RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 14 Practical Geometry Ex 14.6
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 14 Practical Geometry Ex 14.6 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 6. Students can also read RBSE Class 6 Maths Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 6 Maths Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Students are advised to practice अनुपात और समानुपात के प्रश्न class 6 of the textbook questions.
RBSE Class 6 Maths Solutions Chapter 14 Practical Geometry Ex 14.6
Question 1.
Draw ∠POQ of measure 75°, and find its line of symmetry.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
1. Draw a ray \(\overline{O Q}\).
2. Place the centre of the protractor at O and the zero edge along \(\overline{O Q}\).
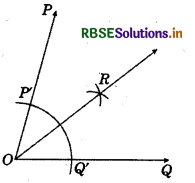
3. Start with O near Question Mark point P at 75°.
4. Join \(\overline{O P}\). Then, ∠POQ = 75°.
5. With 0 as centre and using compass, draw an arc that cuts both rays of ∠POQuestion Label the points of intersection as F and Q'.
6. With Q' as centre, draw (in the interior of ∠POQ) an arc whose radius is more than half the length Q'P'.
7. With the same radius and with P' as centre, draw another arc in the interior of ∠POQ. Let the two arcs intersect at R.
Then, OR is the bisector of ∠POQ which is also the line of symmetry of ∠POQ as ∠POR = ∠ROQ.

Question 2.
Draw an angle of measure 147° and construct its bisector.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(1) Draw a line \(\overline{O A}\).
(2) Using protractor, construct ∠AOB = 147°
(3) Taking the centre as O and any suitable radius, draw an arc which cuts the arms \(\overline{O A}\) and OB at P and Q respectively.
(4) Taking P as the centre and radius more than half of PQ, draw an arc.
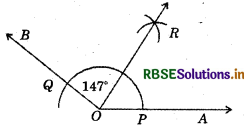
(5) Taking Q as centre and with the same radius, draw another arc which cut the previous arc at R.
(6) Join OR and produce it.
Thus, OR is the required bisector of ∠AOB.
Question 3.
Draw a right angle and construct its bisector.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(1) Draw a line PQ and take a point 0 on it.
(2) Taking O as centre and convenient radius, draw an arc which intersect, PQ at A and B.
(3) Taking A and B as centres and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which intersect each other at C.
(4) Join OC. Thus, ∠COQ is the required right angle.
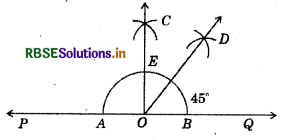
(5) Taking B and E as centre and radius more than half of BE, draw two arcs, let these arcs meet at the point D.
(6) Join OD. Thus OD is the required bisector of ∠COQ.
Question 4.
Draw an angle of measure 153° and divide it into four equal parts.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
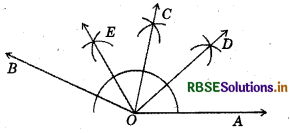
- Draw a ray OA.
- At O, with the help of a protractor, construct ∠AOB = 153°.
- Draw OC as the bisector of ∠AOB.
- Again, draw OD as bisector of ∠AOC.
- Again, draw .OE as bisector of ∠BOC.
- Thus, OC, OD and OE divides ∠AOB in four equal parts.

Question 5.
Construct with ruler and compasses, angles of following measures :
(1) 60°
(2) 30°
(3) 90°
(4) 120°
(5) 45°
(6) 135°
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(1) 60°
(i) Draw a ray \(\overline{O L}\).
(ii) Taking O as centre and convenient radius, draw an arc which intersects \(\overline{O L}\) at P.
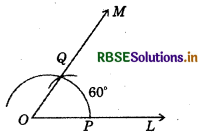
(iii) Taking P as centre and same radius, cut previous arc at Q.
(iv) Join OQ.
Thus, ∠MOL is required angle of 60°.
(2) 30°
(i) Draw a ray \(\overline{O L}\).
(ii) Taking O as centre and convenient radius. Draw an arc, which intersects at P.
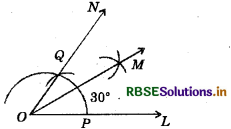
(iii) Join OQ.
Thus, ∠MOL is required angle of 60°.
(iv) Draw an angle bisector of ∠MOL such that
∠NOL = \(\frac{1}{2}\)∠MOL = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 60° = 30°
Thus, ∠NOL is required angle of 30°.
(3) 90°
(i) Draw a ray \(\overline{O L}\).
(ii) Taking O as centre and convenient radius, mark an arc, which intersects \(\overline{O L}\) atX
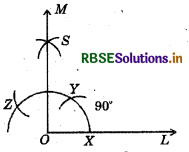
(iii) Taking X as centre and same radius, cut previous arc at Y.
(iv) Taking Y as centre and same radius, draw another arc intersecting the same arc at Z.
(v) Taking Y and Z as centres and same radius, draw two arcs intersecting each other at S. .
(vi) Join OS and produce it to form a ray OM. Thus, ∠MOL is required angle of 90°.
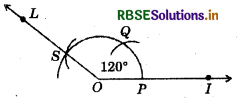
(4) 120°
- Draw a ray \(\overline{O I}\).
- Taking O as centre and convenient radius, mark an arc which intersects \(\overline{O I}\) at P.
- Taking P as centre and same radius, cut previous arc at Q.
- Taking Q as centre and same radius cut the arc at S.
- Join OS. Thus, ∠IOL is required angle of 120°.
(5) 45°
- Draw a ray \(\overline{O I}\).
- Taking O as centre and convenient radius, mark an arc which intersects \(\overline{O I}\) at X.
- TakingX as centre and same radius, cut previous arc at Y.
- Taking Y as centre and same radius, draw another arc intersecting the same arc at Z.
- Taking Y and Z as centres and same radius, draw two arcs intersecting each other at S.
- Join OS and produce it to form a ray OJ. Thus, ∠JOI = 90°.
- Draw the bisector of ∠JOI, therefore ∠MOl = 45°.
Thus, ∠MOl is required angle of 45°.
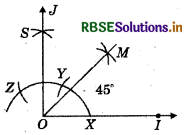
(6) 135°
(i) Draw a line PQ and take a point O on it.
(ii) Taking O as centre and convenient radius, mark an arc which intersects PQ at I and J.
(iii) Taking I and J as centres and radius more than half of IJ, draw two arcs intersecting each other at R.
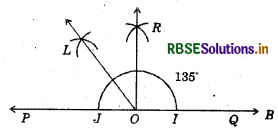
(iv) Join OR.
Thus, ∠QOR = ∠POR = 90°.
(v) Draw OL the bisector of ∠POR.
Thus, ∠QOL is required angle of 135°.

Question 6.
Draw an angle of measure 45° and bisect it.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw a line PQ and take a point O on it.
(ii) Taking O as centre and a convenient radius, draw an arc which intersects PQ at two points A and B. .
(iii) Taking A and B as centres and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which meet at C.
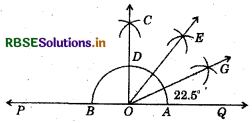
(iv) Join OC.
Thus, ∠COQ is an angle of 90°.
(v) Draw \(\overline{O E}\) as the bisector of ∠COQ. Thus, ∠QOE = 45°:
(vi) Again draw \(\overline{O G}\) as the bisector of ∠QOD. Thus, ∠QOG = ∠EOG = 22.5.
Question 7.
Draw an angle of measure 135° and bisect it.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw a line PQ and take a point O on it.
(ii) Taking O as centre and convenient radius, mark an arc which intersects PQ at A and B.
(iii) Taking A and B as centres and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs intersecting each other at R.
(iv) Join OR.
Thus, ∠QOR = ∠POR = 90°.
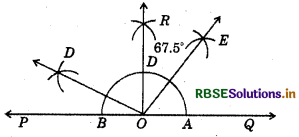
(v) Draw \(\overline{O D}\) the bisector of POR. Thus, ∠QOD is required angle of 135°.
(vi) Now, draw \(\overline{O E}\) as the bisector of ∠QOD. Thus, ∠QOE = ∠DOE = 67.5°.
Question 8.
Draw an angle of 70°. Mark a copy of it using only a straight edge and compasses.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw an angle 70° with protractor, i.e. ∠POQ = 70°.
(ii) Draw a ray \(\overline{A B}\).
(iii) Place the compasses at O and draw an arc to cut the rays of ∠POQ at L and M.
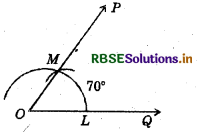
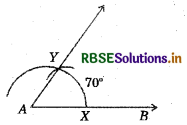
(iv) Use the same compasses, setting to draw an arc with A as centre, cutting AB at X
(v) Set your compasses setting to the length LM with the same radius.
(vi) Place the compasses pointer at X and draw the arc to cut the arc drawn earlier at Y.
(vii) Join AY.
Thus, ∠YAX = 70°.

Question 9.
Draw an angle of 40°, Copy its supplementary angle.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw an angle of 40° with the help of protractor, naming ∠AOB.
(ii) Draw a line PQ.
(iii) Take any point M on PQ.
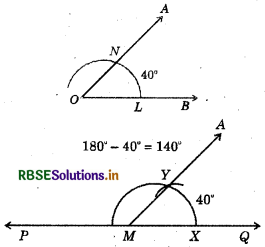
(iv) Place the compasses at O and draw an arc to cut the arms of ∠AOB at L and N.
(v) Use the same compasses setting to draw an arc M. as centre, cutting MQ at X.
(vi) Set your compasses to length LN and with the same radius. Place the compasses at X and draw the arc to cut the arc drawn earlier T.
(vii) Join MY.
Thus, ∠QMY = 40° and ∠PMY is supplementary of it.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers InText Questions
- RBSE Class 6 Maths Important Questions Chapter 1 अपनी संख्याओं की जानकारी
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 भिन्न Intext Questions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Ex 7.4
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Knowing our Numbers Ex 1.1
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Knowing our Numbers InText Questions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions InText Questions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Ex 7.6
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Ex 7.5
- RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Ex 7.3