RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts
RBSE Class 7 Science Acids, Bases and Salts InText Questions and Answers
Page 50
Question 1.
Can I taste all substances to find their taste?
Answer:
No, we should not taste unknown substances as they could harm us.

Page 52
Question 2.
Why a turmeric stain on my white shirt is turned to red when it is washed with the soap?
Answer:
It is because the soap solution is basic in nature.
Page 53
Question 3.
I am not getting the same result when using solid baking soda on dry litmus paper, why?
Answer:
The solid baking soda does not change colour of dry litmus paper because in solid state, ions are not free to move whereas, solution of baking soda has free ions that change the colour of the litmus paper.
Question 4.
Coffee is brown and bitter in taste. Is it an acid? Or a base?
Answer:
Coffee is an add because it turns blue litmus red. It is slightly acidic in nature with pH nearly 5.0.
RBSE Class 7 Science Acids, Bases and Salts Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
State differences between acids and bases.
Answer:
Differences between acids and base are as follows:
|
Acids |
Bases |
|
1. Sour in taste. |
Bitter in taste. |
|
2. Turns blue litmus red. |
Turns red litmus blue. |
|
3. Acids are not soapy to touch. |
Bases are soapy to touch. |
|
4. Release H+ ions. |
Release OH- ions. |
|
5. Phenolphthalein remains colourless. |
Phenolphthalein gives pink indicator. |
|
6. No reaction with turmeric indicator. |
Gives red colour with turmeric indicator. |
|
7. Gives dark pink colour with China rose extract. For example - Citric acid, tartaric acid, sulphuric acid. |
Gives green colour with Chinarose extract. For example- Milk of magnesia, ammonium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide. |
Question 2.
Ammonia is found in many household products such as window cleaners. It turns red litmus blue. What is its nature?
Answer:
Ammonia is basic in nature. Product like window cleaner contains ammonium hydroxide which is a base.
Question 3.
Name the source from which litmus solution is obtained. What is the use of this solution?
Answer:
Litmus solution is extracted from lichens, it is used as an indicator. Litmus solution gives red colour with acids and blue colour with bases.
(Blue litmus turns red - acids)
(Red litmus turns blue - bases)
Question 4.
Is the distilled water acidic / basic / neutral? How would you verify it?
Answer:
Distilled water is neutral in nature. To verify it, take a small amount of distilled water in two test tubes. Add blue litmus paper to one test tube and red litmus paper to another. It is observed that there is no change in colour of either blue or red litmus paper. This shows distilled water is neither acidic nor basic, but neutral.
Question 5.
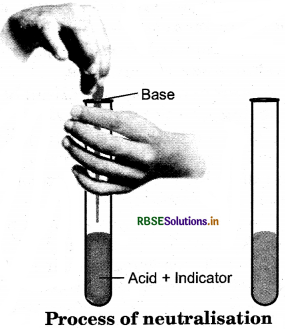
Describe the process of neutral¬isation with the help of an example.
Answer:
Neutralisation is a process in which an acid reacts with a base to produce salt and water.
Acid + Base → Salt + Water + Heat
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) + Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) → Sodium Chloride (NaCl) + Water (H2O)
Procedure:
Take some dilute HCl in a test tube and add 2-3 drops of phenolphthalein. The solution will remain colourless, now add few drops of sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH) with the help of a dropper and shake the test tube, after adding each drop. Stop adding sodium hydroxide drop on the appearance of pink colour in the test tube. This is the point where neutralisation reaction has taken place. On adding one more drop of dil HCl, the solution becomes colourless again. The resulting solution in neutralisation reaction is neither acidic nor basic, but heat is evolved in this reaction.
Question 6.
Mark T if the statement is True and F if it is false.
(i) Nitric acid turns red litmus blue. (T/F)
(ii) Sodium hydroxide turns blue litmus red. (T/F)
(iii) Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric add neutralise each other and form salt and water. (T/F)
(iv) Indicator is a substance which shows different colours in acidic and basic solutions. (T/F)
(v) Tooth decay is caused by the presence of a base. (T/F)
Answer:
(i) False
(ii) False
(iii) True
(iv) True
(v) False.

Question 7.
Dorji has a few bottles of soft drink in his restaurant. But unfortunately, these are not labelled. He has to serve the drinks on the demand of customers. One customer wants acidic drink, another wants basic and third one wants neutral drink. How will Dorji decide which drink is to be served to whom?
Answer:
Doiji can test a small amount of drink with litmus paper. The drink which turns blue litmus red is addic.The drink which turns red litmus blue is basic and the drink which does not change the colour of the litmus paper is neutral drink.
Question 8.
Explain why:
(a) An antacid tablet is taken when you suffer from acidity.
(b) Calamine solution is applied on the skin when an ant bites.
(c) Factory waste is neutralised before disposing into the water bodies.
Answer:
(a) An antacid tablet contains a mild base like magnesium hydroxide which neutralises the excess of hydrochloric acid present in the stomach.
(b) The sting of an ant is acidic in nature since it contains formic acid. This is neutralised by applying calamine solution which contains basic zinc carbonate.
(c) Factory wastes contain harmful adds and if it is disposed off in water bodies without neutralising, it will be harmful for plants and animals.
Question 9.
Three liquids are given to you. One is hydrochloric acid, another is sodium hydroxide and third is a sugar solution. How will you identify them? You have only turmeric indicator.
Answer:
Take small amount of the liquids and add turmeric indicator. The solution which gives red colour with turmeric is sodium hydroxide. Since, we already identified sodium hydroxide solution, we will pour the same in other two test tubes. The liquid which gets warm after pouring sodium hydroxide (base) in it, is hydrochloric acid because heat is evolved in neutralisation reaction. The last one which shows no effect is sugar solution.
Question 10.
Blue litmus paper is dipped in a solution. It remains blue. What is the nature of the solution? Explain.
Answer:
The solution can be either a base or a neutral solution. Acidic solution change blue litmus red, hence, it is not acidic. Bases change red litmus blue. Neutral solutions have no effect on litmus paper. In this case, there is no change in colour of blue litmus paper. Therefore, the given solution is either acidic or a neutral solution.
Question 11.
Consider the following statements:
(a) Both acids and bases change colour of all indicators.
(b) If an indicator gives a colour change with an acid, it does not give a change with a base.
(c) If an indicator changes colour with a base, it does not change colour with an acid.
(d) Change of colour in an acid and a base depends on the type of the indicator.
Which of these statements are correct?
(i) All four
(ii) (a) and (b)
(iii) (b) and (c)
(iv) Only (d)
Answer:
(iv) Only (d).
