RBSE Class 4 English Grammar
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 4 English Let's Learn English Grammar Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 4 English Grammar
Personal Pronouns
[he, him, himself, she, her, herself]
Personal pronouns (व्यक्तिवाचक सर्वनाम) वे शब्द होते हैं जो व्यक्तिवाचक संज्ञा के स्थान पर प्रयुक्त होते हैं।
He, him, himself पुरुष के लिए तथा she, her, herself स्त्री के लिए प्रयुक्त होते हैं।
उदाहरण
1. He works very hard.
2. Everybody likes her much.
3. "Am I right?' she asked herself.
व्याख्या
1. प्रथम उदाहरण में pronoun 'He' कार्य का करने वाला (Doer/Subject) है। He तथा She को वाक्य के Subject (कर्ता) के रूप में ही प्रयोग करें।
2. द्वितीय उदाहरण में 'her' क्रिया 'likes' से प्रभावित व्यक्ति (receiverlobject) है। her तथा him को 'क्रिया (verb)' के बाद object (कर्म) के रूप में प्रयोग करें।
3. तृतीय उदाहरण में 'herself कार्य का doer व receiver है| herself तथा himself का प्रयोग वाक्य में प्रयुक्त she या he के अनुसार करें।

Exercise 1.
Complete the blanks of the following sentences with 'he', 'him' and 'himself
निम्न वाक्यों के रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति he, him तथा himself से करें
1. .............. loves children.
2. Children also love .........
3. He washes his clothes .........
4. .............. is a good teacher.
5. Students like..............very much.
6. He does his homework..........
Answers:
1. He
2. him
3. himself
4. He
5. him
6. himself
Exercise 2.
Complete the blanks of the following sentences with 'she', 'her' and 'herself.
निम्न वाक्यों के रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति she, her तथा herself से करें.
1. ..............is a good mother.
2. I gave..............my notebook.
3. She writes the answers............
4. .............always makes use of her time.
5. My mother advised..............to work hard.
6. She made the pictures...............
Answers:
1. She
2. her
3. herself
4. She
5. her
6. herself

Nouns Nouns
(संज्ञाएँ) वे शब्द होते हैं जो किसी व्यक्ति (Person) अथवा व्यक्तियों (Persons), जानवर (Animal), अथवा जानवरों (Animals), स्थान (Place) अथवा स्थानों (Places), वस्तु (Thing) अथवा वस्तुओं (Things) का ज्ञान कराते हैं। जैसे teacher and students (Persons), mice and cats (Animals), windows and room (Places), ice-cream and plates (things) इत्यादि।
Nouns चार प्रकार (Kinds) के होते हैं-
1.Common Nouns व्यक्तियों, जानवरों, स्थानों तथा चीजों के नामों को कहा जाता है। जैसे--Man, Cow, Class-room, Pencil if Common Nouns हैं।
2. Proper Nouns किसी विशेष व्यक्ति अथवा स्थान के नाम को Proper Noun कहा जाता है। जैसे—Ram, Sita, Jaipur, Hawa Mahal, आदि।
3. Collective Nouns-जब एक Noun व्यक्तियों अथवा वस्तुओं के समूह (Collection) की ओर संकेत करता है तो इसे Collective Noun कहा जाता है। जैसे-Army, Crowd, Flock, Class आदि। (Army सैनिकों का समूह है, Crowd लोगों का समूह है, Flock भेड़ों का समूह है तथा Class छात्रों का समूह है।)
4. Material Nouns जब एक Noun किसी पदार्थ की ओर संकेत करता है जिससे वस्तुएँ बनती हैं तो वह Material Noun कहलाता है। जैसेIron (लोहा), Wood (लकड़ी), Silver (चाँदी), Gold (सोना),Cotton (कपास) आदि।
Exercise
Identify the Noun in the following sentences.
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में संज्ञा (Noun) पहिचानिये
1. Ram is my friend.
2. Mohan likes mangoes.
3. The students are sitting in the classroom.
4. India has a large army.
5. The Hawa Mahal is in Jaipur.
6. My shirt is made of cotton.
7. His chair is made of wood.
8. My house is small in the colony.
9. Sanjay works in an office.
10. There are ten boys in this room.
Answers :
1. Ram, friend
2. Mohan, mangoes
3. students, classroom
4. India, army
5. Hawa Mahal, Jaipur
6. shirt, cotton
7. chair, wood
8. house, colony
9. Sanjay, office
10. boys, room

Adjectives
[Formation by adding '-ful' and '-able
Adjective (विशेषण)/Describing words (वर्णन करने वाले शब्द) उन words (शब्दों) को कहते हैं जो किसी संज्ञा की विशेषता बताते हैं या संज्ञा के बारे में अतिरिक्त सूचना देते हैं।
(A) Formation of adjectives by adding
उदाहरण
1. She is a careful girl.
2. She is a beautiful lady.
व्याख्या
1. प्रथम व द्वितीय उदाहरणों में संज्ञा शब्दों क्रमशः care तथा beauty के अन्त में -ful' जोड़कर विशेषण बनाए गए हैं।
2. द्वितीय उदाहरण में beauty के अंतिम अक्षर 'y' को _'' में बदलकर '-ful' जोड़ा गया है। 'y' से समाप्त होने वाले nouns में आपको भी ऐसा ही करना है।
ऐसे Adjectives की सूची
painful, joyful, fruitful, cheerful, harmful, colourful, delightful, doubtful, faithful, fearful, forceful, lawful, shameful, tearful, fanciful, merciful, pitiful, weariful, plentiful
(B) Formation of adjectives by adding -able
उदाहरण
1. He has a readable book.
2. It is a remarkable book.
व्याख्या
1. प्रथम व द्वितीय उदाहरणों में क्रिया शब्दों क्रमशः
read तथा remark के अन्त में '-able' जोड़कर विशेषण बनाए गए हैं।
Exercise : 1
(Based on Let's Learn English)
Add -ful' to each noun to make an adjective
पायेक संज्ञा के साथ ' ful ' जोड़िएा एवं विशेषण बनाइए
1. Success
2. Help
3. Beauty
4. Use
5. Care
6. Faith
7. colour
8. power
Answers :
1. successful
2. helpful
3. beautiful
4. useful
5. careful
6. faithful
7. colourful
8. powerful

Exercise 2.
Add - able to each word, to make an adjective.
प्रत्येक शब्द के साथ '-able' जोडिए और विशेषण बनाइए -
1. agree
2. advise
3. believe
4. decorate
5. divide
6. hate
7. injure
8. invite
9. like
10. more
Answers :
1. agreeable
2. advisable
3. believable
4. decoratable
5. dividable
6. hatable
7. injurable
8. invitable
9. likable
10. morable
Exercise 3.
Add '-ful' to the words given below. And then complete each of the following sentences with the most appropriate word
नीचे दिये गये शब्दों में :-ful' जोड़कर सही शब्द से रिक्त स्थान भरें
hope, watch, hate, help, need, duty
1. She is a.............lady.
2. I am.............for the best marks.
3. Please do the .............
4. People like the ............. employees in offices.
5. Our guard is.
6. It's.............to give pains to others.
Answers:
1. helpful
2. hopeful
3. needful
4. dutiful
5. watchful
6. hateful

Adverb
Adverb (क्रिया-विशेषण) का प्रयोग Adjective (विशेषण), Verb (क्रिया) तथा दूसरी adverb (क्रिया-विशेषण) के लिए किया जाता है। नोट-चूंकि आपकी पाठ्यपुस्तक में. Adverbs of
manner, place तथा time से सम्बन्धित अभ्यास ही दिया गया है अतः यहाँ इन्हें ही समझाया जा रहा है।
(i) Adverbs of manner-ये हमें बतलाते हैं कि कोई कार्य किस प्रकार हुआ। इन Adverbs के अन्त में -ly जुड़ा होता है।
Example:

Explanation :
(i) उपर्युक्त सभी sentences में (वाक्य संख्या 5 को छोड़कर) -ly adverb को adjective से बनाया गया है, जैसे loving (adj.) + ly, attractive (adj.) + ly, angry (adj.) + ly, clear (adj.) + ly.
(ii) Sentence number 5 में -ly adverb को noun से बनाया गया है, जैसे week (noun) + ly. अतः -ly adverb का निर्माण अधिकतर , adjectives के अन्त में -ly जोड़कर किया जाता है व कभी-कभी कुछ nouns के अन्त में -ly जोड़कर किया जाता है।
(iii)-ly adverb की position (स्थान), verb के बाद या object के बाद या prepositional phrase से पूर्व या verb से पूर्व, यदि कोई phrase/clause इसे modify (विशेषता बताता) करता है, होती है।
A Short List of Some Adverbs ending in-ly
(happy + ly) happily, (ready + ly) readily, (heavy + ly) heavily, (single + y) singly, | (double + y) doubly, wisely, finely, kindly, quickly, cleverly, foolishly, bravely, largely, easily, jointly, unitedly, tiredly, boringly, smilingly, calmly, beautifully, carefully, slowly, swiftly, hopelessly, industriously, laughingly, affectionately, faithfully etc.
(ii) Adverbs of time-ये समय को दर्शाने वाले शब्द होते हैं, जैसे today, yesterday, early, Monday, in 2006 etc.
(iii) Adverbs of place-ये स्थान सूचक शब्द होते हैं, जैसे-here, there, somewhere, outside, etc.

Exercise 1.
(Based on Let's Learn English)
Underline the adverbs in the following sentences
1. What about the match tomorrow?
2. Seema saw Ritu under a tree there.
3. Suddenly there was a blow of stick on the python.
4. Ritu fought bravely.
5. The camel fair of Pushkar is held on Kartik Purnima every year.
6. Riti and Tarun were waiting inside.
7. They all set out for home happily.
8. Kalpna Chawla passed her Higher Secondary Examination in 1976.
9. My friend will be here any minute.
10. We didn't really have a fight.
Answers :
1. What about the match tomorrow?
2. Seema saw Ritu under a tree there.
3. Suddenly there was a blow of stick on the python.
4. Ritu fought bravely.
5. The camel fair of Pushkar is held on Kartik Purnima every year.
6. Riti and Tarun were waiting inside.
7. They all set out for home happily.
8. Kalpna Chawla passed her Higher Secondary Examination in 1976.
9. My friend will be here any minute.
10. We didn't really have a fight.
Exercise 2.
Underline the adverbs in the following sentences
निम्न वाक्यों में Adverbs को रेखांकित कीजिए --
1. Kailash works foolishly.
2. Sarita helps him honestly.
3. Babulal took coffee yesterday.
4. Yogita lives there.
5. Neeraj will call her tomorrow.
6. Naresh walked slowly.
7. Jagdish works here.
8. The students used to answer the questions wisely.
9. Priya faced the difficulties bravely.
10. Guru Dayal Sharma looked for his lost mobile everywhere.
Answers :
1. Kailash works foolishly.
2. Sarita helps him honestly.
3. Babulal took coffee yesterday.
4. Yogita lives there.
5. Neeraj will call her tomorrow.
6. Naresh walked slowly.
7. Jagdish works here.
8. The students used to answer the questions wisely.
9. Priya faced the difficulties bravely.
10. Guru Dayal Sharma looked for his lost mobile everywhere.
Modals
(can, could, will, should, must]
1. Modal का अर्थ -
Modal शब्द अंग्रेजी के Mood शब्द से बना है। Mood का अर्थ है - मनोभाव, मानसिक दशा। अत: वे.helping verbs जो वक्ता (व्यक्ति) के मनोभाव को प्रकट करते हैं, Modals कहलाते हैं। दूसरे शब्दों में, वे helping verbs जो main verb (मुख्य verb) के mode अर्थात् attitude को व्यक्त करते हैं, modals अथवा Modal Auxiliaries (मनोभाव प्रदर्शक सहायक क्रियाएँ) कहलाती हैं।

2. Modals की विशेषताएँ
1. Modals (अर्थात् Modal Auxiliaries) कभी अकेले नहीं आते हैं। ये सदैव main verb के साथ प्रयुक्त होते हैं। ये वास्तव में Helping Verbs होते हैं।
2. Modals पर Subject, number, gender व person का कोई प्रभाव नहीं पड़ता है।
3. Modals के बाद 'verb' में -s कभी नहीं लगता है।
4. Modals के बाद आने वाले 'verb' में -ing नहीं लगता है।
5. Modals के बाद 'not' लगाने से, वाक्य negative बन जाते हैं।
6. Modals को Subject के पहले रख देने से वाक्य Interrogative बन जाते हैं। _
7. Modal के बाद हमेशा verb की I Form
(अर्थात् Present Tense) का प्रयोग होता है। ध्यान दो, Modal के बाद to + main verb गलत है। किन्तु ought तथा used के साथ
infinitive to' का प्रयोग अवश्य होता है। आपकी पाठ्यपुस्तक में Modals में can, could, should, will तथा must एवं इनके negatives को ही शामिल किया गया है। अतः यहाँ केवल इनका वर्णन किया जा रहा है।
1. 'Can' का प्रयोग
1. Can का प्रयोग शक्ति (Power), सामर्थ्य (Capability), क्षमता (Capacity) व योग्यता (Ability) का भाव प्रकट करने के लिए किया जाता है।
Inability के लिए Present में can't का use करें।
(i) He can run fast. (Power)
(उसमें इतनी शक्ति है कि) वह तेज दौड़ सकता है।
(ii) Ramesh is very rich. He can buy a car. (Capability)
(रमेश इतना धनी है कि उसमें सामर्थ्य है कि) वह एक कार खरीद सकता है।
(iii) She can drive a car. (Ability)
(उसमें इतनी योग्यता है कि) वह कार चला सकती है।
2. Can का प्रयोग- आज्ञा देने (Permission), अनुमति लेने या अनुमति देने के लिए किया जाता है।
(i) You can sit here. (Permission)
(तुम्हें आज्ञा दी जाती है कि) तुम यहाँ बैठ सकते हो।
(ii) Can I take your scooter for two hours?
(अनुमति माँगता हूँ कि) क्या मैं तुम्हारा स्कूटर दो घण्टों के लिए ले लूँ?
(iii) You can't move on the field.
(तुम्हें खेत में चलने की आज्ञा नहीं है।)
3. सामान्य सम्भावना (General Possibility) प्रकट करने के लिए।
(i) Television can be found in every middle-class family.
2. 'Could' का प्रयोग
Can Past Tense-could I Could not इसका negative होता है। भूतकाल में योग्यता (ability), सामर्थ्य (capability) के लिए can के स्थान पर could का प्रयोग किया जाता है, जैसे
(i) He could run fast in his younger age. वह अपनी युवावस्था में तेज दौड़ सकता था।

3. Will' का प्रयोग-उदाहरण
He could swim in his youth.
I तथा We के साथ will अवश्य (certainty), धमकी (threat), आदेश (order), वादा (promise) के अर्थ को दर्शाने के लिए will का जबकि शेष कर्ता (Subjects) के साथ shall का प्रयोग होता है। |
(i) I will give you a book.
(मैं तुम्हें किताब अवश्य दूंगा। (Promise) का भाव है।)
(ii) We will go to cinema the next week -- (certainty)
(भाव यह है कि हम अगले सप्ताह सिनेमा अवश्य जायेंगे।) शेष सभी कर्ता (you, he, she, they, Mohan, father, teacher आदि) के साथ अवश्य (certainty), धमकी (threat), आदेश (order), वायदा (promise) तथा दृढ़ निश्चय (determination) के लिए shall का प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे
(iii) He shall help me.
(भाव यह है कि वह मेरी अवश्य सहायता करेगा) |
(iv) Boys shall be punished. (threat)
(भाव यह है कि लड़कों को अवश्य सजा मिलेगी)
4. Should' का प्रयोग
'Should' का अर्थ है'चाहिए'। सलाह (Advice), परामर्श (Suggestion), प्रस्ताव (Proposal) तथा नैतिक कर्त्तव्य (Moral Duty) का भाव प्रकट करने के लिए 'should' का प्रयोग किया जाता है। 'should' में बाध्यता अथवा अनिवार्यता का भाव नहीं होता है। Negative के लिए should not का प्रयोग किया जाता है। |
(i) You should respect your teachers.
(Moral Duty)
(ii) Sita should not go there at night.
(Advice)
(ii) She should get up early in the morning.
(Suggestion)
Use of Had better/Should Had better का प्रयोग लोगों को सलाह (advice) या सुझाव (suggestion) देने के लिए किया जाता है। यह should का समानार्थी है।
Example:
1. You had better reach school in time.
2. I had better do my homework regularly.
उपर्युक्त वाक्यों को हम 'had better' के स्थान पर 'should' का प्रयोग कर इस प्रकार लिख सकते हैं
1. You should reach school in time.
2. I should do my homework regularly.

5. 'Must' का प्रयोग
'Must' का अर्थ होता है-'अवश्य चाहिए।' इसमें 'बाध्यता' का भाव होता है। इसके negative के लिए must not का प्रयोग किया जाता है। 'must' का प्रयोग बाध्यता (Compulsion), अनिवार्यता (Necessity), कर्त्तव्य (Duty), पक्की धारणा (Certainty), दृढ़ निश्चय (Firm determination), निषेध (Prohibition) आदि का भाव देता है। जैसे
(i) You must sleep at night. (Compulsion)
(ii) She must cook food for her family. (Necessity)
(iii) They must respect their parents. (Duty)
(iv) You must not drive fast on crowded roads. (Prohibition)
(v) must का प्रयोग strong probability (possibility) बताने के लिए होता है। The lights are on so someone must be in the room.
Exercise 1.
Fill in the blanks with can/could/should as required.
आवश्यकतानुसार रिक्त स्थानों में can/could/ should को भरें
1. Kiran..........speak English well.
2. Rohit..........swim in the river.
3. Ankit ran as fast as he...........
4. Sunil is ill. He..........take rest.
5. Ravi is capable. He..........run fast.
6. Everybody..........meet an accident.
7. Mohit...........run fast when he was young
8. Annu.......... have helped Neeshu byt she didn't.
9. Waiter, ..........you bring some more water?
10. Tannu is intelligent. She....... solve it.
Answers:
1. can
2. can
3. could
4. should
5. can
6. can
7. could
8. could
9. can
10. can.

Exercise 2.
Fill in the blanks with should/must/will as required
आवश्यकतानुसार रिक्त स्थानों में should/must/will
1. I...........join army in 2025.
2. People..........grow more and more trees.
3. Walk carefully lest you..........fall down.
4. To drive a vehicle, you..........have a licence.
5. You..........not smoke here. It's no smoking zone.
6. I..........repeat this topic tomorrow.
7. We........... arrest the criminals till 2025.
8. You..........consult a good doctor.
9. Payal is ill. She..........call a doctor.
10. We..........respect our elders.
Answers:
1. will
2. should
3. should
4. must
5. must
6. will
7. will
8. should
9. must
10. should
Exercise 3.
Fill in the blanks with cannot/could not/ must not as required
आवश्यकतानुसार रिक्त स्थानों में cannot/could not/must not को भरें
1. She is dull. She................. answer the questions.
2. It is a public place. You............smoke here.
3. When he was sick, he............run fast.
4. They................play on the road.
5. He is physically weak. He.............lift up the heavy log.
Answers:
1. cannot
2. must not
3. could not
4. must not
5. cannot

Exercise 4.
Rewrite the following sentences using “had better
नीचे के नाक्यों को 'had better' का प्रयोग कर पुनः लिखिए -
1. Children/drink milk.
2. We/work hard.
3. Everybody/play games.
4. We/wash our hands before eating.
5. Prakash/play with Ram.
Answers:
1. Children had better drink milk.
2. We had better work hard.
3. Everybody had better play games.
4. We had better wash our hands before eating.
5. Prakash had better play with Ram.
Exercise 5.
Rewrite the following sentences using "should' in place of 'had better
नीचे के नाक्यों को 'had better' का प्रयोग कर should' का प्रयोग कर पुनः लिखिए-
1. Ram had better learn his lesson.
2. The rich had better help the poor.
3. Children had better obey their parents.
4. Ram had better take part in games.
5. We had better follow the traffic rules.
Answers:
1. Ram should learn his lesson.
2. The rich should help the poor.
3. Children should obey their parents.
4. Ram should take part in games.
5. We should follow the traffic rules.

Prepositions
Preposition एक वह शब्द होता है जो प्रायः किसी noun/pronoun (संज्ञा/सर्वनाम) के ठीक पहले यह दर्शाने के लिए प्रयोग किया जाता है कि इस noun/ pronoun का वाक्य के अन्य शब्द/शब्दों से किस प्रकार का सम्बन्ध है।
Preposition अनेक होते हैं लेकिन आपकी पाठ्यपुस्तक में केवल at, in तथा on को शामिल किया गया है। अतः हम यहाँ केवल इन्हीं का वर्णन कर रहे हैं। At, In तथा On के प्रयोग
1. at के प्रयोग
(i) निश्चित स्थान से पूर्व
She is at home.
(ii) निश्चित समय से पूर्व
I go to school at 7 a.m.
(iii) स्थिति/दशा बताने के लिए
She is at work.
2. in के प्रयोग
(i) स्थान के लिए (within an area)
I live in Jaipur.
(ii) समय के साथ (week, month, year,
season, period of time आदि)
I went there in January.
(iii) परिवहन का साधन बताने के लिए
She went in a car.
(नोट-in के बाद a, an, the आदि कोई determiner आता है।)
3. on के प्रयोग
(i) स्थिर अवस्था में एक वस्तु, दूसरी वस्तु के
ऊपर छूती हुई हो, के पूर्व
The bag is on the table.
(ii) किसी स्थान के समीप होना बताने के लिए
My school is on the main road.
(iii) दिन, दिनांक, विशेष अवसर आदि बताने के लिए
I go to the gym on weekends.

Exercise 1.
(Based on Let's Learn English)
Fill in the blanks with appropriate preposition at/on/in
रिक्त स्थानों को उपयुक्त preposition-at/on/in से भरिये
1. Devendra Jhajharia was born..... 1981.
2. What do you drink..........the summer.
3. Kalpna Chawla wanted to become an astronaut ..........the age of thirteen.
4. There are more than 2000 species of birds.........our country.
5. .......... November, the tribals gathered for a meeting.
6. ..........the age of eight, he touched a live electric cable.
7. I'm not..........the team any more!
8. There were tears.......... her eyes.
9. Prakash and Ram play games. p.m. daily.
10. I will put it..........the teacher's table to be corrected.
11. Suddenly there was a blow of stick ..........the python.
12. Kalpna Chawla was born.......July 1st.
Answers:
1. in
2. in
3. at
4. in
5. In
6. At
7. in
8. in
9. at
10. on
11. on
12. on

Exercise 2.
Fill in the blanks with prepositions choosing the correct option from the brackets below --
नीचे कोष्ठकों में से उपयुक्त विकल्प का चुनाव करते हुए निम्न रिक्त स्थानों में prepositions भरें -
1. Guru Dayal teaches Simran some rhymes and songs.........home. (in, at, on)
2. Khushboo plays.........Sundays. (on, in, at)
3. Neesha went.........a bullock cart. (on, at, in)
4. Priya got married.........20th January, 2008. (in, at, on)
5. We play games.........the evening. (at, in, on)
6. Jagdish and Neeraj visited me......... Sunday last year. (at, on, in) .
7. Naresh started.........six. (at, in, on)
8. We can find a preface.........the beginning of every book. (in, at, on)
9. I want to read books.........History. (at, on, in)
10. I watched a good film. .........T.V. (at, in, on)
Answers:
1. at
2. on
3. in
4. on
5. in
6. on
7. at
8. in
9. on
10. on
Verbs
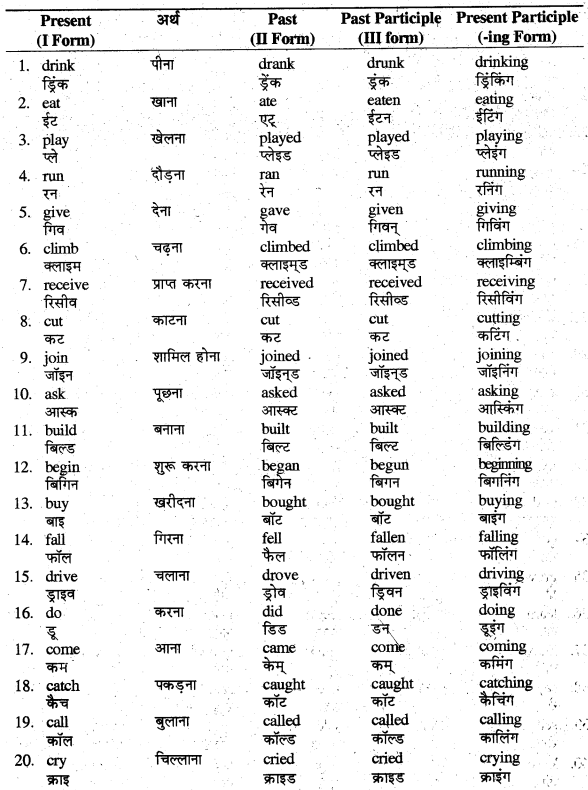
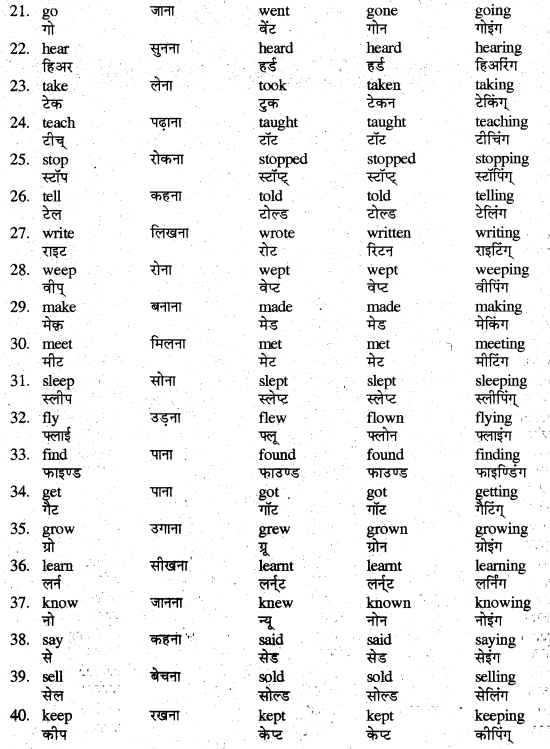
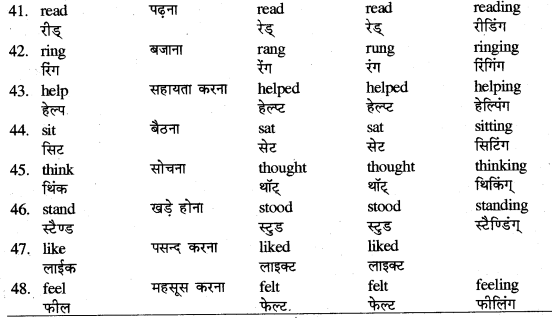
Verb का अर्थ है 'क्रिया'। यह किसी काम के होने या न होने को बतलाती है। इसकी चार Forms होती हैं
(1) Present Form (IForm)
(2) Past Form (II Form)
(3) Past Participle (III Form)
(4) Present Participle (-ing Form)
आपकी पाठ्यपुस्तक में आयी Verbs तथा कुछ अन्य महत्त्वपूर्ण Verbs तथा उनकी Forms अग्र प्रकार-

Exercise 1.
(Based on Let's Learn English)
Write the past form (II form) of the following verbs निम्न verbs की past form (II form) लिखिए-
1. live
2. see
3. play
4. go
5. cry
6. strike
7. attack
8. shout
9. say
10. reply
11. cut
12. save
13. walk
14. come
15. write
16. eat
17. pick
18. tell
19. arrive
20. enjoy
Answers :
1. lived
2. saw
3. played
4. went
5. cried
6. struck
7. attacked
8. shouted
9. said
10. replied
11. cut
12. saved
13. walked
14. came
15. wrote
16. ate...
17. picked
18. told
19: arrived
20. enjoyed

Tenses
(Correct forms of the Verbs]
Tense (काल)-Tense से आशय Verb की form से है जो किसी action (कार्य) या state (स्थिति) के होने के काल (present/past/future) को इंगित करती है।
Tense ore-Tense or old तथा इनके चार-चार उपप्रकार होते हैं|
1. Present Tense :
(i) Simple Present/Present Indefinite
(ii) Present Progressive/Present Continuous
(iii) Present Perfect
(iv) Present Perfect Progressive (Continuous)
2. Past Tense :
(i) Simple Past/Past Indefinite
(ii) Past Progressive/Past Continuous
(iii) Past Perfect
(iv) Past Perfect Progressive (Continuous)
3. Future Tense :
(i) Simple Future/Future Indefinite
(ii) Future Progressive/Future Continuous
(iii) Future Perfect
(iv) Future Perfect Progressive (Continuous)
[नोट-चूँकि आपकी पाठ्यपुस्तक में Simple Present Tense, Simple Past Tense Te Past Continuous Tense के अभ्यास ही दिये गये हैं। अतः यहाँ इन्हें ही समझाया जा रहा है।]

1. Simple Present Tense
इसका प्रयोग सामान्य सच्चाई, सार्वभौमिक सत्यता, वैज्ञानिक तथ्य, नियमित कार्य तथा सत्यता पर आधारित कार्यों को दर्शाने के लिए किया जाता है। पहचान-हिन्दी में ऐसे वाक्यों के अन्त में ता है, ती है, ते हैं आदि आते हैं। Helping Verb do, does
• वाक्य रचना
1. Affirmative Sentences (साधारण वाक्य)

• बनाने के नियम
(i) हमेशा verb की first form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) यदि वाक्य का Subject (कर्ता), He, She It या एक व्यक्ति /वस्तु है तो verb की first form के अन्त में s या es जोड़ें। यदि verb का अन्तिम अक्षर 0, x, sh, ch, s है तो इसके पीछे''-es' जोडें, तथा शेष सभी verbs के अन्त में '-s' जोड़ें।
(iii) यदि वाक्य state (स्थिति) बता रहा हो तो is/are/am का प्रयोग verb के रूप में करें।
(iv) यदि वाक्य, possession (स्वामित्व) बता रहा हो तो has/have का प्रयोग verb के रूप में करें। |
2. Negative Sentences (नकारात्मक वाक्य)--
बनाने का तरीका-Sub + H.V. + not+V-I+......
(i) वह अपना समय व्यर्थ नहीं करती है।
She does not waste her time.
(ii) वे अभद्र नहीं बोलते हैं।
They do not speak discourteously.
[नोट-ध्यान रखें, Singular Subjects (एकवचन कर्ता) के साथ does सहायक क्रिया (Helping Verb) का प्रयोग करें तथा Plural Subjects (बहुवचन कर्ता) व I (आई) के साथ do सहायक क्रिया का प्रयोग करें।
3. Interrogative Sentences (प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य) --
बनाने का तरीका - H.V. + Sub. + V-I + .....?
Or
'Wh' Word + HV + S+ MV-I + .....?
(i) क्या वह देरी से आता है?
Does he come late?
(ii) वह देरी से क्यों आता है?
Why does he come late?
(iii) क्या आप अच्छी किताबें रखते हैं?
Do you have good books?

4. Who वाले वाक्य बनाने के तरीके
Who + V-I या V-I + s/es + .....?
तथा
Who + HV + not + V-I+ .....?
(i) असफलताएँ कौन चाहता है?
Who wants failures?
(ii) कौन नहीं हँसता है?
Who does not laugh?
Exercise 1.
Complete the following blanks with the correct simple present tense form of the verbs given in brackets:
निम्न रिक्त स्थानों को कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं की सही simple present tense form से पूरा करें
1. Shivam............to school daily. (go)
2. Nitin............a student of class V: (be)
3. They always............in a park. (play)
4. Children usually............early in the morning. (walk)
5. The Yoga teacher often........... different : poses of pranayam... (make)
6. I............a lie. (not speak)
7. Roshanlal seldom............his savings. (waste)
8. Kalibai............of pranayam daily....(not practise)
9. He frequently............after the thieves. (run)
10. We rarely.........garbage into a dustbin. (put)
Answers to Exercise:
1. goes
2. is
3. play
4. walk
5. makes
6. do not speak
7. wastes
8. does not practise
9. runs
10. put
2. Simple Past Tense
(a) पहचान-(a) हिन्दी वाक्य के अन्त में ता था. ती थी, ते थे आदि आयें।
(b) हिन्दी वाक्य के अन्त में आ, इ, ई, ए, ऐ आदि की ध्वनि उत्पन्न हो। जैसे-
(i) हम वहाँ पहुंचे।
(ii) मेरी दादी धार्मिक किताब पढ़ती थी।
⇒ ये वाक्य कार्य के भूतकाल में समाप्त/पूर्ण होने की सूचना देते हैं।

(b) वाक्य रचना
1. Affirmative sentences (साधारण वाक्य)


• वाक्य बनाने का तरीका
S+ V-II + O+/A+ /C
• वाक्य बनाने के नियम
(i) हमेशा verb की second form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) वाक्य बनाने के तरीके का अनुसरण करें।
2.Negative sentences (नकारात्मक वाक्य) --

• वाक्य बनाने का तरीका- .....
S+ HV + not + V-I +O+/Adv. + /C
व
S+V-II + not +O+ /Adv.+/C .

• वाक्य बनाने के नियम
(i) Action वाले (क्रियात्मक) वाक्यों में did...not के साथ verb की first form का - प्रयोग करें। देखें वाक्य (i)
(ii) State (स्थिति) बताने वाले वाक्यों में was/were not का प्रयोग करें तथा अन्य कोई verb न लगाएं। देखें उदाहरण (ii)
(iii) Possession (स्वामित्व) बताने बाले - वाक्यों में had not का प्रयोग करें तथा अन्य ... कोई verb न लगाएं। देखें उदाहरण (iii)
(iv) वाक्य बनाने के तरीकों का अनुसरण करें। -
3. Interrogative sentences (प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य)


• वाक्य बनाने का तरीका
HV+S+ V-I+O+IA + /C? . . .... व . . .
Wh word+ HV+S+V-I+O+/A+/C?
Was/Had +S+O+/A + /C?
• वाक्य बनाने के नियम. --
(i) Action वाले वाक्यों में सहायक क्रिया did ... का प्रयोग करें तथा verb की first form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) जहाँ आवश्यक हो वहाँ Wh word का- प्रयोग करें।
(iii) State (स्थिति) तथा possession
(स्वामित्व) वाले वाक्यों में क्रमश: Was/Were तथा Had का प्रयोग करें तथा अन्य कोई Verb तथा Helping verb का प्रयोग न करें।
(iv) वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न लगाएं।
(v) वाक्य बनाने के तरीकों का अनुसरण करें।

Exercise
Based on Let's Learn English.
Fill in the blanks using simple past tense forms of the verbs given in the brackets
कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं के simple past tense रूप से रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए।
1. They...............(see) a big clock there.
2. They...............(go) there with their father.
3. Ritu..........(fight) with python yesterday.
4. The train...............(arrive) on time.
5. The children...............(enjoy) a lot at the railway station.
6. A rich man..............(live) is a small town in Rajasthan.
7. Last year ...............(go) to visit my uncle.....(write) a letter yesterday.
Answers :
1. saw
2. went
3. fought
4. arrived
5. enjoyed
6. lived
7. went
8. wrote
Exercise
Fill in the blanks of the following sentences with the simple past tense form of the verbs given in brackets
निम्न वाक्यों के रिक्त स्थानों को कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं a simple past tense form
1. He............(speak) nicely yesterday.
2. ..............(read) an interesting story last week.
3. We..............(have) a good bath yesterday.
4. They.............(be) there.
5. Then, the children..........(start) to play.
6. Some children..............(make) a drawing yesterday.
7. They..............(laugh) at her.
8. The match...........(end) in a draw.
9. The teacher..............(tell) a story to the class...
10. She..............(sit) on the stool.
Answers :
1. spoke
2. read
3. had
4. were
5. started
6. made
7. laughed
8. ended
9. told
10. sat

3. Past Continuous/Progressive Tense.
1. पहचान-हिन्दी के वाक्य के अन्त में रहा था, रही । थी, रहे थे आदि आयें। - ये वाक्य के भूतकाल में किसी कार्य के जारी रहने की सूचना देते हैं।
2. वाक्य बनाने के नियम :
1. साधारण वाक्य : नियम --
(i) हमेशा Verb की '-ing' form का प्रयोग करें।
(ii) Singular Subject व I के साथ सहायक क्रिया was का प्रयोग करें तथा plural subject के साथ were का प्रयोग करें।
वाक्य बनाने का तरीका --
S+ was/were+V-ing +/O+/C+/A
(i) वह खेल रही थी।

2. नकारात्मक वाक्य
S+ was/were+not+V-ing+/O+/C+/A.
(i) वह अपना समय नष्ट नहीं कर रही थी।

3. प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य --
(i) Was/Were+S+V-ing +/O+/C+/A?
(ii) 'Wh' + was/were + S+V-ing+/O+/C+/A?

4. नकारात्मक-प्रश्नात्मक वाक्य :
(i) Was/Were + S + not + V-ing +/O+/C+/A?
(ii) 'Wh'+was/were + S+not+v-ing+/O+ /C+/A ?
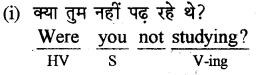
(ii) वह क्यों नहीं पढ़ रही थी ?
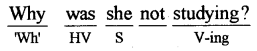

Exercise
(Based on Let's Learn English)
Fill in the blanks with the past continuous tense forms of the verbs given in brackets
कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं के past continuous tense
1. The booking clerk.............(issue) tickets.
2. Vendors...............(sell) eatables.
3. The porters..............(push) carts near the goods train.
4. Your friend...............(run) away.
5. The children...............(beat) a puppy.
6. The lion...............(roar) angrily.
7. Ritu.............(fight) with the python.
8. The master...........(sharpen) the knife.
Answers :
1. was issuing
2. were selling
3. were pushing
4. was running
5. were beating
6. was roaring
7. was fighting
8. was sharpening.
Exercise
Fill in the blanks of the following sentences with the past continuous tense from of the verbs given in the brackets-
निम्न वाक्यों के रिक्त स्थानों को कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं की past continuous tense रूप से रिक्त स्थानों को भरिये -
1. It.........(rain) heavily last night.
2. She.........(attend) classes regularly when she was alive.
3. He.........(play) in the ground.
4. I.........(clean) pots when my mother came back.
5. She.........(take) a bath when the bell Ran.
6. Rohit.........(fly) a kite.
7. They.........(dig) pits yesterday.
8. We.........(tear) the papers.
9. Kuntal and Teekam.........(make) new plans.
10. Manisha.........(write) a letter.
Answers :
1. was raining
2. was attending
3. was playing
4. was cleaning
5. was taking
6. was flying
7. were digging
8. were tearing
9. were making
10. was writing
Exercise
Translate these sentences into English
निम्न वाक्यों को अंग्रेजी में बदलिए
1. हम क्रिकेट खेलते थे।
2. वह स्कूल नहीं जाता था।
3. क्या मुकेश तथा प्रिया झूठ बोलते थे?
4. प्रिया कार क्यों नहीं चलाती थी?
5. गुरुदयाल शर्मा अंग्रेजी पढ़ा रहा था।
6. मनीषा भोजन नहीं पका रही थी।
7. नवीन क्या खेल रहा था?
8. मुस्कान कहाँ जा रही थी?
9. योगिता ने जयपुर छोड़ दिया।
10. नीरज कल पेड़ पर क्यों नहीं चढ़ा?
11. क्या नरेश ने कल मेहमानों का स्वागत किया?
12. जगदीश ने ताजमहल क्यों नहीं देखा?
13. विद्यार्थी पुस्तकालय में गये।
14. क्या राजेश अंग्रेजी बोल रहा था?
Answers :
1. We played cricket.
2. He did not go to school.
3. Did Mukesh and Priya tell a lie?
4. Why did Priya not drive a car?
5. Guru Dayal Sharma was teaching English.
6. Manisha was not cooking food.
7. What was Naveen playing?
8. Where was Muskan going to?
9. Yogita left Jaipur.
10. Why did Neeraj not climb up a tree yesterday?
11. Did Naresh Welcome the guests yesterday?
12. Why did Jagdish not see the Taj Mahal.
13. The students went to library.
14. Was Rajesh speaking English?

Exercise
(Based on Let's Learn English)
Change the following sentences into negative sentences
निम्न वाक्यों को नकारात्मक वाक्यों में बदलें
1. Seema was happy to see Ritu.
2. It had a diesel engine.
3. He received medical attention.
4. He won gold medal in 2015.
5. Seema was fighting with the python.
6. Ramu ate both the mangoes.
7. Seema was crying for help.
8. The coolies were carrying the passengers luggage.
9. The children were enjoying at the railway station.
10. They saw a big clock there.
Answers :
1. Seema was not happy to see Ritu.
2. It did not have a diesel engine.
3. He did not receive medical attention.
4. He did not win gold medal in 2015.
5. Seema was not fighting with the python.
6. Ramu did not eat both the mangoes.
7. Seema was not crying for help.
8. The coolies were not carrying the passengers luggage.
9. The children were not enjoying at the railway station.
10. They did not see a big clock there.
Exercise
Change the following sentences into interrogative sentences
निम्न वाक्यों को प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में बदलें
1. Anuj took Karan to the market. ?
2. Netrika was teasing Kritika.
3. Ankit dug a deep hole.
4. Lokesh and Nikita were happy.
5. Jaswant learnt a lesson.
6. Pooja was taking rest.
7. Aman obeyed his father.
8. They were taking tea.
9. He welcomed his guests.
10. They built a high wall.
Answers:
1. Did Anuj take Karan to the market?
2. Was Netrika teasing Kritika?
3. Did Ankit dig a deep hole?
4. Were Lokesh and Nikita happy?
5. Did Jaswant learn a lesson?
6. Was Pooja taking rest?
7. Did Aman obey his father?
8. Were they taking tea?
9. Did he welcome his guests?
10. Did they build a high wall?

Correct word/Suitable word
इसके अन्तर्गत बॉक्स में कुछ शब्द दिए होते हैं जो संज्ञा (Noun), विशेषण (Adjective), क्रिया (Verb) आदि होते हैं।
• संज्ञा-संज्ञा, नाम वाले शब्द होते हैं। ये किसी
व्यक्ति, वस्तु, स्थान, पशु, पक्षी, विचार आदि का नाम होते हैं। विशेषण–ये शब्द वर्णन करने वाले शब्द होते हैं । ये संज्ञा की विशेषता बताते हैं तथा प्राय: संज्ञा के पूर्व प्रयोग होते हैं। क्रिया-जो शब्द किसी action को व्यक्त करते हैं। प्रत्येक वाक्य में एक क्रिया अवश्य होती है।
Exercise 1.
(Based on Let's Learn English)
Complete the following sentences by choosing the correct word from the box
बॉक्स से सही शब्द चुनकर निम्न वाक्यों को पूरा करें
father, bought, went, entered, clerk, people
1. Riti and Tarun.........to the railway station.
2. They went there with their..........
3. Their father......... three platform tickets.
4. They saw that......... were standing in a queue.
5. The booking......... was issuing tickets.
6. Their father.........the platform with both of them.
Answers:
1. went
2. father
3. bought
4. people
5. clerk
6. entered
Exercise 2.
(Based on Let's Learn English)
[kind, means, water, aware, planet, known
1. Most people are not really.........of the actual meaning of the word environment.
2. In simple terms it.........surroundings.
3. This includes........., land, air, light etc
4. The earth is the only known...... which has life.
5. No other planet is.........to have the conditions that are necessary for life.
6. Let us be.........to her.
Answers:
1. aware
2. means
3. water
4. planet
5. known
6. kind

Infinitive
Infinitive का तात्पर्य 'to + V-1 से होता है। इसका प्रयोग मुख्य क्रिया के अलावा दूसरी verb हेतु 'के लिए' के अर्थ में होता है। Fill in the blanks with the correct words given in the box. नीचे बॉक्स में दिए गए सही शब्दों को रिक्त स्थानों में भरिए
Exercise 1.
to cut, to watch, to read, to play, to call, to arrest
1. We have a T.V..........cricket match.
2. She has a knife.........apples.
3. There is a ball.........football.
4. The police went.........the thieves.
5. He was asked.........the police.
6. Students have books.........daily.
Answers:
1. to watch
2. to cut
3. to play
4. to arrest
5. to call
6. to read
Exercise 2.
to fly, to graze, to knock, to join, to waste, to write
1. She wants.........us
2. There are cows.........grass.
3. He has decided.........kites.
4. We have decided not.........time.
5. He has a pen.........a letter.
6. She was asked.........the door.
Answers:
1. to join
2. to graze
3. to fly
4. to waste
5. to write
6. to knock
Use of 'There'
There at the subject (dummy subject) की तरह काम में लिया जाता है। इसका उपयोग
वाक्य को आरम्भ करने के लिए किया जाता है। यह .. कहीं पर किसी व्यक्ति या वस्तु का होना या न होना बतलाता है। जैसे
There is no school in my village.
There are cows in the field.
Present Tense में There के साथ is/are का प्रयोग होता है। एकवचन के लिए प्रयोग होने पर is
तथा बहुवचन के लिए प्रयोग होने पर are का प्रयोग होता है।
Exercise
(Based on Let's Learn English)
Fill in the blanks with 'There is' or 'There are'रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति 'There is' अथवा 'There are' से कीजिए
1. .............a small tribal village in Rajasthan.
2. ..............a big python.
3. .............camels, horses, oxen and buffaloes.
4. ........... the famous Pushkar lake.
5. ............about 500 temples in the city.
6. .............a beautiful peacock
7. ..... many venders too.
8. .............a book shop also.
Answers:
1. There is
2. There is
3. There are
4. There is
5. There are
6. There is
7. There are
8. There is

English words for the Hindi words
इस topic द्वारा आपके हिन्दी तथा अंग्रेजी के शब्दों के ज्ञान को समृद्ध किया जाता है। परीक्षा में हिन्दी के शब्द देकर उनके समरूप (equivalent) अंग्रेजी शब्द पूछे जाते हैं। आपकी सुविधा के लिए पाठ्यपुस्तक के ऐसे परीक्षोपयोगी शब्दों की सूची नीचे दी जा रही है
(Based on Let's Learn English)
हिन्दी शब्द -- अंग्रेजी शब्द
1. भोजन -- food
2. घर -- house
3. टहलना -- walk
4. पहनना -- wear
5. देखना -- see
6. देना -- give
7. भूल जाना -- forget
8. मोच लगना -- sprain
9. स्थान -- place
10. प्रसन्न -- happy
11. परिवार -- family
12. बहादुर -- brave
13. चिल्लाना -- cry
14. अजगर -- Python
15. भूमि -- land
16. अचानक -- suddenly
17. चिन्ता करना -- worry
18. आक्रमण करना -- attack
19. बचाना -- save
20. पसन्द करना -- like
Imperative Form/
Imperative Sentences
Imperative Form/Sentences, क्रिया (Verb) की first form से आरम्भ कर बनाया जाता है तथा यह 'आदेश' या 'परामर्श' या 'निवेदन' व्यक्त करता है।
Exercise 1.
Read the following sentences and write the command sentences for them,
निम्न वाक्यों को पढ़ें तथा इनके लिए आदेशात्मक वाक्यं लिखें|
1. You should attend classes regularly.
.................................................
2. I request you to shut the door when you are alone.
.................................................
3. I suggest you to repeat the topics.
.................................................
4. You should walk for a while after dinner.
.................................................
5. I suggest you to eat healthy food.
.................................................
Answers:
1. Attend classes regularly.
2. Shut the door when you are alone.
3. Repeat the topics.
4. Walk for a while after dinner.
5. Eat healthy food.

Exercise 2.
Read the following sentences and write the command sentences, using 'Don't' for them.
निम्न वाक्यों को पढ़ें तथा उनके लिए 'Don't' का प्रयोग करते हुए आदेशात्मक वाक्य लिखें
1. I advise you not to cheat anybody.
.................................................
2. You are advised not to harm the birds.
.................................................
3. You should not kill the animals.
.................................................
4. I advise you not to pluck flowers.
.................................................
5. You should not tear your text book.
.................................................
Answers:
1. Don't cheat anybody.
2. Don't harm the birds.
3. Don't kill the animals.
4. Don't pluck flowers.
5. Don't tear your text book.
Passive Forms/Active Voice
and Passive Voice
Note-चूँकि आपकी पाठ्यपुस्तक में Simple Present Tense के ही Passive Forms दिए गए हैं अतः यहाँ इसे ही समझाया जा रहा है।
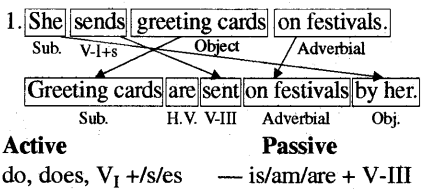
do, does, V1 +/s/es -- is/am/are + V-III व्याख्या-Subject तथा Object को एक-दूसरे के स्थान पर रखा जाता है। मुख्य क्रिया (main verb) की Third form का प्रयोग होता है। Subject को object के स्थान पर रखकर उससे पहले 'by' लगाया जाता है। H.V. को बदला जाता है। शेष शब्दों का स्थान नहीं बदला जाता है। Subject we, they को हटा दिया जाता है।
Exercise 1.
Change the following sentences into Passive Voice
निम्न वाक्यों को Passive Voice में परिवर्तित करें -
1. He helps Kritika daily.
2. Mobile phones receive messages.
3. They plant roses around the beds.
4. The President addresses the nation.
5. The Prime Minister unfurls the National flag.
6. We celebrate our national festivals every year.
7. The postman delivers the letters.
8. The mouse selects the output.
9. We waste electricity because of carelessness.
10. We do our homework daily.
Answers:
1. Kritika is helped by him daily.
2. Messages are received by mobile phones.
3. Roses are planted around the beds.
4. The nation is addressed by the President
5. The National flag is unfurled by the Prime Minister.
6. Our national festivals are celebrated every year.
7. The letters are delivered by the postman.
8. The output is selected by the mouse.
9. Electricity is wasted because of carelessness.
10. Our homework is done daily.

Exercise 2.
Write the correct passive form of each verb given in brackets
कोषठकों में दी गई क्रिया की सही passive form लिखिए -
1. Plants.........(grow) by Karina every year.
2. English.........(learn) by Madhu day and night.
3. The class......(teach) by Soniya daily.
4. Many problems.........(solve) by Priyanka.
5. Tea.........(take) by Seema and Kiran.
6. Water.........(draw) from the wells by Ashish.
7. Games.........(play) by Rahul and Trilok in the evening.
8. Electricity.........(save) by Sunil and Bhanu.
9. Time.........(not waste) by us.
10. The old men .........(always help).
Answers:
1. are grown
2. is learnt
3. is taught
4. are solved
5. is taken
6. is drawn
7. are played
8. is saved
9. is not wasted
10. are always helped.
Connectives/Conjunctions
ऐसे 'शब्द' या 'शब्दों का समूह' जिनसे दो या दो से अधिक Subjects, Verbs, Objects या sentences को जोड़ा जाता है, conjunctions कहलाते हैं। [नोट-चूँकि आपकी पाठ्यपुस्तक में Conjunction and' तथा 'but' ही पूछा गया है अतः यहाँ इसे ही समझाया जा रहा है।] |
(i) 'and' के प्रयोग द्वारा दो संज्ञा (Noun), सर्वनाम | (Pronoun), क्रिया (Verb), विशेषण (adjec ive), वाक्यों आदि को जोड़ा जाता है। 'and' का प्रयोग different information (भिन्न सूचना) को जोड़ने के लिए किया जाता है।
(ii) 'but' का प्रयोग different information (भिन्न सूचना) को जोड़ने के लिये किया जाता है।
Exercise
Join the following pairs of sentences with the connective 'and'/'but'
वाक्यों के निम्न युग्मों को connective and'/ 'but' से जोड़िए
1. My friend lives in Phagi. I live in Jaipur.
2. I am a boy. I am a student.
3. He reads in this school. She reads in this school.
4. Reenu takes tea. Reena takes tea.
5. Monika reads English. She reads Hindi.
6. Sachin runs fast. Vinod runs fast.
7. Deepak writes English. He reads English.
8. Sahil waters the plants. His sister waters the plants.
9. She is regular. She is dull. (but)
10. She is poor. She is honest. (but)
Answers :
1. My friend lives in Phagi and I live in Jaipur.
2. I am a boy and a student.
3. He and she read in this school.
4. Reenu and Reena take tea.
5. Monika reads English and Hindi.
6. Sachin and Vinod run fast.
7. Deepak writes and reads English.
8. Sahil and his sister water the plants.
9. She is regular but dull.
10. She is poor but honest.

Subject Predicate
अंग्रेजी के वाक्य के मुख्य रूप से दो अंग होते हैं- 1. Subject तथा 2. Predicate. वह व्यक्ति या वस्तु जिसके बारे में हम बात करना चाहते हैं, Subject कहलाता है तथा शेष शब्दों को Predicate कहा जात है।
Exercise
Mark/Underline the words which are Subject-Predicate.
Subject-Predicate को रेखांकित/चिह्नित करें।
1. Women cook food for the children.
2. Neeraj obeys his wife.
3. Naresh beats the students.
4. We have started a new job.
5. They will perform a programme tomorrow.
6. She was teasing the boys yesterday.
7. Priya does not eat fast food.
8. Mukesh cannot chop the wood.
9. Jagdish played cricket.
10. Alka recites the poem.
Answers:

Words and Phrases as
Sentence Linkers-First, Next,
Then, After that, Finally
कुछ शब्द तथा शब्द-समूह (Phrases) वाक्यों को जोड़ने में मदद करते हैं। हम इन्हें वाक्य-जोड़क (Sentence Linkers) कहकर पुकार सकते हैं। इन्हें वाक्य के प्रारम्भ में अथवा अन्य स्थानों पर भी रखा जा सकता है। यहाँ हम काल-क्रम (Time Sequence) बताने वाले जोड़क शब्दों, जैसे - First, Next, Then....आदि के प्रयोग को एक उदाहरण से सीखेंगे। मान लीजिए हम चाय बना रहे हैं। हमें बहुत सारे कार्य क्रमबद्ध रूप से करने होंगे। उन कार्यों का क्रम उपरोक्त श दों का प्रयोग कर इस प्रकार दिखाया जाएगा।
First - I take a mixture of water and milk.
Next - I add sugar and tea leaves to it.
Then - I let the mixture boil for 2-3'' minutes.
After that - I filter the tea into cups with ' the help of a sieve
Finally - I serve it to the guests.

Exercise.
Use the words, 'next', 'first', 'finally, 'then', 'after that' to link the given sentences
A magician came to our school today. He showed an amazing trick
1 he took off his hat and put it on the table .......2........ he covered the hat with a piece of cloth. He ........3........ waved a stick over the hat. ........4........ he took the cloth off and out jumped three little rabbits! ........5........ he took out sweets from inside an empty box Answers to the
Answers:
1. First
2. Next
3. Then
4. After that
5. Finally
Phrasal Verbs-Take care of,
To Look after
जब कोई क्रिया (verb) किसी preposition अथवा adverb से मिलकर एक शब्द-समूह बनाती है तो एक विशेष अर्थ ग्रहण कर लेती है। यह अर्थ शब्द-समूह के अलग भागों के अर्थ से भिन्न अर्थ रखता है। उदाहरण
Look for (तलाश करना)
Look into (जाँच करना)
Look after (देखभाल करना)
Phrasal Verbs का प्रयोग किसी भी tense में आवश्यकतानुसार किया जा सकता है। जैसे
I was looking for my book.
(मैं अपनी पुस्तक की तलाश कर रहा था।)
I looked for my book every where.
(मैंने अपनी पुस्तक की सभी जगह तलाश की।)
I am still looking for my book, (मैं अब भी अपनी पुस्तक की तलाश कर रहा हूँ।)
यहाँ Look for, Look into तथा Look after Phrasal Verbs के उदाहरण हैं।
'Look after' and 'Take care of दोनों ही Phrasal Verbs हैं।
दोनों का अर्थ एक ही है--किसी वस्तु अथवा व्यक्ति की देखभाल करना अथवा उसे संभालना। .....
प्रयोग--
Ram looks after/takes care of his old father. (राम अपने बूढ़े पिता की देखभाल करता है।)

Exercise 1.
Put the correct form of the phrasal verb, 'look after/take care of in the blank spaces in the following sentences
1. Who will...........me after you leave home?
2. His brother will...........his house after he has gone abroad.
3. I have to...........my friend's property in his absence.
4. ............yourself during the journey.
5. He...........his father when he was alive.
6. We should...........our money.
Answers to the Exercise :
1. look after
2. look after
3. look after
4. Take care of
5. took care of
6. take care of.
Describing a process
इसके अन्तर्गत एक process (प्रक्रिया) का वर्णन किया जाता है। इसके लिए Imperative sentences का प्रयोग किया जाता है जो सामान्यत: verb (क्रिया) की first form से आरम्भ होते हैं तथा नकारात्मक वाक्यों में इससे पूर्व Don't का प्रयोग होता है।
उदाहरण-कैमरे (camera) से फोटो खींचने की प्रक्रिया

Exercise 1.
Describe the process of making Kheer by filling the correct word in the blanks from the box below
बॉक्स से सही शब्द लेकर निम्न रिक्त स्थानों को भरते हुए खीर बनाने की प्रक्रिया का वर्णन करें
keep, add, take, mix, wait, serve
1. ...........a vessel with some milk and put it on a stove.
2. ...........till the milk started to boil.
3. .........some rice and sugar to it.
4. ...the liquid with a tablespoon until sugar and rice has mixed completely.
5. ...........the vessel on the stove for half an hour.
6. ............the Kheer in plates.
Answers:
1. Take
2. Wait
3. Add
4. Mix
5. Keep
6. Serve

Exercise 2.
Describe the process of polishing shoes by completing the sentences with the correct word from the box below
बॉक्स से सही शब्द लेकर निम्न वाक्यों को पूर्ण करते हुए जूतों को पॉलिश करने की प्रक्रिया का वर्णन करें
Apply, Take, Keep, Touch, Brush
1. ...........a polish box and a brush.
2. ............the brush to the polish.
3. ............this polish on to the shoes.
4. ..........the shoes till they have shining.
5. ..........the brush and the polish box back at their place.
Answer:
1. Take
2. Touch
3. Apply
4. Brush
5. Keep
Names Of Vehicles
(वाहनों के नाम)
Bus (बस)-बस
Motor-Car (मोटर-कार)-मोटर
Train (ट्रेन)-रेलगाड़ी
Wagon (वैगन)-मालगाड़ी का डिब्बा
Aeroplane (ऐरोप्लेन)-हवाई जहाज
Cab (कैब)-भाड़ा गाड़ी
Ship (शिप)-पानी का जहाज
Chariot (चैरिअट)-रथ
Boat (बोट)-नाव
Car (कार)-कार
Cart (काः)-ठेला, गाड़ी
Bicycle (बाईसिकल)-साइकिल
Rickshaw (रिक्शा)-रिक्शा
