RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 16 Water A Precious Resource
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 16 Water A Precious Resource Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 7. Students can also read RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 7 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The class 7 science chapter 4 heat extra questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Important Questions Water A Precious Resource
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following are processes of conversion between the various states of water?
(a) Sublimation
(b) Evaporation
(c) Condensation
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 2.
Water can be conserved by:
(a) Terrace farming
(b) Crop rotation
(c) Drip irrigation
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these

Question 3.
Industrialization depletes groundwater reserves:
(a) in order to avoid water-related problems near the industries
(b) to build more factories
(c) to use groundwater as a source of mineral-rich water
(d) none of these
Answer:
(d) none of these
Question 4.
Deforestation:
(a) increase runoff
(b) decrease infiltration
(c) affects the birds, water cycle, and animals
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 5.
The water cycle does not involve:
(a) infiltration
(b) sea breeze
(c) land breeze
(d) decomposition
Answer:
(d) decomposition
Question 6.
The water table is the highest in:
(a) coastal areas
(b) desert areas
(c) hilly areas
(d) polar areas
Answer:
(a) coastal areas
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
Infiltration is the process of rainwater and water from water bodies such as ponds, rivers or lakes into the soil.
Answer:
seepage
Question 2.
of rainwater can redirect water directly to the grounds instead of the drains.
Answer:
Harvesting
Question 3.
The melting temperature of ice is the same as the temperature of liquid water.
Answer:
freezing
Question 4.
2% of the world’s water is frozen as
Answer:
glaciers
Question 5.
The year 2003 is celebrated as of freshwater.
Answer:
International year.
State Whether True or False
Question 1.
Tubewell water is free of germs.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
Steam and water vapor are both gaseous states of water.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
73% of the Earth is water.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Baris is a tribal group that practices water conservation.
Answer:
False

Question 5.
Rivers and oceans have saltwater.
Answer:
False
Match the following
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Air, Soil |
(a) Upper limit of groundwater |
|
2. Water scarcity |
(b) Freshwater |
|
3. Groundwater |
(c) Solid to vapor state |
|
4. Water table |
(d) Groundwater |
|
5. Salt-water |
(e) Roots |
|
6. Glaciers |
(f) Aquifers |
|
7. Sublimation |
(g) Villages |
|
8. Tube wells |
(h) Water cycle |
|
9. Edmund Halley |
(i) Water |
|
10. Drip irrigation |
(j) Not potable |
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Air, Soil |
(i) Water |
|
2. Water scarcity |
(g) Villages |
|
3. Groundwater |
(f) Aquifers |
|
4. Water table |
(a) Upper limit of groundwater |
|
5. Salt-water |
(j) Not potable |
|
6. Glaciers |
(b) Freshwater |
|
7. Sublimation |
(c) Solid to vapor state |
|
8. Tube wells |
(d) Groundwater |
|
9. Edmund Halley |
(h) Water cycle |
|
10. Drip irrigation |
(e) Roots |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How much amount of water is recommended by United Nations for a person to use for daily chores?
Answer:
50 liters of water per. day.
Question 2.
Which is the international year for freshwater?
Answer:
The year 2003.
Question 3.
What is potable water?
Answer:
Potable water is the water that is considered fit for drinking or cooking.
Question 4.
How does the water of the Earth remain constant?
Answer:
The total water of the Earth remains constant because of the continuously operating water cycle.
Question 5.
Is water a renewable natural resource?
Answer:
Yes, water is a renewable natural resource, as it can be replenished within a short period of time by natural processes.
Question 6.
What is hydrogeology?
Answer:
Hydrogeology is the study of groundwater.

Question 7.
What do you mean by wilting?
Answer:
Wilting refers to the drooping or bending of plants due to loss of water or extreme heat.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is World Water Day? When is it celebrated?
Answer:
It is a day, celebrated throughout the world to increase awareness about the importance and conservation of water. It is celebrated on March 22 of every year.
Question 2.
Why does Earth appear blue in satellite images?
Answer:
Earth is composed of 71% of water in the form of oceans, rivers, etc., and only 29% of the island area. So, the reflection of blue light from these water bodies makes it appear blue.
Question 3.
What is saltwater?
Answer:
Saltwater generally refers to the water present in the oceans and seas that have a high concentration of salts dissolved in it.
Question 4.
Where is freshwater found?
Answer:
Freshwater is found in the rivers, tanks, and ponds; below the ground in aquifers, and in extremely cold regions such as glaciers or ice-caps.
Question 5.
What are the three states in which water exists?
Answer:
Water in its 3 forms:
- Solid (ice/snow),
- Liquid (water), and
- Gas (steam/water vapor).
Question 6.
What is the difference between evaporation and sublimation?
Answer:
Evaporation is the process in which liquid water converts into a vapor state upon heating. And sublimation is the process in which solid water directly converts into a vapor state (without passing through a liquid state).
Question 7.
Give two applications of ground, water
Answer:
Applications of groundwater are as follows:
- Supply of drinking water:
- Supply of water for irrigation.
Question 8.
How is the availability of groundwater affected by a change in the measure of the water table?
Answer:
As the water table goes down, the groundwater is no more available for consumption. This is because groundwater is available only below the water table.
Question 9.
Define infiltration. How does it differ from runoff?
Answer:
Infiltration is the process when rainwater or water from nearby water bodies, penetrates the soil surface to reach the groundwater that is reserved below. Whereas runoff is the process in which top layers of soil are carried away with the flow of water.
Question 10.
Give 3 examples of activities that deplete groundwater.
Answer:
Activities that deplete groundwater include:
- Construction of buildings
- Traditional farming practices.
- Industrialization.
Question 11.
Give 2 examples of activities that replenish groundwater.
Answer:
Activities that replenish groundwater include:
- Increasing the forest cover.
- Rainwater harvesting techniques.
Question 12.
How does uneven rainfall affect groundwater reserved in agricultural areas?
Answer:
Uneven rainfall results in the drying of the canal. As a result, the farmers are forced to draw out underground water which results in lowering the water table.

Question 13.
Where is water abundance more: In Punjab or Rajasthan? Why?
Answer:
The water abundance is more in Punjab compared to Rajasthan. This is because of the uneven distribution of rainfall in India.
Question 14.
Can water shortage be overcome by individual efforts?
Answer:
Yes, by adopting practices that avoid water wastage as well as increasing awareness about the depleting natural resource, we can overcome water shortage through individual efforts.
Question 15.
Will the scarcity of water affect only plants? Explain.
Answer:
The plant is an essential part of the ecosystem, on which many other organisms (insects, animals, humans) depend for shelter, food, and other things; the scarcity of water will indirectly affect each form of life on the Earth as well water cycle.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the water cycle?
Answer:
The movement of water from the earth to the atmosphere and back on the earth is known as the water cycle.
- Firstly, as the sun heats up the water bodies, water evaporates and forms water vapor.
- Water vapor moves higher from the Earth's surface and starts to cool down to form tiny water droplets by the process of condensation. The collection of tiny water droplets results in the formation of big drops of water.
- Big drops of water form clouds and come down as rain by the process of precipitation.
- The air above is cool and if it gets cooler, the water drops may become snow and fall on the Earth's surface. When this snow melts, it becomes part of a river and stream.
- The water returns to the oceans and seas and completes the water cycle.
- This process continues.
Question 2.
Does the water table remain constant? Explain.
Answer:
No, the water table keeps varying. The main reasons are:
Variation from place to place:
As all regions of the Earth are not topologically the same. Some have dry climates and others have wet.
Variation from season to season:
As it doesn’t rain equally throughout the year, it affects the infiltration process and hence, the water table level keeps varying.
Question 3.
Explain the following terms in relation to each other:
- Groundwater,
- Aquifer,
- Water table
Answer:
Groundwater is the water present below the surface of the Earth. The upper limit, of this reserved water, is called the water table. Below the water, the table is a region of rocks and large soil particle that is saturated with water. This region is called the aquifer.
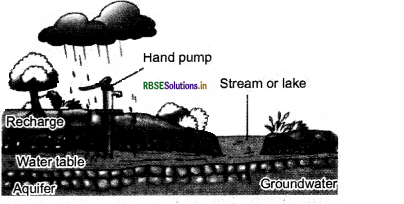
Question 4.
Is it possible, that water distribution can affect by man?
Answer:
Efforts by man can affect the availability of water in different regions to a certain extent. For example, by the construction of dams and reservoirs and planting trees, the infiltration process can be speed up resulting in increased water availability through better water management.

Question 5.
Describe an alternative irrigation method to conserve water.
Answer:
As opposed to traditional irrigation, the farmers could practice drip irrigation to conserve water and overcome the shortage of water.

In this method, the plants are watered through narrow pipes that deliver water directly at the base of the plant. This avoids wastage of water that cannot be avoided in traditional irrigation methods.
Question 6.
Explain with an example how can the building of dams affect groundwater levels?
Answer:
The best example is that of Bhujpur in the Kutch area of Rajasthan. The building of dams over the river Rukmavati increased the collection and resultant percolation of water through the ground. The replenished aquifers thus increased the groundwater levels.
Question 7.
What do you mean by being water-wise?
Answer:
Being water-wise means being conscious or aware of the ways in which water can be better used and less waste. Some water-wise activities include:
- Turn off taps when not in use.
- Repairing leaks in the pipes.
- Collecting rainwater for later use.
- Mopping the floor instead of washing.
Question 8.
How can one harvest rainwater?
Answer:
Rainwater can be harvested very easily by a rainwater harvesting system. The rainwater falling on the roofs of buildings can be directed to flow through a deep trench in the ground. This replenishes groundwater instead of entering the rivers through drains.
Question 9.
How does water shortage affect the village people?
Answer:
Water shortage is an acute problem in most villages due to the lack of well-organized device bodies and water supply systems. This affects the daily life of these villagers as:
- They have to travel long distances in search of water.
- They have to stand in a long queue for a long period of time.
- They are unable to maintain basic hygiene.

- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Electric Current and its Effects
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- RBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 8 शरीर में गति
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline