence वह होता है जिसमें एक प्रधान उपवाक्य (Principal clause) तथा एक या अधिक आश्रित उपवाक्य (Subordinate Clauses) होते हैं ।
उक्त वाक्य में 'I told him' Principal Clause है तथा when he was reading in the room एक Subordinate Clause है क्योंकि यह Principal Clause के लिए Adverb का काम रहा है । यहाँ पर यह स्पष्ट हो जाता है कि Subordinate Clause को Principal Clause से जोड़ने के लिए एक
Conjunction का प्रयोग किया जाता है । यहाँ पर दोनों वाक्यों को जोड़ने के लिए when का प्रयोग किया गया है जो कि एक conjunction है ।
नोट - एक Principal Clause को Subordinate Clause से जोड़ने के लिए जिन conjunctions का प्रयोग किया जाता है, वे Subordinating Conjunctions कहलाते हैं ।
अब निम्नलिखित उदाहरण को ध्यानपूर्वक देखो
(1) I know it.
(2) The thief has escaped.
हम इन दोनों ही वाक्यों को इस प्रकार से जोड़ सकते हैं कि दूसरा वाक्य पहले वाक्य के object के स्थान पर लग जाये व object का काम करे ।
I know that the thief has escaped.
Clause "that the thief has ecaped", Principal Clause "I know" के लिए directobject का काम कर रहा है और इस प्रकार से यह एक Subordinate Clause है ।
एक Complex sentence में Clauses की संख्या का पता लगाना अत्यन्त ही आसान है। एक Complex sentence में जितनी finite verbs होती हैं उसमें उतने ही Clauses होते हैं।
अर्थात् – The number of finite verbs = the number of clauses
जैसे -- I am writing a book.
उक्त वाक्य में केवल एक ही finite verb-writing दी हुई है, अतः इसमें केवल एक ही Clause है व यह एक साधारण वाक्य (Simple sentence) है । लेकिन
This is the boy who stole my pen.
इस वाक्य में दो finite verbs-is व stole दी हुई हैं । अतः इस वाक्य में दो
Clauses -
(1) This is the boy
(2) who stole my pen I who stole my pen won Subordinate clause 78 who 10 Subordinating conjunction है।
इसी प्रकार से – If you do not strike while the iron is hot, you cannot mould it. उक्त वाक्य में तीन finite verbs-strike, is a mould हैं ।
अतः उक्त वाक्य में तीन Clauses हैं :
(i) If you do not strike
(ii) while the iron is hot.
(iii) you cannot mould it तथा if व while दो Subordinating conjunctions हैं ।

Principal Clause व Subordinate Clause को पहचानना
एक Complex Sentence में Principal Clause व Subordinate Clause को पहचानना अत्यन्त ही आसान है ।
Shortcut - Subordinate Clause के पूर्व किसी न किसी Subordinating Conjunction का प्रयोग अवश्य ही होता है जबकि एक Principal Clause के पूर्व किसी भी Conjunction का प्रयोग नहीं होता है । जैसे – She feels that we should buy a car.
उक्त वाक्य में that का प्रयोग we should buy a car के पूर्व हुआ है, अतः यह एक Subordinate Clause है तथा She feels के पूर्व किसी भी Conjunction का प्रयोग नहीं हुआ है, अतः यह एक Principal Clause है ।
अन्य उदाहरण -
Exercise 1.
Identify the main clause, the subordinate clause and the conjuction in each of the following sentences :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में प्रधान उपवाक्य, सहायक उपवाक्य व संयोजक को पहचानिये
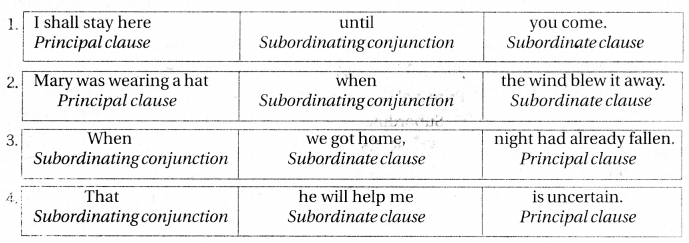
1. It depends on what you want.
2. Can you tell me when he left and where he has gone?
3. I am proud that you have won.
4. Do whatever you like.
5. If you want to talk to me, please call me between 5 and 6.
Answers:
|
Principal Clause |
Subordinate Clause |
Conjunction |
|
1. It depends on |
you want |
what |
(1) Noun Clause
A noun clause is a subordinate clause that can be used in one of the positions that is usually occupied by a noun/pronoun/noun phrase in a sentence - subject, object or complement.
एक Noun clause वह आश्रित उपवाक्य होता है जो किसी संज्ञा/सर्वनाम/noun phrase द्वारा किसी वाक्य में किये जा रहे subject, object या complement का कार्य करे ।
अर्थात् - Noun Clause वह Clause है जो Noun का काम करे ।
Noun Clause को निम्नलिखित पाँच रूपों में पहचान सकते हैं
(1) Subject to aVerb(क्रिया के subject के रूप में) :
1. What he said pleased me.
2. Where she is going is not known.
3. That he went there is uncertain.
उपर्युक्त वाक्यों में तिरछे छपे शब्द Subordinate Noun Clauses हैं । ये Sentences में subjects का कार्य करते हैं।
नोट – ऐसा प्रयोग सदैव Principal Clause के पहले होता है और Principal Clause का कर्ता 'it' छिपा रहता है ।
(2) Object to aVerb (क्रिया के object के रूप में):
1. He told me that he was going to Kolkata.
2. I do not know where he lives.
उपर्युक्त वाक्यों में तिरछे छपे शब्द अपने-अपने Sentence में Object का कार्य कर रहे हैं । अतः ये Subordinate Noun Clauses हैं।
नोट - ये प्राय: Principal Clause के बाद आते हैं ।
(3) Object to a Preposition ( Preposition के कर्म के रूप में):
1. Listen to what your teacher says.
2. It all depends on how she does.
उपर्युक्त वाक्यों में तिरछे अक्षरों में छपे Clauses, Subordinate Noun Clauses हैं । ये Prepositions - to तथा on के बाद प्रयुक्त हुए हैं ।

(4) Complement to aVerb (क्रिया के पूरक के रूप में):
1. This is what I want to say.
2. Life is what we make.
उपर्युक्त वाक्यों में तिरछे अक्षरों में छपे Clauses अपूर्ण क्रिया के पूरक हैं । ये Subordinate Noun Clauses हैं और अपने पूर्व आने वाले Clauses की Verbs के Complements हैं।
(5) Case in Apposition to a Noun or Pronoun (संज्ञा/सर्वनाम के समानाधिकरण के रूप में) :
1. The news that he died is incorrect.
2. It is good that he has come back.
जब एक Noun या Pronoun के बाद दूसरा Noun या Pronoun आये और वे दोनों समानार्थक हों अर्थात् एक ही व्यक्ति या वस्तु के लिए प्रयुक्त हों तो दूसरा Noun या Pronoun पहले वाले Noun या Pronoun का Case in Apposition कहलाता है ।
वाक्य 1 में news (Noun) के लिए he (Pronoun) died; वाक्य 2 में it (Pronoun) के लिए he (Pronoun) has come back; आये हैं । अतः ये सभी दूसरे शब्द पहले शब्दों के Case in Apposition हैं । अध्ययन की सुविधा की दृष्टि से हम Noun Clause को दो भागों में बाँट सकते हैं
(1) That-Noun Clause - वे clause जो केवल statement को जोड़ने के लिए प्रयुक्त होते हैं ।
(2) Question Clause - वे clause जो प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य को जोड़ने के लिए प्रयुक्त होते हैं ।
That-Noun Clause
ये केवल statements को ही जोड़ते हैं तथा इनमें Subordinating conjunction के रूप में केवल that का ही प्रयोग किया जाता है । - यह निम्नलिखित प्रकार से वाक्य में प्रयुक्त हो सकता है
(A) Subject के रूप में : एक That-Noun clause एक वाक्य में subject का कार्य कर सकता है । | He will tell a lie.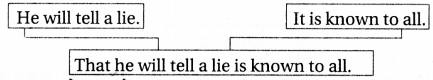
(B) Direct Object के रूप में : एक That-Noun Clause एक सकर्मक क्रिया के direct-object का काम कर सकता है । जैसे I know it

उक्त उदाहरण कि that they have won the match एक that-noun clause है जो Principal clause "I know" के लिए Subordinate Clause का काम कर रहा है।
(C) Subject Complement के रूप में : Linking verb 'be' (is, am, are, was, were) के पश्चात् That Noun Clause का प्रयोग कर्ता के पूरक के रूप में किया जा सकता है ।
.
(D) Adjective complement के रूप में : That-Noun Clause का प्रयोग कभी-कभी एक adjective के complement के रूप में भी हो सकता है। जैसे -
(i) We were glad that everybody helped us.
(ii) It is good that everybody was pleased.
इस प्रकार का structures सामान्यतय निम्नलिखित adjectives के साथ प्रयुक्त होता है :
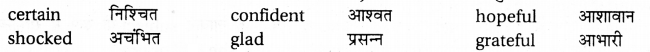
(E) Noun complement के रूप में : कुछ abstractnouns (भाववाचक संज्ञाओं) के साथ that-noun clause का प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे
(i) The fear that someone will beat him is baseless.
(ii) The hope that we shall win is not fulfilled.
Exercise - 2.
Combine sentences 'a' and 'b' in the following sentences in sucha way that sentence 'b' is used as the 'that noun clause' at an appropriate position in sentence 'a' :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों के युग्मों 'a' व 'b' को इस प्रकार से संयोजित करो कि वाक्य 'b' वाक्य 'a' के that - noun clause के रूप में उचित स्थिति में प्रयुक्त हो जाए। जैसे -
a. I thought it -- b. You were coming tomorrow.
I thought that you were coming tomorrow.
1. a. It has disturbed us. -- b. She has failed in the exam.
2. a. He believed it. -- b. She could not do it.
3. a. She said it. -- b. She had looked into the matter.
4. a. It is glad. -- b. She has phoned me.
5. a. I told her something. -- b. They had gone yesterday.
6. a. It was sad. -- b. We had to do that.
7. a. It is a fact. -- b. The earth is round.
Answer:
1. That she has failed in the examination has disturbed us.
2. He believed that she could not do it.
3. She said that she had looked into the matter.
4. It is glad that she has phoned me.
5. I told her that they had gone yesterday.
6. It was said that we had to do that.
7. It is a fact that the earth is round.
Noun Clauses Derived from Questions प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों से बनने वाले Noun Clauses को भी दो भागों में बाँटा जा सकता है -
(A) Wh - Clauses
(B) Yes - No Question Clauses
(A) Wh - Clauses
वे Noun Clauses जिनको wh - question word वाले प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों से जोड़कर बनाया जाता है । जैसे - Where are you going?
यह एक Wh - question word से बनने वाला प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य है । यदि इसका प्रयोग एक subordinate clause के रूप में किया जाए तो यह इस प्रकार से होगा -
I don't know where you are going. प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य को साधारण वाक्य में बदल दिया जाता है।
अन्य उदाहरण
(i) I never believed it. What did you tell her?
Answer: I never believed what you told her.
(ii) May I know it. When can I go home?
Answer: May I know when I can go home.
(iii) I don't know it. Who is she?
Answer: I don't know who she is.
(B) Yes-No Question Clauses
(i) Are you coming with me?
(ii) Can I leave office now?
(iii) Can you remember it?
उपरोक्त तीनों ही वाक्य Yes-No answer type प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य हैं । इनका प्रयोग भी Subordinate clauses के रूप में object की तरह से किया जा सकता है । इस प्रकार के वाक्यों के conjunction के रूप में "if" का प्रयोग किया जाता है। जैसे -
(i) He asked me if you are coming with me.
(ii) Tell me if I can leave office now.
(iii) I wonder if you can remember it.
नोट - object के रूप में if / whether का प्रयोग किया जा सकता है लेकिन subject के रूप में सामान्यतया whether का ही प्रयोग किया जाता है।
जैसे - I don't know if/whether she is ill or not.
Noun Clauses with Imperatives : request, order, advise, demand, suggest, propose, recommend, के साथ इस प्रकार का प्रयोग होता है। जैसे
The students urged that the exams should be postponed.
नोट- (i) इनमें that - Noun Clause का प्रयोग होता है।
(ii) ये वाक्य में object के रूप में प्रयुक्त होते हैं।

Exercise 3.
Put the most suitable words in the spaces to complete the following sentences choosing from the bracket given against each space :
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्मुख दिये गए कोष्ठक में से सबसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो
1. She is sure ........................ (that/where/which) he will make a mistake.
2. Do you want to know ........................ (where/how/why) the train comes late?
3. Do you know .................... (what/if/which) he has passed the exam ?
4. Do you know .................. ... (where/which/that) he has passed the exam?
5. ......... (What/That/which) he told a lie was his fault.
6. ........... (What/That/Where) he will come with us is not sure.
7. Tell me ........................ (where/that/which) you nave
8. Ask her ....................... (where/which/if) she is ready
9. I would like to know ........................ (what/where/if) he was at home yesterday.
10. Ask the bus conductor ................ .. (where/what/if) it is time for the bus to start.
11. I am sure .................... (where/that/what) the train is going to depart.
Answers:
1. that
2. why
3. if
4. that
5. That
6. That
7. where
8. if
9. if
10. if
11. that.
Exercise 4.
Combine each of the following set of sentences into one complex sentence using conjunctions given in bracket:
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों के समूहों को कोष्ठक में दिए गए conjunctions का प्रयोग ad guya complex sentence
1. He will make a mistake. She is sure of it. (that)
2. Your opinion is not correct. Mohan is a thief. (that)
3. That was his fault. He told a lie. (that)
4. He will come with us. That is not sure. (that)
5. I don't know. Will it rain? (if)
6. Good students work hard. It is true. (that)
7. The train is going to depart. I am sure of it. (that)
8. No one can doubt this fact. He is an intelligent student. (that)
9. My father said something. I did not hear that. (what)
10. How did you find my purse ? Can you tell me ? (how)
Answers:
1. She is sure that he will make a mistake.
2. Your opinion that Mohan is a thief is not correct.
3. That he told a lie was his fault.
4. That he will come with us is not sure.
5. I don't know if it will rain.
6. It is true that good students work hard.
7. I am sure that the train is going to depart.
8. No one can doubt that he is an intelligent student.
9. I did not hear what my father said.
10. Can you tell me how you found my purse ?
Exercise 5.
Combine each set of simple sentence into one complex sentence by using conjunctions given in the bracket :
Simple sentence के प्रत्येक युग्म को कोष्ठक में दिए गए conjunctions का प्रयोग करते हुए To complex sentence of
1. It is clear. You have committed a crime. (that)
2. The earth moves round the sun. My teacher told me. (that)
3. He is very sincere. Nobody doubts it. (that)
4. Who wrote the Ramcharitmanas? Can you tell me ? (who)
5. You are kind to me. I will not forget it. (that)
6. He is very honest. I do not doubt it. (that)
7. You have acted wrongly. I believe so. (that)
8. The rains would come. That was our hope. Our hope was wrong. (that)
9. Honesty is the best policy. That is known to all. (that)
10. You told a lie. Do you accept it ? (that)
Answers:
1. That you have committed a crime is clear.
2. My teacher told me that the earth moves round the sun.
3. Nobody doubts that he is very sincere.
4. Can you tell me who wrote the Ram Charit Manas ?
5. I will not forget that you are kind to me.
6. I do not doubt that he is very honest.
7. I believe that you have acted wrongly.
8. Our hope that the rains would come was wrong.
9. That honesty is the best policy is known to all.
10. Do you accept that you told a lie ?

(2) Relative Clause
Relative Clause वह clause है जो वाक्य में एक adjective का कार्य करे अर्थात् जो किसी Noun या Pronoun को qualify करे । यह अपनी पूर्ववर्ती-संज्ञा (Antecedent Noun) के बारे में कुछ बताता है । जैसे --
(i) This is the camera which I have recently bought.
(ii) You can buy the books that you need.
(iii) The boy whom you helped is very poor.
(iv)The man who stole your purse has been arrested. ।
उपर्युक्त उदाहरणों में :
...................which I have recently bought. कैमरे के बारे में बताता है । ...................that you need. पुस्तकों के बारे में बताता है । ..................whom you helped .................. लड़के के बारे में बताता है । तथा ..................who stole your purse .................. व्यक्ति के बारे में बताता है । Relative clause को जोड़ने में प्रयुक्त होने वाले शब्द Relative Pronouns कहलाते हैं ।
Relative Clauses दो प्रकार के होते हैं -
(1) Defining Clauses : ये किसी व्यक्ति/वस्तु/जानवर के विषय में 'विशेषण' के रूप में जानकारी प्रदान करते हैं | Defining Clauses के बिना किसी संज्ञा की पहचान अधूरी रहती है । Defining Clauses में commas (,) का प्रयोग नहीं किया जाता है । ये संज्ञा के विषय में Restrictive Meaning प्रदान करते हैं, जैसे - My brother who lives in London visited us last week.
(Defining Clause) यहाँ My brother की विशेषता who lives in London से बताई गई है । उक्त वाक्य का आशय यह हुआ कि 'मेरा (एकमात्र) भाई जो लन्दन में रहता है पिछले सप्ताह हमारे यहाँ आया ।' इस प्रकार Defining Clause ने 'My brother' के Meaning को Restrict (सीमित) कर दिया ।
(2) Non-defining Clauses : ये अपने पूर्ववर्ती संज्ञा के विषय में सीमित जानकारी प्रदान नहीं करते । ये संज्ञा के विषय में Continuative Meaning प्रदान करते हैं । Non-defining clauses में clauses को commas (,) द्वारा बंद किया जाता है, जैसे -
My brother, who lives in London, visited us last week. (Non-defining Clause)
Commas (,) के प्रयोग के कारण यहाँ 'who lives in London Non-defining Clause है ।
इस वाक्य का अर्थ होगा ‘मेरा (एक) भाई जो लन्दन में रहता है वह पिछले सप्ताह हमारे यहाँ आया ।' अतः Non-defining Clauses के कारण My brother का meaning Restrictive (सीमित) न होकर continuative हो गया । दोनों वाक्यों का अन्तर निम्न प्रकार रहा -
(1) Defining Clause वाले वाक्य के अनुसार 'मेरा केवल एक ही भाई है जो लन्दन में रहता है ।' (Restrictive Meaning)
(2) Non-defining Clause के अनुसार 'मेरा एक भाई लन्दन में रहता है तथा मेरे अन्य भाई भी हैं ।' (Continuative Meaning)
Relative Pronouns जो Defining Relative Clauses में प्रयुक्त होते हैं --
|
|
Subject |
Object |
Preposition |
Possessive |
|
For persons |
who |
whom/who |
that....... |
whose |
|
For things |
who |
which |
that .... |
of which |
Relative Pronouns जो Non-defining Relative Clauses में प्रयुक्त होते हैं --
|
|
for persons |
for things |
|
Subject |
---who---, |
---,which---, |
Relative Pronouns के प्रयोग जब वाक्य में रिक्त स्थान दिया हो
Shortcuts
Who का प्रयोग- जो, जिसने यदि रिक्त स्थान से पूर्व कोई (Person) व्यक्ति है तथा रिक्त स्थान के पश्चात् कोई Verb (क्रिया) है तो उत्तर who ही आयेगा । Pattern (सूत्र) : Person + ............... + Verb.....
1. I know Mr Sharma, ............... teaches you English.
Answer: who
2. The boy.............. is standing there is my brother.
Answer:
who Whom का प्रयोग- जिसे, जिसको यदि रिक्त स्थान से पूर्व कोई व्यक्ति (Person) तथा रिक्त स्थान के पश्चात् कोई व्यक्ति (Person) + Verb हो तो उत्तर whom ही आयेगा । Pattern (सूत्र) : Person + ............... + Subject (person) + Verb
1. The boy ............... he gave money was very poor. Person Person + Verb
Answer: whom
2. The man .. .... I helped was in trouble. Person Person + Verb
Answer: whom

3. Whose का प्रयोग - जिसका, जिनका, जिसकी आदि ।
यदि रिक्त स्थान इस प्रकार से दिया हो तो whose का प्रयोग किया जा सकता है।
Pattern : Person ................... + thing + Verb
Person ................... + thing + person + Verb...
Person ................... + person + person + Verb.......
Person ..... . + person + Verb किन्तु whom तथा whose का अन्तर समझने में सावधानी अवश्य रखें ।
1. The man..............shirt is blue is my uncle. Person (thing + verb)
Answer: whose
2. Theman..............car you borrowed is my neighbour. Person (thing + person + verb)
Answer: whose
3. The man ..............son you taught is my uncle. Person (person + person + verb)
Answer: whose
4. The boy..............father is a doctor is my friend. Person (person + verb)
Answer: whose
4. Which का प्रयोग -
जिसका, जिसकी, जिसके रिक्त स्थान से पूर्व यदि कोई Lifeless thing या Animal (निर्जीव वस्तु या जानवर) हो तथा रिक्त स्थान के पश्चात् Noun या Verb हो तो रिक्त स्थान में which का प्रयोग होता है । जैसे -
1. The dog .................. bit you is his.
Answer: which
2. The book... ....................Mohangave me is yours.
Answer: which नोट -- यदि रिक्त स्थान से पूर्व वस्तु/जानवर + Preposition हो तो रिक्त स्थान में which का ही प्रयोग होगा। जैसे -
1. The post for .............. I was selected is temporary.
Answer: which
2. I don't like the house in .............. he lives.
Answer: which

5. What का प्रयोग - जो
(1) वाक्य के प्रारम्भ में रिक्त स्थान होने पर ।
(2) Verb के पश्चात् रिक्त स्थान होने पर ।
(3) Verb + Object के पश्चात् रिक्त स्थान होने पर तथा वाक्य में कोई भी Antecedent नहीं होने पर । जैसे
1. .............. cannot becured must been dured
Answer: What (वाक्य के प्रारम्भ में रिक्त स्थान)
2. This is .............. he likes (verb)
Answer: what
3. Do ..............you please. (verb)
Answer: what
4. Give him.............. he demands. (verb + obj.)
Answer: what
5. Please tell me.............. you need (verb + obj.)
Answer: what
6. When का प्रयोग - जब, जिस समय
यदि रिक्त स्थान के ठीक पहले समय दिया हो तो when का ही प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे -
1. It was midnight........... the thief entered the house.
Answer: when
2. It was Sunday ........... We went on a picnic.
Answer: when
7. Where का प्रयोग -
जहाँ यदि वाक्य में रिक्त स्थान के पूर्व दिये गए शब्द का सम्बन्ध स्थान से हो या स्थान सूचक हो तो where का प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे -
1. This is the temple ........... Gandhiji was shot dead.
Answer: where
2. This is the school........... I studied for five years.
Answer: where
8. Why का प्रयोग - कि -- क्यों
जब रिक्त स्थान के पूर्व reason (कारण) दिया हो । जैसे -
1. This is the reason........... he didn't come.
Answer: why
2. This is the reason........... I called you.
Answer: why
9. That का प्रयोग
That के प्रयोग की पाँच प्रमुख शर्ते - हम who, whom या which के स्थान पर that का प्रयोग कहाँ करें, इसकी प्रमुख शर्ते निम्न प्रकार हैं -
(i) यदि वाक्य में रिक्त स्थान के पहले वाले Noun (Antecedent) से पूर्व superlative degree हो। जैसे
Mohan is the tallest boy.......... reads in our school. (boy से पहले superlative degree)
Answer: that
(ii) यदि वाक्य Interrogative है तो Relative Pronouns-who, whom, which के स्थान पर that का प्रयोग होता है। जैसे -
1. Who is he.......... troubles you?
Answer: that
2. What is it.......... worries him so much?
Answer: that
(iii) यदि रिक्त स्थान के पूर्वonly,any, same,all, nothing, no one, nobody, anybody, anything, none, little आदि शब्द हों । जैसे -
1. All.......... glitters is not gold.
Answer: that
2. This is the same person .......... you beat.
Answer: that
(iv) यदि किसी वाक्य में रिक्त स्थान के पूर्व व्यक्ति + वस्तु (Person + thing) या व्यक्ति + जानवर (Person + Animal) आये हों तो that लगेगा । जैसे
1. The man and the dog ......... you see live the next door.
Answer: that
2. The cowherd and his cow.......... we see walking on the ground live in this village.
Answer: that
(v) यदि Preposition का प्रयोग Relative Clause की Verb के पश्चात् हुआ हो तो that का प्रयोग होगा न कि who, whom या which का । जैसे -
1. I know the man about whom you are talking. (Prep.)
2. I know the house that he lives in. (Prep.)
3. This is the book that I told you about. (Prep.)

Exercise 1.
Fill in the blanks with suitable Relative Pronouns given in the bracket:
1. The building ............... (where/that/who) I live in was built in the 1920s.
2. That's Peter, the boy ............... (who/which/whom) has just arrived at the airport.
3. Do you remember the name of the man ........ (whom/whose/that) car you crashed into ?
4. I mean ................. (that/which/what) I say.
5. The hotel ................. (that/which/where) we stayed in was very good for the price.
6. This is the best book ................. (that/which/whose) I've ever loved.
7. Mrs Richa, .............. (that/who/whom) is a taxi driver, lives in a village.
8. Thank you very much for your e-mail ................. (that/who/when) was very interesting.
9. The man ................ (whose/which/that) father is a professor forgot his umbrella.
10. The children ................ (whom/who/that) shouted in the street are not from our school.
Answers:
1. that
2. who
3. whose
4. what
5. where
6. that
7. who
8. that
9. whose
10. who.
Exercise 2.
Fill in the blanks with when, where or why:
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति when, where या why से करो :
1. We visited the school ................ my father taught.
2. I met her last year ............... he came to my house.
3. We all looked at the place ................. the fire had started.
4. I met him in the cafe ................. he was working as a waiter.
5. Do you remember the time ................. Vinod fell off his bicycle ?
6. Did they tell you the reason ................. they were late ?
7. The cat sat on the wall ................. it had a good view of the birds.
8. I'm talking about the time ................. they didn't have cars.
9. Last year I spent my holiday in Spain, ................. I met Shashi.
10. I couldn't understand the reason ................. they were so rude.
Answers:
1. where
2 when
3. where
4. where
5. when
6. why
7. where
8. when
9. where
10. why.
Relative Pronouns का प्रयोग करके दो वाक्यों को जोड़ना
(A) The Use of Who/That (Defining)
Who is the subject of the relative clause.
नीचे दिये गये उदाहरणों को ध्यानपूर्वक देखो -
(i) The woman is a doctor.
(ii) She lives next door.
इन दोनों वाक्यों में दूसरा वाक्य She lives next door, पहले वाक्य के subject-The woman के बारे में बता रहा है, अतः जब इन दोनों वाक्यों को एक साथ लिखा जाएगा तो she lives next door को The woman के ठीक बाद इस प्रकार से लिखा जाएगा
The woman (she lives next door) is a doctor.
अब यहाँ पर The woman व she एक ही व्यक्ति के लिए प्रयुक्त हुए हैं व she दूसरे वाक्य का subject है । अतः यहाँ पर उपयुक्त relative pronoun 'who' लगाया जाएगा और एक Relative Clause बनेगा ।
The woman who lives next door is a doctor.
यहाँ पर अर्थ में बगैर कोई परिवर्तन हुए who के स्थान पर that भी लगाया जा सकता है ।
The woman that lives next door is a doctor.
अन्य उदाहरण --
(i) We know a lot of boys. They play here.
We know a lot of boys who/that play here.
(ii) The boy is my brother. He is standing there.
The boy who/that is standing there is my brother.

Exercise 3.
Join the following pairs of sentences using who/that:
who/that का प्रयोग करते हुए निम्नलिखित वाक्यों के जोड़ों को संयोजित करो -
1. The girl lives near me. She found the dog.
2. The boy is my friend. He broke the chair.
3. The man came to see us. He lost his money.
4. The woman wants to see you. She saw the accident.
5. The man was caught by the police. The man stole the money.
6. The player was very happy. He scored the goal.
7. The man is my uncle. He told you about the fire.
Answers:
1. The girl who found the dog lives near me.
2. The boy who broke the chair is my friend.
3. The man who lost his money came to see us.
4. The woman who saw the accident wants to see you.
5. The man who stole the money was caught by the police.
6. The player who scored the goal was very happy.
7. The man who told you about the fire is my uncle.
(B) The Use of Whom/Who/That (Defining)
whom का प्रयोग Relative Clauses के object के रूप में किया जा सकता है । उसके स्थान पर Who का प्रयोग भी सम्भव है । कुछ स्थितियों में इनके स्थान पर that का प्रयोग भी किया जा सकता है । नीचे दिये गये उदाहरण को ध्यानपूर्वक देखो -
(i) The woman was on holiday.
(ii) I want to see her.
इन दोनों वाक्यों में दूसरा वाक्य I want to see her प्रथम वाक्य के शब्द The woman के बारे में कुछ बता रहा है, अतः इसे इस प्रकार से लिखा जाएगा The woman (I want to see her) was on holiday.
यहाँ पर दूसरे वाक्य का her एक object है तथा यह शब्द The woman के लिए प्रयुक्त हुआ है, अत: her को हटाकर the woman के ठीक पश्चात् whom लिखा जाएगा । whom का प्रयोग object (me/us/you/him/them/ her) के प्रतिनिधित्व करने के लिए किया जाता है ।
The woman whom I want to see was on holiday.
अन्य उदाहरण -
(i) A girl has written this letter. You selected her.
A girl - you selected her -- has written this letter.
A girl whom you selected has written this letter.
(ii) This is the boy. You beat him.
This is the boy - you beat him.
This is the boy whom you beat.
उपरोक्त सभी उदाहरणों में Whom के स्थान पर who या that का प्रयोग किया जा सकता है तथा relative pronoun को छोड़ा भी जा सकता है। जैसे .........
(i) The girl whom I had gone to see was sitting in the chair.
या The girl who I had gone ...............
या The girl that I had gone .................
या The girl I had gone to see was sitting in the chair.
Exercise 4.
Combine the following pairs of sentences using 'whom':
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों के जोड़ों को whom का प्रयोग करते हुए संयोजित करो
1. The man is a beggar. You gave him money.
2. The girl is my daughter. You teach her.
3. The boy is very poor. She gave him some money.
4. This is the boy. All like him.
5. The man is my friend. You met him.
6. The writer was the only person. The conductor took him very friendly.
7. I know the boy. The Principal punished him.
Answers:
1. The man whom you gave money is a beggar.
2. The girl whom you teach is my daughter.
3. The boy whom she gave some money is very poor.
4. This is the boy whom all like.
5. The man whom you met is my friend.
6. The writer was the only person whom the conductor took very friendly.
7. I know the boy whom the Principal punished.

(C) The Use Of Which/That (Defining)
which/that का प्रयोग एक Defining Relative Pronoun के रूप में वस्तुओं तथा जानवरों के लिए किया जाता है । यह एक Relative Clause के Subject या Object दोनों के लिये प्रयोग किया जा सकता है । जैसे
(i) Where is the cheese ? It was in the fridge.
Where is the cheese ? - it was in the fridge.
Where is the cheese which/that was in the fridge ?
(ii) The dog is Mohan's. It bit you.
The dog - it bit you - is Mohan's.
The dog which/that bit you is Mohan's.
Exercise 5.
Join the following pairs of sentences using 'which':
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों के जोड़ों को which का प्रयोग करते हुए संयोजित करो -
1. The boat is still at the bottom of the river. It sank yesterday.
2. The car was badly damaged. It hit the truck.
3. The dog had been chained up. It bit him yesterday.
4. The tree was very big. It fell on their house.
5. The dress was very nice. She made it last week.
6. The camera was very expensive. She bought it last month.
7. The grass was green. The cows were eating it.
Answers:
1. The boat which sank yesterday is still at the bottom of the river.
2. The car which hit the truck was badly damaged.
3. The dog which bit him yesterday had been chained up.
4. The tree which fell on their house was very big.
5. The dress which she made last week was very nice.
6. The camera which she bought last month was very expensive.
7. The grass which the cows were eating was green.
(D) Position of Preposition in Relative Clauses (Defining)
जब Subordinate Clause के Object के पूर्व कोई Preposition दिया हुआ होता है तो या तो इसे Relative Pronoun के ठीक पूर्व रख दिया जाता है तथा object हटा देते है |
... Preposition + Relative Pronoun (whom/which) .......
(i) The forest was full of wild animals. They went through it.
The forest, they went through it - was full of wild animals.
The forest through which they went was full of wild animals.
(ii) Do you know the man? Hari is talking to him.
Do you know the man ? - Hari is talking to him.
Do you know the man to whom Hari is talking?
या फिर Preposition को अपने स्थान पर ही रहने दिया जाता है व object को हटा देते हैं । ऐसी स्थिति में whom व which के स्थान पर that का प्रयोग करना ही उचित रहता है, जैसे -
(i) The forest that they went through was full of wild animals.
(ii) Do you know the man Hari is talking to?
Exercise 6.
Join the following pairs of sentences using "......... preposition + whom/which ....... " construction and "............ that .......... preposition"
........... that.......... preposition" construction:
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों के जोड़ो को ............. Prepostion + whom/that .......... का व ......... that ............ Prepostion का प्रयोग करते हुए संयोजिता
1. I don't remember the school. I was taught in the school.
2. I got the job. I had applied for it.
3. Who was that man ? I saw you with him.
4. Where is the doctor ? You were talking about him.
5. There is a cottage. A Saint lives in it.
6. This is the pen. I was looking for it.
7. This is the man. I was talking about him.
Answers:
1. I don't remember the school in which I was taught. / I don't remember the school that I was taught in.
2. I got the job for which I had applied. / I got the job that I had applied for.
3. Who was that man with whom I saw you ? / Who was that man that I saw you with?
4. Where is the doctor about whom you were talking ? / Where is the doctor that you were talking about?
5. There is a cottage in which a saint lives. / There is a cottage that a saint lives in.
6. This is the pen for which I was looking. / This is the pen that I was looking for.
7. This is the man about whom I was talking. / This is the man that I was talking about.
(E) Use of whose/of which (Defining)
whose/of which वे Relative Pronouns हैं जिनका प्रयोग Possession बताने के लिए किया जाता है । whose का प्रयोग प्राणियों (persons) के साथ तथा of which का प्रयोग जानवरों तथा निर्जीव वस्तुओं के साथ किया जाता है, जैसे
(i) This is the boy. -- His father teaches you English.
This is the boy whose father teaches you English.
(ii) This is the car -- Its parts are not available now.
This is the car of which parts are not available now.
Exercise 7.
Join the following sentences using whose/of which :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को whose/of which का प्रयोग करते हुए जोड़ा :
1. The man wants to see you. His daughter is your student.
2. This is the man. His son is our college captain.
3. The girl is waiting outside. Her father gave you this letter.
4. This is the car. Its owner has disappeared.
5. The officer wants to give a party. His son has joined IIT Delhi.
6. I met a man. His leg was broken.
7. The teacher is very kind by nature. His knowledge is limitless.
Answers:
1. The man whose daughter is your student wants to see you.
2. This is the man whose son is our college captain.
3. The girl whose father gave you this letter is waiting outside.
4. This is the car of which owner has disappeared.
5. The officer whose son has joined IIT Delhi wants to give a party.
6. I met a man whose leg was broken
7. The teacher whose knowledge is limitless is very kind by nature.
(F) Use of When, Where, What and Why
(i) When
'When' (जब) का प्रयोग वाक्य में 'at which time/at or during the time that/after/just after which आदि के अर्थ में किया जाता है । यदि वाक्य में Antecedent (पूर्वगामी शब्द) 'समय' हो तो इसके पश्चात् भी ! on का ही प्रयोग होता है । जैसे -
1. It was midnight when the thief entered the house.
2. It was Sunday when we went on a picnic.
3. It was 2006 when my father purchased this house.
(ii) Where का प्रयोग
'Where' (जहाँ) का प्रयोग 'the place at / in / to which; the place or situation in which के अर्थ में किया जाता है । यदि वाक्य में Antecedent (पूर्वगामी शब्द) कोई 'स्थानवाची शब्द' है तो इसके पश्चात where का ही प्रयोग होगा । जैसे -
1. This is the temple where Gandhiji was shot dead.
2. This is the school where I read for five years.
3. The house where I am staying is very big.
(iii) What का प्रयोग
'What' (जो) का प्रयोग अज्ञात वस्तुओं, बातों या घटनाओं के लिए किया जाता है । वाक्य में इसका Antecedent (पूर्वगामी शब्द) नहीं होता है । वाक्य में इसका अर्थ that which या the things which होता है । इसका प्रयोग Nominative Case (कर्ता कारक) तथा Objective Case (कर्म कारक) दोनों में किया जाता है।
नोट -- What का प्रयोग हमेशा Singular (एकवचन) में ही होता है, जैसे -
1. What he says is true. (जो वह कहता है सही है ।) (Subject)
2. I shall give what you like. (जो तुम्हें पसन्द है मैं दूंगा ।) (Object)
3. Do what I say. (जो मैं कहता हूँ करो ।) (Object)
4. I don't know what is happening there. (मुझे नहीं पता वहाँ जो घट रहा है ।) (Object) उक्त चारों वाक्यों में what का कोई Antecedent नहीं है ।
(iv) Why का प्रयोग
Why (क्यों) का प्रयोग reason के पश्चात् किया जाता है ।
1. This is the reason why he didn't come.
2. This is the reason why I called you.
Exercise 8.
Join the following pairs of sentences using when, where, what or why:
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों के जोड़ों को when, where, what या why का प्रयोग करते हुए संयोजित करो :
1. Before 1990, I lived in a town. My father lived there.
2. This is the time. He will make you a call then.
3. 1947 was the year. India won freedom then.
4. Can you show me the school ? You teach there.
5. We visited the place. The accident had happened there.
6. Listen to that. Your father says that.
7. We remember the day. We first met then.
Answers:
1. Before 1990, I lived in the town where my father lived.
2. This is the time when he will make you a call.
3. 1947 was the year when India won freedom.
4. Can you show me the school where you teach ?
5. We visited the place where the accident had happened.
6. Listen to what your father says.
7. We remember the day when we first met.

(G) Use of Who/Whom/Whose/Which/Where (Non-defining)
जैसा कि पूर्व में बताया जा चुका है कि Relative Clauses दो प्रकार के होते हैं
(i) Defining Relative Clause
(ii) Non-defining Relative Clause
अभी तक हमने जितने भी Relative Pronouns के प्रयोग देखे हैं वे Defining Relative Clause के हैं । उक्त दोनों Clauses में मुख्य अन्तर निम्नलिखित हैं
|
Defining Relative Clause |
Non-defining Relative Clause |
|
1. यह बताता है कि वक्ता का तात्पर्य किस व्यक्ति या किस वस्तु से है । (i) We know a lot of people who live in London. |
इसमें वक्ता द्वारा बताई गई वस्तु या बताये गये व्यक्ति से हम पूर्व परिचित होते हैं अर्थात् यह किसी व्यक्ति या किसी वस्तु के बारे में नहीं बताता है। यह उनके बारे में अतिरिक्त जानकारी देता है |
|
(2) इसमें Clause को comma द्वारा बन्द नहीं किया जाता है। |
इसमें Clause के शुरू व अन्त में comma लगाया जाता है देखें, उदाहरण (i), (ii), (iv) । यदि अंत में हो तो clauses के शुरू में comma होता है व अन्त में full stop (.) होता है, देखें उदाहरण (iii)। |
|
(3) इसमें who/whom/which के स्थान पर that का प्रयोग किया जा सकता है । |
इसमें that का प्रयोग नहीं होता है । |
(3) इसमें who/whom/which के स्थान पर that इसमें that का प्रयोग नहीं होता है । का प्रयोग किया जा सकता है ।
Exercise 9.
Combine the following sentences using appropriate Relative Pronouns:
उपयुक्त Relative Pronouns का प्रयोग करते हुए निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को जोड़ो
1. I met Meera. Her friends like dogs.
2. I met Dolly. Her request was for a sweet song.
3. I saw Sohan. He was a bus conductor.
4. This is Anil. All like him.
5. This is Ram. Your father was calling him.
6. Where is Dr Singh ? You were talking about him.
7. Mother told stories of Hari Ram. He used to cheer his soldiers.
8. Puneet is living with his uncle. His parents are in abroad.
9. Prachi is studying in Pune. She is my niece.
10. The Taj Mahal was built by Shah Jahan. It is exquisitely beautiful.
Answers:
1. I met Meera, whose friends like dogs.
2. I met Dolly, whose request was for a sweet song.
3. I saw Sohan, who was a bus conductor.
4. This is Anil, whom all like.
5. This is Ram, whom your father was calling.
6. Where is Dr Singh, about whom you were talking ?
7. Mother told stories of Hari Ram, who used to cheer his soldiers.
8. Puneet, whose parents are in abroad, is living with his uncle.
9. Prachi, who is my niece, is studying in Pune.
10. The Taj Mahal, which is exquisitely beautiful, was built by Shah Jahan.
Exercise 10.
Combine each set of Simple Sentences into one Complex Sentence by using an Adjective
Clause : Simple Sentences के प्रत्येक युग्म को Adjective Clause का प्रयोग करते हुए Complex Sentence के रूप में संयोजित करो
1. My brother will come from Delhi. I do not know the time.
2. The pen is mine. It is on the table.
3. Ramesh is a good boy. He belongs to a good family.
4. I have a dog. It is very faithful.
5. The boy is standing there. He is my brother.
6. He did not come to school today. Do you know the reason ?
7. Will you give me the watch ? It is on the table.
8. I bought a pen a few days back. I have lost it.
9. The book is in my hand. I like it most.
10. The doctor is famous. She visited him.
Answers:
1. I do not know the time when my brother will come from Delhi.
2. The pen which is on the table is mine.
3. Ramesh, who belongs to a good family, is a good boy. Or Ramesh, who is a good boy, belongs to a good family.
4. I have a dog which is very faithful.
5. The boy who is standing there is my brother.
6. Do you know the reason why he did not come to school today?
7. Will you give me the watch that is on the table ?
8. I have lost the pen which I bought a few days back.
9. The book which I like most is in my hand.
10. The doctor whom she visited is famous.
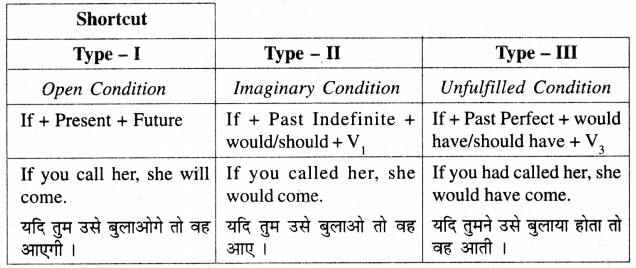
(3) Adverbial Clause Of Condition
(शर्त वाले क्रिया-विशेषण उपवाक्य) शर्तवाचक वाक्य (Conditional Sentence) दो उपवाक्यों (Clauses) से बना होता है
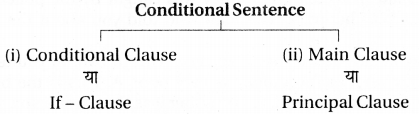
जैसे - If you call him, he will come. यदि तुम उसे बुलाओगे तो वह आएगा ।
उपर्युक्त वाक्य में 'If you call him' को If-Clause, Conditional Clause या Subordinate Clause कहते हैं । इसके द्वारा कोई शर्त व्यक्त की जाती है ।
दूसरा वाक्य 'he will come' Main Clause या Principal Clause कहलाता है । इसके द्वारा शर्त का परिणाम व्यक्त किया जाता है ।
नोट - यहाँ यह आवश्यक नहीं है कि वाक्य रचना हमेशा Conditional Clause + Principal Clause ही हो। यह Principal Clause + Conditional Clause की भी हो सकती है ।
अर्थात् - If you call him, he will come को He will come, if you call him. भी लिख सकते हैं। Conditional Sentences के द्वारा तीन प्रकार की शर्ते व्यक्त की जा सकती हैं -
(A) Open or Probable Conditions.
(B) Hypothetical, Unlikely, Improbable or Imaginary Conditions.
(C) Impossible or Unfulfilled Conditions.
(A) Open or Probable Conditions
(खुली या सम्भाव्य शर्त या Type -I)
इस प्रकार के वाक्यों में Conditional Clause द्वारा ऐसी शर्त रखी जाती है कि यदि उसे पूरा कर दिया जाए तो Main Clause में कही गई बात पूरी हो सकती है । अर्थात् इस प्रकार के वाक्यों से केवल सम्भावना प्रकट होती है। इसलिए इसे Open Condition भी कहते हैं । जैसे -
If you work hard, you will pass. यदि आप कठोर परिश्रम करेंगे तो आप पास होंगे ।
(अर्थात पहली शर्त मानने पर दूसरी बात पूरी हो सकती है ।) इस प्रकार की शर्त व्यक्त करने के लिए
If - clause → present में तथा Main Clause → future में होता है। वाक्य रचना -[If + Present + Future
Main Clause में will के स्थान पर may/can/must का प्रयोग भी हो सकता है । जैसे -
(a) If you call him, he may/might come. (सम्भव है वह आये ।) (possibility व्यक्त करता है।)
(b) If you complete your work, you may go home. (permission)
(c) If you bet, I can lift this. (ability).
(d) (command, request or advice व्यक्त करने के लिए ।)
If you want to lose weight, you must eat less bread.
(e) If + present + present (Natural law, Habitual Reactions, General truth तथा Scientific fact के लिए ।)
If you heat butter, it melts. यदि आप मक्खन को गर्म करते हैं तो यह पिघलता है । (दुसरा कार्य स्वतः ही होता है ।)

Exercise 1.
Fill in the blanks using correct tense and form of the verbs given in brackets :
कोष्ठक में दी गई क्रियाओं के सही tense व form का प्रयोग करते हुए रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करो --
1. If you..............(work) hard, you will get success.
2. If you.............. (have) headache, you can takerest.
3. If you don't do your home work, the teacher .............. (punish) you.
4. If she.............. (be) careless, she will hurt her finger.
5. If he .............. (not work) hard, he will not get through.
6. They will get wet, if it.............. (rain).
7. We .............. (play) chess, if you come to my house tomorrow.
8. The water will suit the patient, if the water .............. (be) fresh.
9. Plants grow quickly, if you.............. (water) them.
10. I cannot understand you, if you .............. (speak) Chinese.
Answers:
1. work
2. have
3. will punish
4. is
5. does not work
6. rains
7. shall play
8. is
9. water
10. speak.
(B) Hypothetical, Unlikely, Improbable or Imaginary Conditions
(असम्भाव्य या काल्पनिक शर्त या Type - II) इस प्रकार के शर्त वाले वाक्यों में If - Clause में ही ऐसी शर्त रख दी जाती है जो वर्तमान में ही पूरी नहीं हो सकती। अत: Main Clause में व्यक्त किये गए परिणाम प्राप्त हो ही नहीं सकते । इस प्रकार के वाक्यों में If-Clause past tense में व main clause-would/should +V की I form में होता है अर्थात्
If + Past + ............ would / should + V की I Form
If I knew his address, I would give you. यदि मुझे उसका पता याद हो तो मैं तुम्हें दूँ । (अर्थात् न तो वर्तमान में मुझे पता याद है और न ही मैं दूंगा ।)
ज्ञात तथ्यों के विपरीत परिकल्पना (contrary to known facts) प्रस्तुत करने के लिए - If+.............. were ............. + ........... would/should............ का प्रयोग किया जाता है, जैसे -
If I were a bird, I would fly in the sky. यदि मैं एक पक्षी होऊँ, तो मैं आसमान में उडूं।
(अर्थात् न तो मैं पक्षी हूँ और न ही आसमान में उगा ।)
(ii) Were Iyou, I would buy this. यदि मैं तुम जैसा होऊँ तो मैं यह खरीद लूँ । (If के स्थान पर were का प्रयोग किया जा सकता है ।)
Exercise 2.
Fill in the blanks using correct form and tense of the verbs given in brackets:
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं के सही form व tense से करो -
1. I would lend you, if I ............(have) money.
2. If I were the Prime Minister, I ............(make) you the Home Minister.
3. I............(read) this book, if I knew Chinese.
4. If I were you, I ............(help) her.
5. If he............(work) hard, he would pass.
6. I would not do it, if I ............(be) you.
7. If I saw Radha, I ............ (be) delighted.
8. The bridge............(collapse), if a heavy truck went over it.
9. What would happen, if she............(call) me?
10. He ............(speak) to you, if he saw you.
Answers:
1. had
2. would make
3. would read
4. would help
5. worked
6. were
7. would be,
8. would collapse
9. called
10. would speak.
(C) Impossible or Unfulfilled Condition
(असम्भव या अपूर्ण शर्त या Type - III)
इस प्रकार के वाक्यों में If-clause द्वारा जो शर्त व्यक्त की जाती है वह भूतकाल की होती है जिसे वर्तमान में पूरा नहीं किया जा सकता है इसलिए Main Clause में व्यक्त परिणाम भी प्राप्त नहीं होगा । अतः इन्हें Impossible Condition कहते हैं। जैसे -
If I had run fast, I would have caught the train. यदि मैं तेज दौड़ा होता तो मैंने गाड़ी पकड़ ली होती ।
(अर्थात् न तो मैं तेज दौड़ा और न ही गाड़ी पकड़ी
Note--If के स्थान पर had का प्रयोग करके भी इस प्रकार के conditional sentence को बनाया जा सकता है । Subject के पहले had लगाने पर यह If का कार्य करेगा । जैसे -
Had I run fast, I would have caught the train. वाक्य रचना - |
If + Past perfect + .......... would/should + have +V की III form.......... अर्थात् -
If-clause Past Perfect में होगा व Main Clause में would / should+ have+V की III formआएगी।

Exercise 3.
Fill in the blanks using the correct form and tense of the verbs given in brackets :
कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं के सही form a tense का प्रयोग करते हुए रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करो -
1. If she had caught the train, she..............(reach) in time.
2. You wouldn't have been hungry now, if you ..............(take) lunch.
3. If I had known that you were ill, I ..............(visit) you in the hospital.
4. You would have saved money, if you ..............(buy) this bike last year.
5. If they had played better, they..............(win) the match.
6. If you.............. (be) at the meeting, I should have seen you.
7. They would have heard better, if you .............. (speak) louder.
8. It would have been better, if they .............. (not come).
9. If he hadn't explained it to me, I ............. (never understand).
10. She would have done it, if they .............. (know) how to.
Answers:
1. would have reached
2. had taken
3. would have visited
4. had bought
5. would have won
6. had been
7. had spoken
8. had not come
9. would never have understood
10. had known.
Different Ways of Expressing Conditions
निम्नलिखित में से किसी भी रूप में Condition व्यक्त की जा सकती है
1. Unless = If ............. not के द्वारा । जैसे
(i) If you do not work hard, you will not pass.
Unless you work hard, you will not pass. यदि आप कठोर परिश्रम नहीं करोगे तो आप पास नहीं होंगे ।
याद रखिये Unless वाले Clause में not नहीं लगाया जाता है परन्तु
(ii) If you work hard, you will pass.
Unless you work hard, you will not pass.
यदि If-clause में not नहीं है तो unless लगाने पर main clause में not लगाया जाता है ।
2. 'should, were, had' helping Verbs से जो वाक्य आरम्भ होते हैं, वे condition का अर्थ रखते हैं,
जैसे - (i) Should you be feeling unwell, you may go.
Or If you should be feeling unwell, you may go.
(ii) Were I a king, I would reward you.
Or If I were a king, I would reward you.
3. Conjunctional Phrase जैसे in case के द्वारा । जैसे
यह सम्भावना के प्रति सजगता (carefulness) को प्रदर्शित करता है तथा इसमें हमेशा
main clause + in case + subordinate clause होता है।
Take an umbrella in case it rains. छाता ले लो अगर वर्षा हो जाए ।
4. Participle Phrase “Provided/Provided that, on condition that, so long as"
का प्रयोग करके, जब शर्त का भाव strong तरीके से व्यक्त करना हो । जैसे
(i) You can use my bike so long as you don't give it to anybody else.
(ii) Provided you allow me, I shall speak to him.
5. Imperative Mood का प्रयोग करके । जैसे
(i) Work hard and you will pass.
Or If you work hard, you will pass.
B (ii) Neglect your work and you will fail.
Or If you neglect your work, you will fail.
6. Interrogative sentences द्वारा । जैसे
(i) Will you go there? Then I will also go with you.
Or If you go there, I will also go with you.
(ii) Have you paid the cost? Then take away the cycle.
Or If you have paid the cost, take away the cycle.
7. Prepositional Phrase 'But for' को अपने Object के साथ प्रयोग करके । जैसे
But for your help, I should have been ruined.
= If it had not been your help, I should have been ruined.
यदि तुम्हारी मदद नहीं होती तो मैं बर्बाद हो गया होता ।
8. Phrase 'One more' का प्रयोग करके । जैसे
One more such loss and we are ruined.
9. Suppose/Supposing का प्रयोग करके । जैसे
Suppose/Supposing + past + past (असंभव कल्पना व्यक्त करने के लिए
Suppose/Supposing + present + future (ऐसी कल्पना जो पूरी हो सकती है ।)
(i) Suppose you get a hundred rupee note, what will you do?
= What will you do if you get a hundred rupee note ?
मान लो आपको 100 रुपये का एक नोट मिले तो आप क्या करोगे ?
(ii) Supposing the plane came late, what would happen?
= What would happen if the plane came late?
मान लो हवाई जहाज देरी से आए तो क्या हो ?
10. Whether........ or = if ............ or (इसका प्रयोग दो विकल्पों में से एक विकल्प का चुनाव करने के लिए किया जाता है ।)
You will have to do it whether you are ready or not.
= You will have to do it if you are ready or not.
आपको यह करना है चाहे आप तैयार हों या ना हों ।
11. If only = wish, hope तथा regret व्यक्त करने के लिए । जैसे
(i) If only + Present / Future = hope (आशा / उम्मीद) व्यक्त करता है -
If only he comes in time. = हमें उम्मीद है कि वह समय पर आएगा ।
(ii) If only + Past / Past Perfect = regret (पश्चाताप) व्यक्त करने के लिए ।
If only she didn't come. = हमें पश्चाताप है कि वह नहीं आएगा ।
(iii) If only + would = वर्तमान कार्य के लिए पश्चाताप व्यक्त करने के लिए ।
वर्तमान कार्य पर पश्चाताप व्यक्त करता है ।
If only it would rain. = We wish it would rain.
हमारी इच्छा है कि बरसात हो जाए, लेकिन नहीं हो रही है ।
12. even if - भले
You must do it even if you are not ready.
भले ही आप तैयार न हो आपको यह करना ही है । जैसे-
(i) If you permit me, I shall go there.
(ii) Unless you permit me, I shall not go there.
(iii) Supposing you permit me, I shall go there.
(iv) Provided you permit me, I shall go there.
(v) I'shall go there, in case you permit me.
(vi) Permit me and I shall go there.

Exercise 4.
Write the correct form of the verbs given in brackets so as to complete the following Conditional Sentences :
कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं के सही रूप का प्रयोग करते हुए निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Conditional Sentences के रूप में पूरा कीजिए -
(4) Adverbial Clause Of Time
ये Complex Sentences होते हैं । इनमें भी एक Principal Clause व एक या अधिक Subordinate Clauses होते हैं । जैसे -
(i) Imet Kavita after she had taken food.
(ii) I have not seen him since he left Mathura.
(iii) While I was watching TV, my brother was studying.
उक्त तीनों ही वाक्यों में after she had taken food, since he left Mathura व While I was watching TV Subordinate Clauses हैं जो समय को व्यक्त कर रहे हैं।
वे Subordinate Clause जो समय को व्यक्त करते हैं Time Clause कहलाते हैं ।
Position of Time Clauses:
(i) After the Main Clause - सामान्यतया Time Clause को Main Clause के ठीक बाद में रखा जाता है।
RAH - She phoned me when I was not at home.
(ii) Before the Main Clause – Time Clause को Main Clause के पूर्व भी रखा जा सकता है । जैसे -
After I had taken food, I went home.
(iii) In the middle of the Main Clause-Time Clause को कभी-कभी Main Clause के बीच में भी रखा
जा सकता है । जैसे - His father, when he was at Kota, was a manager in Carrier Point.
Chief Conjunctions
Conjunctions जिनका प्रयोग time clauses के साथ होता है वे सामान्यतया निम्नलिखित हैंwhen, as soon as, as long as, until (till), before, after, by the time, while, as, since, no sooner ........ than, scarcely (hardly) ................ when, आदि ।
विशेष - Time Clause कभी भी Future Tense में नहीं होता है । जब किसी Future Tense के वाक्य को Time Clause के रूप में प्रयुक्त किया जाता है तो उसे Present में बदल दिया जाता है । जैसे -
(i) He will come. वह आएगा ।
We will take food. हम खाना खाएंगे।
When he comes, we will take food. जब वह आएगा, हम खाना खाएंगे ।
(ii) I will be at school. I will learn English.
When I am at school, I will learn English. जब मैं स्कूल में होऊँगा तो मैं अंग्रेजी सीखंगा ।
महत्त्वपूर्ण Subordinate Conjunctions के प्रयोग
(A) When
(1) जब किसी लम्बी चलती घटना के बीच में कोई छोटी घटना घटित हो -
They were watching TV when they heard the door bell. जब उन्होंने दरवाजे की घण्टी सुनी वे टी.वी. देख रहे थे।
(2) जब एक घटना के बाद दूसरी हो
When the rain stops, we will go out. जब बरसात रुकेगी तो हम बाहर जायेंगे।
(3) भूतकाल की समयावधि या जीवन की अवधि की बात करने के लिए -
When I was a baby, I was called Guddu. जब मैं बच्चा था तब मुझे गुड्डू पुकारा जाता था।
(4) हर समय
When my mother comes in my room, I am studying.
जब जब भी मेरी माँ मेरे कमरे में आती है मैं पढ़ता रहता हूँ।
(B) As
(1) जब दो घटनाएँ एक साथ हों या एक घटना के पूरी होते-होते ही दूसरी घटना भी घटित हो जाए
('ठीक उसी समय' के अर्थ में)
As you turn, you will see me. जैसे ही तुम घूमोगे तो तुम मुझे देख लोगे ।
(2) जब आप कोई एक कार्य कर रहे होते हैं तभी दूसरा कार्य हो जाए ।
He was seen as he was climbing over the wall. दीवार फाँदते समय उसे देखा गया ।
(3) As + a situation = because.
(i) As he was not there, he didn't know anything.
चूँकि वह वहाँ पर नहीं था इसलिए उसे कुछ भी पता नहीं है।
(C) While इसका प्रयोग जब, जिस समय के अर्थ में होता है -
I met a lot of people while I was on a holiday.
जिस समय मैं छुट्टी पर था उस समय में कई लोगों से मिला ।
(D) As soon as = ज्यों ही जब एक कार्य के पूरा होते ही दूसरा हो -
(i) He saw me. He called me.
As soon as he saw me, he called me. ज्यों ही उसने मुझे देखा, उसने मुझे पुकारा ।
(E) No sooner..................than.
No sooner के साथ verb उसी प्रकार से प्रयुक्त होती है जिस प्रकार से एक प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य में होती है अर्थात् उसमें helping verb को subject के पूर्व रखा जाता है। Pattern- No sooner + H.V. + subject + M.V. +.......+ than + subject + Verb
He saw me. He called me.
No sooner did he see me than he called me.
(F) Hardly/Scarcely........... when.
इसका प्रयोग भी उसी प्रकार से होता है जैसे No sooner......... than का होता है ।
Pattern -
Hardly/Scarcely + H.V. + Subject + M.V. ... + when + Subject + Verb...
Hardly/Scarcely had he taken food when he began to feel drowsy.
Hardly तथा Scarcely के साथ when का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
(G) Before = पहले
जब दो कार्यों में एक कार्य के समाप्त होने से पहले दूसरा समाप्त हो जाए ।
Pattern -- Past Perfect + before + Past Indefinite Or
Before + Past Indefinite + Past Perfect
अर्थात् Subordinate Clause Past Indefinite में होगा ।
The patient had died before the doctor came. Or
Before the doctor came, the patient had died.
डॉक्टर के आने के पहले मरीज मर चुका था ।
(H) After = पश्चात्
जब दो कार्यों में एक कार्य के समाप्त होने के पश्चात् दूसरा कार्य समाप्त हो ।
Pattern - After + Past Perfect + Past Indefinite. Or Past Indefinite + after + Past Perfect.
अर्थात् after के साथ वाला clause (Subordinate Clause) Past Perfect में होगा ।
The patient died after the doctor had come.
डॉक्टर के आ जाने के पश्चात् मरीज मरा ।
(I) Since ( तब ) से, ( उस समय) से इसका प्रयोग
Perfect Tenses के साथ होता है । जैसे -
I haven't seen her since I left school. जब से मैंने स्कूल छोड़ा तब से मैंने उसे नहीं देखा है।
(J) till/until = जब तक कि नहीं
Wait here till (until) the light changes to green.
जब तक लाइट हरी नहीं हो जाए तब तक यहीं इंतजार करो।

Exercise 1.
Put the most suitable words in the space to complete the following sentences choosing from the bracket given against each space :
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्मुख दिये गए कोष्ठक में से सबसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो
1. I will cook food .................. (as soon as/till/before) I come home.
2. I want to finish my work .................. (till/after/before) we go out.
3. She is going to look after the cat .................. (as/before/while) I am away on holiday.
4. I'll e-mail you .................. (as soon as/while/till) I arrive.
5. We'll find a hotel .................. (when/till/no sooner) we arrive in Mathura.
6. Don't cross the road .................. (as/when/until) you see the red signal.
7. I'll give you a ring .................. (when/before/until) we get back from our vacation.
Answers:
1. as soon as
2. before
3. while
4. as soon as
5. when
6. until
7. when.
Exercise 2.
Put the most suitable words in the space to complete the following sentences choosing from the bracket given against each space :
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्मुख दिये गए कोष्ठक में से सबसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो
1. ........... (When/As/Since) I was much younger, I enjoyed camping out.
2. ........ (After/As long as/Before) the man had stopped his car to help, Ramesh recognized him.
3. You seem happy .................. (till/when/after) you help others.
4. .................. (When/As/Since) the cat is away, the mice will play.
5. I will wash up .................. (before/when/while) he goes to bed.
6. .............. (No sooner/When/Hardly) it gets cold, I'll light the fire.
7. ............. (When/Till/Then) the queen arrives, the audience will stand up.
Answers:
1. When
2. After
3. when
4. When
5. before
6. When
7. When.
Exercise 3.
Combine the following sentences using the conjunction that is provided in the brackets :
1. She will give the children their dinner. He comes home. (before)
2. She will stay in bed. The clock strikes seven. (till)
3. She will go on. He tells her to stop. (until)
4. The lift will not start. You press that button. (until)
5. Rani studied very hard. She took the exam on Thursday. (before)
6. The door bell rang. Ravi was taking a shower. (when)
7. Govinda was backing into a parking space. He heard a crunch. (while)
8. I met him. I was in Udaipur. (when)
9. Anurag was thoroughly exhausted. He ran the Boston Marathon (26 miles). (after)
10. John was eating his dinner. He was watching the news on TV. (When or while)
Answers:
1. She will give the children their dinner before he comes home.
2. She will stay in bed till the clock strikes seven.
3. She will go on until he tells her to stop.
4. The lift will not start until you press that button.
5. Rani had studied very hard before she took the exam on Thursday.
Or
Before Rani took the exam on Thursday, she had studied very hard.
6. When the door bell rang, Ravi was taking a shower.
7. While Govinda was backing into a parking space, he heard a crunch.
8. When I was in Udaipur, I met him.
9. Anurag was thoroughly exhausted after he had run the Boston Marathon. (26 miles).
10. While he was watching the news on TV, John was eating his dinner.
Or
John was eating his dinner while he was watching the news on TV.

Miscellaneous Exercises
Practice Exercise 1.
Combine the following sentences using the words given in brackets:
1. If you do not work hard. You will not succeed. [unless]
2. If he does not come to me. I will not help him. [unless]
3. He finished his work. He went to bed. [after]
4. This is my pen. I bought it yesterday. [that]
5. He reached the hall. Then the film started. [after]
6. I know the reason. He did not succeed. [why]
7. I reached school. It began to rain. [as soon as]
8. As soon as I reached the hall. The film started. [no sooner. ...........than]
9. I was writing a letter. The light went off. [while]
10. I had finished my homework. I went to bed. [when]
Answers:
1. Unless you work hard, you will not succeed.
2. Unless he comes to me, I will not help him.
3. After he had finished his work, he went to bed.
4. This is my pen that I bought yesterday.
5. After he had reached the hall, the film started.
6. I know the reason why he did not succeed.
7. As soon as I reached school, it began to rain.
8. No sooner did I reach the hall than the film started.
9. While I was writing a letter, the light went off.
10. When I had finished my homework, I went to bed.
Practice Exercise 2.
Combine the following sentences using the words given in brackets:
1. Work hard. You will pass. [if]
2. Do not work too much. You will lose your health. [if]
3. I waited for Ravi. I waited till his arrival. [till]
4. The doctor came. The patient died. [after]
5. The counter opened. There was rush for tickets then. [when]
6. It is raining. Stay here during that time. [as long as]
7. He won a prize in the lottery. The news is correct. [that]
8. The book has coloured pictures. The child wants it. [which]
9. Sarla beat a girl. I know her. [whom]
10. This is the hospital. Here Anand was born. [where]
Answers:
1. If you work hard, you will pass.
2. If you work too much, you will lose your health.
3. I waited for Ravi till he arrived.
4. The doctor came after the patient had died.
5. When the counter opened, there was rush for tickets.
6. Stay here as long as it is raining.
7. The news that he won a prize in the lottery is correct.
8. The book which the child wants has coloured pictures.
9. I know the girl whom Sarla beat.
10. This is the hospital where Anand was born.
Practice Exercise 3.
Combine the following sentences using the words given in brackets:
1. The guard blew the whistle. The train left the station. [as soon as]
2. Will you go to the movie with me? I want to know. [if]
3. He will pass. It is certain. [that]
4. He went to the garden. He plucked flowers. [where]
5. The villagers caught the thief. He was trying to run away with a bag. [who]
6. He saw me. He hid himself. [no sooner ........than]
7. The boy was happy. He had found his lost book. [when]
8. She went to bed. She took food. [after]
9. Milton was a famous English poet. He was blind. [who]
10. He will come at any time. I don't know the exact time. [when]
Answers:
1. As soon as the guard blew the whistle, the train left the station
2. I want to know if you will go to the movie with me.
3. It is certain that he will pass.
4. He went to the garden where he plucked flowers.
5. The villagers caught the thief who was trying to run away with a bag.
6. No sooner did he see me than he hid himself.
7. The boy was happy when he had found his lost book.
8. She went to bed after she had taken food.
9. Milton, who was a famous English poet, was blind.
10. I don't know the exact time when he will come.
Practice Exercise 4.
Put the most suitable words in the spaces to complete the following sentences choosing from the brackets given against each space:
1 The king didn't know......(i)......... (that/which/why] the bearded man was his enemy. He simply saw...... (ii)......... (which/why/ that) a bearded man came running to him. He had wound in his stomach from ......(iii)......... [when/where/why] blood was coming out. ...... (iv)......... [When/Where/Why) the king noticed it, he thought to help the man.
2 Katie was one of those girls ...... (i)......... (who/whom/when) had been tricked by the boys earlier in the night. The girls wanted to trick the boys the next night. For it they collected all the boys under the tree ...... (ii)......... (where/when/while) they could play their trick. ...... (iii)......... (After/Before/As) all the boys had gathered, they started their plan. The head girl told all others...... (iv)......... (that/when/what] they must keep quite.
3 Gangi went to the Thakur's well from...... (i)......... (where/when/while) the whole village drank water. They were the only persons...... (ii)......... (who/whom/which) could not drink water from there. ...... (iii)......... [If/As/Unless) Gangi's family did not belong to low caste, they would be allowed to drink water. It was night ...... (iv)......... (when/while/as] she went there.
Answers:
1. (i) that (ii) that (iii) where (iv) when
2. (i) who (ii) where (iii) after (iv) that

Practice Exercise 5.
Put the most suitable words in the spaces to complete the following sentences choosing from the brackets given against each space:
1 ...... (i)......... [If/Unless/Had) you happen to disturb someone accidently, you should say 'sorry' to the person ...... (ii)......... (whom/which/where) you have disturbed. Similarly, ...... (iii)......... [if/until/as) you happen to break some rules of politeness or of good manners you should show regret by saying 'sorry' to the person ...... (iv)......... [whom/ who/which) is affected by your act.
2 ...... (i)......... (When/Where/Which) we are on a bus or a train, we can show politeness towards women by giving them our seats...... (ii)......... (if/as/unless] they are standing. We can open a door of a bus for women ...... (iii)......... [when/while/which) they need it. It is an act...... (iv)......... [that/what/why) is called kindness.
Answers:
1. (i) If (ii) whom (iii) if (iv) who
2. (i) when (ii) if (iii) when (iv) that

- The Tale of Melon City Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 8 RBSE Solutions
- Birth Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 7 RBSE Solutions
- The Ghat of the Only World Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 6 RBSE Solutions
- Mother’s Day Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 5 RBSE Solutions
- Albert Einstein at School Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 4 RBSE Solutions
- Ranga’s Marriage Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 3 RBSE Solutions
- The Address Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 2 RBSE Solutions
- The Summer of the Beautiful White Horse Question Answer Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 1 RBSE Solutions
- Father to Son Question Answer Class 11 English Hornbill Chapter 5 RBSE Solutions
- Childhood Question Answer Class 11 English Hornbill Chapter 4 RBSE Solutions
- The Voice of the Rain Question Answer Class 11 English Hornbill Chapter 3 RBSE Solutions