RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 12 Biology Solutions Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease
RBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health and Disease Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the various public health measures, which you would suggest as safeguard against infectious disease?
Answer:
Public Hygiene: It can be improved by sanitation and public health measures.
- Proper sanitation of public places such as parks, cinemas halls, schools, offices and hospitals should be taken care of.
- Proper disposal of waste and excreta. Garbage containers should be properly covered and garbage is not be allowed to litter on the streets or garbage collection sites.
- Standard practices of hygiene at public catering. Eating at places such road side dhabas and rehris should be checked for cleanliness.
- No stagnation of water around residential areas and drains should be covered to reduce chances of breeding of flies and mosquitoes.
- Periodic cleaning and disinfection of water reservoir, ponds, cesspools and tanks.
- Insecticides should be sprayed in residential areas at regular intervals to reduce the number of mosquitoes.
- People should be vaccinated against various infection such as cholera, typhoid, tuberculosis, whooping cough and other diseases.
- Breading places of disease carrying insects should be destroyed and adult vector killed by spraying insecticides.

Question 2.
In which way has the study of biology helped us to control infectious diseases?
Answer:
Biology is a vast field of science dealing with life forms and its processes. It has helped in controlling infectious diseases in following ways:
- Complete eradication of fatal disease such as small pox was possible with the use of immunization schemes and vaccines.
- Other infectious diseases such as diptheria, polio, pneumonia etc. have been successfully controlled with the use of vaccines.
- Treatment of several infectious diseases have successfully been carried out with the use of antibiotics and other drugs.
Question 3.
How does the transmission of each of the following diseases take place?
(a) Amoebiasis
(b) Malaria
(c) Ascariasis
(d) Pneumonia
Answer:
The transmission of diseases is as given in the table:
|
None of the Disease |
Transmission |
|
Amoebiasis |
Ingestion of quadrinucleated cysts of Entamoeba histolytica can cause the cysts to be passed from patient faeces via water and food. |
|
Malaria |
Plasmodium or the malarial parasite is communicated to a healthy person from a patient when bities a female Anopheles mosquito. |
|
Ascariasis |
It can be passed by ingesting contaminated water and food with the enbryonated eggs of Ascaris. |
|
Pneumonia |
Transmitted by droplets and sputum given out when patient coughs. It is a bacterial disease. |
Question 4.
What measure would you take to prevent water bore disease?
Answer:
Measures taken to prevent water - bore diseases are as follows:
- Provision of clean water for drinking.
- Industries should prohibited form discharging waste into water bodies.
- Frequent cleaning and disinfecting water tank and reservoirs.
Question 5.
Discuss with your teacher what does ‘a suitable gene’ near, in the context of DNA vaccines.
Answer:
The term ‘suitable gene’ is used to refer to a particular section of DNA that can be altered in the host in order to synthesize a particular protein which attacks and kills a specific disease causing entity.
Question 6.
Name the primary and secondary lymphoid organs.
Answer:
Primary Lymphoid Organs are: Thymus and bone marrow.
Secondary Lymphoid Organs are: Mucosal - associated lymphoid tissues (MALT), lymph nodes, spleen, peyer’s patches (small intestine).
Question 7.
The following are some well - known abbreviations, which have been used in chapter.
Expand each one to its full form:
(a) MALT
(b) CMI
(c) AIDS
(d) NACO
(e) HIV.
Answer:
The expansion is as follows:
(a) MALT - Mucosal - associated lymphoid tissues.
(b) CMI - Cell mediated immunity.
(c) AIDS - Aquired immuno - deficiency syndrone.
(d) NACO - National AIDS control Organization.
(d) HIV - Human Immuno deficiency virus.
Question 8.
Differentiate the following and give example of each -
(a) Innate and acquired immunity
(b) Active and passive immunity
Answer:
(a) Difference between Innate and Acquird immunity.
|
Innate Immunity |
Acquired Immunity |
|
1. Non - specific in nature. |
Specific in nature. |
|
2. Present from birth. |
It is acquired in response to a particular pathogen. |
|
3. Has different barriers. |
Has a memory of antibody. |
|
4. For instance, mucus traps bacteria and other particles. |
For instance, post vaccination antibody respond. |
(b) Difference between Active and Passive Immunity
|
Active Immunity |
Passive Immunity |
|
1. It is slow and provide relief only after long period. |
1. It provides immediate relief. |
|
2. It is long lasting. |
2. It is short lived. |
|
3. It has no side effect. |
3. It may cause reaction. |
|
4. It is developed by an individual's own cells in response to an infection or a vaccine. |
4. It is development when ready made antibodies are inoculated from outside. |
Question 9.
Draw a well - labelled diagram of an antibody molecule.
Answer:
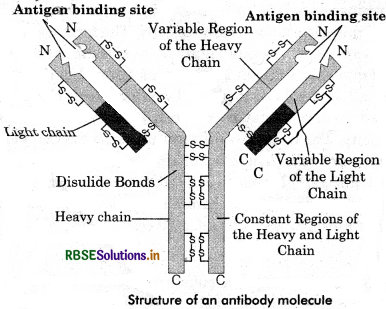
Question 10.
What are the various route by which transmission of human immuno deficiency virus takes place?
Answer:
The various routes by which transmission of human immuno deficiency virus (HIV) takes place is as follows:
- Organs transplantation from an infected person.
- Sexual relation with the infected person.
- Transmitted from mother to the child through the placenta.
- Transfusion of contaminated blood products and blood.

Question 11.
What is the mechanism by which the AIDS virus causes deficiency of immune system of the infected person?
Answer:
Mode of Action of AIDS Virus: After making the entry into the human body. The AIDS virus enters into macrophages where its RNA genome replicates to form viral DNA with the help of enzyme reverse transcriptase. This viral DNA gets incorporated into host DNA and instructed the infected cell to produce numerous virus particles. Therefore, infected macrophages continue to produce virus and their way function as HIV factory.
At this stage HIV enters into helper T - cells (T - lymphocytes), replicates and produces more viruses. The progeny viruses released in the blood and attack other helper T - cells. The repeated attacks on the helper T - cells lead to a gradual decrease in the number of helper T - cells became too low and immune system fail to produce antibodies that fight with the invading pathogens. Now, the host is not able to cope with even those agents which pose no problem to individual with infected immune system.
Question 12.
How is a cancerous cell different from a normal cells?
Answer:
Differences between cancer cells and normal cells
|
Cancer Cells |
Normals Cells |
|
1. The liflspan is not definite. |
1. These cells have a definite lifespan. |
|
2. These cells do not remain adhered and have lost cells to cell contact. |
2. These cells remain adhered i.e., have cell to cells contact. |
|
3. These cells do not undergo differentiation. |
3. These cells undergo differentiation. |
|
4. These cells do not have contact inhibition. |
4. The cells show contact inhibition. |
|
5. These cells divide in an unregulated and uncontrolled manner. |
5. These cells divide in a regulated manner. |
Question 13.
Explain what is meant by metastasis?
Answer:
Metastasis: It is a pathological process that is observed in malignant tumors. In this process, the cancerous cells spread to different body parts and divide indefinitely to form a cluster of cells, called tumor. Some of these cells from the tumor get sloughed off and manage to enter into the blood stream from where they arrive at the distant parts of the body and thus the formation of new tumors is initiated as they actively divide.
Question 14.
List the harmfull effects caused by alcohol / drug abuse.
Answer:
Effects of alcohol:
- Loss of thinking power and self - control.
- Visual problem, staggering and incoherence in speech occurs.
- Neuritis may occur due to the inflammation of axon of neurons.
- Loss of emotional control and moral sense.
Effects of Drugs (On male):
- Acne
- Aggressiveness
- Reduction in size of testes.
- Sperm production lowers.
- Premature baldness.
- Enlargement of prostrate gland.
Effect of Drugs (On female):
- Aggressiveness.
- Masculinisation (features like males).
- Mood swings.
- Depression.
Question 15.
Do you think that friends can influence one to take alcohol / drugs? If yes, how may one protect himself / herself from such an influence?
Answer:
Yes, friends can have an influence on friends to start taking drugs and consume alcohol. The following actions can be taken as precautionary measure to protect oneself from alcohol / drug abuse, they are:
- One must have a strong control over his / her will. One should refrain from experimenting with alcohol just for the sake of trying / curipsity / fun etc.
- Seek elderly advise, or medical assistance.
- Stay away from people who are into drugs.
- Take up some hobby / extracurricular activity.
- If depression or frustration levels persist seek immediate medical or professional help.
- Enlighten yourself with enough knowledge about the consequences of drugs abuse.
- Go in for a counseling session.

Question 16.
Why is that once a person starts alcohol or drugs. It is difficult to get rid of this habit? Discuss it with your teacher.
Answer:
Alcohol consumption and usage of drugs has a severe, addictive impact linked with euphoria, reducing a mometary feeling of well being. Regular intake of drugs can increase the tolerance level of the receptors of the body which further more leads to more drugs consumption.
Question 17.
In your view what motivates youngsters to take to alcohol or drugs and how can this be outsided?
Answer:
There are many factors that are accountable to motivate the youth towards drugs or alcohol. Some of the initial causes are curiosity, excitement adventure, experimentation etc. Some switch to consuming drugs and alcohol to overcome negative emotions such as pressure, depression, stress, frustration etc. in order to perform fairly well in other streams. Few media such as internet, televisions, newspaper, movies etc. are responsible to endorse to the youth the idea of alcohol. Some more resons can be unsupportive family structure, unstable relationships, poor pressure can also cause individuals to take up drugs and alcohol.
Some of the preventive measures against the use of drugs and alcohol are as follows:
- Motivation from parents and elders to develop a strong will power against it.
- Awareness about the ill effects of alcohol should be educated to children by parents. Proper counseling and knowledge regarding the repercussions of alcohol addiction must be carried out.
- Encourage student to dedicate their energy in other activities.
- Parents should take responsibility to monitor the social circle of their children and must advise them against the wrong company.
- Proper medical and professional assistance should be provided if symptoms of depression and frustration is observed.
