RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 8 Winds, Storms and Cyclones
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 8 Winds, Storms and Cyclones Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Important QuestionsWinds, Storms and Cyclones
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
A cyclone warning is a broadcast:
(a) 48 hrs in advance
(b) 25 hrs in advance
(c) 2 days in advance
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) 48 hrs in advance
Question 2.
Air may precipitate but never falls as :
(a) rain
(b) snow
(c) ice
(d) water vapor
Answer:
(d) water vapor
Question 3.
Which of the following cannot be used to determine wind direction?
(a) Movement of water
(b) Movement of leaves
(c) Movement of airplane
(d) Movement of ship
Answer:
(c) Movement of airplane

Question 4.
Tall buildings have a long thin metal rod that:
(a) extends from the roof of the earth beneath
(b) prevents birds from sitting
(c) provides earthing
(d) both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(c) provides earthing
Question 5.
Lightning is always accompanied by thunder. Thunder is:
(a) type of rainfall
(b) noise
(c) storm
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) noise
Question 6.
Pick the odd one out:
(a) Land breeze
(b) Winter monsoons
(c) Cyclones
(d) Winter winds
Answer:
(c) Cyclones
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
The....................of the cyclone is a low-pressure area where the winds are gentle and there is no rainfall.
Answer:
eye
Question 2.
Wind currents are the result of....................heating of land and water.
Answer:
uneven
Question 3.
Japanese people call cyclones by the name....................
Answer:
typhoon
Question 4.
Lightning is almost always accompanied by....................
Answer:
thunder
Question 5.
Cyclones can be monitored with the help of .................... and radars.
Answer:
satellite
State Whether True or False
Question 1.
Winds never move exactly in the north-south direction due to the revolution of the earth.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
Uneven heating causes conventional current.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
The equator comes into the low-pressure belt region.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Typhoons can be restricted by the planting of a thick canopy of trees near the coastal areas.
Answer:
True

Question 5.
The wind has a tilt towards the right in the southern hemisphere.
Answer:
False
Match the following
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Cyclone alert |
(a) Cyclone in the Japanese language |
|
2. 48 hours |
(b) 10-30 km diameter |
|
3. Funnel-shape |
(c) Hot and humid tropical climate |
|
4. Typhoon |
(d) the Equator |
|
5. Eye |
(e) Low-pressure belt |
|
6. Thunderstorm |
(f) Dense |
|
7. 30°N |
(g) Tornado |
|
8. 6O°N |
(h) Anemometer |
|
9. Cold air |
(i) Cyclone watch |
|
10. Wind speed |
(j) Satellite |
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Cyclone alert |
(j) Satellite |
|
2. 48 hours |
(i) Cyclone watch |
|
3. Funnel-shape |
(g) Tornado |
|
4. Typhoon |
(a) Cyclone in the Japanese language |
|
5. Eye |
(b) 10-30 km diameter |
|
6. Thunderstorm |
(c) Hot and humid tropical climate |
|
7. 30°N |
(d) the Equator |
|
8. 6O°N |
(e) Low-pressure belt |
|
9. Cold air |
(f) Dense |
|
10. Wind speed |
(h) Anemometer |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define wind.
Answer:
Moving air is called wind.
Question 2.
What is the direction of the wind?
Answer:
The direction of the wind is from a high-pressure region to a low-pressure one.
Question 3.
When strong/high wind blows, an umbrella held upright at times gets upturned. Explain the reason.
Answer:
High-speed wind passing over the umbrella creates low pressure therefore, the umbrella upturns.
Question 4.
What is a wind vane?
Answer:
A wind vane is an instrument used to determine the direction of blowing wind.
Question 5.
Give two examples of natural phenomena that rely on the expansion of air.
Answer:
Examples:
- Land breeze,
- Cyclone.
Question 6.
Can you name another substance that expands on heating?
Answer:
Water.
Question 7.
What do you mean by wind currents?
Answer:
A wind current can be defined as the movement of wind from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure.
Question 8.
What is a thunderstorm?
Answer:
A severe storm associated with heavy rain, thunder, and lightning is called a thunderstorm.
Question 9.
What do you mean by water wall?
Answer:
A water wall refers to the wall-like huge tidal waves reaching a height of 8-13 meters during an incoming cyclone.
Question 10.
What instrument is used to measure wind speed?
Answer:
An anemometer is used to measure wind speed.

Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by natural calamity?
Answer:
A natural calamity or natural disaster refers to the occurrence of destructive events as a result of some natural process, causing massive loss of life and property. These include earthquakes, landslides, cyclones, etc.
Question 2.
Write the sequence of air pressure in decreasing order of the following:
- Sea level
- Mountains
- Plateaus
- Hills
Answer:
Sea level > plateaus > hills > mountains is the sequence in decreasing order of air pressure.
Question 3.
What is air pressure?
Answer:
The force exerted onto a particular area by the weight of the air is known as air pressure. It is created due to the continuous bombardment of air molecules on a surface.
Question 4.
When do we blow air over a sheet of paper, why does it rise?
Answer:
This is because blowing air above the strip reduces the air pressure there. Thus the pressure from below the strip being higher, makes it move upwards.
Question 5.
Who discovered the property that increased wind speed, and decreases air pressure?
Answer:
Bernoulli was a swiss mathematician, and physicist. Anemometer is an instrument used to measure wind speed. Wind speed is measured in units of knot.
Question 6.
What is happening to a balloon attached to a boiler tube's mouth when it is placed in hot water, followed by cold water?
Answer:
When placed in hot water, the air inside the boiler tube heats expands and rises. As it enters into the balloon, the balloon inflates. When the tube is placed in cold water, the air contracts. This causes the balloon to deflate.
Question 7.
What factors determine/affect wind currents?
Answer:
Factors determining wind currents include:
- Uneven heating of land and water bodies.
- Uneven heating between the equator and the poles.
Question 8.
What is thunder?
Answer:
Thunder is the loud sound/noise which we hear immediately after a bolt of lightning. It occurs due to the expansion of rapidly heated air in the lightning streak. It releases both light and sound.
Question 9.
What are the most affected areas by thunderstorms?
Answer:
The most common areas affected by thunderstorms are those present in hot and humid equatorial regions, such as the tropics, e g. India.
Question 10.
What is a tornado shelter?
Answer:
A tornado shelter is a closed room with no windows bruit underground in the basement of the building or deep within a building to provide shelter from a tornado.
Question 11.
Which one of the following carries high wind speed?
- Cyclone or
- Tornado.
Answer:
Tornado, a tornado consists of wind, whose speed reaches up to 500 km/h, which is much higher than the wind speed of a cyclone ranging between 150-250 km/h.

Question 12.
What is a hurricane? How does it differ from typhoons?
Answer:
A hurricane is an alternative name for cyclones. It is used by the people of America. It does not differ from a typhoon, as typhoon is another name for cyclone, used in Japan and the Philippines.
Question 13.
Which part of India is more vulnerable and which is less vulnerable to cyclones?
Answer:
The whole coastline of India is vulnerable to cyclones, particularly the east coast. The west coast of India is less vulnerable to cyclonic storms both in terms of intensity and frequency of the cyclones.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How does air pressure determine the direction of airflow?
Answer:
When air pressure over an area drops, the air from surrounding areas that have higher pressure tries to rush in, to compensate for the drop and create a state of equilibrium. This determines the direction of airflow from a high-pressure area to a low-pressure area.
Question 2.
Why do winds blow away the roofs of some houses?
Answer:
When winds blow over an area, the air above the tops of the houses moves in a greater speed than the air within the house. This creates a pressure difference because of the higher pressure inside the house and lower pressure above the house. This difference in pressure causes weekly attached roofs to fly away.
Question 3.
Why does air expand on heating?
Answer:
Air molecules get their energy from heat and the energy of air molecules increases. Hence, the air molecules collide with each other and spread out. Thus, the volume of gas increases which results in reduced density. This phenomenon is called thermal expansion.
Question 4.
What is Monsoon? Explain.
Answer:
The word monsoon is derived from the Arabic word mausarrc i.e. season. It arrives as a result of moisture-laden winds blowing in from the South-West Indian Ocean. These winds always blow from cold to warm regions and cause heavy rains from June to September.
Question 5.
Discuss in brief how uneven heating between the equator and the poles generates wind current?
Answer:
We know that the region dose to the equator gets maximum heat from the sun. This makes the air warm which rises up and the cooler air from the regions in the 0-30 degrees latitude belt on either side of the equator moves in. These winds blow from the north and the south towards the equator. On the other hand, in winters, at the poles, the air is colder than at latitudes about 60 degrees. The warm air at these latitudes rises up and the cold wind from the poles rushes in. In this way, wind circulation is set. up from the poles to the warmer latitudes.

The wind flow pattern because of uneven heating on the earth

Question 6.
How does a thunderstorm occur?
Answer:
As the air heats up, it rises and carries moisture with it. As it cools down, it condenses back to water droplets in the upper atmospheric layers. More severe cooling may cause ice crystal formation. Hence a shower of rain brings ice with it. During this downpour, they face resistance from the rising air and start colliding with each other. As a result, static energy is produced and the clouds acquire charge. During the discharge process of the air between two charged clouds or clouds and the ground, an electric spark is produced called lightning followed by thunder. Hence, a thunderstorm occurs.
Question 7.
Describe the structure of a cyclone.
Answer:
- The center of the cyclone is called the ‘eye’. It has a diameter ranging from 10-15 km. It is low pressure with low-speed wind and no rain. It is a calm zone.
- Around the eye is a high-pressure area, about 150 km in diameter with various speed winds of speed between 150-250 km/h. This area is a violently rotating mass of air around the ‘eye’ and compresses thick clouds that cause heavy fain.
Question 8.
How is a cyclone formed? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
The water heats up because of atmospheric heat and turns into vapor. When this water vapor gets condensed, it changes
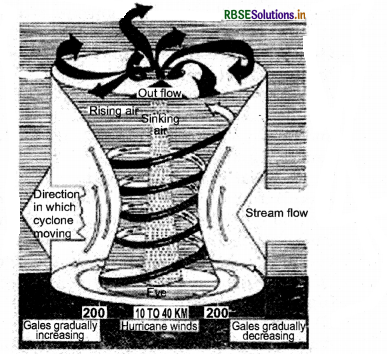
heat into liquid as raindrops. This heat is released to the atmosphere. The heat released to the atmosphere warms the air around. The air tends to rise and causes a drop in pressure. More air rushes to the center of the storm. This cycle is repeated and the. chain of events ends with the formation of a very low-pressure system with very high-speed winds revolving around it. It is the weather condition that we call a cyclone. Factors like wind speed, wind direction, temperature and humidity contribute to the development of cyclones.
Question 9.
How can a cyclone cause destruction?
Answer:
Example of destructions caused by a cyclone :
- It can damage the crops, affecting agriculture.
- It can delay flights affecting aviation.
- It can destroy electric power lines, affecting communication.
- It can spread water-borne diseases, affecting public health.
Question 10.
In case of lightning, what would you advise your friends to do?
Answer:
During lightening, I would give the following advice to my friends :
- Do not stand under a tall tree.
- Move to low-level open places, eg parks.
- Do not swim.
- Do not take shelter under a metal shed.
- Do not use an umbrella with a metal handle.
Question 11.
Why should you avoid moving walking through floods?
Answer:
Floodwater may be contaminated with different types of harmful microbes that cause skin diseases:
- It may hide some snakes that may be poisonous.
- It may hide manholes that you may fall into.
- It may have submerged open wares that may cause electric shock.

Question 12.
Does the wind pressure reduction as the wind velocity increases? If yes, then confirm your answer through an activity.
Answer:
- Take two balloons of approximately equal size and fill a little water into the balloons. Blow up both the balloons and tie each one to a string.
- Hang the balloons 8-10 cm apart on a stick.
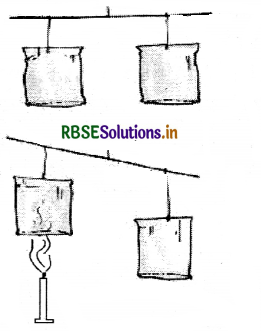
- Blow in the space between the balloons.
- It is observed that the balloons move towards each other when air is blown between the balloons.
- It happens because by blowing air at the gap, the air pressure between the balloons is reduced. The pressure of the surrounding air is greater than that of the gap in between the balloons. It pushes the balloons from the sides and the balloons move towards each other.
Question 13.
Describe an activity to demonstrate that warm air is lighter than cool air.
Answer:
- Take two empty paper cups or two paper bags of the same size.
- Hang the two bags in the inverted position on the two ends of a metal or wooden stick.
- Tie a piece of thread in the middle of the stick
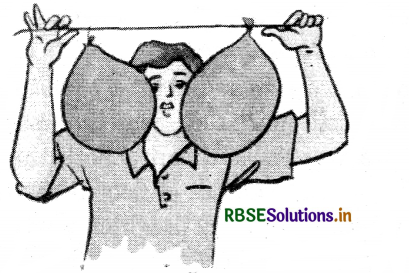
- Hold the stick by the thread as in a balance.
- Put a burning candle below one of the bags.
- It is observed that the balance of the cups gets disturbed. The bag above the candle flame moves upwards and the other end moves downwards.
