RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 7. Students can also read RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 7 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The class 7 science chapter 4 heat extra questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions Reproduction in Plants
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The ovaries of a flower may contain :
(a) only one ovule.
(b) only 2 ovules
(c) one too many ovules
(d) only an odd number of ovules
Answer:
(c) one to many ovules
Question 2.
The ‘eye’ of the potato plant is what:
(a) the roof to any plant
(b) the bud to a flower
(c) the bud is to Biyophyllum leaf
(d) the anther to a stamen
Answer:
(c) the bud is to Biyophyllum leaf
Question 3.
Spores are produced as a mode of reproduction in:
(a) moss
(b) ferns
(c) fungi
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these

Question 4.
The spores of a fungus are contained in its
(a) hyphae
(b) mycelium
(c) sporangium
(d) conidia
Answer:
(c) sporangium
Question 5.
In asexual reproduction, new plants are obtained, without the production of:
(a) spores
(b) seeds
(c) stems
(d) leaves
Answer:
(b) seeds
Question 6.
During the ripening of an ovary the ovule forms the:
(a) seed
(b) zygote
(c) embryo
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) seed
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
A fern or a moss plant reproduces by means of ................
Answer:
spore production
Question 2.
Buds in the ................, develop into shoots.
Answer:
axil
Question 3.
The................have naked seeds, unlike the angiosperms that have seeds protected within an ovary.
Answer:
gymnosperms
Question 4.
After fertilization,................develops into the embryo.
Answer:
zygote
Question 5.
Spores keep floating in the air as they are................
Answer:
light
State whether True or False
Question 1.
After fertilization, the ovules change into seeds and the ovary into fruit.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
The female or male reproductive cell is called a zygote.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
Seed dispersal helps the plants to avoid overcrowding.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Spores can withstand high temperatures, and low humidity as well as other types of environments due to their protective hard coat.
Answer:
True

Question 5.
Coconut seeds are spongy and fibrous which help in their dispersal by means of wind as well as by sticking to the bodies of animals.
Answer:
False
Match the following
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Ovule |
(a) Animals |
|
2. Petals |
(b) Wind |
|
3. Almond |
(c) Complete |
|
4. ‘Eyes’ of potato |
(d) Vegetative propagation |
|
5. Cutting |
(e) Asexual reproduction |
|
6. Xanthium |
(f) Buds |
|
7. Drumstick |
(g) Nodes |
|
8. Bisexual |
(h) Fruit |
|
9. Bryophyllum |
(i) Colourful |
|
10. Spirogyra |
(j) Seed |
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Ovule |
(j) Seed |
|
2. Petals |
(i) Colourful |
|
3. Almond |
(h) Fruit |
|
4. ‘Eyes’ of potato |
(f) Buds |
|
5. Cutting |
(g) Nodes |
|
6. Xanthium |
(a) Animals |
|
7. Drumstick |
(b) Wind |
|
8. Bisexual |
(c) Complete |
|
9. Bryophyllum |
(d) Vegetative propagation |
|
10. Spirogyra |
(e) Asexual reproduction |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do the ‘eyes’ on a potato represent?
Answer:
The ‘eyes’ on a potato are actually buds present at the stems since the potatoes that we eat are actually modified stems.
Question 2.
What do you mean by the vegetative parts of a plant?
Answer:
The stem, leaves, and roots are called the vegetative parts of a plant.
Question 3.
Where is a vegetative bud located?
Answer:
A vegetative bud is located at the nodes of a stem at the axil.
Question 4.
Why do plants need to reproduce?
Answer:
Like animals and other organisms, even plants need to reproduce for the continuation of their species.
Question 5.
What is the difference between a node and a cutting?
Answer:
A node is a region on a stem from which new leaves originate. But a cutting is a piece of stem that has at least one node.
Question 6.
Apart from sweet potato, which another plant can be grown by its roots?
Answer:
Dahlia.
Question 7.
What is a zygote?
Answer:
The fertilization process involves the fusion of a male gamete and a female gamete. The outcome of this fusion process is called a zygote.
Question 8.
What are pollen grains?
Answer:
Pollen grains are tiny spherical particles that contain the male gamete of a plant.
Question 9.
Give an example of dry fruit.
Answer:
Almonds.

Question 10.
Give examples of fleshy fruits.
Answer:
Mango, apple, avocado.
Question 11.
Why is a tomato called a fruit?
Answer:
Tomato is called a fruit because technically the red fleshy part we eat is the ripened and fleshy ovary of the tomato plant.
Question 12.
What is seed dispersal?
Answer:
The distribution or transfer of seeds from the place of their origin to a faraway place is known as seed dispersal.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What sort of reproduction is seen in bread molds?
Answer:
In bread molds, the sporulation type of reproduction is carried out. It is a type of asexual reproduction in which the plant propagates by the production of spores.
Question 2.
How do fungi, spirogyra, and yeast reproduce?
Answer:
|
Organism |
Mechanism of reproduction |
|
1. Fungi |
Spore formation |
|
2. Spirogyra |
Fragmentation |
|
3. Yeast |
Budding |
Question 3.
Why is the flower called a plant’s reproductive part?
Answer:
The flower is the site in a flowering plant that contains the male and female reproductive parts i.e., the stamen and the pistil. In the flower, the fusion of the male and female gametes occurs giving rise to the new plant. Therefore, the flower is called a plant's reproductive part.
Question 4.
Give an advantage of asexual reproduction over sexual reproduction.
Answer:
Asexual reproduction requires only one parent, hence, the energy to find a male is not required. Also since the offsprings produced are identical to their parents so they retain the desired qualities of the parent plant.
Question 5.
How do rhizomes reproduce?
Answer:
Rhizomes like ginger and turmeric are actually modified underground stem that is rich in starch and other nutrients. These reproduce with the help of vegetative buds present on their surface.
Question 6.
What advantage does sexual reproduction have over asexual reproduction?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction produces offspring that have the characteristics of both parents. This allows genetic intermingling and variations that might sometimes be more beneficial for the survival and reproduction of a plant.
Question 7.
Which part of a plant is responsible for sexual reproduction?
Answer:
The flower is responsible for sexual reproduction in a plant. This is because the flowers contain the male and female reproductive parts of the plant.
Question 8.
Why do flowers have colored petals?
Answer:
Flowers have colored petals to attract insects and birds in order to facilitate pollination. When they sit on flowers, some pollen dust gets transferred to their bodies. When they fly off to other flowers, the pollens get transferred.
Question 9.
What special features do plants possess to enable pollination by the wind?
Answer:
For successful pollination by means of wind, the plants have flowers with very small petals or no petals at all. The direct exposure of the anther and stigma to the blowing wind makes it easier for the pollen to be transported from one flower to another flower.
Question 10.
Which part of a plant develops into the seed?
Answer:
The ovules within the ovary develop into the seeds of the plant. Each ovule that has transformed into a seed contains an
the embryo within it, which is protected by the walls of the ovule which develops into a hard shell.
Question 11.
How is seed dispersal beneficial to plants?
Answer:
Seeds dispersal is beneficial because :
- It prevents the parent and offspring to compete for sunlight, nutrients, and water.
- It enables invading new territories and spreading over a wide area.
Question 12.
What type of seed gets dispersed by the wind?
Answer:
For wind dispersal, the seeds should have either of the following characteristics:
- Winged seeds.
- Lightweight.
- Hairy.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How do bisexual flowers pollinate?
Answer:
Bisexual flowers are those flowers that have both the male and female reproductive organs present in the same flower. Due to the close proximity of the anther and stigma, these flowers undergo the process of self-pollination i.e., the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of the same flower.

Question 2.
What are angiosperms and gymnosperms plants?
Answer:
|
Property |
Angiosperm |
Gymnosperm |
|
Fruits |
Bear fruits |
Don’t bear fruits |
|
Seeds |
Seeds are protected by the ovary |
Seeds are naked |
|
Flowers |
Bear flowers |
Don’t bear flowers |
|
Pollination |
Insect pollinated |
Wind pollination |
|
Example |
Apple, wheat, rice, broccoli |
Maidenhair tree, deodar cedar |
Question 3.
Explain the process of reproduction in plants, involving the fusion of cells from male and female parts of flowers.
Answer:
When the reproduction in an organism includes two types of gametes, i.e., male and female from two different parents, it is called sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction takes place by the fusion of male and female gametes by the process called fertilization to form a zygote Sexual reproduction (fertilization) in plants.
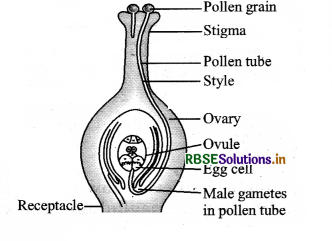
The different steps that take place during sexual reproduction in plants are :
- The pollen is deposited on the stigma and begins to germinate.
- Pollen tube containing male gametes reaches the ovary of the flower.
- The tip of the pollen tubes gets dissolved and male gametes come out of the pollen tube.
- Inside the ovary, male gametes fuse with the female gamete or egg present in the ovule.
- The fusion of both the gametes will result in a fertilized egg cell which is also called a zygote.

- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Electric Current and its Effects
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- RBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 8 शरीर में गति
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline