RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Heat
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Heat Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 7. Students can also read RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 7 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The class 7 science chapter 4 heat extra questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 4 Heat
RBSE Class 7 Science Heat InText Questions and Answers
Page 36
Question 1.
Boojho says, “My left hand tells me that the water in mug C is hot and the right hand tells me that the same water is cold. What should I conclude?”
Answer:
It can be concluded that sense of touch is an unreliable method of measuring the hotness of any object.

Question 2.
Boojho wondered which of the two scales shown in figure he should read.

Answer:
India has adopted the Celsius scale and we should read this scale. The other scale is Fahrenheit scale (°F) with the range of 94 - 108 degrees. Earlier, Farhenheit scale was in use.
Page 37
Question 3.
Paheli measured her body temperature. She got worried as it was not exactly 37°C.
Answer:
This is because a normal temperature of body which is 37°C is actually just an average temperature of a large number of healthy persons. It could be slightly higher or lower for individual one.
Page 38
Question 4.
Boojho got a naughty idea. He wanted to measure the temperature of hot milk using a clinical thermometer. Paheli stopped him from doing so.
Answer:
Clinical thermometer is designed to measure the temperature of human body only. It has range 35°€ to 42°C. Hot milk has very high temperature which cannot be measured by clinical thermometer. It may break.
Page 39
Question 5.
Boojho now understand why clinical thermometer cannot be used to measure high temperatures. But still wonders whether a laboratory thermometer can be used to measure his body temperature.
Answer:
A laboratory thermometer also cannot be used to measure the temperature of body due to the absence of the kink above its bulb. It prevents mercury level from falling on its own.
Question 6.
Boojho wonders why the level of mercury should change at all when the bulb of the thermometer is brought in contact with another object.
Answer:
When the bulb is brought in contact with another object, its mercury level changes as the temperature of other object. So mercury is highly sensitive to even slight change in temperature. It needs to be change every time.
Page 40
Question 7.
Paheli asks, “Does it mean that heat will not be transferred if the temperature of two objects is the same?”
Answer:
Yes, heat will not transfer if both objects are at same temperature.
RBSE Class 7 Science Heat Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
State similarities and differences between the laboratory thermometer and the clinical thermometer.
Answer:
Similarities between laboratory thermometer and clinical thermometer:
|
Basis |
Similarity |
|
Structure and Material |
Both the thermometer are made of glass, have a long and narrow hollow centre with a bulb at one end, filled with mercury. |
|
Scale |
Both have the Celsius or centigrade scale for temperature measurement. |
|
Measuring substance |
Both have mercury. |
Differences:
|
Basis |
Laboratory Thermometer |
Clinical Thermometer |
|
Range |
Reads between - 10°C to 110°C |
Reads between 35°C to 45 °C. |
|
Kink |
Absent |
Present |
|
Use |
To measure any temperature |
To measure body temperature. |
Question 2.
Give two examples each of conductors and insulators of heat.
Answer:
Conductors of heat are steel and copper. Insulators of heat are wood and plastic.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks:
1. The hotness of an object is determined by its ......................
2. Temperature of boiling water cannot be measured by a ...................... thermometer.
3. Temperature is measured in degree ......................
4. No medium is required for transfer of heat by the process of ......................
5. A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk. It transfers heat to its other end by the process of ......................
6. Clothes of ...................... colours absorb heat better than clothes of light colours.
Answer:
1. temperature
2. clinical
3. Celsius
4. radiation
5. conduction
6. dark.

Question 4.
Match the items given in column I with those in column II:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Land breeze |
(a) summer blows during |
|
2. Seabreeze |
(b)winter blows during |
|
3. Dark colour |
(c) day clothes are preferred during |
|
4. Light coloured |
(d) night clothes are preferred during |
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Land breeze |
(d) night clothes are preferred during |
|
2. Seabreeze |
(c) day clothes are preferred during |
|
3. Dark colour |
(b)winter blows during |
|
4. Light coloured |
(a) summer blows during |
Question 5.
Discuss why wearing more layers of clothing during winter keeps us warmer than wearing just one thick piece of clothing.
Answer:
During winters, we prefer wearing more layers of clothing than just one thick piece of clothing because air gets trapped in between the various clothing layer. Being a poor conductor of heat, air prevents the heat loss from our body. Hence, layers of clothing keep us warm.
Question 6.
Look at fig. mark where the heat is being transferred by conduction, by convection and by radiation.
Answer:
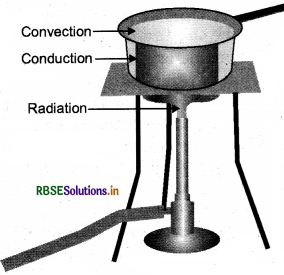
Question 7.
In places of hot climate it is advised that the outer walls of houses be painted white. Explain.
Answer:
Different colours have different properties of heat such as absorption, reflection or transmission. Light colours have the lowest absorbance and highest reflection property. Hence, white colour painted house reflects the most of the radiations of the sun and keep the house protected from the heat outside. Such houses remain cool for longer period of time.
Question 8.
One litre of water at 30°C is mixed with one litre of water at 50°C. The temperature of the mixture will be:
(a) 80°C
(b) more than 50°C but less than 80°C
(c) 20°C
(d) between 30°C and 50°C
Answer:
(d) between 30°C and 50°C.
Question 9.
An iron ball at 40°C is dropped in a mug containing water at 40°C. The heat will:
(a) flow from iron ball to water.
(b) not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball.
(c) flow from water to iron ball.
(d) increase the temperature of both.
Answer:
(b) not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball.
Question 10.
A wooden spoon is dipped in a cup of ice cream. Its other end:
(a) becomes cold by the process of conduction.
(b) becomes cold by the process of convection.
(c) becomes cold by the process of radiation.
(d) does not become cold.
Answer:
(d) does not become cold.

Question 11.
Stainless steel pans are usually provided with copper bottoms. The reason for this could be that:
(a) copper bottom makes the pan more durable.
(b) such pans appear colourful.
(c) copper is a better conductor of heat than the stainless steel.
(d) copper is easier to clean than the stainless steel.
Answer:
(c) copper is a better conductor of heat than the stainless steel.

- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Electric Current and its Effects
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- RBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 8 शरीर में गति
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline