RBSE Class 6 English Grammar Tenses
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 6 English Grammar Tenses Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
The questions presented in the RBSE Solutions Class 6 English are solved in a detailed manner. Get the accurate RBSE Solutions for Class 6 all subjects will help students to have a deeper understanding of the concepts. Students who gain good command in stories for class 6 can easily score good marks.
RBSE Class 6 English Grammar Tenses
Tenses (Correct Form Of The Verb)
अर्थ - हमारी समय की अवधारणा के अनुरूप tense, क्रिया (Verb) की form को इंगित करता है। नोट-ध्यान रखें कि tense का अर्थ time नहीं होता है। अर्थात् Present Tense में present time की बातें तो बताई ही जाती हैं, साथ में, past time या future time की कुछ निश्चित परिस्थितियाँ भी बताई जा सकती हैं। कुल मिलाकर, यह कहा जा सकता है। कि Present Tense द्वारा present या past या future time की बातें बताई जा सकती हैं। इसी प्रकार, Past Tense व Future Tense से भी तीनों प्रकार के times की बातें बताई जा सकती हैं।

Tense के प्रकार : 1. Present Tense :
(i) Simple Present/Present Indefinite
(ii) Present Progressive/Present Continuous
(iii) Present Perfect
(iv) Present Perfect Progressive (Continuous)
2. Past Tense :
(i) Simple Past/Past Indefinite
(ii) Past Progressive/Past Continuous
(iii)Past Perfect
(iv) Past Perfect Progressive (Continuous)
3. Future Tense :
(i) Simple Future/Future Indefinite
(ii) Future Progressive/Future Continuous
(iii) Future Perfect
(iv) Future Perfect Progressive (Continuous)
इन सभी Tenses का वर्णन निम्न प्रकार है
1. Simple Present Tense
1. पहचान: ये वाक्य नित्य प्रति होने वाले कार्य (routine actions)/आदतन कार्य (habitual actions) आदि को बताते हैं,
जैसे -
(i) मैं सुबह जल्दी उठता हूँ।
(ii) फूल बसंत में खिलते हैं। इस Tense के हिन्दी वाक्यों के अन्त में 'ता है', 'ती है', 'ता हूँ', 'ते हैं' आते हैं।
2. Adverb of Frequency: इस Tense में प्रायः adverb of frequency के रूप में usually, generally, still, everyday, every year, seldom, frequently, always, never शब्द आते हैं।
3. वाक्य बनाने के नियम
1. साधारण वाक्य (Affirmative Sentences)
नियम-
(i) हमेशा verb की first form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) यदि वाक्य का subject (कर्ता), Third Person Singular (He/She/It या एक व्यक्ति/वस्तु का नाम) है तो Verb की first form के अन्त में 's' या 'es' लगाएं।
[नोट - यदि verb का अन्तिम अक्षर O, x, sh, ch या ss हो तो 'es' लगायें। शेष सभी verbs के साथ 's' लगायें।]
(iii) यदि verb (क्रिया) 'स्थिति' (state) बता रही हो तो is/are/am का ही प्रयोग verb के रूप में
करें व यदि verb 'स्वामित्व' (Possession) बता रही | हो तो has/have का प्रयोग Verb के रूप में करें।।
वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :

2. नकारात्मक वाक्य (Negative Sentences) वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
S+do/does+ not +V (first form) +/O+/C+/A.

(i) अच्छे विद्यार्थी समय बर्बाद नहीं करते हैं।
Good students do not waste time.
(ii) पाठ्यपुस्तक विद्यार्थियों को उत्साहहीन नहीं करती है।
A textbook does not discourage the students.
[नोट - सहायक क्रिया do का प्रयोग 'I' व plural subjects के साथ करें तथा does का प्रयोग third person singular subjects के साथ करें]
3. प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य (Interrogative Sentences)
3.1. सहायक क्रिया से आरंभ होने वाले प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
Do/Does+S+ V (first form)+/O+ /C+/A?
(i) क्या आप अपने देश से प्रेम करते हैं?
Do you love your country ?
(ii) क्या प्रत्येक विषय नवीन ज्ञान देता है? .
Does every subject give new knowledge ?
3.2. 'Wh' words (What क्या, Which कौनसा, Who कौन, Whose किसका, Whom किसे, Why क्यों, When कब, Where कहाँ, How कैसे) से आरंभ होने वाले प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य : वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
'Wh' word + do/does + S+ V (first form) + /O+/C+ /A?
(i) अध्यापक क्या चाहता है?
What does the teacher want?
(ii) आपको कौनसी पुस्तक चाहिए?
Which book do you want ?
4. नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य (NegativeInterrogative Sentences) : वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
(i) Don't/Doesn't+S+ V+/O+/C+/A?
Or
Do/Does + S + not + V+/O+/C+/A ?
(ii) Wh' word + don't/doesn't+S+V+/O+/C+/A?
Or
'Wh' word + do/does + S + not + V+/O+/C+/A?

(i) क्या आप पाठ का दोहरान नहीं करते हैं?
Don't you revise your lesson ?
Or
Do you not revise your lesson ?
(ii) आप पाठ का दोहरान क्यों नहीं करते हैं?
Why don't you revise your lesson ?
Or
Why do you not revise your lesson ?
2. Present Progressive Tense
1. पहचान : इस tense में वर्तमान काल में कार्य का जारी रहना प्रकट होता है। हिन्दी में इस 'Tense' के वाक्यों में रहा हूँ', 'रहा है', 'रही है', 'रहे हैं', 'हुआ है', 'हुई है', 'हुए हैं' आदि आते हैं। Is, am, are + ing form लगाकर वाक्य बनाते हैं।
2. Adverb of Frequency: इस Tense में प्रायः today, at this time, at this moment, at present, now, these day, now a days जैसे शब्द आते हैं।
(i) मैं अब विद्यालय जा रही/रहा हूँ।
(ii) वह इन दिनों योग सीख रही/रहा है।
3. वाक्य बनाने के नियम :
1. साधारण वाक्य: नियम –
(i) हमेशा verb की first form + ing का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) सहायक क्रिया am का प्रयोग 'I' के साथ, is का प्रयोग He/She/It या एक व्यक्ति/वस्तु के साथ तथा are का प्रयोग plural subjects के साथ करें।
वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
S+ HV + V+ing + /O+/C+/A.
(i) मैं कक्षा-कक्ष की सफाई कर रहा हूँ।
I am cleaning the classroom.
2. नकारात्मक वाक्य :
S+ HV + not + V-ing +/O +/C+/A.
वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
(i) Don't/Doesn't+S+ V+/O+/C+/A?
Or
Do/Does + S + not + V+/O+/C+/A ?
(ii) Wh' word + don't/doesn't+S+V+/O+/C+/A?
Or
'Wh' word + do/does + S + not + V+/O+/C+/A?

(i) क्या आप पाठ का दोहरान नहीं करते हैं?
Don't you revise your lesson ?
Or
Do you not revise your lesson ?
(ii) आप पाठ का दोहरान क्यों नहीं करते हैं?
Why don't you revise your lesson ?
Or
Why do you not revise your lesson ?
2. Present Progressive Tense
1. पहचान : इस tense में वर्तमान काल में कार्य का जारी रहना प्रकट होता है। हिन्दी में इस 'Tense' के वाक्यों में रहा हूँ', 'रहा है', 'रही है', 'रहे हैं', 'हुआ है', 'हुई है', 'हुए हैं' आदि आते हैं। Is, am, are + ing form लगाकर वाक्य बनाते हैं।
2. Adverb of Frequency: इस Tense में प्रायः today, at this time, at this moment, at present, now, these day, now a days जैसे शब्द आते हैं।
(i) मैं अब विद्यालय जा रही/रहा हूँ।
(ii) वह इन दिनों योग सीख रही/रहा है।
3. वाक्य बनाने के नियम :
1. साधारण वाक्य: नियम –
(i) हमेशा verb की first form + ing का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) सहायक क्रिया am का प्रयोग 'I' के साथ, is का प्रयोग He/She/It या एक व्यक्ति/वस्तु के साथ तथा are का प्रयोग plural subjects के साथ करें।

वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
S+ HV + V+ing + /O+/C+/A.
(i) मैं कक्षा-कक्ष की सफाई कर रहा हूँ।
I am cleaning the classroom.
2. नकारात्मक वाक्य :
S+ HV + not + V-ing +/O +/C+/A.
(i) लहरें तट पर नहीं पहुँच रही हैं।
Waves are not reaching the coast.
3. प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य (सहायक क्रिया व 'Wh' वाले):
(i) HV + S + V-ing + /O+/C+/A ?
(ii) Wh' + HV +S+ V-ing + /O+/C+/A?
(i) क्या किसान अपनी फसलों की सिंचाई कर रहे हैं?
Are the farmers irrigating their crops ?
नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य:
(i) HV+S+ not + V-ing +/0+/C+ /A?
(ii) Wh' + HV+S+ not + V-ing + /O +/C+/A?
(i) क्या मैं आपकी सहायता नहीं कर रहा हूँ?
Am I not helping you?
(ii) आप व्याकरण को मजबूत क्यों नहीं कर रहे हैं?
Why are you not strengthening grammar?
3. Present Perfect Tense
1. पहचान : ये वाक्य कार्य के पूरा हो जाने की सूचना देते हैं। हिन्दी के वाक्यों के अन्त में 'चुका है, चुकी है, चुके हैं, पूछा है, दिया है, देखा है' आदि शब्द आते हैं।
(i) मैंने अपने पाठों का दोहरान कर लिया है।
(ii) वह तीन दिन हॉस्पिटल में रहा है (रह चुका है)

2. Adverb of Frequency :
इस Tense में प्राय: already, never, since (अनिवार्य नहीं) for, just, yet (अधिकांश negative) आदि शब्द आते हैं।
3. वाक्य बनाने के नियम :
1. साधारण वाक्य:
नियम – (i) हमेशा verb की third form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) सहायक क्रिया has का प्रयोग He/She/It या एक व्यक्ति/वस्तु के साथ व have का प्रयोग तथा plural subjects के साथ करें।
वाक्य बनाने का तरीका:
S+ has/have + V-III +/O +/C +/A.
(i) हम यह चिड़ियाघर देख चुके हैं। .
We have seen this zoo.
(ii) न्यायाधीश अपना निर्णय सुना चुका है।
The judge has given his decision.
2. नकारात्मक वाक्य :
S+ has/have + not +V-III + /O+/C +/A.
(i) मैंने अपना समय बर्बाद नहीं किया है।
I have not wasted my time.
(ii) दर्जी ने वस्त्र नहीं सिले हैं।
The tailor has not sewn the clothes.
3. प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य (सहायक क्रिया व 'Wh' वाले):
(i) Has/Have+S+ V-III + /O+ /C+/A?
(ii) 'Wh'+ hashave+S+V-III +/O+/C+/A?
(i) क्या आपने एक म्यूजियम देखा है?
Have you seen a museum ?
(ii) इस पाठ को किसने याद किया है?
Who has learnt this lesson ?
4. नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) Has/Have+S+ not+V-III+/O+/C+/A?
(ii) Wh + HV+S+ not+V-III +/O+/C+/A?
(i) क्या आपने एक महासागर नहीं देखा है?
Have you not seen an ocean ?

(ii) किसकी बहन को ईनाम प्राप्त नहीं हुआ है?
Whose sister has not received the prize ?
4. Present Perfect
Progressive Tense
1. पहचान : ये वाक्य यह बताते हैं कि कोई कार्य भूतकाल में कब आरंभ हुआ, वर्तमान काल में जारी है, व भविष्य में कुछ समय और जारी रहने की संभावना रहेगी। जैसे
(i) मैं दो घंटे से प्रतीक्षा कर रही हूँ।
(ii) वर्षा सोमवार से हो रही है।
2. वाक्य बनाने के नियम :
1. साधारण वाक्य:
नियम -
(i) हमेशा verb की first form + ing का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) सहायक क्रिया has been का प्रयोग He/She/It या एक व्यक्ति/वस्तु के साथ करें तथा have been का प्रयोग 'I' व plural subjects के साथ करें।
(iii) Preposition, since' का प्रयोग 'निश्चित समय' (point of time) के साथ व 'for' का प्रयोग 'समयावधि' (period of time) के साथ करें। वाक्य बनाने का तरीका:
S+ has been/have been + V-ing +/O +/A + since/for + time.
(i) मैं 1997 से शिक्षा प्राप्त कर रहा हूँ।
I have been receiving education since 1997.
(ii) वह पन्द्रह वर्ष से शिक्षा प्राप्त कर रही है।
She has been receiving education for fifteen years.
2. नकारात्मक वाक्य : S+ has not been/have not been +V-ing+/O +/A+since/for + time.
(i) डॉक्टर, रोगी को सोमवार से इंजेक्शन नहीं दे रहे हैं।
The doctors have not been giving injection to the patient since Monday.
(ii) रोगी दो दिन से बेचैनी नहीं दिखा रहा है।
The patient has not been showing discomfort for two days.

3. प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य (सहायक क्रिया व 'Wh' वाले):
(i) Has/Have+S+been+V-ing +/O +/A + since/for + time?
(ii) 'Wh'+ has/have + S + been +V-ing+O+/A+ since/for + time?
(i) क्या आप 1997 से अंग्रेजी सीख रहे हैं?
Have you been learning English since 1997?
(ii) वह एक सप्ताह से समय बर्बाद क्यों कर रही
Why has she been wasting time for a week ?
4. नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) Has/Have +S+ not + been +V-ing + /O+/A+since/for + time?
(ii) 'Wh' + has/have + S + not + been + V ing + /O + /A + since/for + time?
(i) क्या सन्त लोगों को वर्षों से आशीर्वाद नहीं दे रहे
Have saints not been blessing people for years?
(ii) वह सोमवार से पढ़ाई क्यों नहीं कर रही है?
Why has she not been studying since Monday?
5. Simple Past Tense
1. पहचान : ये वाक्य कार्य के भूतकाल में समाप्त होने की सूचना देते हैं। जैसे
(i) हम वहाँ पहुँचे।
(ii) उन्होंने हमसे बात की।
2. Adverb of Frequency: इस Tense में प्राय: yesterday, last sunday, last year, in the year (1930, 2010 etc.), ago, before, previous night, last night, a few days ago, long long ago, in older time आदि शब्द आते हैं।
3. वाक्य बनाने के नियम :
1. साधारण वाक्य : नियम-(i) केवल साधारण वाक्य में ही Verb की second form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) यदि verb 'स्थिति' (state) बताए तो was/ were का प्रयोग करें तथा verb 'स्वामित्व' (possession) बताए तो had का प्रयोग verb के रूप में करें। वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
S+ V-II +/O+/C+/A.
(i) विद्यार्थियों ने कल पौधों में पानी दिया।
The students watered the plants yesterday.
(ii) हम वहाँ थे।
We were there.
(iii) मेरे पास दो थैले थे।
I had two bags.
2. नकारात्मक वाक्य: S+ did + not + V-I + /O+/C+/A.
(i) हम वहाँ नहीं गए।
We did not go there.
(ii) उसने झूठ नहीं बोला।
She did not tell a lie.

3. प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) Did + S+ V-I +/O+/C+/A?
(ii) 'Wh' + did + S + V-I + /O + /C+ /A?
(i) क्या आप वहाँ खेले?
Did you play there?
(ii) वह यहाँ कब आई?
When did she come here?
4. नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) Did+S+not + V-I+/O+/C+/A ?
(ii) Wh'+did +S+ not+V-I+/O+/C+/A?
(i) क्या तुम वहाँ नहीं गईं?
Did you not go there ?
(ii) तुमने अपना बैग कहाँ नहीं रखा?
Where did you not keep your bag?
6. Past Progressive Tense
1. पहचान : ये वाक्य भूतकाल में किसी कार्य के जारी रहने की सूचना देते हैं।
2. Adverb of Frequency: इस Tense में प्रायः at that moment, at that time, those days, continuously, that day आदि शब्द आते हैं।
3. वाक्य बनाने के नियम :
1. साधारण वाक्य :
नियम–(i) हमेशा Verb की '-ing' form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) Singular Subject व के साथ सहायक क्रिया was का प्रयोग करें तथा plural subject के साथ were का प्रयोग करें। वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
S+ was/were+V-ing +/O+/C+/A.
(i) वह खेल रही थी।
She was playing.
(ii) हम वहाँ जा रहे थे।
We were going there.

2. नकारात्मक वाक्य :
S+ was/were+not+V-ing+/O+/C+/A.
(i) वह अपना समय नष्ट नहीं कर रही थी।
She was not wasting her time.
(ii) हम शोर नहीं मचा रहे थे।
We were not making a noise.
3. प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) was/were + S + V-ing + /O + /C+ /A?
(ii) Wh'+was/were+S+V-ing+/O+/C+/A?
(i) क्या तुम हँस रहे थे?
Were you laughing ?
(ii) वह कहाँ जा रही थी?
Where was she going ?
4. नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य:
(i) Was/were+S+ not+V-ing + /O+ /C+ A?
(ii) Wh'+was/were+S+not+V-ing+/O+/C+/A?
(i) क्या तुम नहीं पढ़ रहे थे?
Were you not studying ?
(i) वह क्यों नहीं पढ़ रही थी?
Why was she not studying ?
7. Past Perfect Tense
1. पहचान : ये वाक्य भूतकाल में किसी निश्चित समय तक कार्य की पूर्णता की सूचना देते हैं। जैसे
(i) मैं 2013 तक सातवीं कक्षा पास कर चुका था।
(ii) डॉक्टर के आने से पहले रोगी मर चुका था।
2. Adverb of Frequency: इस Tense में प्रायः after, when, before (इसके बाद वाला वाक्य), already
आदि शब्द आते हैं।
3. वाक्य बनाने के नियम :
1. साधारण वाक्य : नियम-
(i) हमेशा Verb की third form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) हमेशा had सहायक क्रिया का प्रयोग करें।
(iii) यदि वाक्य में दो कार्य (actions) हों तो पहले पूर्ण हुए कार्य को past perfect में लिखें व दूसरे कार्य को simple past में लिखें। वाक्य बनाने का तरीका:
S + had + V-III +/O + /A.
(i) वह घर जा चुकी थी।
She had gone home.
(ii) मेरे स्कूल पहुंचने से पहले घंटी बज चुकी थी।
The bell had rung before I reached school.
2. नकारात्मक वाक्य :
S+ had + not + V-III +/O+ /A.
(i) उसने विद्यालय नहीं छोड़ा था।
She had not left school.
(ii) मैं वहाँ नहीं गया था।
I had not gone there.
3. प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) Had+S+ V-III + /O + /A?
(ii) Wh' + had + S+ V-III + /O + /A?

(i) क्या तुम होमवर्क पूरा कर चुके थे?
Had you completed homework ?
(ii) उसने पाठ क्यों दोहराये थे?
Why had he revised the lessons ?
4. नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) Had + S + not + V-III + /O + /A?
(ii) 'Wh'+ had+S+ not + V-III + /O+ /A?
(i) क्या उसने खेलों में भाग नहीं लिया था?
Had she not participated in the games ?
(ii) तुम क्यों नहीं गए थे? Why had you not gone ?
8. Past Perfect
Progressive Tense
1. पहचान : ये वाक्य उन कार्यों की सूचना देते हैं जो भूतकाल में किसी निश्चित समय आरंभ हुए थे व भूतकाल में ही जारी रहे थे तथा भूतकाल में ही समाप्त हो गए थे। जैसे
(i) वह 1998 से शिक्षा ग्रहण कर रहा था।
(ii) हम दो वर्ष से प्रशिक्षण ले रहे थे।
2. वाक्य बनाने के नियम :
1. साधारण वाक्य: नियम-
(i) हमेशा Verb की '-ing' form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) हमेशा had been सहायक क्रिया का प्रयोग करें।
(iii) 'since' का प्रयोग point of time (निश्चित समय) के साथ करें व 'for' का प्रयोग period of time (समयावधि) के साथ करें। वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
S + had been + V-ing +/O+/A+ since/for + time.
(i) हम जनवरी से पाठों का दोहरान कर रहे थे।
We had been revising lessons since January.
(ii) वह दो वर्ष से एक किताब लिख रही थी।
She had been writing a book for two years.
2. नकारात्मक वाक्य : S + had + not + been + V-ing +/O + /A+ since/for + time.
(i) वह तीन वर्ष से प्रशिक्षण नहीं ले रही थी।
She had not been taking training for three years.
(ii) वे 10.00 बजे से नहीं खेल रहे थे।
They had not been playing since 10 o'clock.

3. प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) Had + S+ been + V-ing + /O + /A + since/for + time?
(ii) Wh' + had + S + been + V-ing + /O +/A + since/for + time ?
(i) क्या आप 10 बजे से पढ़ रहे थे?
Had you been studying since 10 o'clock ?
(ii) आप एक सप्ताह से कहाँ रह रहे थे?
Where had you been living for a week?
4. नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) Had + S + not + been + V-ing + /O + A + since/for + time?
(ii) Wh' + had + S + not + been + V-ing + /O+ /A + since/for + time?
(i) क्या आप 10 बजे से नहीं पढ़ रहे थे?'
Had you not been studying since 10 o'clock?
(ii) आप 10 दिन से क्यों नहीं पढ़ रहे थे?
Why had you not been studying for ten days?
9. Simple Future Tense
1. पहचान : ये वाक्य भविष्य में होने वाले कार्यों की साधारण सूचना देते हैं। जैसे
(i) हम अपने पाठों का दोहरान करेंगे।
(ii) वे अजमेर जायेंगे।
2. Adverb of Frequency:
इस Tense में प्रायः tomorrow, next day, next time, in future, in 2030, any future time or day आदि शब्द आते हैं।
3. वाक्य बनाने के नियम :
1. साधारण वाक्य : नियम-
(i) हमेशा Verb की first form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) यदि वाक्य का subject, 'I' या 'We' हो तो +shall' सहायक क्रिया का प्रयोग करें व अन्य subjects के साथ 'will' का प्रयोग करें।

वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
S+ shall/will + V-I+/O+ /C+ IA.
(i) हम कल पुस्तकें खरीदेंगे।
We shall buy books tomorrow
(ii) वे इस पाठ को पढ़ेंगे।
They will read this lesson.
2. नकारात्मक वाक्य: S+ shall/will + not + V-I + /O + /C + /A.
(i) मैं बाजार नहीं जाऊँगा।
I shall not go to market.
(ii) आप अपना समय बर्बाद नहीं करेंगे।
You will not waste your time.
3. प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) Shall/Will + S + V-I + /O+ /C+/A?
(ii) Wh' +shall/will +S+ V-I+/O+/C/A?
(i) क्या वह अध्यापक बनेगी?
Will she become a teacher ?
(ii) वह अध्यापक कब बनेगी?
When will she become a teacher ?
4. नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) Shall/Will +S+ not +V-I +/O+ /C+ A?
(ii) 'Wh+shall/will + S+ not+V-I +/O+ /C +/A?
(i) क्या वह अध्यापक नहीं बनेगी?
Will she not become a teacher ?

(ii) वह अध्यापक क्यों नहीं बनेगी?
Why will she not become a teacher ?
10. Future Progressive Tense
1. पहचान : ये वाक्य भविष्य में किसी कार्य के जारी रहने की सूचना देते हैं। जैसे
(i) हम जून में कश्मीर घूम रहे होंगे।
(ii) वे अगले वर्ष नवीं कक्षा में पढ़ रहे होंगे।
2. वाक्य बनाने के नियम :
1. साधारण वाक्य : नियम-
(i) हमेशा Verb की -ing form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) I व We के साथ shall be का प्रयोग करें व शेष subjects के साथ will be का प्रयोग करें। वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
S + shall be/will be + V-ing +/O+/C+/A.
(i) हम कल स्टेडियम में अभ्यास कर रहे होंगे।
We shall be practising in the stadium tomorrow.
(ii) किसान अगले माह फसल काट रहे होंगे।
The farmers will be harvesting the crops next month.
2. नकारात्मक वाक्य: S+ shall/will + not + be+V-ing +/O+/A.
(i) हम कल अभ्यास नहीं कर रहे होंगे।
We shall not be practising tomorrow.
(ii) वे अगले सप्ताह अजमेर नहीं जा रहे होंगे।
They will not be going to Ajmer next week.

3. प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) Shall/Will + S + be + V-ing + /O+ /A?
(ii) 'Wh'+ shall/will+S+ he+V-ing +/O+/A?
(i) क्या आप कल अजमेर जा रहे होंगे?
Will you be going to Ajmer tomorrow?
(i) हम नौकरी कब कर रहे होंगे?
When shall we be doing job?
4. नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(1) Shall/Will + S +not+be+V-ing +/O +/A?
(ii) Wh' + shall/will + S + not + be + Ving + /O+ /A?
(i) क्या हम कल अजमेर नहीं जा रहे होंगे?
Shall we not be going to Ajmer tomorrow?
(ii) वे कल अभ्यास क्यों नहीं कर रहे होंगे?
Why will they not be practising tomorrow ?
11. Future Perfect Tense
1. पहचान : ये वाक्य भविष्य में किसी निश्चित समय पर कार्य के पूरा हो जाने की सूचना देते हैं। जैसे
(i) मैं 2025 तक दसवीं कक्षा पास कर चुका होऊँगा।
(ii) वे रात 10 बजे तक अपना कार्य समाप्त कर चुके होंगे।
2. Adverb of Frequency: इस Tense में प्रायः by the end of + time आता है।
3. वाक्य बनाने के नियम : 1. साधारण वाक्य :
नियम-(i) हमेशा Verb की third form का | प्रयोग करें।
(ii) 'I' व 'We' के साथ shall have सहायक क्रिया का प्रयोग करें तथा शेष सभी subjects के साथ will have का प्रयोग करें। वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
S+ will have/shall have +V-III + /O+/C+ /A.

(i) वह 2025 तक अध्यापिका बन चुकी होगी।
She will have become a teacher by 2025.
2. नकारात्मक वाक्य :
S+ shall/will + not + have +V-III+/O+/C+/A.
(i) वह 2025 तक अध्यापिका नहीं बन चुकी होगी।
She will not have become a teacher by 2025.
3. प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
Wh'+/Shall/Will + S+ have + V-III + /O+ /C+/A?
(i) हम आठवीं कक्षा कब पास कर चुके होंगे?
When shall we have passed the 8th class ?
4. नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
'Wh' + /Shall/Will + S+ not + have + V-III + /O+ /C + /A?
(i) क्या आप 2025 तक दसवीं कक्षा नहीं पास कर
चुके होंगे? Will you not have passed the 10th class by 2025?
12. Future Perfect
Progressive Tense
1. पहचान : ये वाक्य किसी कार्य के भविष्य में आरंभ होने व भविष्य में ही जारी रहने की सूचना देते हैं। इसमें point of time (निश्चित समय) या period of time (समयावधि) का उल्लेख भी होता है।
(i) हम 2023 से नवीं कक्षा में पढ़ रहे होंगे।
(ii) कल वह एक घंटे से भोजन पका रही होगी।
2. वाक्य बनाने के नियम :
1. साधारण वाक्य: नियम-
(i) हमेशा Verb की -ing form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) [ व We के साथ shall have been सहायक क्रिया का प्रयोग करें तथा शेष सभी subjects के साथ will have been का प्रयोग करें।
(iii) since' का प्रयोग 'निश्चित समय' (point of time) के साथ व 'for' का प्रयोग 'समयावधि' (period of time) के साथ करें। वाक्य बनाने का तरीका :
S+ shall have been/will have been + V-ing + /O+ /A.
(i) हम 2023 से नवीं कक्षा में पढ़ रहे होंगे।
We shall have been studying in the 9th class since 2023.
2. नकारात्मक वाक्य : S+ shall/will+not+have been+V-ing+/O+ /A.
(i) हम सोमवार से विद्यालय 7.00 बजे नहीं जा रहे होंगे।
We shall not have been going to school at 7.00 a.m. since Monday.

3. प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य : 'Wh'+ /Shall/Will + S + have been + V-ing +/O+/A?
(i) क्या सीमा एक घंटे से भोजन पका रही होगी?
Will Seema have been cooking food for an hour ?
4. नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
'Wh+ /Shall/Will + S+ not + have been + V-ing + /O + IA?
(i) टीमें सोमवार से मैच क्यों नहीं खेल रही होंगी?
Why will teams not have been playing the match since Monday?
Filling In Correct
Form Of Verbs
Verb की correct form भरने के लिए लेखक ने Golden Rules बनाये हैं। इनका पालन करने से आप correct form of verb सरलता से व सही भर सकेंगे। इनका अध्ययन ध्यान से समझ कर करिये।
Correct Form Of Verbs
भरने के
Golden Rules
Rule : 1: यदि वाक्य में yesterday, last (last Monday, last night, last week, last month, last year ...) अथवा the other day हो तो रिक्त
स्थान में verb की II Form आयेगी, क्योंकि ये शब्द Past Tense के सूचक हैं।
1. We ......... to go for a picnic last Sunday. (decide)
Answer: We decided to go for a picnic last Sunday.
2. He ........... to Ajmer yesterday. (go)
Answer: He went to Ajmer yesterday.
Rule: 2: यदि समय से पहले for, since अथवा all हो तथा वाक्य समाप्त हो गया हो तो रिक्त स्थान
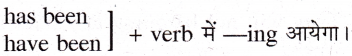
1. I ......... this book since 12 a.m. (read)
Answer: I have been reading this book since 12 a.m.
2. He ......... a story for two hours. (write)
Answer: He has been writing a story for two hours.
Rule : 3 : यदि वाक्य में tomorrow अथवा
next (next day, next week, next month, next year ... आदि) हों तो shall अथवा will + verb Form 3-
1. .....him to go outside tomorrow. (allow)
Answer: I shall allow him to go outside tomorrow.

2. She ........ to Bikaner next week. (go)
Answer: She will go to Bikaner next week.
Rule : 4: यदि वाक्य में yet, just अथवा already हो तो रिक्त स्थान में has अथवा have + verb की III Form आयेगी।
1. I ......... just ........ my clothes. (wash)
Answer: I have just washed my clothes.
2. Leela....... not yet...... her homework. (do)
Answer: Leela has not yet done her homework.
Rule : 5 : यदि वाक्य के बीच में before हो, और
(i) यदि before के पहले had हो तो-दूसरे वाक्य में verb की II Form आयेगी।
(ii) यदि before के बाद verb की II Form हो तो पहले वाक्य में had + verb की III Form आयेगी।
Structure :
.... had + verb की III Form ..... before .... verb की II Form ...
1. The bell ........ before I reached school. (go)
Answer: The bell had gone before I reached school.
2. The train ....... before she reached the station. (start)
Answer: The train had started before she reached the station.
Rule : 6 : यदि वाक्य में generally (जनरली = आम तौर पर), usually (यूजुअली = आम तौर पर) अथवा often (ऑफन = प्रायः) हो तो verb की I Form आती है।
1. Deepawali generally ...... in the month of November (fall)
Answer: Deepawali generally falls in the month of November.
2. She usually......... food in the evening.(cook)
Answer: She usually cooks food in the evening
Rule : 7 : (a) यदि वाक्य के आरम्भ में रिक्त स्थान हो तो verb की I Form आयेगी। (क्योंकि यह Imperative वाक्य है।)
1. .......... me a glass of water..(bring)
Answer: Bring me a glass of water.
2. ......... a letter to your father. (write)
Answer: Write a letter to your father.

Rule : 7 : (b) यदि Please के बाद रिक्त स्थान हो तो verb की I Form आयेगी।
1. Please ......... me some food. (give)
Answer: Please give me some food.
Rule : 8 : यदि वाक्य में by now दिया हो तो रिक्त-स्थान में has अथवा have + verb की III Form आयेगी।
1. It's five o'clock now. By now I ... eight letters. (type)
Answer: By now I have typed eight letters.
Rule: 9: 'and' के पहले जिस Tense का verb है, 'and' के बाद भी उसी Tense का verb आयेगी।
1. He came here and ........... to me. (talk)
Answer: He came here and talked to me.
2. She comes here and ........ food. (cook)
Answer: She comes here and cooks food.
Singular 7 Plural Verbs: Singular Verbs:
(a) is, was, has
(b) जिस verb के अन्त में -s अथवा –es हो, वह Singular verb है, जैसे - eats, goes, runs, writes .......
Plural Verbs: (a) are, were, have
(b) जिस verb के अन्त में -s अथवा - es नहीं हो, वह Plural verb है, जैसे -- eat, go, run, write ..........
नोट : Singular तथा Plural Verb केवल Present (Indefinite) Tense में ही होते हैं।
Rule verb हमेशा Subject के अनुसार आता | है, अर्थात्
(a) Subject यदि singular है तो verb भी | singular आयेगा;
(b) Subject of plural verb et plural आयेगा।
|
Singular Subjects |
Plural Subjects |
|
he |
we |
निम्नलिखित में --
SS = Singular Subject
PS = Plural Subject
SV = Singular Verb
PV = Plural Verb
x = गलत
√ = सही

ध्यान से समझिए (Present Tense)

Practice Exercise : 1:
Select the proper form of verb for the blank space :
रिक्त स्थान के लिए क्रिया के उचित रूप का प्रयोग कीजिए
Question 1.
I..............I could restore it.
(a) think
(b) thought
(c) thinking
(d) thinks
Answer:
(b) thought
Question 2.
The veneer........... ...almost everywhere.
(a) had lifted
(b) lifting
(c) lift
(d) lifts
Answer:
(a) had lifted

Question 3.
Then they............... out to us from across : no man's land.
(a) was calling
(b) has calling
(c) were calling
(d) has calling
Answer:
(c) were calling
Question 4.
"Come on, boys'. What.............. we ........... for?
(a) are waited
(b) is waiting
(c) are waiting
(d) waiting
Answer:
(c) are waiting
Question 5.
I am from Dusseldorf. ................the cello in the orchestra.
(a) play
(b) plays
(c) playing
(d) player
Answer:
(a) play
Question 6.
We................ all he knew of England from school.
(a) has learned
(b) am learning
(c) was learning
(d) had learned
Answer:
(d) had learned
Question 7.
The old lady................in a wheelchair.
(a) has sitting
(b) had sitting
(c) was sitting
(d) were sitting
Answer:
(c) was sitting

Question 8.
When the tremors came early in the morning, the family ..............
(a) are sleeping
(b) was sleeping
(c) sleeping
(d) slept
Answer:
(b) was sleeping
Practice Exercise : 2:
Question 1.
At last they.............to test each other's strength.
(a) decide
(b) decides
(c) decided
(d) did decided
Answer:
(c) decided
Question 2.
I................a car for you to go to Netarhat.
(a) has fixed
(b) is fixed
(c) had fixed
(d) fix
Answer:
(c) had fixed
Question 3.
One evening .................tea with you in a veranda of your bungalow.
(a) is
(b) has
(c) had
(d) am
Answer:
(c) had

Question 4.
He..............to leave with the feeling that he hadn't tried enough.
(a) don't wish
(b) weren't wish
(c) didn't wish
(d) hasn't wish
Answer:
(c) didn't wish
Question 5.
He...............open the envelope and took out the letter
(a) tear
(b) tored
(c) teared
(d) tore
Answer:
(d) tore
Question 6.
It.............the eternal love for adventure in man.
(a) is
(b) have
(c) am
(d) are
Answer:
(a) is
Question 7.
I am a big boy now and...............to drink milk.
(a) amn't need
(b) don't need
(c) didn't need
(d) hasn't need
Answer:
(b) don't need
Question 8.
He wondered for an instant if he................his direction.
(a) is mistaken
(b) has mistaken
(c) had mistaken
(d) mistaken
Answers:
(c) had mistaken
Practice Exercise 3:
1. She usually ........... Hindi. (speak)
2. The baby ............... because it is hungry now. (cry)
3. The train ................. just now. (arrive)
4. I........... here for half an hour. (wait)
5. We .............. last month. (join)
6. At that time, I .............. a T.V. program. (watch)
7. I played after . ........... my homework. (do)
8. They ............... for two months before they found gold. (dig)
9................ of fifteen years on my next birthday. (be)
10. We ............... for her when she returns home. (wait)
Answers:
1. speaks
2. is crying
3. has arrived
4. have been waiting
5. joined
6. was watching
7. had done
8. had been digging
9. shall be
10. shall be waiting

Practice Exercise : 4:
1. The earth................. round the sun. (move)
2. .............. a letter at present. (write)
3. We have recently .......... a new car. (buy)
4. He ............. in this town since 1947. (live)
5. The other day, they............... a beggar. (help)
6. What was she ............ when you called on her ? (do)
7. We ............ the course by that time. (revise)
8. She said that she .. house since 1947. (live)
9. The guests will soon ................ here.(be)
10. I wonder what she .................. at this time tomorrow. (do)
Answers:
1. moves
2. am writing
3. bought
4. has been living
5. helped
6. doing
7. had revised/shall have revised
8. had been living
9. be
10. will be doing

- What if Question Answer Class 6 English Honeysuckle Chapter 8 RBSE Solutions
- Vocation Question Answer Class 6 English Honeysuckle Chapter 7 RBSE Solutions
- The Wonderful Words Question Answer Class 6 English Honeysuckle Chapter 6 RBSE Solutions
- Where Do All the Teachers Go Question Answer Class 6 English Honeysuckle Chapter 5 RBSE Solutions
- Beauty Question Answer Class 6 English Honeysuckle Chapter 4 RBSE Solutions
- The Quarrel Question Answer Class 6 English Honeysuckle Chapter 3 RBSE Solutions
- The Kite Question Answer Class 6 English Honeysuckle Chapter 2 RBSE Solutions
- A House, A Home Question Answer Class 6 English Honeysuckle Chapter 1 RBSE Solutions
- The Banyan Tree Question Answer Class 6 English Honeysuckle Chapter 10 RBSE Solutions
- Desert Animals Question Answer Class 6 English Honeysuckle Chapter 9 RBSE Solutions
- A Game of Chance Question Answer Class 6 English Honeysuckle Chapter 8 RBSE Solutions