RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Solutions Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
RBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account?
Answer:
For the classification of living organisms, common fundamental characteristics are considered. If we consider specific characteristics, then each organism will be placed in a separate group and the entire objective of classification would not be achieved. Classification of animals is also important in comparing different organisms and judging their individual evolutionary significance. If only a single characteristic is considered, then this objective would not be achieved.

Question 2.
If you are given a specimen; what are the steps that you would follow to classify it?
Answer:
Following are the steps to be taken to classify a specimen:
- Classify Level of organisation; classify arrangement of cells in cellular and tissue level organization.
- Symmetry: Classify the organism as radial or bilateral symmetry.
- Classify diploblastic or triploblastic organization.
- Presence or absence of body cavity.
- Type of coelom development.
- Classify segmentation.
- Differentiate the presence or absence of notochord.
Question 3.
How useful is the study of the nature of body cavity and coelom in the classification of animals?
Answer:
Coelom is a fluid filled space between the body wall and digestive tract. The presence or absence of body cavity or coelom plays a very important role in the classification of animals. Animals that possess a fluid filled cavity between body wall and digestive tract are known as coelomates. Annelids, molluscs, arthropods, echinodermates, and chordates are examples of coelomates. On the other hand, the animals in which the body cavity is not lined by mesoderm are known as pseudocoelomates. In such animals, mesoderm is scattered in between ectoderm and endoderm. Aschelminthes is an example of pseudocoelomates. In certain animals, the body cavity is absent. They are known as acoelomates. An example of acoelomates is Platyhelminthes.
Diagrammatic sectional view of:
- Coelomate
- Pseudocoelomate
- Acoelomate
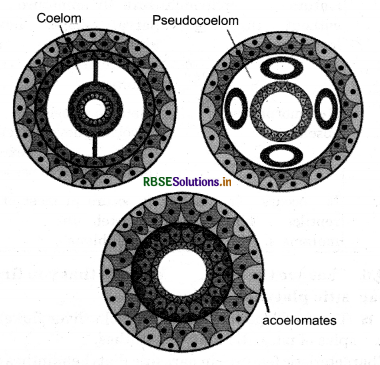
Question 4.
Distinguish between intracellular and extracellular digestion?
Answer:
Difference between intracellular and extracellular digestion:
|
Intracellular digestion |
Extracellular digestion |
|
1. The digestion of food occurs within the cell. |
1. The digestion occurs in the cavity of alimentary canal. |
|
2. Digestive enzymes are secreted by the surrounding cytoplasm into the food vacuole. |
2. Digestive enzymes are secreted by special cells into the cavity of alimentary canal. |
|
3. Digestive products are diffused into the cytoplasm. |
3. Digestive products diffuse across the intestinal wall into various parts of the body. |
|
4. It is a less efficient method. |
4. It is a more efficient method of digestion. |
|
5. It occurs in unicellular organisms. |
5. It occurs in multicellular organisms. |
Question 5.
What is the difference between direct and indirect development?
Answer:
Difference between direct and indirect development:
|
Direct development |
Indirect development |
|
1. It is a type of development in which an embryo develops into a mature |
1. It is a type of development that involves a sexually - immature larval stage, having different food requirements than adults. |
|
2. Metamorphosis absent. |
2. Metamorphosis involving development of larva to a sexually mature adult is present. |
|
3. It occurs in fishes, reptiles, birds, and mammals. |
3. It occurs in most of the invertebrates |
Question 6.
What are the peculiar features that you find in parasitic platyhelminthes?
Answer:
Taenia (Tapeworm) and Fasciola (liver fluke) are examples of parasitic Platyhelminthes.
Characteristic features in parasitic Platyhelminthes are:
- They have dorsiventrally flattened body and bear hooks and suckers to get attached inside the body of the host.
- Their body is covered with thick tegument, which protects them from the action of digestive juices of the host.
- The tegument also helps in absorbing nutrients from the host's body.
Question 7.
What are the reasons that you can think of for the arthropods to constitute the largest group of the animal kingdom?
Answer:
The phylum, Arthropoda, consists of more than two - thirds of the animal species on earth. The reasons for the success of arthropods are as follows.
- Jointed legs that allow more mobility on land.
- Hard exoskeleton made of chitin that protects the body.
- The hard exoskeleton also reduces water loss from the body of arthropods making them more adapted to terrestrial conditions.

Question 8.
Water vascular system is the characteristic of which group of the following:
(a) Porifera
(b) Ctenophora
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Chordata
Answer:
(c) Echinodermata.
Question 9.
“All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates”. Justify the statement.
Answer:
Presence of notochord and paired pharyngeal gill slits are the characteristic features of phylum chordata. But in sub phylum vertebrata notochord present in the embryo gets replaced by bony vertebral columns in adults. Hence, it is said “All vertebrates are chordates, but all chordates are not vertebrates”.
Question 10.
How important is the presence of air bladder in Pisces?
Answer:
Gas bladder or air bladder is a gas filled sac present in fishes. It helps in maintaining buoyancy. Thus, it helps fishes to ascend or descend and stay in the water current.
Question 11.
What are the modifications that are observed in birds that help them fly?
Answer:
Birds have undergone many structural adaptations to suit their aerial life. Some of these adaptations are as follows.
- Streamlined body for rapid and smooth movement.
- Covering of feathers for insulation.
- Forelimbs modified into wings and hind limbs used for walking, perching, and swimming.
- Presence of pneumatic bones to reduce weight.
- Presence of additional air sacs to supplement respiration.

Question 12.
Could the number of eggs or young ones produced by an oviparous and viviparous mother be equal? Why?
Answer:
No, in oviparous animals, eggs are laid outside the body of female. Some eggs may get the favourable conditions for develpment and hatching and may degenerate. To compensate for such losses, many eggs are laid. In viviparous animals, the development of embryo occurs inside the mother. Therefore only one or few young ones could be supported.
Question 13.
Segmentation in the body is first observed in which of the following:
(a) Platychelminthes
(b) Aschelminthes
(c) Annelida
(d) Arthropoda.
Answer:
(c) Annelida.
Question 14.
Match the following:
|
(a) Operculum |
(i) Ctenophora |
|
(b) Parapodia |
(ii) Mollusca |
|
(c) Scales |
(iii) Porifera |
|
(d) Comb plates |
(iv) Reptilia |
|
(e) Radula |
(v) Annelida |
|
(f) Hairs |
(vi) Cyclostomata and Chondrichthyes |
|
(g) Choanocytes |
(vii) Mammalia |
|
(h) Gill slits |
(viii) Osteichthyes |
Answer:
|
(a) Operculum |
(viii) Osteichthyes |
|
(b) Parapodia |
(v) Annelida |
|
(c) Scales |
(iv) Reptilia |
|
(d) Comb plates |
(i) Ctenophora |
|
(e) Radula |
(ii) Mollusca |
|
(f) Hairs |
(vii) Mammalia |
|
(g) Choanocytes |
(iii) Porifera |
|
(h) Gill slits |
(vi) Cyclostomata and Chondrichthyes |
Question 15.
Prepare a list of some animals that are found parasitic on human beings.
Answer:
- Taenia (Tapeworm)
- Ascaris (Round worm)
- Ancylostoma (Hook worm)
- Enterobius (Pin worm)
- Trichuris (Whip worm)
- Wuchereria (Filarial worm)
- Dracunculus (Guinea worm)
- Pediculus (Human louse).
