RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 7. Students can also read RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 7 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The class 7 science chapter 4 heat extra questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
RBSE Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plants InText Questions and Answers
Page 133
Question 1.
Paheli thought that new plants always grow from seeds. But she has never seen the seeds of sugarcane, potato and rose. She wants to know how these plants reproduce.
Answer:
Some plants can produce offsprings by vegetative propagation. For example - sugarcane, potato and rose can be reproduced using stem or buds of the parent plants.

Page 135
Question 2.
Boojho wants to know if there is any advantage of vegetative propagation.
Answer:
Vegetative propagation has several advantages such as they require only a single parent, and plant parts such as stem, root and leaves for reproduction. They take less time to grow and to produce flowers and fruits. Since, they are exactly like the parent plant, any desired characteristics of the parent plant can be conserved from generation to generation.
Page 137
Question 3.
Boojho wants to know how the male gamete in the pollen grain reaches the female gamete present in the ovule.
Answer:
The male gamete in the pollen grain reaches the female gamete in the ovules by a series of processes. Firstly, they are transferred via various means such as wind, water, insects etc. from the anther to the stigma. Upon reaching the stigma, the pollens respond to as sweet fluid secreted, by the stigma and grows downwards in the form of a thin - tube called pollen tube within the style. Upon reaching the ovule through micropyle, the male gamete reaches the female gamete and a zygote, formation takes place.
Page 138
Question 4.
Boojho wants to know why flowers are generally so colourful and fragrant. Is it to attract insects?
Answer:
Yes, some flowers can only reproduce with the help of insect mediated pollination. In order to attract insects, plants produce flowers with bright colours and nice fragrances.
RBSE Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plants Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called ..................................
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called ..................................
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as ..................................
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as ..................................
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of .................................., .................................. and ..................................
Answer:
(a) vegetative propagation
(b) unisexual flower
(c) pollination
(d) fertilisation
(e) wind, water, insect
Question 2.
Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Answer:
Asexual reproduction can be carried out by the following modes:
1. Vegetative reproduction: The method involves the development of new offsprings by using the vegetative parts of the parent plant. These include the roots, stem, leaves or buds. For example - Growth from stem in roses and leaves in bryophyllum.
2. Budding: This form of reproduction occurs by the formation of bulb like projections called bud from the mother cell. Upon reaching a particular size, the buds detach and grow as individual cells. For example - Budding in yeast.
3. Fragmentation: This method occurs by the breaking up or fragmentation of parent organism into two or more fragments, each of which can then grow into an individual plant. For example - Fermentation in spirogyra (algae).
4. Spore formation : This method involves the production of asexual spores, which are hard, spherical particles that can germinate into new plants when the climatic conditions are favourable. For example - sporulation in bread mould.
Question 3.
Explain, what do you understand by sexual reproduction?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction is the process of reproduction that involves two parents. One gamete from each parent is produced which then fuse to form a zygote, that form the embryo followed by seed formation.
Question 4.
State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Answer:
Difference between asexual and sexual reproduction.
|
Property |
Sexual reproduction |
Asexual reproduction |
|
1. Requirement of seed |
Required |
Not required |
|
2. Parents involved |
Two : One male, one female |
One : Only single parent |
|
3. Involvement of sex cells (gametes) |
Yes |
No |
|
4. Genetic makeup of offspring |
Different from parents (a mix of both) |
Same as parent |
|
5. Organs involved |
Flower |
Leaves, stem, root, buds, sporangium etc. |
Question 5.
Sketches the reproductive parts of a flower.
Answer:
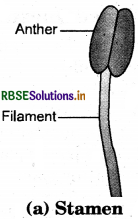
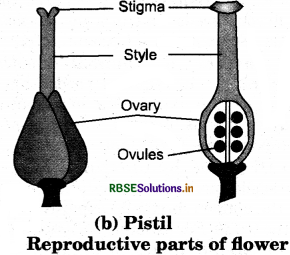
Question 6.
Explain the difference between self - pollination and cross - pollination.
Answer:
Difference between self - pollination and cross - pollination:
|
Property |
Self-pollination |
Cross pollination |
|
1. Pollen and stigma involved |
Are of same flower |
Are of different flowers |
|
2. Medium of pollination |
Plant’s stamen shed pollen onto its own stigma |
Wind, water or insect |
|
3. Flower type |
Bisexual or complete |
Unisexual or incomplete |
|
4. Genetic makeup of progeny |
Same as parent |
Different from parent |
|
5. Example |
Pea, wheat, sunflower |
Apple, grapes, pears |
Question 7.
How does the process of fertilisation take place in flowers?
Answer:
Fertilisation begins with the transfer of pollen grain onto the stigma of the flower. This is followed by the secretion of some fluids that induce the pollen to germinate. They produce a long, pollen tube which grows and approaches to ovary through style carrying male gametes with it. Male gamete enters in ovule where female gametes called eggs are present in the ovules. Fusion of female'and male gametes take place to form the zygote. This is called fertilisation.
Question 8.
Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed.
Answer:
The dispersal of seeds can occur by means of wind, water, insects or animals.
(a) Wind dispersal: It requires light weight hairy or winged seeds. For example Grasses, oak or maple.
(b) Water dispersal: It requires spongy or fibrous seeds that are able to float on water. For example - Coconut, lotus.
(c) Insects or animal mediated dispersal: It requires seeds that can attach to the skin or fur of an animal’s body by means of spikes, hooks or spines. For example - Xanthium.
(d) Dispfersal by bursting: Sometimes the seeds can be scattered far away simply by the sudden forcefully explosive opening of the fruits. For example - Castor, balsam.

Question 9.
Match items in column I with those in column II:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(a) Bud |
(i) Maple |
|
(b) Eyes |
(ii) Spirogyra |
|
(c) Fragmentation |
(iii) Yeast |
|
(d) Wings |
(iv) Bread mould |
|
(e) Spores |
(v) Potato |
|
|
(vi) Rose |
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(a) Bud |
(iii) Yeast |
|
(b) Eyes |
(v) Potato |
|
(c) Fragmentation |
(ii) Spirogyra |
|
(d) Wings |
(i) Maple |
|
(e) Spores |
(iv) Bread mould |
Question 10.
Tick (√) the correct answer:
(a) The reproductive part of a plant is the:
(i) leaf
(ii) stem
(iii) root
(iv) flower
Answer:
(iv) flower.
(b) The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called:
(i) fertilisation
(ii) pollination
(iii) reproduction
(iv) seed formation
Answer:
(i) fertilisation.
(c) Mature ovary forms the:
(i) seed
(ii) stamen
(iii) pistil
(iv) fruit
Answer:
(iv) fruit
(d) A spore producing plant is:
(i) rose
(ii) bread mould
(iii) potato
(iv) ginger
Answer:
(ii) bread mould.
(e) Bryophyllum can be reproduced by its:
(i) stem
(ii) leaves
(iii) roots
(iv) flower
Answer:
(ii) leaves.

- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Electric Current and its Effects
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- RBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 8 शरीर में गति
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline