RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 7. Students can also read RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 7 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The class 7 science chapter 4 heat extra questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Important Questions Physical and Chemical Changes
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which metal is used in the process of galvanisation?
(a) Copper
(b) Zinc
(c) Sodium
(d) Tin
Answer:
(b) Zinc
Question 2.
The common name of acetic acid is
(a) salt
(b) sugar
(c) vinegar
(d) curd
Answer:
(c) vinegar
Question 3.
A change in which one or more new substance is formed is called
(a) chemical change
(b) physical change
(c) thermal change
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) chemical change
Question 4.
The nature of magnesium hydroxide is
(a) acidic
(b) basic
(c) neutral
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) basic

Question 5.
The explosion of a firework is a
(a) physical change
(b) chemical change
(c) thermal change
(d) no change
Answer:
(b) chemical change
Question 6.
Salt is obtained from seawater by which process?
(a) Ionisation
(b) Heating
(c) Crystallisation
(d) Galvanisation
Answer:
(c) Crystallisation
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
Rust is a layer of.................deposited on the surface of iron objects.
Answer:
iron oxide
Question 2.
Copper sulphate is also known as.................
Answer:
blue vitriol
Question 3.
A chemical change is also called a.................
Answer:
chemical reaction
Question 4.
The process of crystallisation involves cooling of................. solution.
Answer:
saturated
Question 5.
Extraction of metal from ore is a.................change.
Answer:
chemical
State Whether True or False
Question 1.
When you cut an apple with a knife, the exposed surface of the apple takes up the brown colour.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Changes that are temporary and can be reversed are called irreversible changes.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
The burning of a candle is a chemical change whereas the melting of wax is a physical change.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Changes that are temporary and cannot be reversed are called reversible changes.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Crystallisation is a method to prevent rust.
Answer:
False

Match the following
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Chemical change |
(a) Zinc coating |
|
2. Vinegar + Baking soda |
(b) Oxidation |
|
3. Galvanisation |
(c) Iron gates |
|
4. Cut vegetables |
(d) Carbon dioxide |
|
5. Painting |
(e) Pure solid form |
|
6. Crystal |
(f) Usually irreversible |
|
7. Rust |
(g) Acetic add |
|
8. CO2+ Lime water |
(h) Iron oxide |
|
9. Neela t hot ha |
(i) Calcium carbonate |
|
10. Vinegar |
(j) Copper sulphate |
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Chemical change |
(f) Usually irreversible |
|
2. Vinegar + Baking soda |
(d) Carbon dioxide |
|
3. Galvanisation |
(a) Zinc coating |
|
4. Cut vegetables |
(b) Oxidation |
|
5. Painting |
(c) Iron gates |
|
6. Crystal |
(e) Pure solid form |
|
7. Rust |
(h) Iron oxide |
|
8. CO2+ Lime water |
(i) Calcium carbonate |
|
9. Neela t hot ha |
(j) Copper sulphate |
|
10. Vinegar |
(g) Acetic add |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name some physical properties of the substance.
Answer:
Properties such as size, shape, colour and state of substance are called physical properties.
Question 2.
Give two examples of the physical changes which are not reversible.
Answer:
- Cutting of paper,
- Breaking of glass.
Question 3.
Melting of wax is a change where a solid changes to a liquid state. Give two more such changes which you observe in your surroundings.
Answer:
Melting of ice and melting of butter.
Question 4.
What kind of change is an explosion of a firework?
Answer:
The explosion of a firework is a chemical change as it produces heat, light, sound and unpleasant gases that pollute the atmosphere.
Question 5.
A slice of apple acquires a brown colour if it is not consumed immediately. Explain.
Answer:
The change in colour, in this case, is due to the formation of new chemical substances.
Question 6.
What are the conditions necessary for rusting?
Answer:
The presence of water (moisture) and air are necessary for rusting.

Question 7.
What kind of change is crystallisation?
Answer:
Crystallisation is a physical change because no new substance is formed.
Question 8.
What are crystals?
Answer:
Crystals are the pure solid form of a substance having a typical shape.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write characteristics of physical change.
Answer:
Characteristics of physical change are as follows:
- It is generally reversible.
- It does not involve the formation of a new substance.
- It is a temporary change.
- It involves a change in physical properties only.
Question 2.
Give four examples of the changes that can be reversed.
Answer:
- Melting of ice,
- Boiling of water,
- Heating of the blade and any other metal,
- Melting of butter.
Question 3.
A list of a few changes is given, and sort them on the basis of reversible physical changes and irreversible physical changes
- Melting of butter
- Chopping a log of wood
- Cutting of vegetables
- Crushing of chalk piece
- Condensation of vapour
- Heating the metal blade
Answer:
|
Reversible physical change |
Irreversible physical change |
|
Melting of butter |
Chopping a log of wood |
|
Condensation of vapour |
Cutting of vegetables |
|
Heating the metal blade |
Crushing of chalk piece |
Question 4.
What kind of change is the “beating of aluminium into thin sheets”?
Answer:
The beating of aluminium into thin sheets is a physical change. Malleability is a property by virtue of which a metal can be changed/beaten into thin sheets.

Question 5.
The evaporation of water and its condensation into clouds is a physical change. Comment.
Answer:
Evaporation is the change of water into water vapours. Whereas condensation is the change of water vapours into water droplets. In both cases, change in the state of the substance has taken place without the formation of any new chemical substance. Hence, it is a physical change.
Question 6.
What is the difference between reactant and product?
Answer:
Difference between reactant and product:
|
Reactant |
Product |
|
The original substances that react in a chemical change are called reactants. |
The new substances that are formed are called the products. |
Question 7.
What are the characteristics of chemical reactions?
Answer:
Characteristics of chemical reactions are as follows :
- Change of colour.
- Effervescence i.e., the evolution of the gas in the form of a bubble.
- Absorption or release of heat.
- Generation of characteristic smell.
Question 8.
What is rusting?
Answer:
On leaving a piece of iron in the presence of water and air for some time, it acquires a film of brownish substance. This Substance is called rust and the process is called rusting.
Iron + Water (moisture) + Oxygen →Iron oxide (rust)
Question 9.
Why stainless steel does not rust?
Answer:
Stainless steel does not rust because it is made by mixing iron with carbon and metals like chromium, nickel and manganese, such a new substance formed is called an alloy.
Question 10.
What happens when magnesium oxide is dissolved, in water? What kind of reaction is this?
Answer:
Magnesium hydroxide is formed when magnesium oxide is dissolved in water,
Magnesium oxide (MgO) + Water (H2O)→ Magnesium hydroxide[Mg(OH)2]
This reaction is a chemical change as a new substance like Mg(OH)2 is formed.
Question 11.
When food gets spoiled, it produces a foul smell. Shall we call this change a chemical change?
Answer:
Spoiled food produces a foul smell because of the chemical reaction occurred in it which alters the chemical composition of a substance. Entirely, a new chemical substance is formed due to the decomposition reaction by the decomposers.

Question 12.
Why formation of manure from leaves is a chemical change?
Answer:
The formation of manure from leaves is a chemical change because the manure formed has a different composition from the leaves. The biodegradation action of micro-organisms yields manure.
Question 13.
Name some of the processes in which both physical and chemical changes take place.
Answer:
- Digestion of food: Food is physically broken down by chewing and chemically broken down by a digestive enzyme in the saliva and acid in the stomach.
- Burning of candle: Melting of wax is a physical change and its combustion is a chemical change.
Question 14.
What kind of change is rusting?
Answer:
Rusting is a chemical change as a new substance is formed. Iron changes to iron oxide in rusting.
Iron + Water (moisture) + Oxygen→ Iron oxide (Rust)
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write differences between a physical change and a chemical change.
Answer:
Differences between a physical change and chemical change :
Question 2.
- What will happen if you bring the tip of the magnesium ribbon near a candle flame.
- Write the chemical equation to represent the reaction.
Answer:
1. On bringing the tip of the magnesium ribbon near a candle flame, it burns with a brilliant white light. When it is completely burnt, it leaves behind powdery ash which is magnesium oxide.
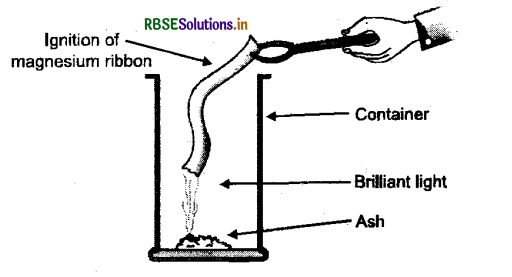
Fig Magnesium ribbon burning
2. Magnesium (Mg) + Oxygen (O)→Magnesium oxide (MgO)
Question 3.
- What will happen when you will dip an iron blade in blue coloured copper sulphate solution?
- Write a chemical equation to support your answer.
- What kind of reaction is this?
Answer:
- On dipping an iron blade in blue coloured copper sulphate solution, changes in the colour of the solution are observed. The blue coloured solution turns green due to the formation of iron sulphate.
- Copper sulphate + Iron (blue)→ Iron sulphate + Copper (green) (brown deposit)
- This is called displacement reaction. The more reactive iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution to form iron sulphate.
Question 4.
Give an example of a chemical reaction for each of the following situation
- A change in colour is observed.
- Gas is evolved.
- Sound is produced.
Answer:
- (a) Reaction between copper sulphate and iron metal. Blue coloured solution of copper sulphate changes to the green colour of iron sulphate.
- CuSO4 + Fe → FeSO4 + Cu (blue) (green)
- The reaction between sodium hydrogen carbonate and acetic add. CO2 gas is evolved.
- Acetic acid + Sodium hydrogen carbonate → Carbon dioxide + Other substances
- The burning of the cracker produces a loud sound.

Question 5.
Give a few examples which indicate that chemical changes are very important in our life?
Answer:
A change in which the compositions of a substance are altered is called a chemical change. Few examples which indicate that chemical changes are very important in our life as follows:
- Medicine is the end product of the chain of a chemical reaction.
- Photosynthesis.
- Digestion of food.
- Production of useful materials like pesticides, detergents etc.
Question 6.
How can you prevent rusting?
Answer:
Some ways to prevent rusting are as follows:
- Galvanisation: Process of depositing layer zinc on iron to prevent rusting.
- Pointing: Coating of paint on an iron object' cuts off the air supply and prevents contact with moisture.
- Alloying: Mixing iron with metals and non-metals to form a new substance is called alloying.
- Oiling: Applying grease and oil, cut off the contact with air and moisture.
Question 7.
Why do ships suffer a lot of damage from rusting in spite of being painted?
Answer:
Ships suffer a lot of damage from rusting because a part of them remains underwater. On the part above water, water drops keep clinging to the ship's outer surface. Moreover, the water of the sea contains many salts. The saltwater makes the process of rust formation faster. Hence, they suffer a lot of damage and a fraction of ships' iron has to be replaced every year.
Question 8.
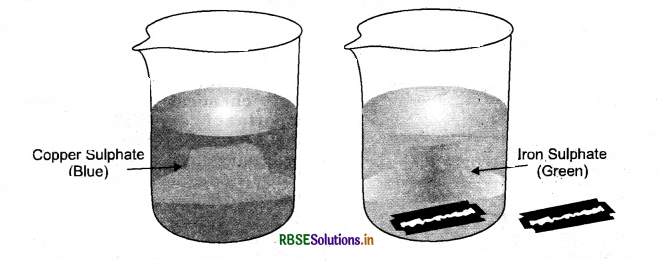
Explain with an experiment that due to a reaction between copper sulphate and iron, the colour of copper sulphate solution changes.
Answer:
- Dissolve about a teaspoonful of copper sulphate in about half a cup of water in a beaker.
- Add a few drops of dilute sulphuric add to the solution. The solution will change in a blue coloured solution.
- Drop a nail or a used shaving blade into this solution.
- It is observed that after one hour, the colour of the solution changes from blue to green due to the formation of iron sulphate solution.
- It is also noticed that the brown colour is deposited on the blade due to the copper deposition. The reaction can be written as:
- CuSO4(aq + Fe(s) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s) Copper sulphate solution (blue)+ Iron → Iron sulphate solution (green)+ Copper (brown deposit)

- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Electric Current and its Effects
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- RBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 8 शरीर में गति
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline