RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 9 Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
RBSE Class 9 Social Science Natural Vegetation and Wildlife InText Questions and Answers
Page No. 43
Question 1.
Why are the southern slopes in Himalayan region covered with thick vegetation cover as compared to northern slopes of the same hills?
Answer:
The growth of vegetation depends upon the amount of sunlight and rainfall received. The southern slopes in the Himalayan region receive heavy rain and enough sunlight for a major part of the year. Therefore, plants grow here quickly. On the other hand, the northern slopes of the Himalayas do not receive much rainfall and sunlight. These areas experience low temperatures and many are covered with snow. So, the southern slopes are covered with thick vegetation as compared to the northern slopes.

Question 2.
Why are the western slopes of the western ghats covered with thick forests and not the eastern slopes?
Answer:
The western slopes of the western ghats receive heavy annual rainfall, which is more than 200 cm. Hence, these are covered with thick vegetation. But, the eastern slopes of the Western Ghats receive low annual rainfall between 50-70 cm. Therefore, these do not have dense vegetation.
Page No. 43
Question 3.
Study the bar graph (Figure 5.1 on page 44) and answer the following questions.
(i) Name the state having maximum area under forest cover.
Answer:
Mizoram
(ii) Name the union territory having minimum area under forest cover and why?
Answer:
The union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry have minimum forest cover. Lakshadweep are coral islands, and soil here does not support growing of forests except for coconut trees. The forest area is land marked as forest land by the government or authorities. Since coconut trees are used commercially, there is no declared forest in Lakshadweep. Puducherry has low forest cover because of urbanisation.
Let us Discuss
Question 4.
What will happen if plants and animals disappear from the earth’s surface? Can the human beings survive under such a situation? Why is biodiversity necessary and why should it be conserved?
Answer:
If plants and animals will disappear from the earth’s surface then survival of human Natural Vegetation and Wildlife beings on this planet will become impossible. Plants and animals both are very much essential in maintaining ecological balance on earth. Plants provide us oxygen and food. Animals provide us meat, eggs and are used for transportation. Many insects help in pollination of crops and fruit trees and exerting biological control on such insects is harmful. Every species has a role to play in the ecosystem. HenCe, conservation is essential.

Page No. 48
Question 5.
Can you identify the type of forest shown in this picture (Refer figure in Textbook)? Identify some trees in it. What type of similarity/dissimilarity you notice in this type of vegetation from the one found in your region?
Answer:
To be done by the students themselves.
(Hint: Montane forest, Pine and Aspen trees can be seen. In my region Pajasthan such type of forest can not be seen. Here, we find thorny type of vegetation.)
RBSE Class 9 Social Science Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
(i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong to?
(a) Tundra
(b) Tidal
(c) Himalayan
(d) Tropical Evergreen
Answer:
(d) Tropical Evergreen
(ii) Cinchona trees are found in the areas of rainfall more than
(a) 100 cm
(b) 50 cm
(c) 70 cm
(d) less than 50 cm
Answer:
(a) 100 cm

(iii) In which of the following state is the Simlipal bio-reserve located?
(a) Punjab
(b) Delhi
(c) Odisha
(d) West Bengal
Answer:
(c) Odisha
(iv) Which one of the following bio-reserves of India is not included in the .world network of bioreserve?
(a) Manas
(b) Nilgiri
(c) Gulf of Mannar
(d)Nandadevi
Answer:
(a) Manas
Question 2.
Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) What factors are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India?
Answer:
Factors responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India are:- relief (land and soil) and climate (temperature, photoperiod, humidity and precipitation).
(ii) What is a bio-reserve? Give two examples.
Answer:
A bio-reserve is a large protected terrestrial or coastal ecosystem where vegetation, wildlife and environment are conserved to preserve the biodiversity and for the improvement of relationship between humans and environment. Examples of the two bio-reserves of India are Sundarban biosphere reserve in West Bengal and Nanda Devi biosphere reserve in Uttarakhand.
(iii) Name two animals having habitat in tropical and montane type of vegetation.
Answer:
Tiger and elephant have habitat in tropical and snow leopard, spotted deer have habitat in montane type of vegetation.

Question 3.
Distinguish between:
(i) Flora and Fauna
Answer:
The difference between flora and fauna are as follows :
|
Flora |
Fauna |
|
1. The plant species of a particular region or period are called flora. |
1. The animal species of a particular region or period are called fauna. |
|
2. Most species of flora make their own food. A few of them like carnivorous plants depend on fauna for food. |
2. Fauna can not make their own food, it depends on flora for food. |
|
3. The roots of flora fix them to soil ahdthey can not move. |
3. Fauna can move from one place to another. |
|
4. Flora are studied in botany. |
4. Fauna are studied in zoology. |
(ii) Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous forests
Answer:
The difference between Tropical Evergreen and Tropical Deciduous Forests are as follows :
|
Tropical Evergreen Forests |
Tropical Deciduous Forests |
|
1. These forests are restricted to heavy rainfall areas of the Western Ghats and the island groups of Lakshadweep, Andaman and Nicobar, upper parts of Assam and Tamil Nadu coast. |
1. These are most widespread forests of India. These forests exists in eastern part of country - north eastern states, along the foot hills of the Himalayas, Jharkhand, West Odisha, Chhattisgarh and on the eastern slopes of Western Ghats. |
|
2. The trees reach great heights upto 60 metres or even above. Since the region is warm and wet throughout the year, it has all kinds of vegetation - trees, shrubs and creepers. |
2. On the basis of water availability, these forests are further divided into moist and dry decidious. |
|
3. There is no definite time for trees to shed their leaves. These forest appear green all the year around. |
3. Trees of this forest shed their leaves for about six to eight weeks in dry summer. |
|
4. Some ofthe commercially important trees of this forest are ebony, mahogany, rosewood, rubber and cinchona. |
4. Teak, bamboos, sal, shisham, sandalwood, khair, kusum, arjun and mulberry are some of the commercially important trees of this forest. |
|
5. Common animals found in these forests are elephant, monkey, lemur and deer. One-homed rhinoceroses are found in the jungles of Assam and West Bengal. |
5. Lion, tiger, pig, deer and elephant are the common animals found in this forest. |
|
6. Besides animals plenty of birds, bats, sloth, scorpions and snails are also found in these jungles. |
6. A huge variety of birds, lizards, snakes and tortoises are found in this jungle. |
Question 4.
Name different types of vegetation found in India and describe the vegetation of high altitudes.
Answer:
The following are the different types of vegetation found in India :
- Tropical Rain Forests
- Tropical Deciduous Forests
- Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs
- Montane Forests
- Mangrove Forests
Vegetation of High Altitudes: Montane Forests
(i) Montane forests are found at high altitudes.In mountainous areas, the temperature decreases with increasing altitude, which leads to the corresponding change in natural vegetation. Hence, there exists a succession of natural vegetation belts in these areas.

(ii) The wet temperate type of forests are found between a height of 1000 and 2000 metres. They majorly have evergreen broad-leaf trees
such as oaks and chestnuts.
(iii) Between 1500 and 3000 metres, the temperate forests exist, which have coniferous trees like pine, deodar, silver fir, spruce and cedar.These trees are conical in shape so that it is easy for the snow to slide down.
(iv) The temperate grasslands are commonly found at higher elevations.
(v) Alpine forests are generally found at altitudes higher than 3,600 metres. Silver fir, junipers, pines and birches are the commonly found trees of these forests.
(vi) The vegetation continues to get stunted as it nears the snow-line. The shrubs and scrubs ultimately merge into the Alpine grasslands, which are widely used for grazing by nomadic tribes like the Gujjars and the Bakarwals.
(vii) Tundra vegetation exists at higher altitudes. Mosses and lichens form part of tundra vegetation.
Question 5.
Quite a few species of plants and animals are endangered in India. Why?
Answer:
Quite a few animals species are endangered and become extinct in India. Some main causes for this major threat to nature are :
- unting by greedy hunters for commercial purposes.
- Pollution due to chemical and industrial waste and acid deposits.
- Introduction of alien species.
- Reckless cutting of the forests to bring land under cultivation and inhabitation.
Question 6.
Why India has a rich heritage of flora and fauna?
Or
Why does India possess a great variety of flora and fauna?
Answer:
The term Flora is used to denote plants of a particular region or period. Similarly, the species of animals are referred to as fauna. This huge diversity in flora and fauna kingdom is due to the following factors :
(i) Relief:
(a) Land : Land affects the natural vegetation directly and indirectly. The nature of land influences the type of vegetaton. The fertile level is generally devoted to agriculture. The undulating and rough terrains are areas where grassland and woodlands develop and give shelter to a veriety of wildlife.
(b) Soil: The soils also vary over space. Different types of soil provides basis for different types of vegetation. The sandy soils of the desert support cactus and thorny bushes, while wet, marshy, deltaic soils support mangroves and deltaic vegetation. The hill slopes with some depth of soil have conical trees.

(ii) Climate:
Temperature :
The character and extent of vegetation are mainly determined by temperature along with humidity in the air, precipitation and soil. On the slopes of the Himalayas and the hills of the Peninsula above the height of 1915 metres, the fall in the temperature affects the types of vegetation and its growth, and changes it from tropical to subtropical temperate and alpine vegetation.
(b) Photoperiod (sunlight):
The variation in duration of sunlight at different places is due to differences in latitude, altitude, season and duration of the day. Due to longer duration of sunlight, trees grow faster in summer.
(c) Precipitation : In India, almost the entire rainfalls is brought in by the advancing southwest monsoon (June to September) and retreating northeast monsoons. Areas of heavy rainfall have more dense vegetation as compared to areas of less rainfall.

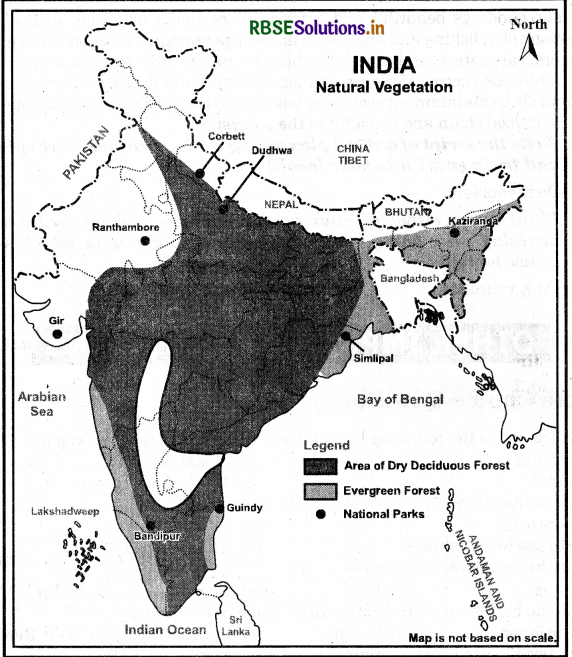
Map skills
Question 1.
On an outline map of India, label the following.
(i) Areas of Evergreen Forests
(ii) Areas of Dry Deciduous Forests
(iii) Two national parks each in Northern, Southern, Eastern and Western parts of the Country
Answer:
(iii)
- North - Corbett National park, Dudhwa National Park.
- East -Simlipal National Park, Kaziranga National Park.
- West -Gir National Park, Ranthambore National Park.
- South -Bandipur National Park, Guindy National Park.
Project Activity
(i) Find some trees in your neighbourhood having medicinal values.
Answer:
Amla tree, Eucalyptus tree, Arjuntree, Neemtree, Peepaltree, Jamuntree, Kachnar tree, Banyan tree, Sal tree.
(ii) Find ten occupations getting raw material from forests and wildlife.
Answer:
(a) Carpentry
(b) Rubber manufacturing
(c) Tourism and hospitality
(d) Ayurvedic medicine manufacturing
(e) Paper making
(f) Making lacjewellery
(g) Extracting gum and raisins
(h) Making artifacts
(i) Making Ivory items,
(j) Making leaf plates
(k) Collecting honey.
(iii) Write a poem or paragraph showing the importance of wildlife.
Answer:
Wildlife is a precious gift of nature to us. Wildlife comprises of not only wild animals but also includes all undomesticated life forms including birds, insects, plants, fungi and even microscopic organisms. Wildlife provides us food, medicines, raw materials for industries and construction such as timber, rubber, raisins and gum. Many microorganisms, fungi and earthworms decompose plant and animal wastes, keeping the environment clean and healthy.
They make the surroundings beautiful and cater to recreational activities such as hiking, nature photography, fishing and angling. Wildlife also provides livelihood to many such as forest rangers, carpenters, and especially those connected with tourism and construction industry. Numerous species of plants and animals also add to the biodiversity, and play a significant role in maintaining ecological balance on earth. Each living organism has a unique place in food chain and is useful to the ecosystem.

(iv) Write the script of a street play giving the importance of tree plantation and try to enact it in your locality.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
(v) Plant a tree either on your birthday or one of your family members birthday. Note the growth of the tree and notice in which season it grows faster.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
