RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Ex 5.6
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Ex 5.6 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 6. Students can also read RBSE Class 6 Maths Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 6 Maths Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Students are advised to practice अनुपात और समानुपात के प्रश्न class 6 of the textbook questions.
RBSE Class 6 Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Ex 5.6
Question 1.
Name the types of following triangles :
(a) Triangle with lengths of sides 7 cm, 8 cm and 9 cm.
(b) ΔABC with AB = 8.7 cm, AC = 7 cm and BC = 6 cm.
(c) ΔPQR such that PQ = QR = PR = 5 cm.
(d) ΔDEF with m∠D = 90°.
(e) ΔXYZ with m∠Y = 90° and XY = YZ.
(f) ΔLMN with m∠L = 30°, m∠M = 70° and m∠N = 80°.
Answer:
(a) Scalene triangle,
(b) Scalene triangle,
(c) Equilateral triangle,
(d) Right-angled triangle,
(e) Isosceles right-angled triangle,
(f) Acute-angled triangle.

Question 2.
Match the following :
|
Measures of Triangle |
Type of Triangle |
|
(i) 3 sides of equal length |
(a) Scalene |
|
(ii) 2 sides of equal length |
(b) Isosceles right angled |
|
(iii) All sides are of different length |
(c) Obtuse angled |
|
(iv) 3 acute angles |
(d) Right angled |
|
(v) 1 right angle |
(e) Equilateral |
|
(vi) 1 obtuse angle |
(f) Acute angled |
|
(vii) 1 right angle with two sides of equal length |
(g) Isosceles |
Answer:
|
Measures of Triangle |
Type of Triangle |
|
(i) 3 sides of equal length |
(e) Equilateral |
|
(ii) 2 sides of equal length |
(g) Isosceles |
|
(iii) All sides are of different length |
(a) Scalene |
|
(iv) 3 acute angles |
(f) Acute angled |
|
(v) 1 right angle |
(d) Right angled |
|
(vi) 1 obtuse angle |
(b) Isosceles right angled |
|
(vii) 1 right angle with two sides of equal length |
(c) Obtuse angled |
Question 3.
Name each of the following triangles in two different ways :
(You may judge the nature of the angle by observation)
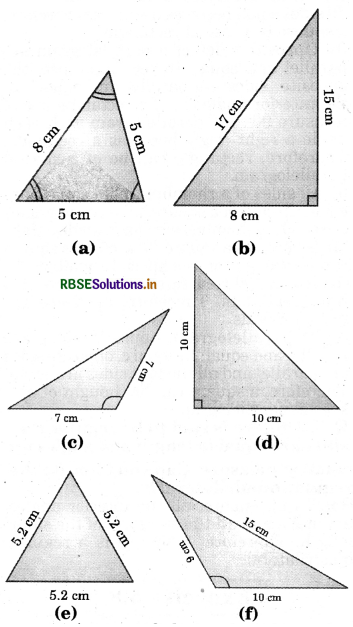
Answer:
(a) Acute-angled triangle and isosceles triangle.
(b) Right-angled triangle and scalene triangle.
(c) Obtuse-angled triangle and isosceles triangle.
(d) Right-angled triangle and isosceles triangle.
(e) Equilateral triangle and acute-angled triangle.
(f) Obtuse-angled triangle and scalene triangle.

Question 4.
Try to construct triangles using matchsticks. Some are shown here. Can you make a triangle with :
(a) 3 matchsticks?
(b) 4 matchsticks?
(c) 5 matchsticks?
(d) 6 matchsticks? (Remember you have to use all the available matchsticks in each case.)
Name the type of triangle in each case. If you cannot make a triangle, think of reasons for it.
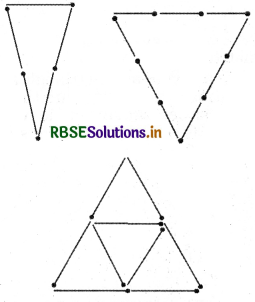
Answer:
(a) 3 matchsticks Yes, by using 3 matchsticks, we can form a triangle as :
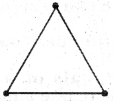
This is an acute-angled triangle and it is possible with 3 matchsticks to make a triangle because sum of two sides is greater than third side.
(b) 4 matchsticks
No, by using four matchsticks, we cannot form a triangle because the sum of the length of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the length of the third side of the triangle. Thus, a square is made.

(c) 5 matchsticks
Yes, an acute-angled triangle is formed with the help of 5 matchsticks because in this case the sum of the two sides is greater than the third side.
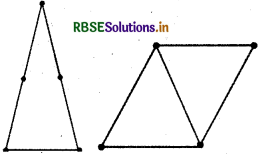
(d) 6 matchsticks
Yes, this is an acute-angled triangle and it is possible to make a triangle with the help of 6 matchsticks because sum of the two scales of a triangle is greater than third side.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers InText Questions
- RBSE Class 6 Maths Important Questions Chapter 1 अपनी संख्याओं की जानकारी
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 भिन्न Intext Questions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Ex 7.4
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Knowing our Numbers Ex 1.1
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Knowing our Numbers InText Questions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions InText Questions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Ex 7.6
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Ex 7.5
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Ex 7.3