RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 7. Students can also read RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 7 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The class 7 science chapter 4 heat extra questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Important Questions Fibre to Fabric
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The process of collecting silk threads from the cocoon is called
(a) rearing
(b) shearing
(c) reeling
(d) scouring
Answer:
(c) reeling
Question 2.
Identify the animal that does not yield any wool
(a) Donkey
(b) Camel
(c) Sheep
(d) Goat
Answer:
(a) Donkey
Question 3.
Pashmina is obtained from
(a) camel
(b) rabbit
(c) sheep
(d) goat
Answer:
(d) goat

Question 4.
The rearing of silkworms for obtaining silk is called:
(a) cocoon
(b) sericulture
(c) silk
(d) silviculture
Answer:
(b) sericulture
Question 5.
Silk is spun by silkworms at which stage?
(a) Cocoon
(b) Pupa
(c) Larval
(d) Egg laying
Answer:
(b) Pupa
Question 6.
During winters, sheep are kept indoors and fed on:
(a) leaves
(b) grains
(c) dry fodder
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
..................is credited with the first production of silk.
Answer:
China
Question 2.
The silk fibres secreted by silkworms are made up of..................
Answer:
protein
Question 3.
A pile of cocoons is used to obtain..................
Answer:
Fibre
Question 4.
A female silk moth lays..................of eggs at a time.
Answer:
hundreds
Question 5.
Sheep are..................and prefer grass and leaves.
Answer:
herbivores
State Whether True or False
Question 1.
Silk fibres are made up of fats and carbohydrates.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
Silkworms are caterpillars of silk moths.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Camels cannot yield wool.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Wool is obtained from silk fibres.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Silk is a plant fibre.
Answer:
False
Match the following
|
Column 1 |
Column II |
|
1. Shearing |
(a) Variety of silk |
|
2. Tussar |
(b) Angora wool |
|
3. Pupa |
(c) Separating hairs of different textures |
|
4. Baby blanket |
(d) Removal of fur from the coat |
|
5. Sorting |
(e) The third stage of development of silkworms |
|
6. Origin of silk |
(f) Small fluffy fibre |
|
7. Sericulture |
(g) Sorter’s disease |
|
8. Patanwadi sheep |
(h) Rearing of silkworms |
|
9. Burr |
(i) China |
|
10. Anthrax |
(j) Gujarat |
Answer:
|
Column 1 |
Column II |
|
1. Shearing |
(d) Removal of fur from the coat |
|
2. Tussar |
(a) Variety of silk |
|
3. Pupa |
(e) The third stage of development of silkworms |
|
4. Baby blanket |
(b) Angora wool |
|
5. Sorting |
(c) Separating hairs of different textures |
|
6. Origin of silk |
(i) China |
|
7. Sericulture |
(h) Rearing of silkworms |
|
8. Patanwadi sheep |
(j) Gujarat |
|
9. Burr |
(f) Small fluffy fibre |
|
10. Anthrax |
(g) Sorter’s disease |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
From where you can obtain wool?
Answer:
Wool is obtained from the fleece (hair) of sheep, goats, camels or yak.
Question 2.
Why do wool yielding animals have a thick covering of hair?
Answer:
Hair traps a lot of air. Air is a poor conductor, of heat. So, hair keeps these animals warm.

Question 3.
What do you understand by the term ‘Rearing’?
Answer:
Raising of animals for meat, fibre, milk, eggs or other products is called rearing.
Question 4.
What are burrs?
Answer:
Burrs are small fluffy fibres in wool.
Question 5.
Which synthetic fibre resembles silk?
Answer:
Rayon.
Question 6.
What is the scientific name of the silk moth?
Answer:
Bombyx mori.
Question 7.
What do you understand by the pupa stage?
Answer:
The pupa stage is the covering of the caterpillar completely by silk fibres. This covering is known as a cocoon.
Question 8.
Which is the most common silk moth?
Answer:
The Mulberry silk moth is the most common Silkmoth.
Question 9.
What is the larval stage of the silk moth called?
Answer:
Caterpillar or silkworm.
Question 10.
Caterpillars secrete fibre that hardens on exposure to air. What is this fibre made up of?
Answer:
The fibre is made up of protein.
Question 11.
In what form does the caterpillar swing its head to secrete fibre?
Answer:
Caterpillar swings its head in the form of eight ‘8’.
Question 12.
A thread of steel is stronger than silk. Is it true?
Answer:
No, it’s a common mistake. A silk thread is as strong as a comparable thread of steel.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the two types of fibres that form fleece?
Answer:
The hairy skin of the sheep has two types of fibres that form its fleece :
- The coarse beard hair
- The fine soft under the hair close to the skin
Question 2.
What is selective breeding?
Answer:
The process of selecting parents for obtaining special characteristics in their offspring such as soft under hair in sheep is termed selective breeding.

Question 3.
What types of sheep are selectively bred? Why?
Answer:
Certain breeds of sheep have a thick coating of hair on their body, which yields good quality wool in large quantities. Such types of sheep are ‘selectively bred’ to develop desired characteristics in the offspring.
Question 4.
Apart from grazing, sheep are fed on a certain diet. Explain.
Answer:
Apart from grazing, sheep are fed on the mixture of pulses, com, sorghum, oil cakes and minerals. In winter, sheep are kept indoors and fed on leaves, grain and dry fodder.
Question 5.
Write some properties of wool.
Answer:
Some properties of wool are as follows
- Durability
- Absorption of moisture
- Resistance to dirt
- Water repellent nature
- Insulating nature
- Warm
Question 6.
Why sorter’s job is considered risky?
Answer:
Sorter’s job is considered risky as they get infected by a bacterium, anthrax which causes a fatal blood disease called sorter’s disease. Such risks faced by workers in any industry are called occupational hazards.
Question 7.
How does good quality wool select?
Answer:
The quality of wool is judged by the wool length, diameter, elasticity, strength, durability, effectiveness as an insulator and its ability to take colouring dyes.
Question 8.
What are the different types of silk?
Answer:
Variety of silk moths yield yams with different textures. Thus we obtain different types of silk-like silk, Muga silk, Kosa silk, Eri silk etc.
Question 9.
What is reeling? How is it done?
Answer:
The process of taking out threads from the cocoon as silk is called reeling of silk. Reeling is done in special machines which unwind the threads or fibres of silk from the cocoon.
Question 10.
Why does caterpillar undergo moulting (shedding of their skin)?
Answer:
Caterpillar eats enormously and grows very fast. It grows so fast that it becomes too big for its own skin. So, the caterpillar has to shed its old skin. The caterpillar undergoes moulting at least four times.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Mention various types of wool along with the places, from where they are obtained by the wool yielding animals.
Answer:
Yak wool was obtained in Tibet and Ladakh.
Angora wool is obtained from Angora goats found in the hilly areas such as Jammu and Kashmir.
Alpaca-Llama wool is obtained from Llama and Alpaca, found in South America.
Question 2.
Write various steps for processing fibres into wool?
Answer:
The various steps for processing fibres into wool are as follows :
Step 1 ⇒ Shearing: Removal of fleece.
Step 2 ⇒ Scouring: The sheared hair is washed to remove grease, dust and dirt.
Step 3 ⇒ Sorting: Different textures of hair are separated.
Step 4 ⇒ Separating- burrs: Small fluffy fibres are picked out from the hair.
Step 5 ⇒ Dyeing: The fibres are dyed in various colours.
Step 6 ⇒ Carding: Straightening of the fibres rolling into yam.
Step 7 ⇒ Weaving: Interlocking of fibres to make a fabric.
Question 3.
Explain the phrase unity is strength’ on the basis of the making of fabric from the fibre.
Answer:
Fibres and fabric play a large role in everyday applications. Fibre is a hair-like stand of material. Fibres can be spun into yarn and made into fabric. A single fibre is too weak to break but when some fibres together from a fabric, it is difficult to tear. The fabric needs more energy to tear apart as compared to a single fibre.
Question 4.
Write the steps for the production of silk.
Answer:
The steps are as follows :
- Female silk moths lay eggs.
- Eggs are warmed to a suitable temperature for the larvae to hatch from eggs.
- The larvae/caterpillars or silkworms are kept in clean trays along with freshly chopped mulberry leaves.
- After 25-30 days the caterpillars stop eating and start spinning cocoons.
- Cocoons are kept under the sun or boiled in water.
- Fibres are taken out from the cocoon.
Question 5.
Describe the life history of the silk moth.
Answer:
Step 1
Egg: The egg is the first stage of the silkworm’s life cycle. The female moth lays eggs during summer. The warmth of spring stimulates the egg to hatch.
Step 2
Larva: The eggs hatch into larvae which is called caterpillar or silkworms, that feed on tender mulberry leaves for 27 days.
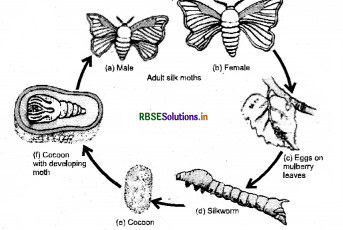
Step 3
Pupa: The caterpillar spins fine silk filament around itself to form a cocoon.
Step 4
Silkmoth: The pupa changes into a moth, which comes out of the cocoon The female adult lays eggs and the cycle continues.
Question 6.
How silk was discovered?
Answer:
The silk was discovered in China. Empress Si-Lung-Chi was asked by the emperor Huang-Ti to find the cause of the damaged leaves of mulberry trees growing in the garden. The empress found white worms eating up mulberry leaves. She also noticed that they were spinning shiny cocoons around them. Accidently, the cocoon dropped in her cup of tea and a tangle of delicate threads separated from the cocoon. From here, the silk was discovered.
Question 7.
What are the various occupational hazards in the silk industry?
Answer:
Various occupational hazards associated with the silk industry are as follows :
- Handling of dead worms causes infections.
- Vapour originating while boiling of cocoons can cause respiratory problems.
- Workers can be infected by a bacterium, anthrax.

- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Electric Current and its Effects
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- RBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 8 शरीर में गति
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline