RBSE 11th Geography Practical Book Solutions Chapter 3 Latitude, Longitude and Time
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Practical Book Chapter 3 Latitude, Longitude and Time
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Geography Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE 11th Geography Practical Book Solutions Chapter 3 Latitude, Longitude and Time
RBSE Class 11 Geography Latitude, Longitude and Time Textbook Questions and Answers
Short Answer Type Questions
1. Answer the following questions in about 30 words :
(i) Which are the two natural points of reference on the Earth?
Answer:
North pole and South pole.

(ii) What is a great circle?
Answer:
A circle that divides the earth into two equal parts.
(iii) What are co-ordinates?
Answer:
Latitudes and Longitude.
(iv) Why does the sun appear to be moving from East to West?
Answer:
Due to rotation of earth from West to East.
(v) What is meant by local time?
Answer:
It is the time of its own meridian.
2. Distinguish between latitudes and longitudes.
Answer:
|
Latitude |
Longitude |
|
1. Latitude is the angular distance of a place North or South of the Equator. |
1. Longitude is the angular distance of a place East or West of Prime meridian. |
|
2. The latitude value increases in North South direction from the Equator. |
2. The longitude value increases in East-West directions from the meridian. |
|
3. Its value ranges between 00 to 90°N,0°to 90° 5 |
3. Its value ranges between 00 to 1800 E, 00 tol8O° W. |
RBSE Class 11 Geography Latitude, Longitude and Time Important Questions and Answers
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
“The degree of longitude decreases in length poleward.” Why?
Answer:
Equator is the longest parallel on the earth. All other parallels become shorter polewards due to spherical shape of the Earth. So the meridians near the poles have a narrow space. One degree of longitude is the longest at the Equator (111 km), at 45° latitude it is 79 km, at 60° latitude it is 55 km and at poles, it is zero km.
Question 2.
“There is a difference of 4 minutes of time for one degree of longitude.” Why?
Answer:
There is a close relation between longitude and time. The Earth makes one complete rotation of 360 degrees in 24 hours. It passes through 15 degrees in one hour or one degree in four minutes. Thus, there is difference of 4 minutes of time for one degree of longitude. As the Earth moves from West to East, the places east to Greenwich gain time whereas the places west of Greenwich lose time.
Question 3.
“The difference between the G.M.T. and I.S.T. is 514 hours.” Why?
Answer:
G.M.T. is measured from Greenwich meridian i.e. 0° meridian; while Indian Standard Time is measured from 821/2° E meridian.
Local time for Eastward places is advanced. So the
I.S.T. will be ahead of that of G.M.T. The difference of
time for l longitude is 4 minutes. 165
∴ for 82½0 longitude the difference in time \(=\frac{165}{2} \times 4\)
= 330 minutes
= 5 hrs.-30 minutes
Question 4.
“The zero degree meridian of longitude is known as prime meridian.” Why ?
Answer:
The zero degree meridian passes through Greenwich near London. The Royal Astronomical Observatory is located here. This is the central meridian from which all meridians radiate Eastwards and Westwards upto 180°. This meridian has been selected by international agreement to serve as a reference line. Therefore it is known as prime meridian.
Question 5.
"The difference between two consecutive (£) parallels of latitude is equal to about 111 km.”
Why ?
Answer:
The circumference of the Earth is approximately 40,000 km. It covers an angle of 360 degrees. The distance between two consecutive parallels of latitude is everywhere
40,000
the same. Therefore, one degree of latitude \(=\frac{40,000}{360}=\)
111 km approximately.
Question 6.
“Lines of latitude are called parallels of latitude.” Why ?
Answer:
Lines of latitudes join the places of same latitude. These are circles drawn round the Earth, parallel to the Equator. Therefore, these are called parallels of latitude.
Question 7.
“Lines of longitude are called meridians of longitude.” Why ?
Answer:
Lines of longitude join the places of same longitude. These are semi-circles joining North Pole and South Pole. The word ‘meridian’ means mid-day. All the places situated on lines of longitude have their noon at the same time, therefore, these lines are called ‘meridians of longitude’.
(fi)
Question 8.
“Canada has six time zones.” Why?
Answer:
Difference in local time in different areas often gives rise to great confusion. To avoid this, the world is divided into 24 time zones, each covering 15° longitude with a difference of 1 hour in time Canada has an extent of about 90° longitude. Therefore, Canada has six time zones each having its own standard time.
Question 9.
What is the main function of longitude in Mathematical Geography?
Answer:
Longitude's main function is to determine local time of a place in relation to Greenwich Mean Time or world time. It is useful in determining the location of a place on the earth.

Question 10.
Explain the effect of latitude on the temperature of a place.
Answer:
The temperature decreases gradually from the Equator towards the poles. The angle of incidence of sun's rays increase away from the Equator. Thus, intensity of sun's rays decreases with the increase in latitude.
Question 11.
What is the effect of longitude on time?
Answer:
All the places located on the same meridian have the same local time. As the Earth rotates from West to East, the places in the East will have sunrise earlier than places on the West. The places in the East gain time while the places in the West lose time. The Rule is : (East-gain-Add, West-Lose-Subtract).
Question 12.
Define Equator. What is its main function?
Answer:
Equator is the parallel of zero degree latitude. It is an imaginary circle round the Earth bisecting it into two halves i.e. Northern hemisphere and Southern hemisphere. It serves as reference line for the location of different places on the earth.
Question 13.
What is a Chronometer?
Answer:
A chronometer is a highly accurate time piece which is used to keep Greenwich Mean Time. The Greek word ‘chronos’ means time. It helps in determining the longitude of a place.
Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the latitude and longitude of a place.
Answer:
Geographical Position:
The Earth is not a plain surface. The Earth is spherical in shape. It is not easy to locate any place on it without using a mathematical method. The Earth rotates on its axis. The two ends of the axis are called North Pole and South Pole. The lines drawn from Pole to Pole are called lines of longitude. The Equator lies half way between the two poles. The lines drawn parallel to the Equator are called lines of latitude. The network formed by the intersection of the lines of longitude and the lines of latitude is called Earth Geoid. It helps us to determine the location of any point on the globe. For example, Delhi is situated at 77° E, (longitude) and 29° N (latitude). With the help of these intersecting lines it is easy to locate the position of Delhi on a map.
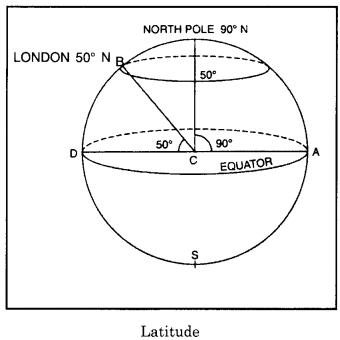
Latitude of a Place:
The Equator is the natural reference line as it bisects the Earth into two equal parts i.e. Northern hemisphere and Southern hemisphere. The latitude of a place is the angular distance of place North or South of the plane of the Equator.
For example, in the diagram given ahead, London makes an angle of 50° towards the North of equator, its latitude will be 50° N Longitude of Place The Greenwich meridian is the reference line because it bisects the Earth into two equal parts i.e. Eastern hemisphere and Western hemisphere. The longitude of a place is the angular distance of place along the equator,
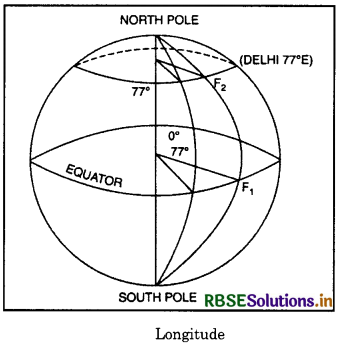
Longitude of Place:
The Greenwich meridian is the reference line because it bisects the Earth into two equal parts i.e. Eastern hemisphere and Western hemisphere. The longitude of a place is the angular distance of place along the equator,
Question 2.
What are the lines of latitude and longitude?
What are their uses? What is relation between longitude and Time?
Answer:
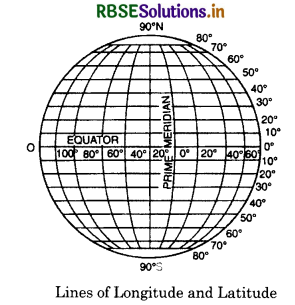
Lines of Latitude. Lines of latitude are imaginary lines passing through the places having same latitude. These are circles drawn round the Earth. These are drawn parallel to equator (West to East) and, therefore, called parallels of latitude. The equato?s value is 00 latitude and it is the longest circle on the earth. The value of Poles is 90° N and 90° S shown as points. The total number of lines of latitude is 180 -1 = 179. The length of the parallels becomes smaller and smaller as we move away from the equator towards the poles. This is due to the spherical shape of the earth. 60° parallel is half the length of the Equator. The distance between two consecutive parallels of 1° is equal ta about 111 km.
10° of latitude \(=\frac{\text { Circumference of the Earth }}{360^{\circ}}\)
\(=\frac{40,000 \mathrm{~km}}{360}=111 \mathrm{~km}\)
Important Parallels of Latitude
the inclination of the axis of the Earth \(\left(23 \frac{1}{2}^{\circ}\right)\) helps
us to mark the five important parallels of latitude.
(a) 00 parallel is called the Equator.
(b) \(23 \frac{1^{\circ}}{2}\)N parallel is called the Tropic of Cancer.
east or west of the Prime meridian. For example, in the diagram given below, Delhi makes an angle of 770 towards East of Prime meridian. so its longitude will be 770 E.
(c) \(23 \frac{1^{\circ}}{2}\) SparalleliscalledtheTropicofCapricorn.
(d) \(66 \frac{1^{\circ}}{2}\) N parallel is called the Arctic circle.
(e) \(66 \frac{1^{\circ}}{2}\) S parallel is called the Antarctic circle.
Uses of Latitudes .
(i) We can find out the temperature of a place with the help of latitude. We can have an idea of climate and natural vegetation of a place if its latitude is known.
(ii) We can find out the distance of a place from the Equator with the help of its latitude. (1° latitude =111 km).

(iii) We can determine the location of a place on the map Lines of Longitude Latitude gives the Northward or Southward distance from the Equator. For determining the location of place, we take East-West distance too. Fur this zero meridian passing through Greenwich (near London) was taken as Prime Meridiwi All other lines of Longitude were drawn East or West of Prime meridian. Lines of Longitude are imaginary lines pieeing through che place of equal longitude, These are semi-c ireles )oining North Pole and South Pole These are also calLed Meridians meaning mid-day. All the places situated on a line of longitude have their noon at the same time. The se are equal in length.
Their value goes upto IÛ E and 180 W. These converge at the poles. AL Equator, the distance for one degree of longitude ial) 1 km. Hut this distance for one degree of longitude goes on decreasing polewards. Due to curvature of the sph erical Earth, the meridians enclose a narrower space in polar arras. One degree of longitude at the equator is 111 km, at 45° ltitud, it is 75km. at 60° latitude it is
55km and at poles it is zero km.
Uses of Longitudes :
- We can determine the location oEa place on the map.
- We can determine the local time of a place with the help of longitudes.
- lines of longitude help us in marking time-sonea on the Earth.
Longitude and Time:
There is a close relation between longitude and Time, The earth rotates round axis from West to East. li completes one rotation of 360° in 24 hours. It passes through 15° of longitude in Cine hour or 1° in 4 minutes Thus, there is a difference of 4 minutes of time for time of one degree of longitudc :‘dl the places on the same meridian have their noon at the same time. But the sun appears earlier at places in the East and later at places in the West. So the places East of Greenwich gain time and the places Vest of Greenwich losie time.
Method of Finding Time:
Eastward, one is ahead of Greenwich nican time (G,M.T.); Conversely, one is behind G.M.T. if one goes westward. lfwe know G.M.T: we have to add 4 minutes for 1 longitude of Eastward place. Similarly, we have w subtract 4 minutes for 1° longitude fir westward pince. The simple rule is:
East-Gain Add.
West-I,oee-Subtract.
SOME SOLVED QUESTIONS ON FINDING TIME
Question 1.
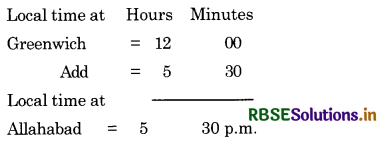
What 1% the local time at Allahabad
\(\left(82 \frac{1^{\circ}}{2} \mathbf{E}\right)\) when it is noon at Greenwich?
Answer:
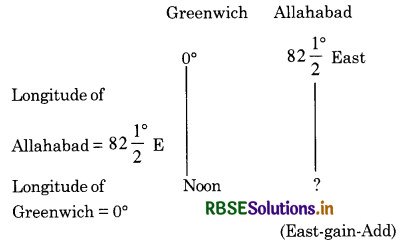
Difference in longitude = \(82 \frac{1}{2}^{\circ}\)
= 330 minutes = 5 hours 30 minutes
Difference in time \(=\frac{165}{2} \times 4\) minutes
As Allahabad is situated East of Greenwich, its local time will be ahead of Greenwich time. So we add.
Question 2.
When it is noon at Cairo (30°E), the local time at New York (750 W) is 5.00 a.m.
Answer:
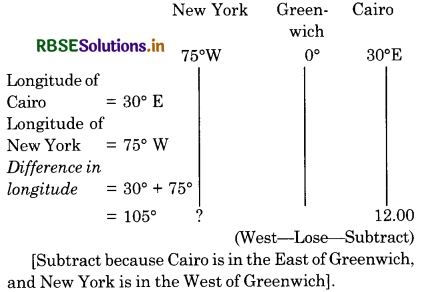
Difference in time = 105 X 4=420 minutes
= 7 Hours
As New York is situated in the West of Greenwich,
its local time will be behind that of Cairo. So we subtract.
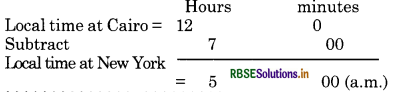
Question 3.
The world heavy weight boxing Championship fight between Mohammed Ali and: Joe Frazeir was held in New York (75°W) at 8.30: p.m. on Wednesday. At what time its cnt: can be listened to in New Delhi (77°E)? :
Answer:
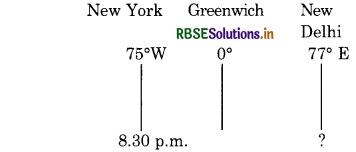
Wednesday (East-Gain-Add)
Longitude of New York = 75°W
Longitude of New Delhi = 77°E
Difference in longitude = 152°
Difference in time
= 152 X 4 = 608 minutes
= 10 hours 08 minutes
As New Delhi is situated in the East of New York, its locai time will be ahead of that of New York. So we add.


Question 4.
When the local time is 11.28 a.m. at R (60°E, 15°N), it is 5.00 p.m. at Q (Lat. 15°N). What is the longitude of Q? Show your working.
Answer:
Hours minute
Local time at Q = 17-00 (5 p.m. = 17.00 Hrs.)
Local time atR = 11-28
Difference in time = 5-32 = 332 minutes
Difference in. longitude \(=\frac{332}{4}\) 83 degrees
As the time at mace Q is ahead of that at place R. the place Q is situated in the East of R.
Lngitude of ‘Q’ is = 600 + 83° = 143° East.
Question 5.
Distinguish between local time and standard time.
Answer:
Local Time
The local time of a place is the time of its own meridian. The local time is calculated by the position of the Sun at noon at a given place. When the Sun at any place is highest in the sky, it is noon, it is 12 o’clock. All the watches of that place should be set according to that time. Characteristics of Local Time
- Every meridian has a different local time.
- The places on the same meridian have the same local time.
- The eastern places will be ahead of western places of local time.
- Sun-dial was a simple and old method to determine local time.
Standard Time:
The standard time is the time of a central meridian of a country and is adopted by all the places. Standard time is a uniform time throughout a country. All the watches of the country are set according to this time. The Indian Standard Time (J.S.T.) is the local time of a
place \(82 \frac{1^{\circ}}{2} \mathrm{E}\) longitude passing in between Allahabad and Varanasi. It is \(5 \frac{1}{2}\) hours ahead of Greenwich
Mean Time. When it is noon at Greenwich. it is 5.30 P.M. in India.
- There is difference of 4 minutes for one degree of longitude. Therefore, there is a lot of difference in the local time of different places. Many difficulties arise out of it. in our daily life.
- There is a great confusion in rail-road time schedule due to the use of local time.
- Travellers going from one end of the country would go on changing their watches if they use local times. It is impracticable and inconvenient. The travellers along the trans Siberian railway line, adjust their watches almost a dozen times before they reach their destination.
- Standard time is used to have a uniformity of time in a country.
- It is essential to have standard time for telecommunication system and long journeys.
QUESTIONS FOR VIVA-VOCE
Question 1.
Name two natural points of reference on the earth.
Answer:
North Pole and South Pole.
Question 2.
What is a grid?
Answer:
The network of lines of latitude and lines of longitude.
Question 3
Which ps is are founci ‘! a gncÌ?
Answer:
Horizontal arid Vertical.
Question 4.
What is a great circle?
Answer:
A circle with longest length (2irR).
Question 5.
Which line of latitude is a great circle?
Answer:
Equator.
Question 6.
What are co-ordinate?
Answer:
Lines of latitude and lines of longitude
Question 7.
What do you mean by latitude of a place?
Answer:
The angular distance of a place from the plane
of equator.
Question 8.
What is the distance covered by 10: latitude? :
Answer:
About 111 kms.
Question 9.
Name two methods of finding latitude of a place:
Answer:
- By altitude of the sun
- By Pole star.
Question 10.
What do you mean by longitude of a place?
Answer:
The Angular distance of a place east or west of prime Meridian.
Question 11.
Where is Prime meridian located?
Answer:
Greenwich observatory (Near London).

Question 12.
Describe the extent of Western Hemisphere.
Answer:
O°to 1800 West longitude.
Question 13.
State the extent of Eastern Hemisphere.
Answer:
O° to 100 East longitude.
Question 14.
What is the rule for change of local time?
Answer:
For every 15° longitude-the time changes by one hour.
Question 15.
At which longitude, is the standard Meridian of India situated?
Answer:
82° East longitude near Prayagraj.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 भारत - स्थिति
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 3 पृथ्वी की आंतरिक संरचना
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Our Rajasthan Chapter 5 उद्योग
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 2 संरचना तथा भूआकृति विज्ञान
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 भूगोल एक विषय के रूप में
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 7 Natural Hazards and Disasters
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 6 Soils
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 4 Climate