RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 4 Heat
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 4 Heat Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Important Questions Heat
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Heat is measured in units of
(a) calorie
(b) Celsius
(c) kelvin
(d) degree Celsius
Answer:
(a) calorie
Question 2.
Water is a poor
(a) insulator
(b) radiator
(c) conductor
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) conductor
Question 3.
Liquids and gases rise upon heating due to
(a) reduced mass
(b) increased volume
(c) increased gravity
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) increased volume

Question 4.
Which one is filled in the bulb of a thermometer?
(a) Lead
(b) Copper
(c) Silver
(d) Mercury
Answer:
(d) Mercury
Question 5.
A good absorber is a/an
(a) good reflector
(b) average reflector
(c) poor reflector
(d) good transmitter
Answer:
(d) good transmitter
Question 6.
Heat is a form of
(a) kinetic energy
(b) thermal energy
(c) fluid
(d) mechanical energy
Answer:
(c) fluid
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
Temperature is a measure of the..............of an object.
Answer:
hotness
Question 2.
Dark colors..............more heat than light colors.
Answer:
absorb
Question 3.
A ..............thermometer does not use mercury.
Answer:
digital
Question 4.
All hot bodies radiate..............
Answer:
heat
Question 5.
The heat transfers from a.............. object to the colder object.
Answer:
hotter

State whether True or False
Question 1.
Heat is a form of fluid.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
All objects radiate heat.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Alcohol is superior to mercury because it is colorless.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
The land breeze flows during the daytime.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Wool transmits heat by convection.
Answer:
False
Match the following:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Radiation |
(a) Requires no medium |
|
2. Land breeze |
(b) Daytime |
|
3. Convection |
(c) Solids |
|
4. Conduction |
(d) Night |
|
5. Sea breeze |
(e) Liquids |
|
6. Thermometer bulb |
(f) Weather report |
|
7. Water |
(g) Mercury |
|
8. Maximum and minimum thermometer |
(h) Clinical thermometer |
|
9. Kink |
(i) Movement of molecules |
|
10. Heat energy |
(j) Poor conductor of heat |
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Radiation |
(a) Requires no medium |
|
2. Land breeze |
(d) Night |
|
3. Convection |
(e) Liquids |
|
4. Conduction |
(c) Solids |
|
5. Sea breeze |
(b) Daytime |
|
6. Thermometer bulb |
(g) Mercury |
|
7. Water |
(j) Poor conductor of heat |
|
8. Maximum and minimum thermometer |
(f) Weather report |
|
9. Kink |
(h) Clinical thermometer |
|
10. Heat energy |
(i) Movement of molecules |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name that device that is used to measure the temperature.
Answer:
Thermometer.
Question 2.
What is temperature?
Answer:
A reliable measurement of the hotness of an object is called temperature.
Question 3.
Can our sense of touch decide whether an object is hot or cold?
Answer:
No, we can only relatively find a hotter or colder object.
Question 4.
Name the units of temperature.
Answer:
Temperature is measured in units of degrees Celsius (°C) or degrees Fahrenheit (°F).
Question 5.
Give examples of substances that can be used to measure temperature in a thermometer.
Answer:
- Mercury,
- Alcohol.
Question 6.
What is the range of the clinical thermometers?
Answer:
35°C to 42°C.

Question 7.
What is a freezing point of water?
Answer:
Pure water at sea level freezes to ice at 0°C.
Question 8.
What is the boiling point of water?
Answer:
Pure water at sea level boils to steam at 100°C.
Question 9.
What is the range of laboratory thermometers?
Answer:
The range of laboratory thermometers is generally from -10°C to 110°C.
Question 10.
What is called quicksilver?
Answer:
Mercury is called quicksilver.
Question 11.
Water and air are poor conductors of heat. Then how does the heat transfer take place in these substances?
Answer:
By convection.
Question 12.
Why dark-colored clothes are preferred in winter?
Answer:
Because dark-colored clothes absorb most of the heat falling on them and keep us warm.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Give one application of alcohol to the thermometer.
Answer:
Alcohol has a very low freezing point. So, it does not freeze even at very low temperatures. As a result, it can be used to measure extremely low temperatures.
Question 2.
Why is the range of a clinical thermometer kept between 35°C and 42°C?
Answer:
The clinical thermometer is designed to measure the temperature of the human body only. The temperature of the human body normally does not go below 35°C or above 42°C. That is the reason that this thermometer has a range between 35°C and 42°C.

Question 3.
Give four types of thermometers.
Answer:
Examples
- Clinical thermometer,
- Laboratory thermometer,
- Maximum-minimum thermometer,
- Digital thermometer.
Question 4.
What is the use of a maximum-minimum thermometer?
Answer:
A maximum-minimum thermometer is used by the weathermen to give weather reports stating the highest and lowest temperature recorded for a particular day.
Question 5.
Describe changes that an object may undergo upon heating?
Answer:
An object can undergo the following changes upon heating:
- The object may expand, eg. boiling of milk.
- The object may change its state, eg. change of water from liquid to vapor state.
- The objects may change chemically, e.g. softening of vegetables upon boiling.
Question 6.
What are conductors? Give examples.
Answer:
Conductors are materials that allow heat to pass through them easily. Most metals are good conductors. For example - iron, copper, and aluminum.
Question 7.
Define conduction and convection.
Answer:
Conduction is a process in which heat flows from the hotter end of an object to the cooler end. It is mostly observed in solids. Convection is a process of heat transfer from one place to another by the movement of the molecules which carry heat with them. It is mostly observed in liquid and gases.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the structure of a clinical thermometer with a diagram.
Answer:
A clinical thermometer consists of a long, narrow, uniform glass tube. It has a bulb at one end. This bulb contains mercury. Outside the bulb, a small shining thread of mercury can be seen. On the glass tube, we can see a temperature scale, usually a celsius scale.

A clinical thermometer
Question 2.
What precautions should we take while reading a clinical thermometer?
Answer:
Precautions to be observed while using a clinical thermometer are :
- The thermometer should be washed before and after use, preferably with an antiseptic solution.
- Ensure that before use, the mercury level is below 35°C.
- Read the thermometer keeping the level of mercury along the line of sight.
- Handle the thermometer with care. If it hits against some hard object, it can break.
- Don’t hold the thermometer by the bulb while reading it.
Question 3.
Explain why it is difficult to use a clinical thermometer for laboratory use?
Answer:
A clinical thermometer has a very limited range of temperatures. It can read only between 35°C to 42°C. It cannot be used for lab purposes where the temperature may vary to great extremes, i.e., below 35°C or above 42°C. The mercury in the bulb may expand beyond the thermometer's ability to hold it. This may cause a crack or break of the thermometer leading to the leaking of mercury which is highly toxic to the human body.

Question 4.
What are the precautions one should keep in mind while using a laboratory thermometer?
Answer:
Several precautions are necessary before using a lab thermometer. Some of these are:
- It should be cleaned before and after each use.
- It should be handled with care.
- It should be held by the end opposite to the bulb to avoid any effect of body temperatures on the mercury level.
- Its bulb should be completely immersed in the substance whose temperature, one wishes to measure.
- The bulb should not touch the bottom or side of the container.
- While reading the temperature, it should be allowed to attain a steady temperature.
- The mercury should be read at eye- level. Tilting may change the reading.
Question 5.
What is the advantage of a digital thermometer over a clinical thermometer?
Answer:
A digital thermometer does not contain mercury. Mercury is a toxic metal, in case a thermometer breaks, the mercury can leak out and easily can be absorbed by the skin or even inhaled. This can result in damage to the nerves and other organizers This can be overcome using a digital thermometer as it uses a strip of temperature-sensitive liquid crystals that change color with temperature.
Question 6.
Why are the handles of kitchen utensils made of wood?
Answer:
Kitchen utensils are generally made from good conductors of heat in order to cook food fast. However, it is not possible to directly hold such utensils with bare hands due to high heat conductance. Wood is a poor conductor of heat and therefore used to cover a portion of the handle to avoid burning our hands.
Question 7.
How does the heat travel in the air? Explain the Seabreeze and land breeze in coastal areas in this reference?
Answer:
The air near the heat source gets hot and rises. It leaves the place, which is filled by the cold air from the sides. In this way, the air gets heated.
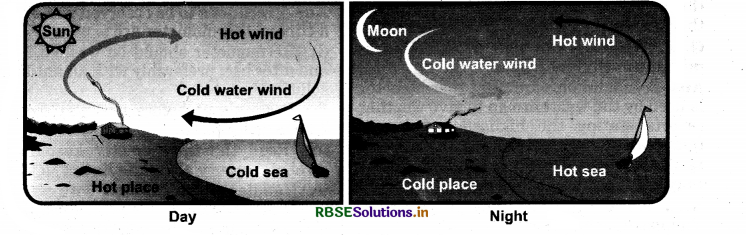
The people in coastal areas experience an interesting phenomenon. During the day, the land gets heated faster than water. The air over the land becomes hotter and rises up. The cooler air from the sea rushes in towards the land to take its place. The warm air from the land moves towards the sea to complete the cycle. The air from the sea is called the sea breeze. At night, it is exactly the reverse. The water cools down more slowly than land. So, the cool air from the land moves towards the sea. This is called the land breeze.
Question 8.
Explain the process conduction by an activity.
Answer:
- Take a rod or flat strip of metal, say aluminum or iron.
- Fix a small wax piece on the rod.
- These pieces should be at nearly equal distances (see fig.)
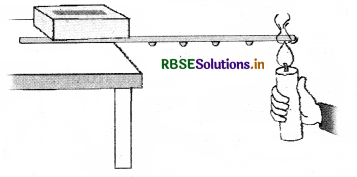
The flow of heat through a metal strip:
- Clamp the rod to a stand or put one end of the rod in between bricks.
- Now, heat the other end of the rod.
- It is observed that upon lighting the candle flame, the wax pieces start falling after a few minutes.
- The piece closest to the flame falls first and the piece nearer to the bricks falls last.
- It happens because the metal rod is heated by a conduction process in which heat transfers from the hot end of the object to the cold end of the object.
Question 9.
Explain through an activity that heat is transferred in water by the convection process.
Answer:
- Take a round bottom flask and fill it two-thirds with water.
- Place it on a tripod, or make some arrangements to place the flask in such a way that you can heat it by placing a candle below it.
- Wait till the water in the flask is still.
- Place a crystal of potassium permanganate at the bottom of the flask gently using a straw.
- Now heat the water by placing the candle just below the crystal.
- It is observed that waves of purple-colored water rise from the bottom and move upwards.
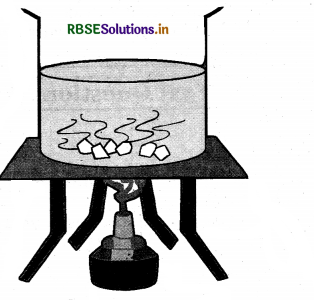
Convection of heat
- Upon reaching the topmost cool layers, the colorless waves returned to the bottom from the sides of the beaker.
- It means that hot water rises up and cold water from the sides moves down.
- This process continues till the whole water becomes colorful and gets heat.
- This process is known as convection.
