RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 7. Students can also read RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 7 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The class 7 science chapter 4 heat extra questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
RBSE Class 7 Science Nutrition in Animals InText Questions and Answers
Page 13
Question 1.
Boojho is fascinated by the highly coiled small intestine. He wants to know its length.
Answer:
The length of small intestine is approx. 7.5 m.

Page 15
Question 2.
Paheli wants to know how food moves in the opposite direction during vomiting?
Answer:
The intense pressure is formed in the stomach when the food is not accepted by the stomach. The content in the stomach is then pushed back. This returned content is expelled out from the mouth in the form of vomiting.
Page 18
Question 3.
Paheli wants to know why these animals (ruminants) cannot chew food properly at the time they take it in?
Answer:
Ruminants cannot chew food properly at the time they take in because their food is rich in cellulose. So, they store the food in part of a stomach called rumen where it is partially digested and is called cud. After the partial digestion of cellulose, it is brought back to the mouth and chewed properly.
Question 4.
Boojho wants to know why we cannot digest cellulose like the cattle do?
Answer:
Humans cannot digest cellulose in their food like cattle due to the absence of a large sac - like structure called ‘caecum’. The cellulose of the food is digested by the action of certain bacteria which are not present in humans.
RBSE Class 7 Science Nutrition in Animals Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks
(a) The main steps of nutrition in humans are ............................ , ............................ , ............................ , ............................
and ............................
(b) The largest gland in the human body is ............................
(c) The stomach releases hydrochloric add and ............................ juices which act on food.
(d) The inner wall of the small intestine has many finger - like outgrowths called ............................
(e) Amoeba digests its food in the ............................
Answer:
(a) ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, egestion
(b) liver
(c) digestive
(d) villi
(e) food vacuole.
Question 2.
Mark 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if it is false:
(a) Digestion of starch starts in the stomach. (T/F)
(b) The tongue helps in mixing food with saliva. (T/F)
(c) The gall bladder temporarily stores bile. (T/F)
(d) The ruminants bring back swallowed grass into their mouth and chew it for sometime. (T/F)
Answer:
(a) False
(b) True
(c) True
(d) True.
Question 3.
Tick (√ ) mark the correct answer in each of the following:
(a) Fat is completely digested in the:
(i) stomach
(ii) mouth
(iii) small intestine
(iv) large intestine
Answer:
(iii) small intestine.
(b) Water from ther undigested food is absorbed mainly in the:
(i) stomach
(ii) food pipe
(iii) small intestine
(iv) large intestine
Answer:
(iv) large intestine.
Question 4.
Match the items of column I with those given in column II:
|
Column I Food components |
Column II Product(s) of digestion |
|
1. Carbohydrates |
Fatty adds and glycerol |
|
2. Proteins |
Sugar |
|
3. Fats |
Amino acids |
Answer:
|
Column I Food components |
Column II Product(s) of digestion |
|
1. Carbohydrates |
Sugar |
|
2. Proteins |
Amino acids |
|
3. Fats |
Fatty adds and glycerol |
Question 5.
What are villi? What is their location and function?
Answer:
Villi are the finger - like projections in the inner walls of the small intestine.
Function: Villi increase the surface area for absorption of digested foods.
Question 6.
Where is the bile produced? Which component of the food does it help to digest?
Answer:
Bile juice is produced by the liver and stored in gall bladder. It helps in digestion of fats present in food.
Fats → Fatty acid + Glycerol

Question 7.
Name the type of carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans. Give the reason also.
Answer:
Cellulose is the carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans because ruminants have large sac like structure called rumen. Certain bacteria are present in rumen which helps in digesting cellulose.
Question 8.
Why do we get instant energy from glucose?
Answer:
Glucose is the simplest sugar which releases CO2 , H2O and energy during respiration. Since, glucose is the simplest form, it is easily absorbed by the blood to give instant energy. Glucose does not require digestion and thus gives instant energy. Thus, no extra time is required for digestion.
Question 9.
Which part of the digestive canal is involved in:
(a) Absorption of food .........................
(b) Chewing of food.........................
(c) Killing of bacteria .........................
(d) Complete digestion of food .........................
(e) Formation of faeces .........................
Answer:
(a) Small intestine
(b) Buccal cavity
(c) Stomach
(d) Small intestine
(e) Large intestine.
Question 10.
Write one similarity and one difference between the nutrition in amoeba and human beings.
Answer:
Similarity:
Both amoeba and humans require energy for the growth and maintenance of their bodies. This energy is derived from the food what they eat. The food is in a complex form and is therefore broken down in simpler forms by the process of digestion. Both of them are heterotrophs.
Difference:
Digestive juices are secreted in buccal cavity, stomach and small intestine in the case of human beings. Whereas, digestive juices are secreted in the food vacuole in the case of amoeba.
Question 11.
Match the items of column with I with suitable items in column II
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(a) Salivary gland |
(i) Bile juice secretion |
|
(b) Stomach |
(ii) Storage of undigested food |
|
(c) Liver |
(iii) Saliva secretion |
|
(d) Rectum |
(iv) Acid release |
|
(e) Small intestine |
(v) Digestion is completed |
|
(f) Large intestine |
(vi) Absorption of water |
|
|
(vii) Release of faeces |
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(a) Salivary gland |
(iii) Saliva secretion |
|
(b) Stomach |
(iv) Acid release |
|
(c) Liver |
(i) Bile juice secretion |
|
(d) Rectum |
(vii) Release of faeces |
|
(e) Small intestine |
(v) Digestion is completed |
|
(f) Large intestine |
(vi) Absorption of water |
Question 12.
Draw the labelled figure of the digestive system.
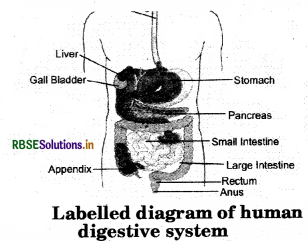

Question 13.
Can we survive only on raw, leafy vegetables / grass? Discuss.
Answer:
Our body has different digestive glands which secrete digestive juices to digest the different components of the food. For example, the saliva produced by salivary glands breaks down starch into sugars, the, digestive juices present in the stomach helps to break down protein into amino adds. The bile secreted by the liver plays an important role in the digestion of fats etc.,
Raw, leafy vegetables / grass contains a complex carbohydrate, cellulose. Our body does ,not have enzymes or digestive juices to digest cellulose. Hence, cellulose cannot be served as an energy source to our body. Therefore, we cannot survive only on raw, leafy vegetables / grass.

- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Electric Current and its Effects
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- RBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 8 शरीर में गति
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline