RBSE 11th Geography Practical Book Solutions Chapter 7 Introduction To Remote Sensing
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Practical Book Chapter 7 Introduction To Remote Sensing
RBSE 11th Geography Practical Book Solutions Chapter 7 Introduction To Remote Sensing
RBSE Class 11 Geography Introduction To Remote Sensing Textbook Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below:
(i) Remote sensing of objects can be done through various means such as A. remote sensors B. human eyes and C. photographic system, which of the following represents the true order of their evolution.
(a) ABC
(b) BCA
(c) CAB
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) BCA.

(ii) Which of the following regions of Electromagnetic spectrum is not used in satellite remote sensing?
(a) Microwave region
(b) Infrared region
(c) X-rays
(d) Visible region
Answer:
(b) Infrared region.
(iii) Which of the following is not used in visual interpretation technique?
(a) Spatial arrangements of object s
(b) Frequency of tonal change on the image
(c) Location of objects with respect to other objects
(d) Digital image processing
Answer:
(c) Location of objects with respect to other objects.
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words:
(i) Why is remote sensing a better technique then other traditional methods?
Answer:
Remote sensing is better technique other than traditional technique because this remote sensing is done by satellites which have capabilities of covering a large area.
(ii) Differentiate between IRS and INSAT series of satellites.
Answer:
The sensors recording the energy that they receive are placed in a near polar sun synchronous orbit at an altitude of 700-900 km. These satellites are known as remote sensing satellites. As against these satellites the weather monitering and telecommunication satellites are place in a geostationary position and revolves around the earth at an altitude of nearly 36,000 km.
3. Answer the following questions in about 125 words:
(i) Describe the operations of a whiskbroom scanner with the help of a diagram. Explain how it is different from pushbroom scanner.
Answer:
Whiskbroom scanner and its operation: The whiskbroom scanner is made up of a rotating mirror and a single detector. The mirror is so oriented that when it completes a rotation, the detector sweeps across the field of view between 90° and 120° to obtain images in a large number of narrow spectral bands ranging from visible to middle infrared regions of the spectrum. The total extent of the oscillating sensor is known as the total field of view of the scanner. The pushbroom scanner consist a large number of ditietois which are equalent to the number obtained by dividing the swath of the senson. Whiskbroom scanner is made up at relating mirror and single distictor.
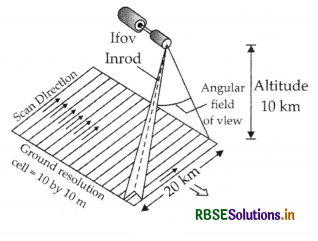
Dwell Time = \(\frac{\text { Scan rate per line }}{\text { Number cells per line }}=\frac{2 \times 10^2 \mathrm{sec}}{2000 \text { cels }}\)
= 1 x 104 sec. cell
Whiskbroom Scanner
(ii) Describe in brief the functioning of pushbroom scanner.
Answer:
The pushbroom scanners consist of a number of detectors which are equivalent to the number obtained by dividing the swath of the sensor by the size of the spatial resolution.
(iii)
Identify and list the changes that can be observed in the vegetation of of Himalayas?
Answer: The coniferous forests are disappeared and the deciduous forests have been taken place of coniferous forests
RBSE Class 11 Geography Introduction To Remote Sensing Important Questions and Answers
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by ‘Remote Sensing’? What are its advantages?
Answer:
Remote Sensing is the science of gathering information about objects from a distance without coming into physical contact with them. It thus includes data gathered through photographs taken from aeroplanes and satellites. The remote sensing is generally done by the satellites, which have capabilities of covering a large area.
Advantages:
The advantages of remote sensing are as follows :
- It gives a synoptic view of a region rather than a district or block.
- It provides a reliable and real or near real time base line information.
- It is relatively fast and economical as compared to ground survey.
- It provides analog and digital data for visual and digital interpretations respectively.
- It provides repetitive coverage of the same area, which is useful for change monitoring.
- It is unaffected by bad weather or difficult ground conditions.
Question 2.
Describe the functions of NRSA in India.
Answer:
Functions of the National Remote Sensing Agency (NRSA) The National Remote Sensing Agency, an autonomous organisation under the Department of Space, Government of India, established in 1974, is primarily responsible for the following activities:
- Remote-sensing satellite data acquisition, storage processing and dissemination;
- Applications of remote sensing for mapping, monitoring and management of natural resources;
- Operational flight facilities to provide aerial remote sensing services;
- Training to users; and
- Research and technology development.

Question 3.
What are satellite imagery?
Answer:
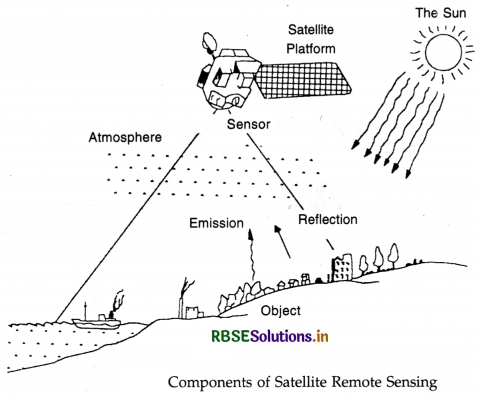
Satellite Imagery:
‘Satellite imagery’ is of practical value to geographers because they provide synoptic coverage of large areas and permit a more accurate regional mapping of natural resources. It is obtained through the techniques of remote sensing. The features on the earth’s surface are captured in these imageries by detecting the characteristics of electromagnetic radiation that is reflected/emitted by the earth's surface. The reflectance/emittance of any object at different wavelengths follows a pattern which is characteristic of that object, known as ‘spectral signature’. Proper interpretation of the spectral signature leads to the identification of the object.
Question 4.
Describe the terms used in Satellite Remote Sensing.
Answer:
(i) Energy : On the basis of source of energy remote sensing is of two types :
(a) Active Remote Sensing :
It is the science of recording the information energy activated by man like flashguns, microwave radar, etc.
(b) Passive Remote Sensing:
It records the reflected or emitted energy which comes from the natural sources like the sun, and the earth's internal thermal radiation.
(ii) Sensor :
Sensor is another parameter to determine the types of remote sensing. According to the sensor, remote sensing is again of two types :
(a) Photographic
(b) Non-photographic.
In image forming remote sensing or photographic remote sensing the information is collected in photographic form. General aerial photographic represents this type.
(iii) Platform :
It varies upon the boarding of sensor as fitted on some platform. Space borne platforms are used. Airborne platforms like air planes are used. If the sensor is on the ground it is called ground band remote sensing
Essay Type Questions
Question 5
(a) What is Remote Sensing? What are its types?
(b) Describe the process of Remote Sensing.
(c) Explain its advantages and application in! India.
(d) How will you identify physical and cultural features on the basis of tone and shape?
Answer:
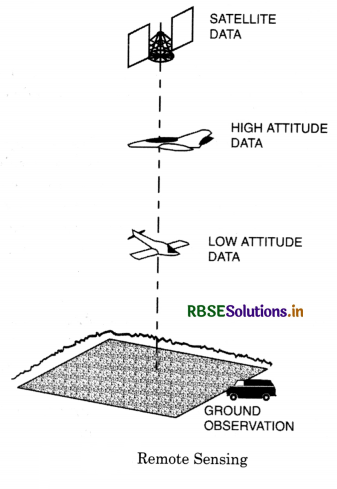
(a) Remote Sensing. The art or science of collecting data and maps about an object or an area at a distance without having any contact with it is called Remote Sensing. Generally ground surveys are used to cover small areas, but it takes a long time to complete it. So Remote Sensing methods are used for accuracy. It includes generally aerial and satellite photographic surveys.
Types of Remote Sensing:
(i) Survey from Elevation. Surveyors uses to climbe a hill or ridge to see large area from a distance. It increases the range or sight.
(ii) Aerial photographs. The first attempt was made in Paris in 1858. When a camera was attached to a Balloon. After First World War, aeroplanes began to be used to take photographs of ground below. Air photographs brought out pattern of relief features, geological structure, drainage land use, etc. and maps related to above prepared.
(iii) Satellite Imageries. With the development of space travel, video cameras were fixed to satellites and the pictures were transmitted to the ground. This helps in weather forecasting. Indian meteorological Deptt. uses INSAT/2B satellite for this. These photographs help in mineral surveys, land use, assessment of Agricultural production.
(Introduction to Remote Sensing)
(b) Remote Sensing System. The system is based on Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR). The reflected emitted, and back scattered radiation carry information about the objects and areas. The long wave radiation recorded by the sensor are known as special signatures. The features can be identified on the basis of tone, texture, shape, size and pattern.

INPUT DEVICES:
Input device especially for map preparations are essential for map printing and positioning (locating). The input devices used are joystick, light pen etc. These devices are used for graphs, flow charts etc.
OUTPUT DEVICES:
The output devices used in the computer are printers, plotters and VDU (video display unit). Besides the input and output devices there are other devices used for storage of the data. The information storage device is known as the memory of the computer. This is a magnetic tape which helps in storing large amount of information. The stored information can be restored to the user when required. Nowadays readymade computer programmes are stored on a disc called '‘floppy disc” which has instructions which would instruct the computer when instructed (like audio and video tapes). Such programmes are available for any computer operations. These are called “software packages”.
(c) Advantages of Remote Sensing
1. The remote sensing, surveying like aerial photograph and satellites imageries of birds eye view of large areas.
2. Unlike human eye aerial photographs and imageries can give us a stop action view of dynamic conditions for example earthquake devastations, moving wildlife, oil spills, forest fires, track and cyclones, etc.
3. Aerial photographs and satellite imageries are permanent records of pre-existing conditions.
4. The earth orbiting satellites give information regarding weather and landuse.
5. The use of remote sensing has made feasible the identification and study of inaccessible areas to men.
6. Remote sensing has lessened the work of ground surveyors and cartographers. Remote sensing aided with computer mapping has helped in the preparations of geologic maps, soil maps land cover maps with greater accuracy and speed.
7. Remote sensing has aided the Resource management especially in estimating snow melt and run off, to estimate the crop yields, identification of encroachments on forest cover, soil erosions etc.
8. Remote sensing has helped in the continuous monitoring of the disasters especially forest fire, land sliders, floods etc.
9. Remote sensing surveys are important to environment scientist to identify the polluted areas.
10. Remote sensing also helps the scientist to find how human environment affects the environment, for example global warming and ozone layer depletion.
11. The most important utility or advantage of remote sensing has been it’s application in planning. Planners greatly rely on the surveys of remote sensing surveys for implementations of programmes so as to achieve a proper and smooth functioning of environment as a whole. The various ways in which the remote sensing has been useful to planners are as
listed below :
(a) Has helped in forest management by identification of the areas of deforestation, disease identification, forest fires etc.
(b) Has helped in ensuring a proper land management by identification of soil degradation, soil alkinity, salinity, land use pattern etc.
(c) Implementing drought relief, flood relief programmes by identifying the drought prone areas, flood affected areas, cyclone hit areas etc.
(d) Agricultural management by identifying the areas of crop stress, water logging, crop disease, areas affected by pest.
(e) In the recent times wherein environmental pollution has been the major field of concern to the planners, remote sensing technology has catered to their needs by providing such areas affected by industrial pollution and the like.
(f) Remote sensing surveys have been used also in the study of population in the periods between consecutive census. Thus we can conclude that remote sensing technology has been a boon to mankind, with it’s speed and accuracy in spotting out areas of disaster and an aid to the scientists from all fields i.e. environment, agriculture, hydrology, meteorology, botany, lithology, geology etc. Application in India. In 1979-81, Bhaskar-I, II were used for assessing resources of India by NRSA (National Remote Sensing Agency), IRS-PS IRS-P6 etc. were used for agricultural purposes.

(d) Identification of Different Features:
1. Tone : Different Surface Objects reflect and emit different amount of radiant energy and these are
recorded in different levels (usually between 0 to 225). The zonal contrast gives clue to the edge or boundary between the objects.
2. Size. It refers to the spatial dimension of the objects on ground on an image it varies depending on the scale. It provides a realistic clue in identifying objects.
3. Shape. It refers to the physical form of an object and is also a function of scale of the image. Size and shape are interrelated in identifying objects.
4. Texture. It is defined as a repetition of basic pattern. It is useful in identification as it creates as visual impression of surface roughness or smoothness.
5. Pattern. It refers to the spatial arrangement of surface feature and the types are linear road, rail, canal, non-linear-streams, continuous-snow, sand, clustered settlement.
6. Cartography. The science of mapping disaster and an aid to the scientists from all fields
(i) environment, agriculture, hydrology, meteorology, botany, lithology, geology etc.
