RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 8 Bill of Exchange
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 8 Bill of Exchange Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Solutions Chapter 8 Bill of Exchange
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Bill of Exchange Textbook Questions and Answers
Test Your Understanding I
Write ‘True’ or ‘False’ against each statement regarding a bill of exchange:
(i) A bill of exchange must be accepted by the payee.
(ii) A bill of exchange is drawn by the creditor.
(iii) A bill of exchange is drawn for all cash transaction.
(iv) A bill payable on demand is called time bill.
(v) The person to whom payment is to be made in a bill or exchange is called payee.
(vi) A negotiable instrument does not require the signature of its maker.
(vii) The hundi Payable at sight is called Darshani hundi.
(viii) A negotiable instrument is not freely transferable.
(ix) Stamping of promissory note is not mandatory.
(x) The time of payment of a negotiable instrument need not be certain.
Answers:
(i) False
(ii) True
(iii) False
(iv) False
(v) True
(vi) False
(vii) True
(viii) False
(ix) False
(x) False

Test Your Understanding II
Fill in the blanks with suitable word(s)
(i) The person to whom the amount mentioned in the promissory note is payable is known as ......................
(ii) Transfer of a negotiable instrument to another person by signing on it, is known as ......................
(iii) In a promissory note, the person who makes the promise to pay is called as ......................
(iv) A person who endorses the promissory note in favour of another is known as ......................
Answers:
(i) Promisee
(ii) Endorsement
(iii) Promissor
(iv) Endorser.
Test Your Understanding III
Fill in the blanks:
(i) A bill of exchange is a ...................... instrument.
(ii) A bill of exchange is drawn by the ...................... upon his ...................... !
(iii) A promissory note is drawn by ...................... in favour of his ......................
(iv) There are ...................... parties to a bill of exchange.
(v) There are ...................... parties to a promissory note.
(vi) Drawer and ...................... cannot be the same parties in case of a bill of exchange.
(vii) Bill of exchange in Indian languages is called ......................
(viii) ...................... days of grace are added in terms of the bill to calculate the date of its ......................
Answers:
(i) Negotiable
(ii) Drawer, Drawee
(iii) Debtor, Creditor
(iv) Three
(v) Two
(vi) Drawee
(vii) Hundi
(viii) Maturity.

Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name any two types of commonly used negotiable instruments.
Answer:
Bills of exchange and promissory note.
Question 2.
Write two points of distinction between bills of exchange and promissory note.
Answer:
Difference between bills of exchange and promissory note.
|
Basis |
Bills of exchange |
Promissory note |
|
Drawer |
It is drawn by the creditor |
It is drawn by the debtor |
|
Acceptance |
Acceptance by drawee |
Not required |
Question 3.
State any four essential features of bill of exchange.
Answer:
Features of bills of exchange:
(i) It must be in writing
(ii) It must contain an unconditional promise to pay.
(iii) It must be signed by the maker.
(iv) It must contain an order to pay a fixed amount
Question 4.
State the three parties involved in a bill of exchange.
Answer:
(a) Drawer: He is the person who sells goods and draws bill of exchange on the buyer of goods to pay the sum of money after a certain period.
(b) Drawee: He is the person who buys the goods, on whom bill of exchange is drawn and accepts the bill of exchange
(c) Payee: He is the person who holds the bill and receives the payment of the bill.
Question 5.
What is meant by maturity of a bill of exchange?
Answer:
It is arrived at by adding three days of grace to the period of the bill. If the due date falls on public holiday, the bill of exchange will become due on the preceding business day.
Question 6.
What is meant by dishonour of a bill of exchange?
Answer:
When the drawee of the bills receivable fails to make payment of the bill, it is known as dishonour of bill.
Question 7.
Name the parties to a promissory note.
Answer:
There are two parties involved. Drawer (maker) and drawee (payee).
Question 8.
What is meant by acceptance of a bill of exchange?
Answer:
When the seller draws the bill of exchange and send it to the buyer and the buyer puts sign on the reverse of this document, it is known as acceptance of bills of exchange. This indicates that the buyer has accepted the responsibility to pay the bills payable due to purchase of goods.
Question 9.
What is Noting of a bill of exchange.
Answer:
When the bill receivables proves dishonoured on its presentation, the holder of the bill has to get it noted through Notary Public. The fee charged for this service is known as noting charges.
Question 10.
What is meant by renewal of a bill of exchange?
Answer:
When old bill of exchange is replaced with new bill of exchange for new period with interest, it is known as renewal of bill of exchange.
Question 11.
Give the performance of a Bills Receivable Book.
Answer:
Bills Receivable Book
|
No.of Bill |
Date |
Date of Bill |
From |
Drawer |
Acceptor |
Where |
Term |
Due |
Ledger |
Amount |
Cash |
Remarks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Question 12.
Give the performance of a Bills payable Book.
Answer:
Bills payable Book
|
No. of Bill |
Date of Bill |
To |
Drawer |
Payee |
Where |
Term |
Due |
Ledger |
Amount |
Date |
Cash |
Remarks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Question 13.
What is retirement of a bill of exchange?
Answer:
When the bill receivable is honoured by die acceptor before the date of maturity, it is known as retirement of bill at rebate.
Question 14.
Give the meaning of rebate.
Answer:
In case of retirement of bill of exchange when payee offers some discount to the drawer (debtor) for early payment.
This discount is known as ‘rebate’. The amount of rebate is a loss to the payee and gain to the drawee (debtor).
Question 15.
Give the performs of a Bill of Exchange.
Answer:

Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
A bill of exchange must contain “an unconditional promise to pay” Do you agree with a statement?
Answer:
The transactions relating to sale and purchase of goods may be on cash or credit basis. The actual payment in case of credit transactions takes place after some time. The creditor may like to get a definite undertaking from the debtor that the payment of the amount due will be made on a certain date. A written undertaking is taken from the debtor where he agrees to pay the amount on the definite date.
It is a legal instrument and may be in the form of a Bill of Exchange or a Promisory Note. Under the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, both are considered as legal documents. In case of non-payment of the bill on the due date, a suit can be filed in the court for recovery the amount. Conclusion: On the basis of above, we agree with the statement that bill of exchange must contained an unconditional promise to pay.

Question 2.
Briefly explain the effects of dishonour and noting of a bill of exchange.
Answer:
Effects of dishonour and noting of bill of exchange:
(1) In case of dishonour, the holder of the bill can recover the amount of the bill from any of the endorsers or the drawer.
(2) The holder of the bill must serve a notice of dishonour to the drawer and each prior endorser whom he seeks to make liable for payment.
(3) The notary charges are paid to the Notary Public first by the holder of the bill, but are ultimately recovered from the acceptor.
Question 3.
Explain briefly the procedure of calculating the date of maturity of a bill of exchange? Give example.
Answer:
Date of Maturity of Bill of Exchange: It is the date on which the bill matures for payment. The bills are payable either on demand or on the expiry of some stipulated period.
(a) If it is payable on demand: It is matured on the day drawer payee wants to get the payment.
(b) If the bills is for a particular period: Date of maturity is calculated by adding 3 days of grace to the date which is calculated from the date of issue upto the stipulated period.
The date arrived at without adding three days of grace.
Note: If the due date falls on public holiday or on Sunday the bill comes mature for payment on the previous day.
Example: If the due date falls on Sunday the bill becomes mature for payment on Saturday. In case of casual holiday, the bill becomes due for payment on the next day.
Question 4.
Distinguish between bill of exchange and promissory note.
Answer:
|
Basis |
Bills of Exchange |
Promissory Note |
|
(1) Order/Promise |
Bills of exchange is an order to the debtor to pay a certain amount. |
It is a promise by a debtor to make payment of a certain amount. |
|
(2) Acceptance |
Bill of exchange must be accepted by the debtor. |
No acceptance on promissory note is required. |
|
(3) Drawer |
It is generally the credtor. |
It is made by a debtor. |
|
(4) Parties |
There are three parties to bill of exchange, viz. Drawer, Drawee and Payee. |
There are two parties to promissory note, viz. Maker and Payee. |
|
(5) Payee |
Drawer can be the payee also. |
Maker cannot be the payee. |
|
(6) Copies |
In case of inland bill one copy is made but in foreign bill three copies are prepared. |
Only one copy of promissory note is prepared. |
Question 5.
Briefly explain the purpose and benefits of retiring a bill of exchange to the debtor and the creditor.
Answer:
Purpose of retiring a bill of exchange before date of maturity: The debtor gets the payment before the date of maturity which he can invest in his business but bears fractional amount in the form of rebate. The creditor has to spare his funds, which otherwise could be used for other purposes but gains on account of rebate.
Question 6.
Explain briefly the purpose and advantages of maintaining of a Bills Receivable Book.
Answer:
When large number of bills are drawn and accepted, through journal entry every transaction recording becomes cumbersome and time consuming exercise. It is then advisable to record them separately in special subsidiary books. Purpose of maintaining bills receivable book
(1) These book records the transactions relating to drawing and acceptance of bills at the common place.
(2) The reason for maintaining bills receivable book is same as for other subsidiary books.
Advantage of maintaining bill receivable book
(1) If B/R book is maintained, it becomes easy for the businessman to keep in mind the due date of bills.
(2) Businessman know the status of bill and according to the requirement, he can offers to drawee to pay before maturity.

Question 7.
Briefly explain the benefits of maintaining a Bills Payable Book and state how is its posting is done in the ledger?
Answer:
Bill Payable Book. It is maintained like a bills receivable book. It is meant to record all the details, relating to the bills accepted by a person as party. The posting from this book is made to the debit of the account of every creditor to whom acceptance has been given and periodical total of the books is credited to the bills payable account in the ledger. Benefits of maintaining a B/P books
(1) If B/P book is maintained separately then all the transactions related to acceptance can be recorded in this book.
(2) This books helps the businessman know the due date of B/P & the payment can be made on time. If there is any surplus of funds with the businessman, he can benefit by rebate/discount etc.
Numerical Questions
Question 1.
On Jan. 01,2013 Rao sold goods ₹ 10,000 to Reddy. Half of the payment was made immediately and for the remaining half Rao drew a bill of exchange upon Reddy payable after 30 days. Reddy accepted the bill and returned it to Rao. On the due date Rao presented die bill to Reddy and received die payment. Journalise the above transactions in the books of Rao and prepare Rao’s account in the books of Reddy.
Solution.
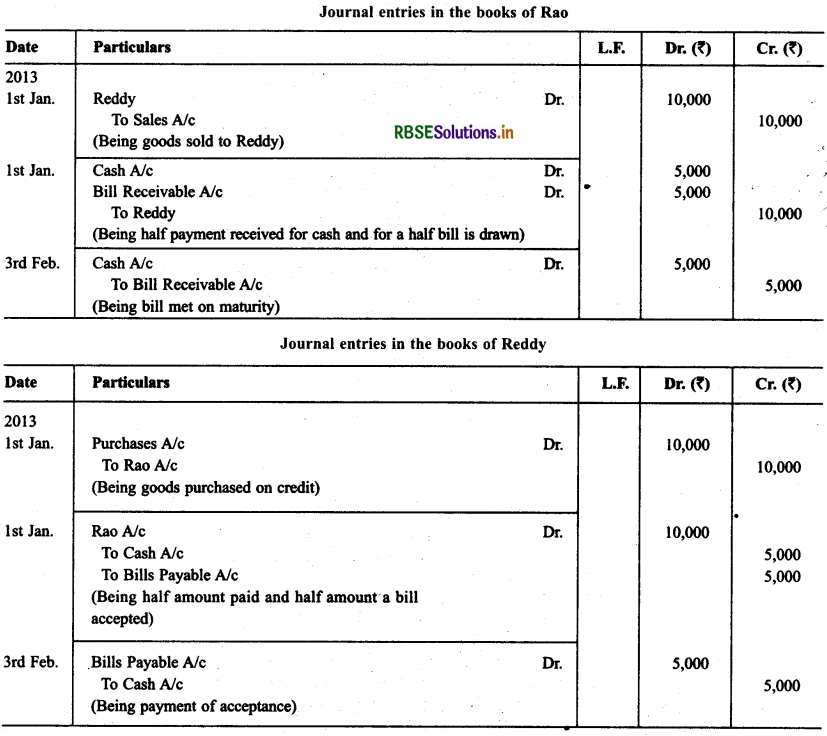

Question 2.
On Jan. 01. 2013, Shankar purchased goods from Parvati for ₹ 8,000 and immediately drew a promissory note in favour of Parvati payable after 3 months. On the date of maturity of the promissory note. The Government of India declared holiday under the Negotiable Instrument Act 1881. Since, Parvati was unaware about the provision of the law regarding the date of Maturity of the bill, she handed over the bill to her lawyer, who duly presented the bill and received the payment. The amount of the bill was handed over by the lawyer to parvati immediately. Record the
Solution:
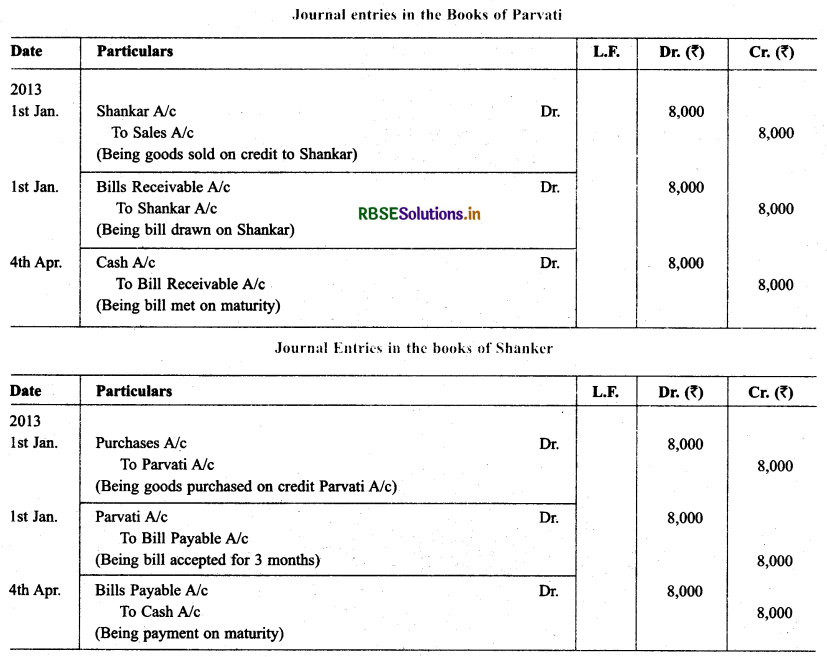
Question 3.
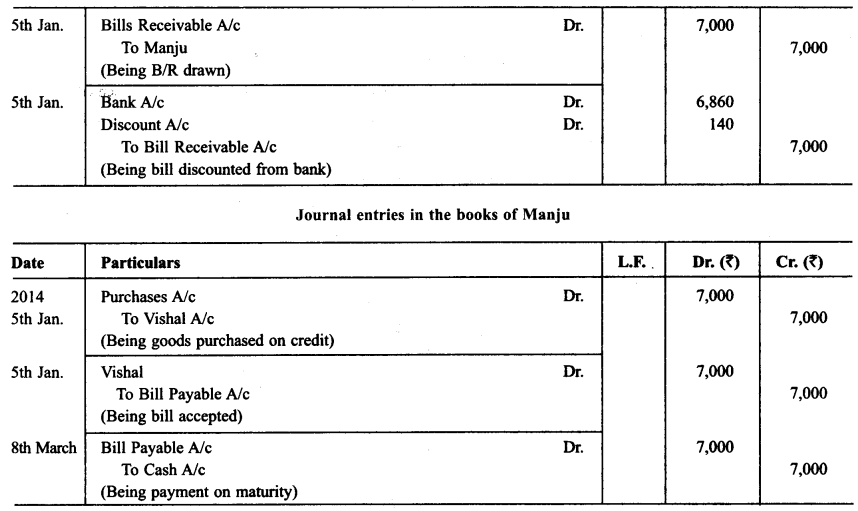
Vishal sold goods for ₹ 7,000 to Manju on Jan 05,2014 and drew upon her a bill of exchange payable after 2 months. Manju accepted Vishal’s draft and handed over the same to Vishal after acceptance. Vishal immediately discounted the bill with his Bank @ 12% p.a. On the due date Manju met her acceptance. Journalise the above transaction in the books of Vishal and Manju.
Solution:


Question 4.
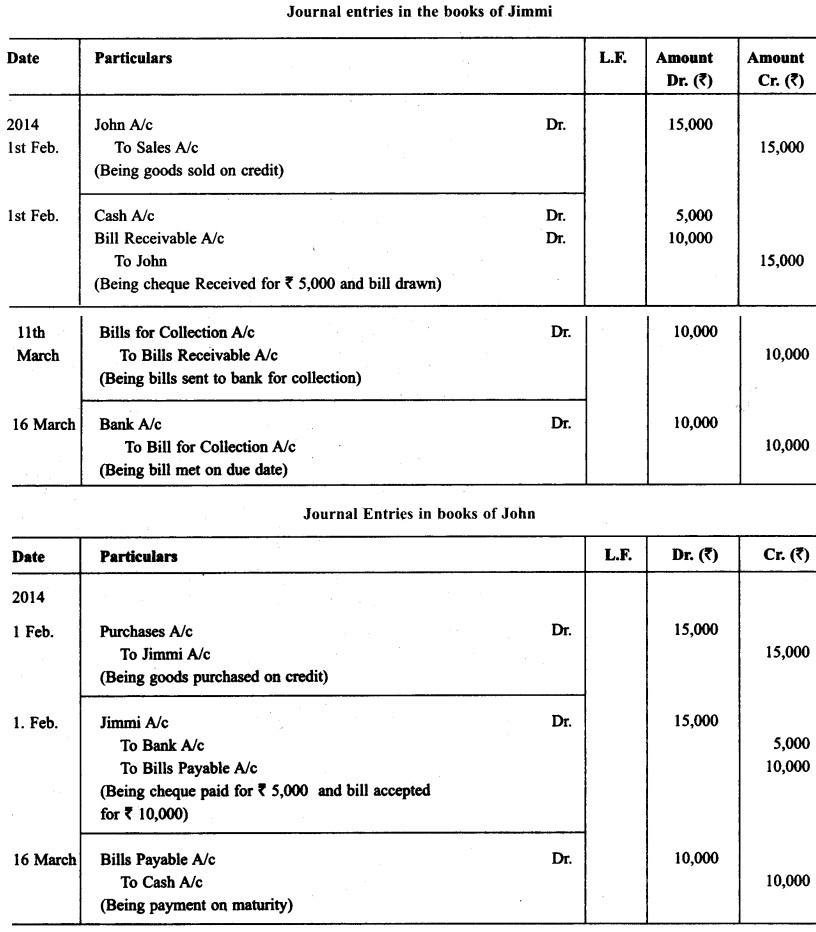
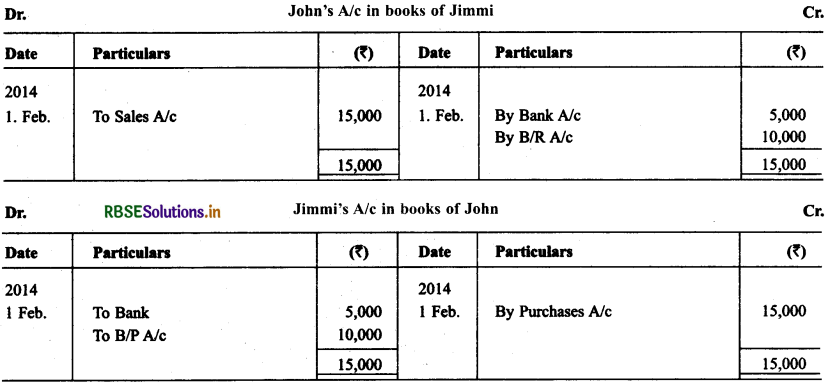
On Feb 01. 2013, John purchased goods for ₹ 15,000 from Jimmi. He immediately made a payment of ₹ 5,000 by cheque and for the balance accepted the bill of exchange drawn upon him by Jimmi. The bill of exchange was payable after 40 days. Five days before the maturity of the bill, Jimmi sent the same to his bank for collection. The bank duly presented the bill to John on the due date who met the bill. The bank informed the same to Jimmi. Prepare John’s account in the books of Jimmi and Jimmi account in the books of John.
Solution:

Question 5.
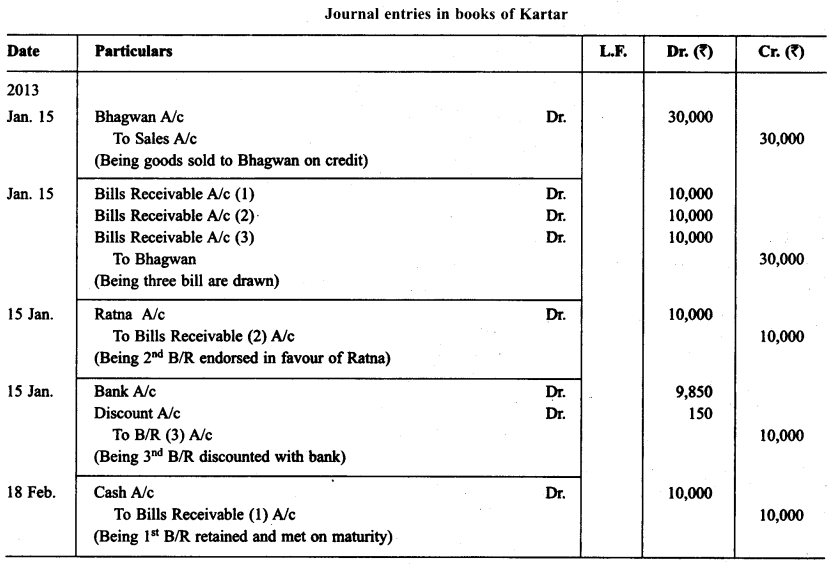
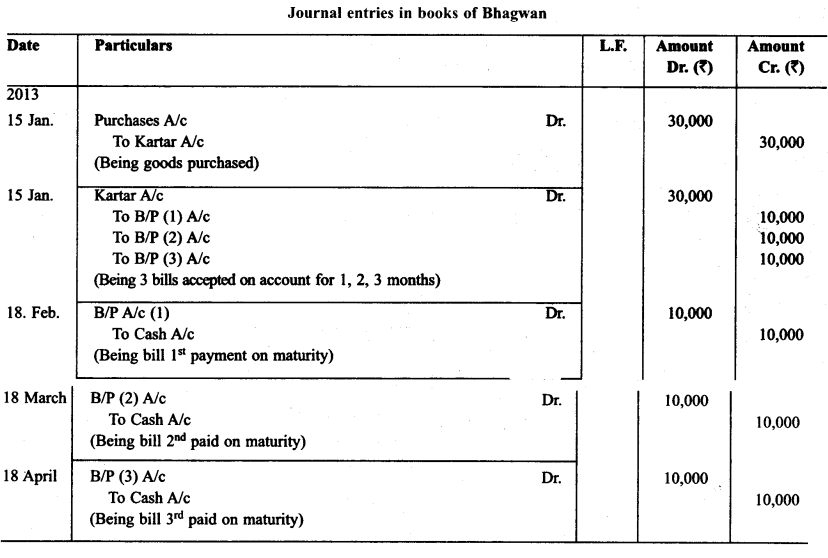
On Jan. 15, 2013 Kartar sold goods for ₹ 30,000 to Bhagwan and drew upon him three bills of exchanges of ₹ 10,000 each payable after one month, two month, and three months respectively. The first bill was retained by Kartar till its maturity. The second bill was endorsed by him in favour of his creditor Ratna and the third bill was discounted by him immediately @ 6% p.a. All the bills were met by Bhagwan. Journalise the above transactions in the books of Kartar and Bhagwan. Also prepare ledger accounts in books of Kartar and Bhagwan.
Solution:

Question 6.
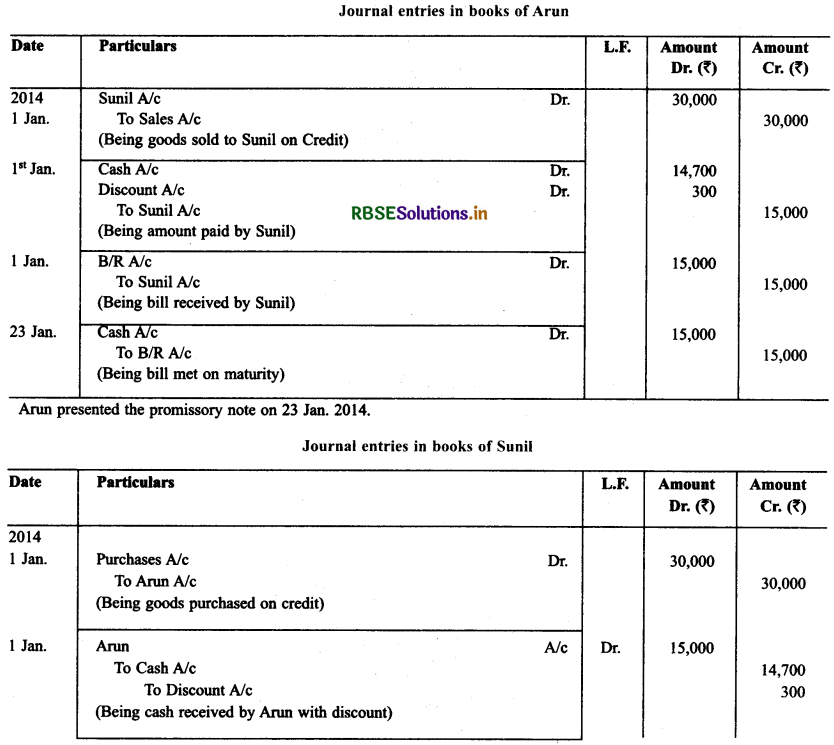
On Jan. 01, 2013 Aran sold goods for ₹ 30,000 to Sunil. 50% of the payment was made immediately by Sunil on which Aran allowed a cash discount of 2%. For the balance Sunil draw a promissory note in favour of Aran payable after 20 days before. Since, the date of maturity of bill was a public holiday. Aran presented the bill on a day before, as per the provisions of Negotiable Instrument Act which was met by Sunil. State the date on which the bill was presented by Aran for payment and Jounalise the above transactions in the books of Aran and Sunil.
Solution:

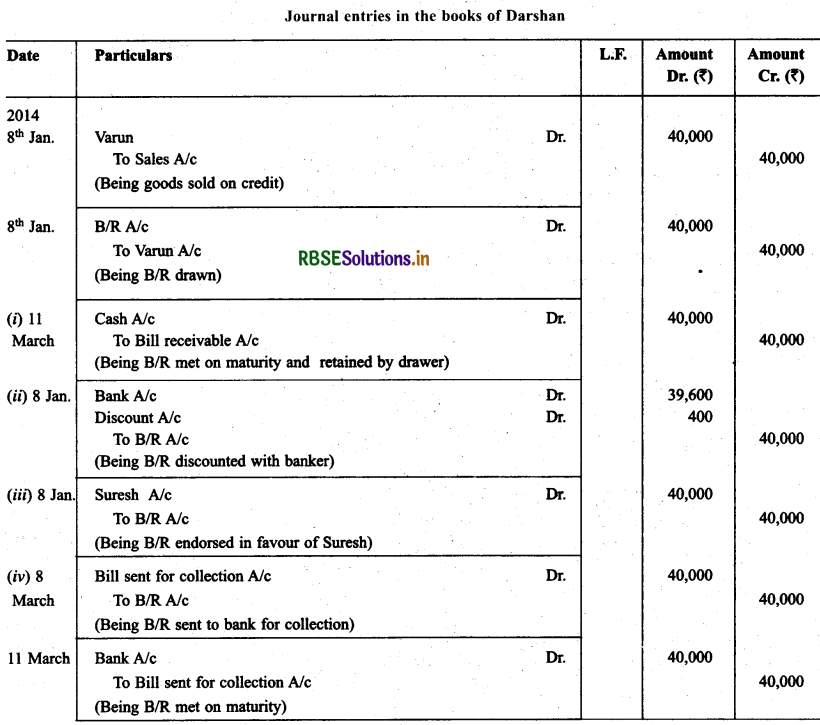
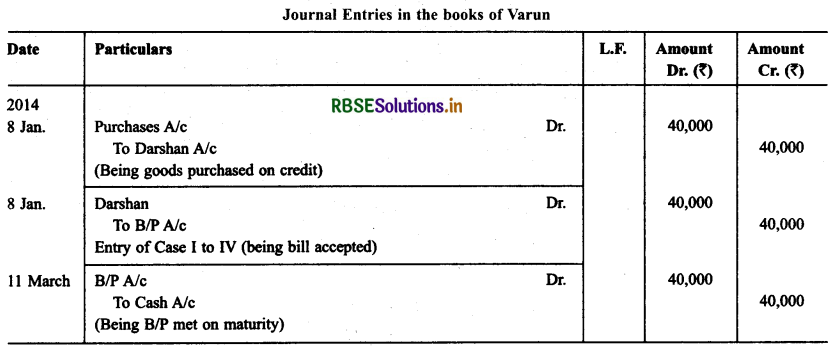
Question 7.
Darshan sold goods for ₹ 40,000 to Varun on 8.1.2014 and drew upon him a bill of exchange payable after two months. Varun accepted the bill and returned the same to Darshan. On the due date the bill was met by Varun. Record the necessary journal entries in the books of Darshan and Varun in the following circumstances.
• When the bill was retained by Darshan till the date of its maturity.
• When Darshan immediately discounted the bill @ 6% p.a. with his bank.
• When the bill was endorsed immediately by Darshan in favour of his creditor Suresh.
• When three days before its maturity, the bill was sent by Darshan to his bank for collection.
Solution:

Question 8.
Bansal Traders allow a trade discount of 10% on the list price of the goods purchased from them. Mohan traders, who runs a retail shop made the following purchases from Banal Traders.
21.12.2014 -- 1.000
26.12.2014 -- 1.200
28.12.2014 -- 2.000
31.12.2014 -- 5.000
For all the purchases Mohan Traders drew promissory note in favour of Bansal Traders payable after 30 days. The promissory note for the sale of Dec. 21,2013 was retained by Bansal Traders with them till the date of its maturity. The promissory note drawn on 26.12.2013 was discounted by Bansal Traders from their bank at 12% p.a. The promissory note drawn on Dec. 28, 2013 was endorsed by Bansal Traders in favour of their creditor Dream Soaps in full settlement of a purchase amounting to ₹ 1,900.
On 25.1.2014 Bansal Traders sent the promissory note drawn on Dec. 31, 2013 to their bank for collection. All the promissory notes were met by Mohan Traders. Record the necessary journal entries for the above transactions in the books of Bansal Traders and Mohan Traders and prepare Mohan Traders account in the books of Bansal Traders and Bansal Traders account in the books of Mohan Traders.
Solution:
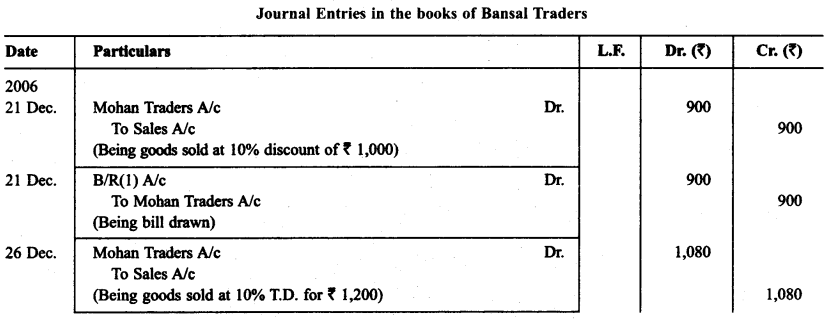
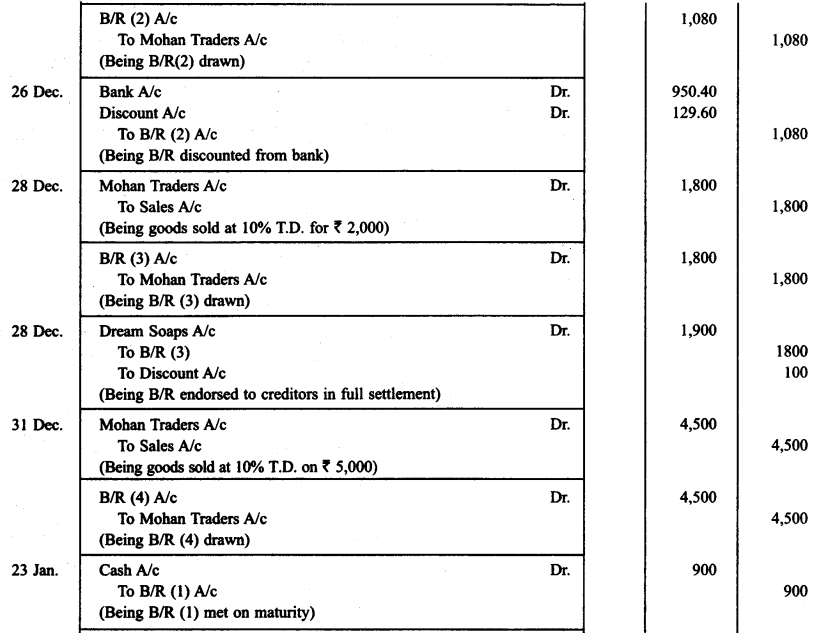
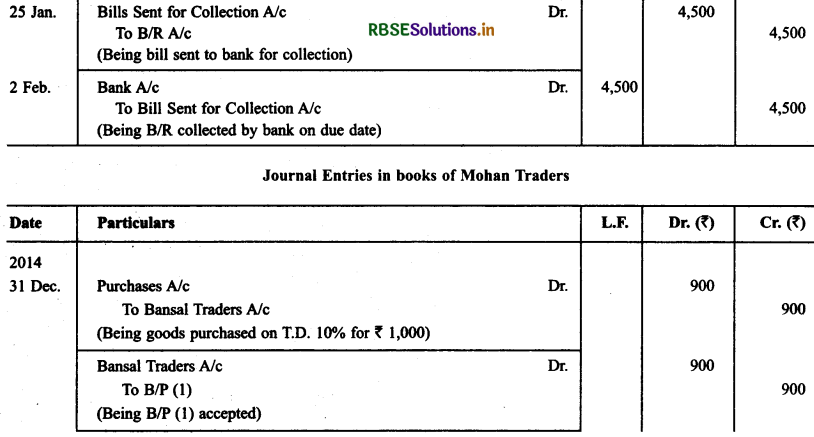
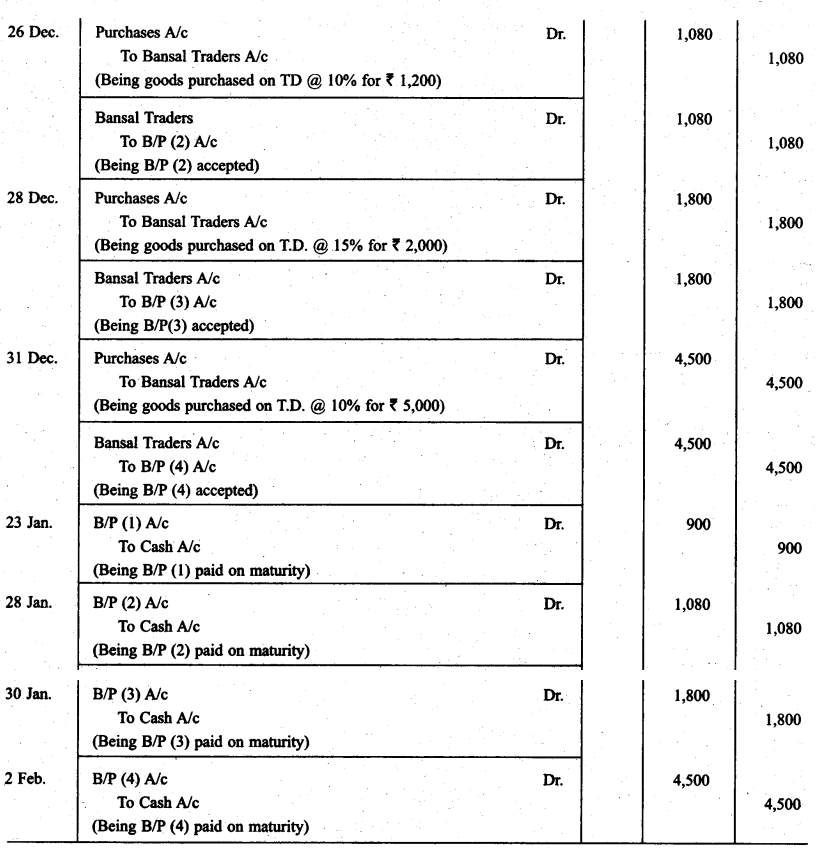

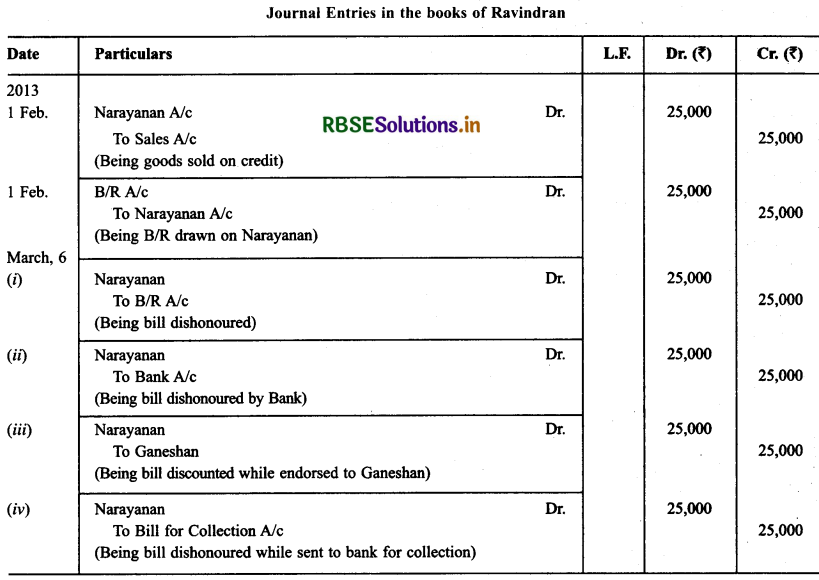
Question 9.
Narayanan purchased goods for ₹ 25,000 from Ravindran on Feb. 01,2013. Ravindran drew upon Narayanan a bill of exchange for the same amount payable after 30 days. On the due date Narayanan dishonoured his acceptance. Pass die necessary journal entries in the books of Ravindran and Narayanan in the following cases:
- When the bill was retained by Ravindran with him till the date of its maturity.
- When the bill was discounted by Ravindran immediately with his bank @ 6% p.a.
- When the bill was endorsed to his creditor Ganeshan.
- When the bill was sent by Ravindran to his bank for collection a few days before its maturity.
Solution:
Question 10.
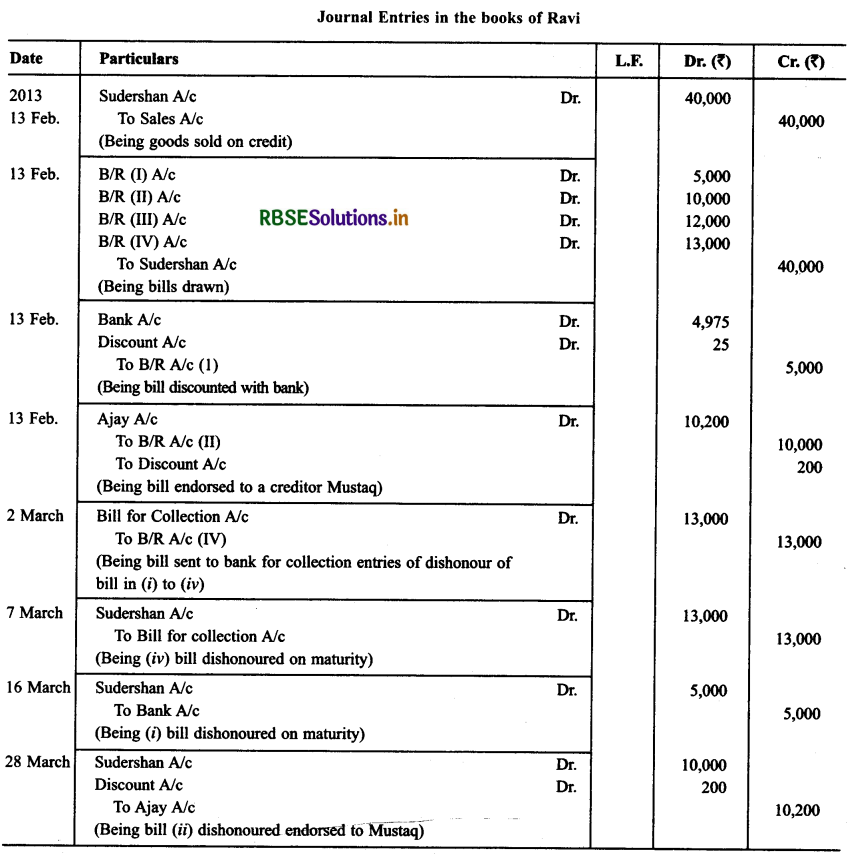
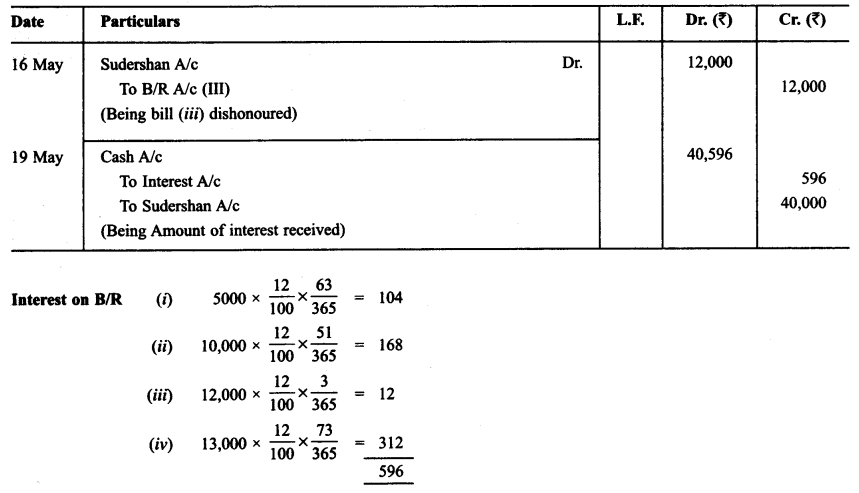
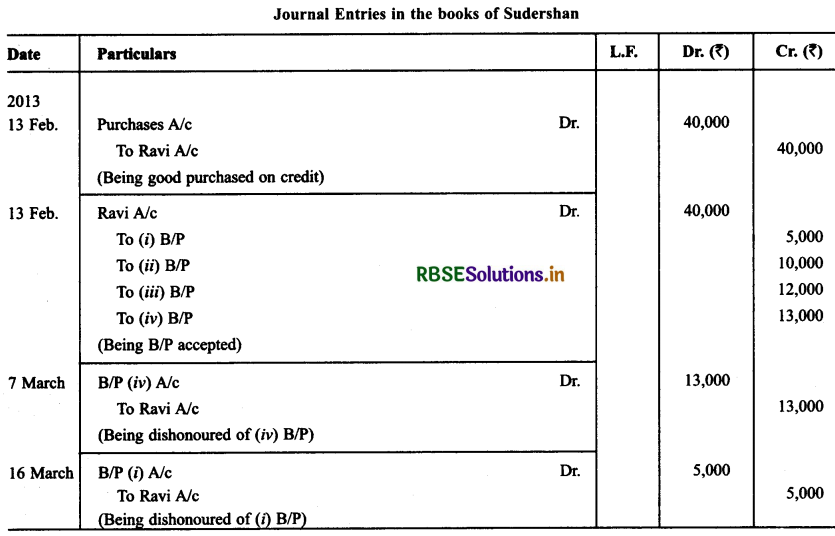
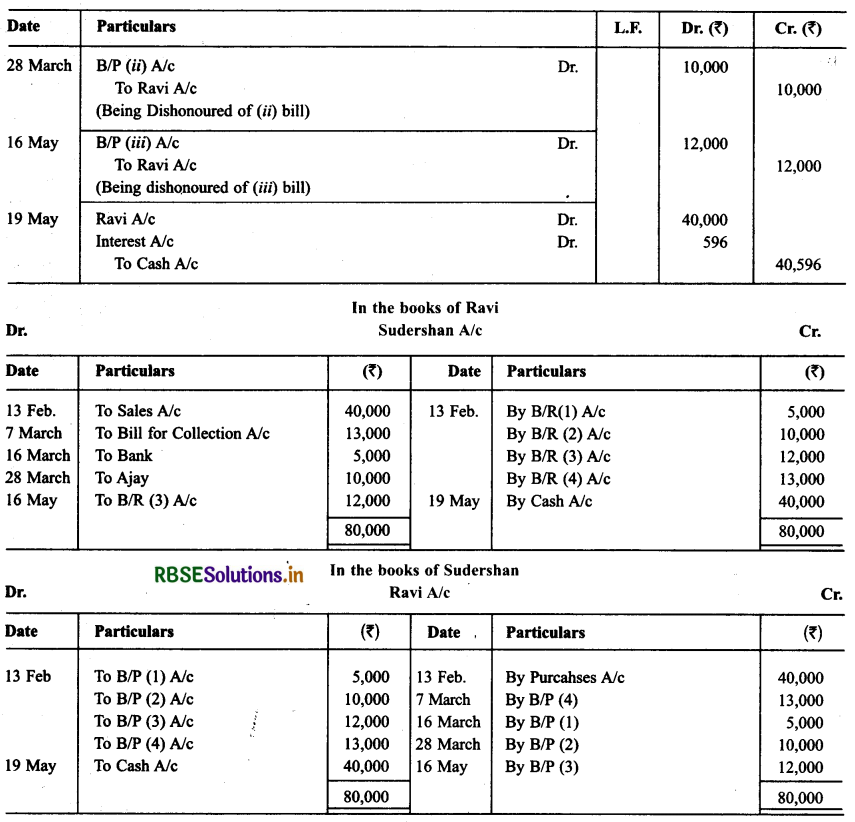
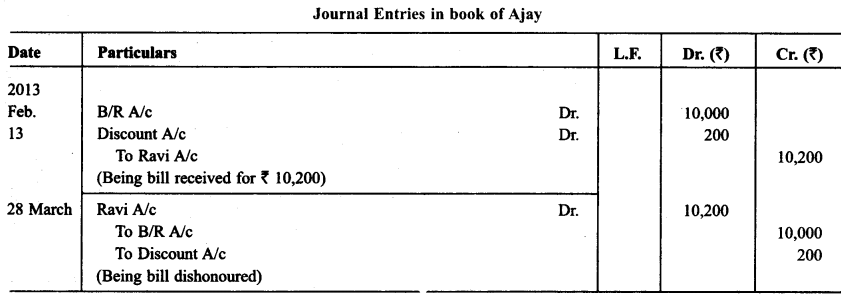
Ravi sold goods for ₹ 40,000 to Sudershan on Feb. 13, 2013. He drew four bills of exchange upon Sudershan. The first bill was for ₹ 5,000 payable after one month. The second bill was for ₹10,000 payable after 40 days; the third bill was for ₹ 12,000 payable after three months and fourth bill was for the balance amount payable after 19 days. Sudershan accepted all the bills and returned the same to Ravi. Ravi discounted the first bill with his bank at 6% p.a. He endorsed the second bill to his creditor Ajay for the full settlement of a debt of ₹ 10,200.
The third bill was kept by Ravi with him till the date of maturity. Five days before the maturity of the fourth bill, Ravi sent the bill to his bank for collection. All the four bills were dishonoured by Sudarshan on maturity. Sudershan settled Ravi’s claim in cash three days after the dishonour of each bill along with interest @ 12% p.a. for the terms of the bills. You are requested to record die necessary journal entries in the books to Ravi, Sudershan, Ajay and Bank for the above transaction. Also prepare Sudershan’s account and Ajay account in the books of Ravi.
Solution:


Question 11.
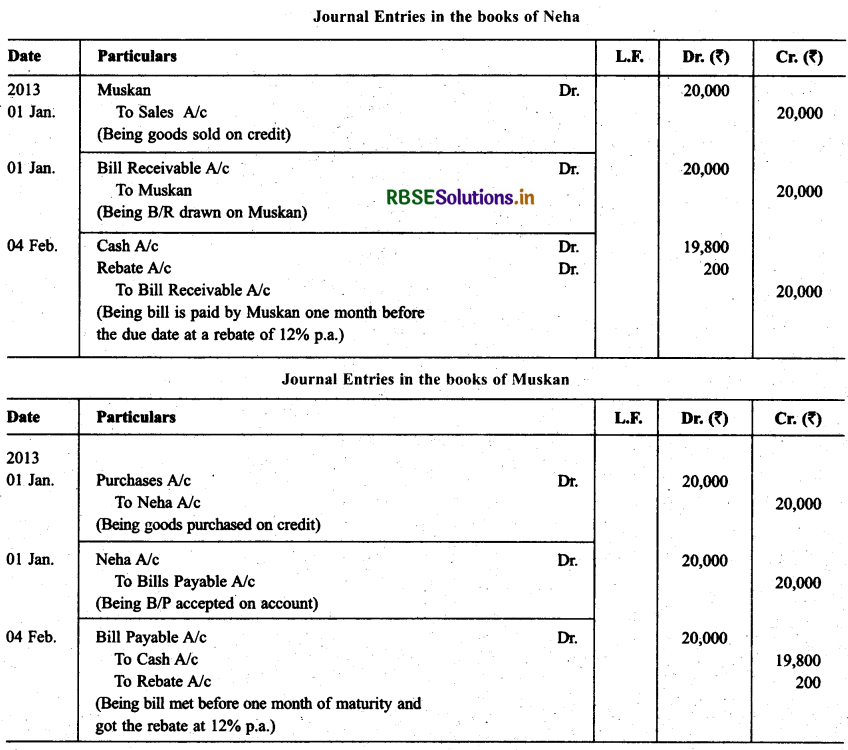
On Jan. 01, 2013 Neha sold goods for 20,000 to Muskan and drew upon her a bill of exchange payable after two months. One month before the maturity of the bill Muskan approached Neha to accepted the payment against the bill at a rebate @ 12% p.a. Neha agreed to the request of Muskan and Muskan retired the bill under the agreed rate of rebate. Journalise the above transaction in the books of Neha and Muskan.
Solution:
Question 12.
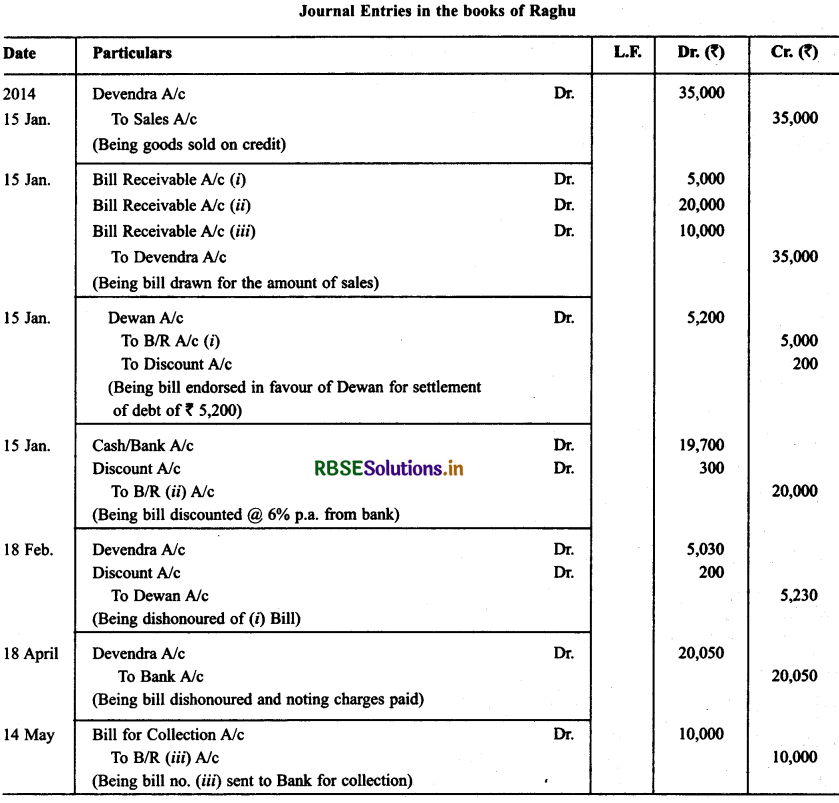
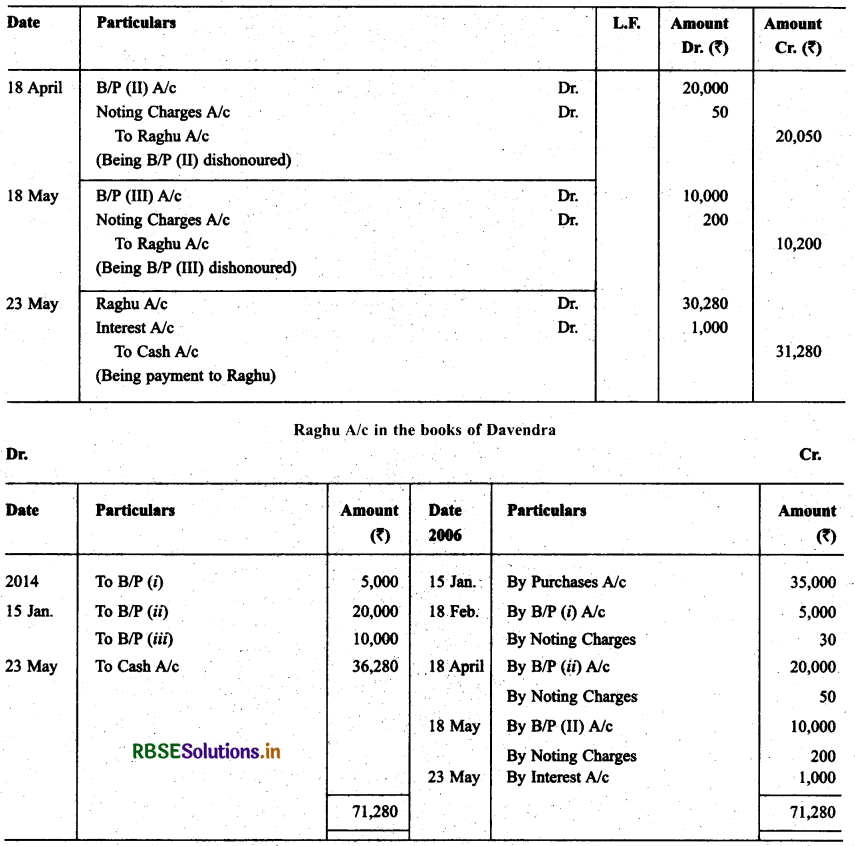
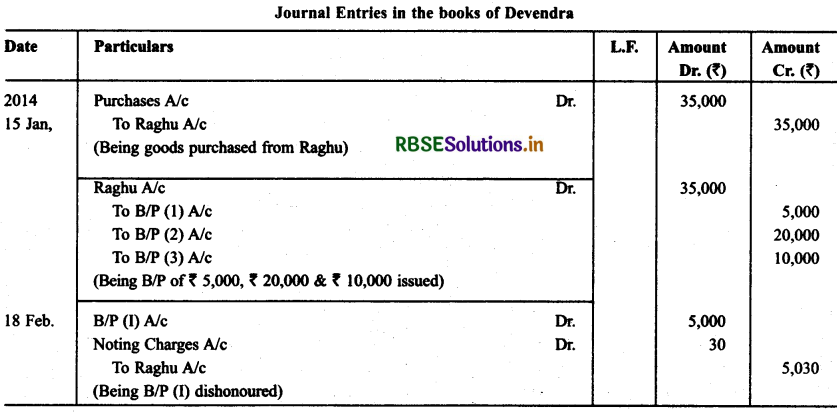
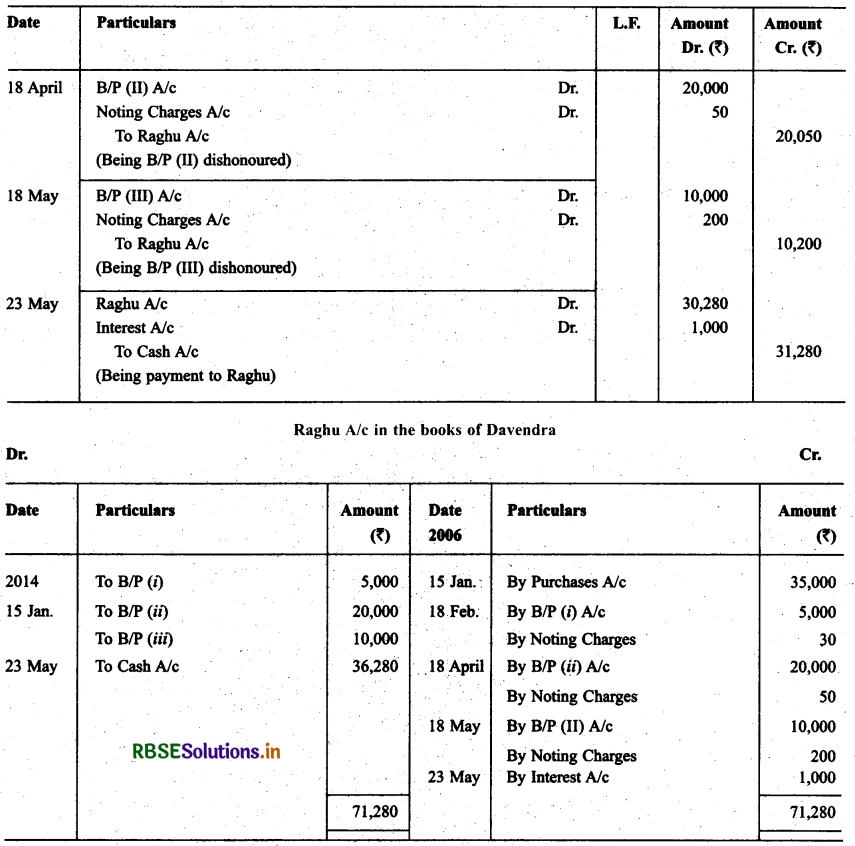
On Jan. 15, 2014 Raghu sold goods worth ₹ 35,000 to Devendra and drew upon the later three bill of exchanges. The first bill was for ₹ 5,000 payable after one month, the second bill was for ₹ 20,000 payable after three months and third bills for balance amount for 4 months. Raghu endorsed the first bill in favour of his creditor Dewan in full settlement of a debt of ₹ 5,200. The second bill was discounted by Raghu @ 6% p.a. and the third bill was retained by Raghu till the date of maturity.
Devendra dishonoured the first bill on maturity and ₹ 30 as noting charges were paid. Second bill was dishonoured by Devender on date of maturity and ₹ 50 were paid for noting charges. Four days before the maturity of the third bill Raghu, sent the same for collection to his bank. The third bill was also dishonoured by Devendra and the bank paid ₹ 200 as noting charges.
Five days after the dishonour of the bill Devendra paid the entire amount due to Raghu along with interest ₹ 1,000 for this purpose Devendra obtained a short-term loan from his bank. You are requested to record the necessary journal entries in the books of Raghu Devendra and Dewan and prepare Devendra’s Account in Raughu’s books and Raghu’s account in devendra’s account.
Solution:

Question 13.
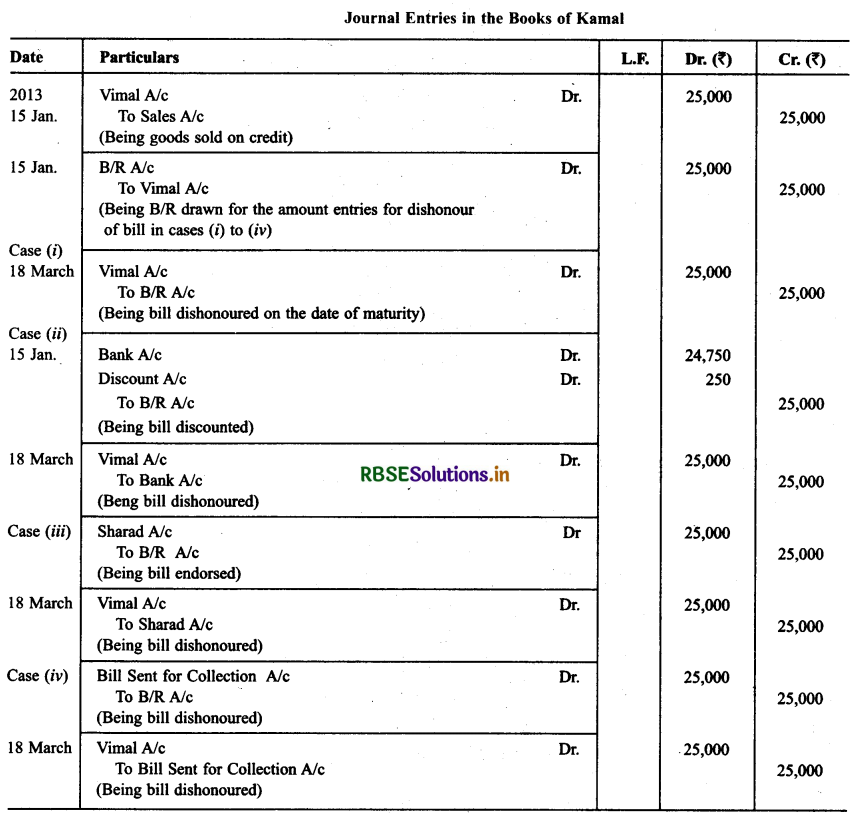
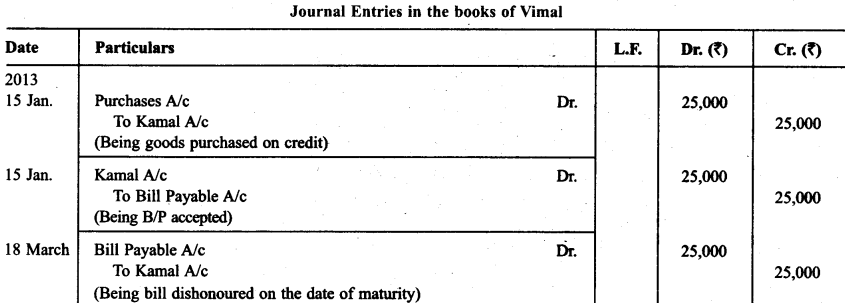
Vimal purchased goods of ₹ 25,000 from Kamal on Jan. 15,2013 and accepted a bill of exchange drawn upon him by Kamal payable afro1 two months. On the date of the maturity the bill was duly presented for payment. Vimal dishonoured the bill.
Record the necessary journal entries in the books of Kamal and Vimal when:
• The bill was retained by Kamal till the date of its maturity.
• The bill was immediately discounted by Kamal with his bank @ 6% p.a.
• The bill was endorsed by Kamal in favour of his creditor Sharad.
• Five days before its maturity die bill was sent by Kamal to his bank for collection.
Solution:
Question 14.
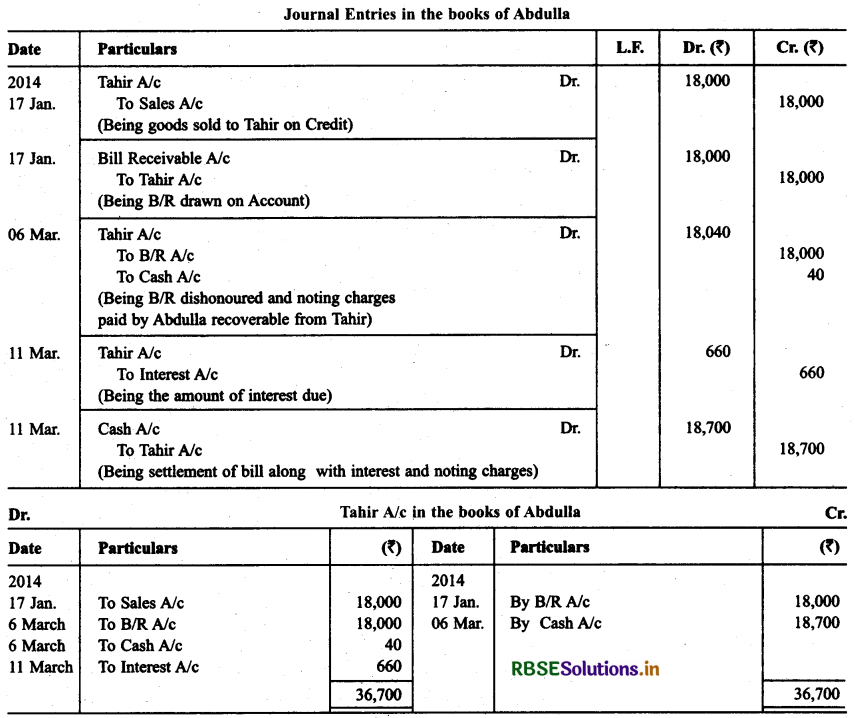
Abdulla sold goods to Tahir on Jan. 17,2014 for ₹ 18,000. He drew a bill of exchange for the same amount on Tahir for 45 days. On the same date Tahir accepted the bill and returned it to Abdulla. On the due date Abdulla presented the bill to Tahir which was dishonoured. Abdulla paid ₹ 40 as noting charges. Five days after the dishonour of his acceptance Tahir settled his debt by making a payment of ₹ 18,700 including interest and noting changes. Record the necessary journal entries in the books of Abdulla and Tahir. Also prepare Tahir’s account in die books of Abdulla and Abdulla’s account in the books of Tahir.
Solution:

Question 15.
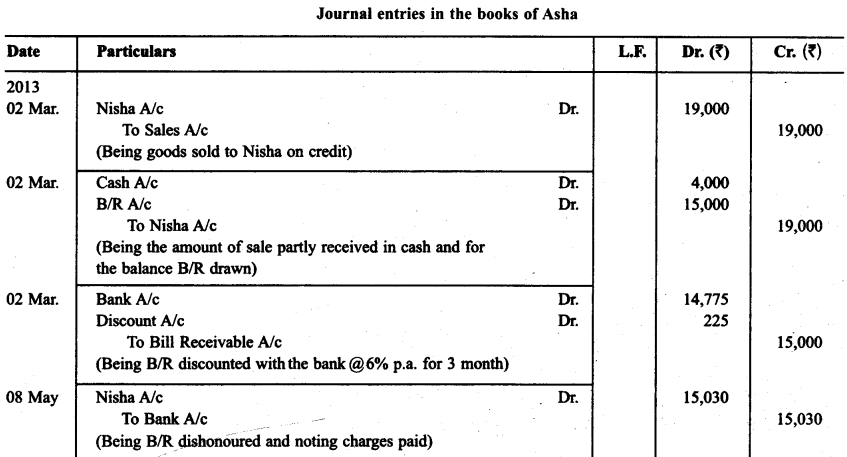
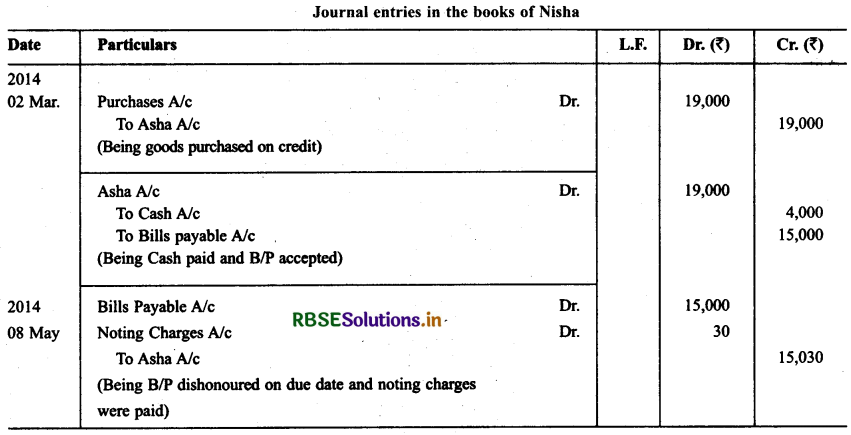
Asha sold goods worth ₹ 19,000 to Nisha on March 02, 2013. ₹ 4,000 were paid by Nisha immediately and for the balance she accepted a bill of exchange drawn upon her by Asha payable after the three months. Asha discounted the bill immediately for ₹ 14,773 with her bank. On the due date Nisha dishonoured the bill and the bank paid ₹ 30 as noting charges. Record the necessary journal entries in the books of Asha and Nisha.
Solution:

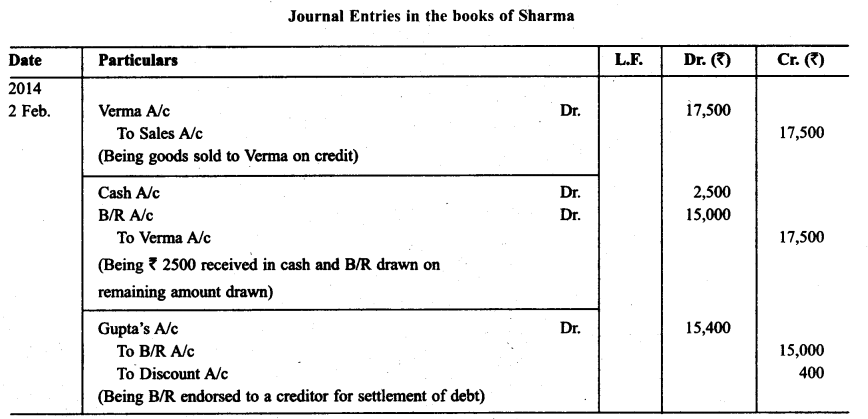
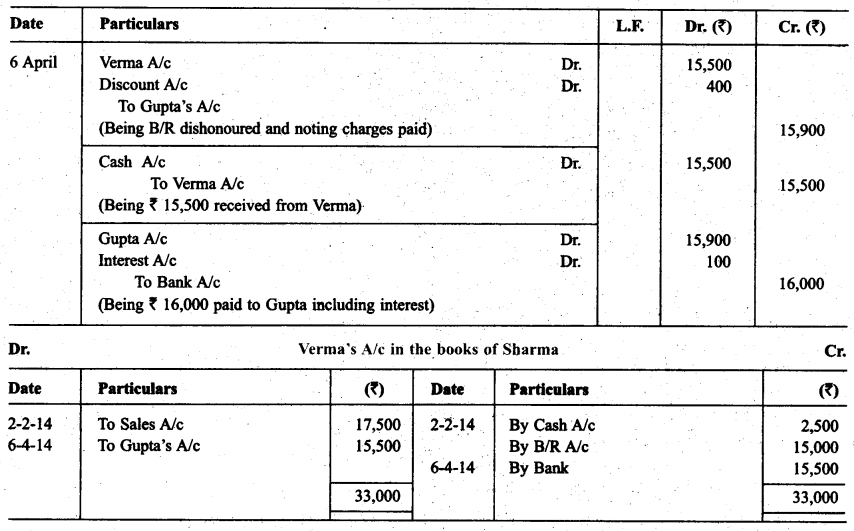
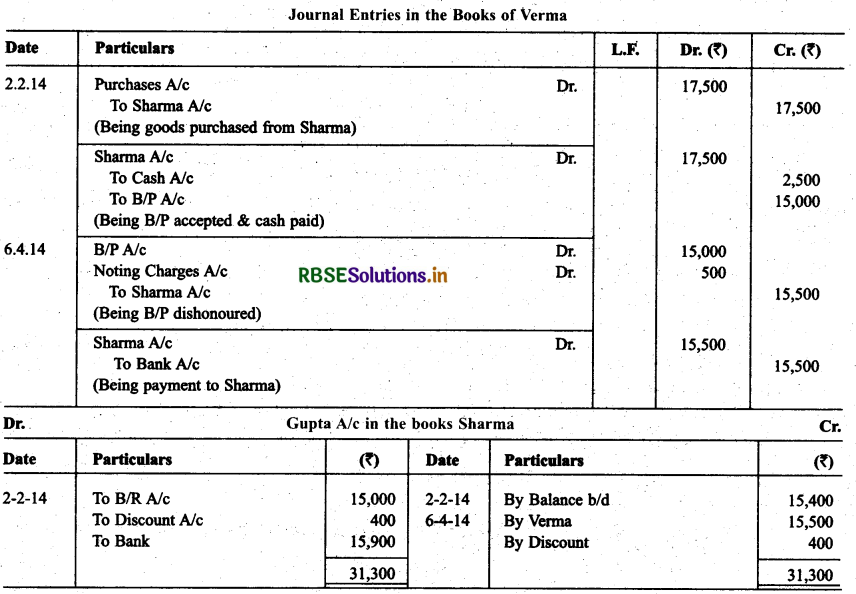
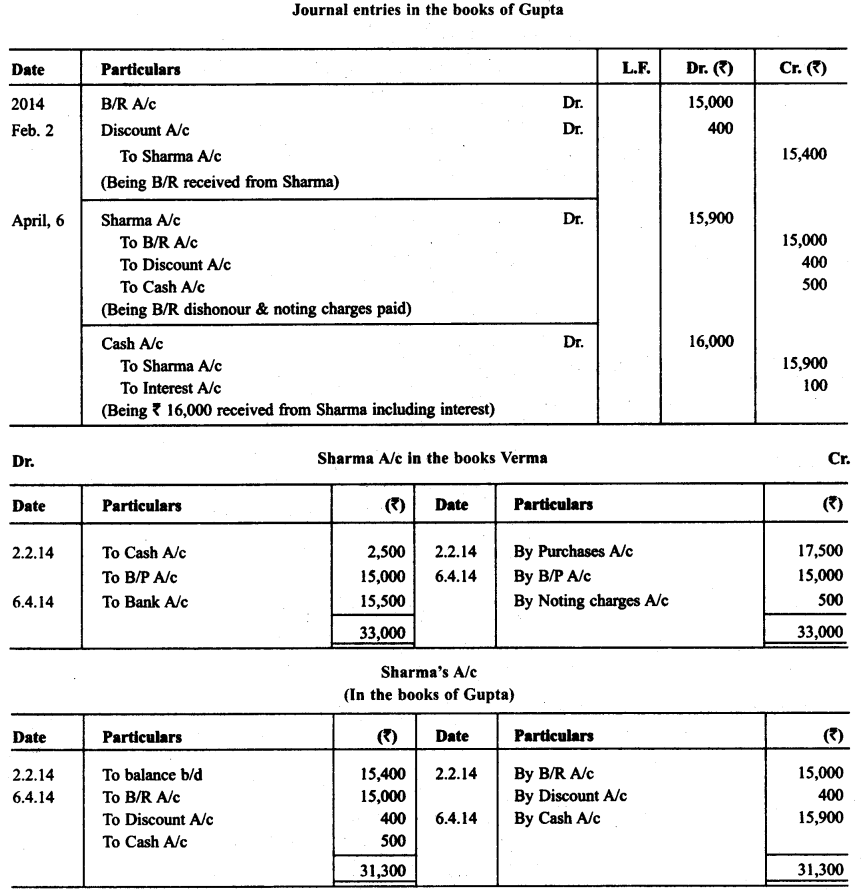
Question 16.
On Feb, 02. 2014. Verma purchased from Sharma goods for ₹ 17,500. Verma paid ₹ 2,500 immediately and for the balance gave a promissory note to Sharma payable after 60 days. Sharma immediately endorsed the promissory note in favour of his creditor. Gupta for the full settlement of a debt of ₹ 15,400. On the due date of the bill Gupta presented the bill to Verma which the latter dishonoured and Gupta paid ₹ 500 noting charges. On the same date Gupta informed Sharma about the dishonour of the bill.
Sharma settled his debt to Gupta by cheque for ₹ 16,000 which includes noting charges and interest. Verma settled Sharma’s claim by cheque for the same amount. Record the necessary journal entries in the books of Sharma, Gupta and Verma for the above transactions and prepare Verma’s and Gupta’s accounts in the books of Sharma. Sharma’s account in the books of Verma. Also Sharma’s account in the books of Gupta.
Solution:

Question 17.
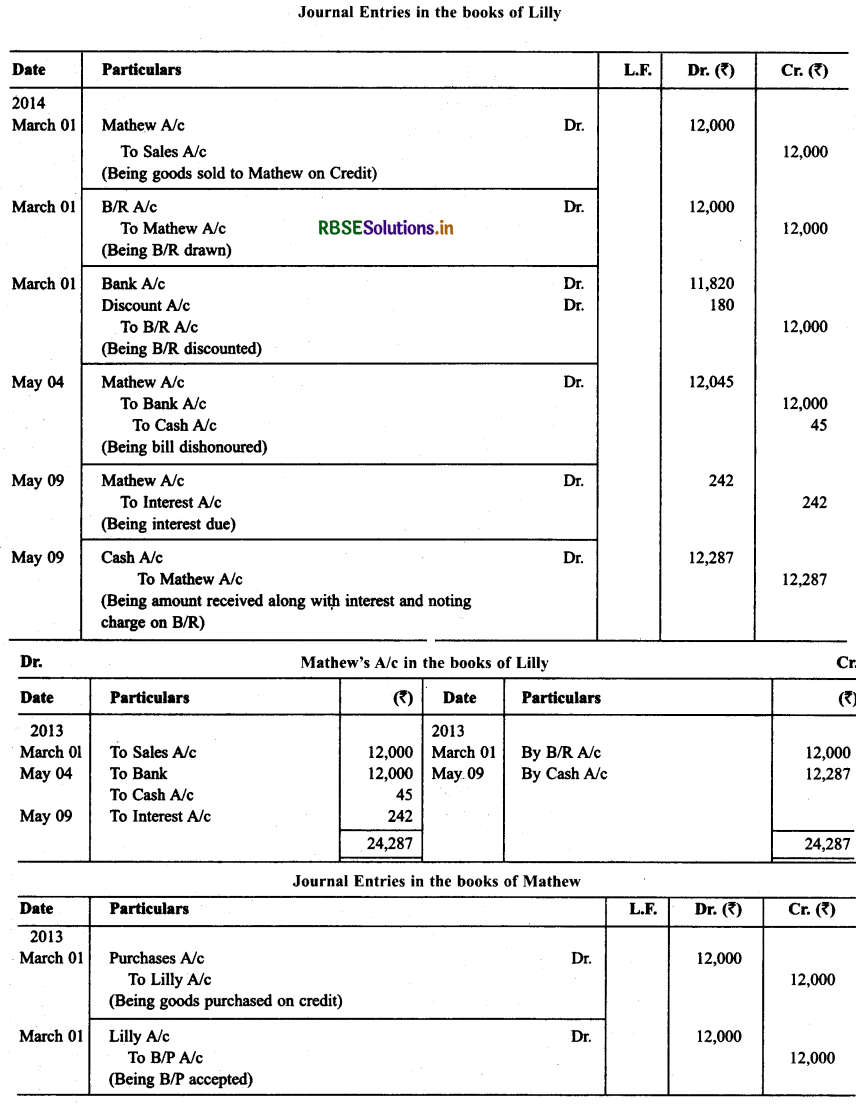
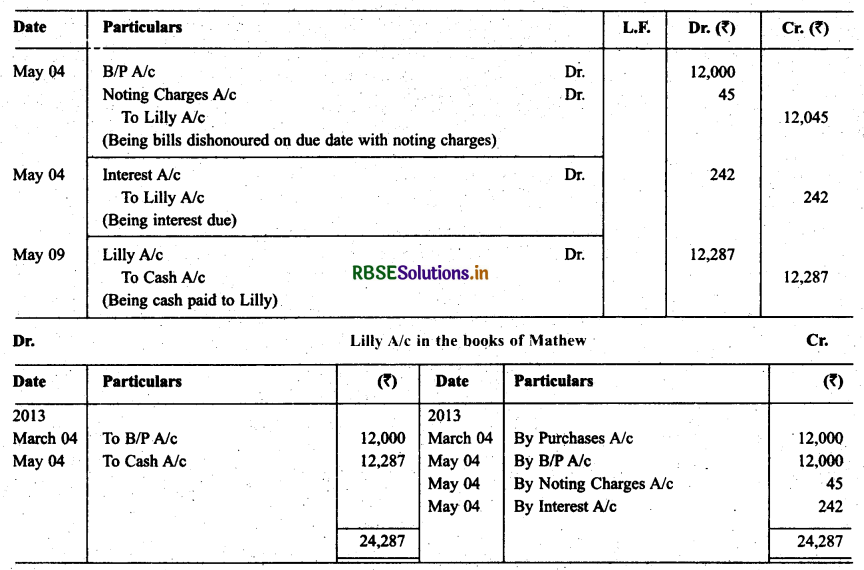
Lilly sold goods to Mathew on 1.3.2013 for ₹ 12,000 and drew upon Mathew a bill of exchange for the same amount payable after two months. Lilly immediately discounted the bill with her bank at 9% p.a. The maturity date of the bill was a non-business day (holiday). Therefore, Lilly had to present the bill as per the provisions of the Indian Instruments Act 1881. The bill was dishonoured by Mathew and Lilly paid ₹ 45 as noting charges.
Methew settled the claim of Lilly five days after the dishonour of the bill, Mathew paid by a cheque, which includes interest @12% for the term of the bill. Journalise the above transactions in the books of Lilly and Mathew and prepare Mathew’s account in the books of Lilly and Lilly’s account in the books of Mathew.
Solution:
Question 18.
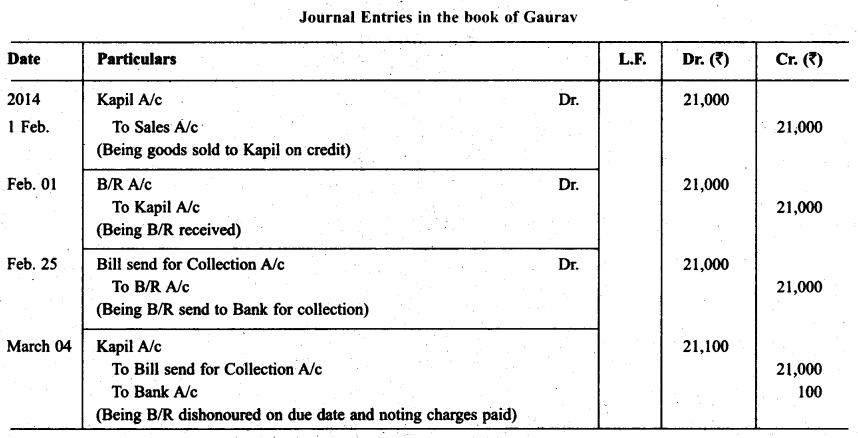
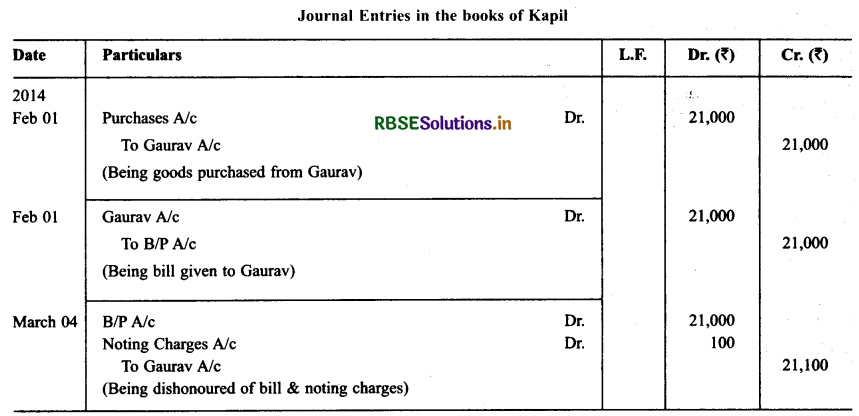
Kapil purchased goods for ₹ 21,000 from Gaurav on 1.2.2014 and accepted a bill of exchange drawn by Gaurav for the same amount. The bill was payable after one month. On 25.2.2000 Gaurav sent the bill to his bank for collection. The bill was duly presented by the bank. Kapil dishonoured the bill and the bank paid ₹ 100 as noting charges. Record the necessary journal entries for the above transactions in the books of Kapil and Gaurav.
Solution:

Question 19.
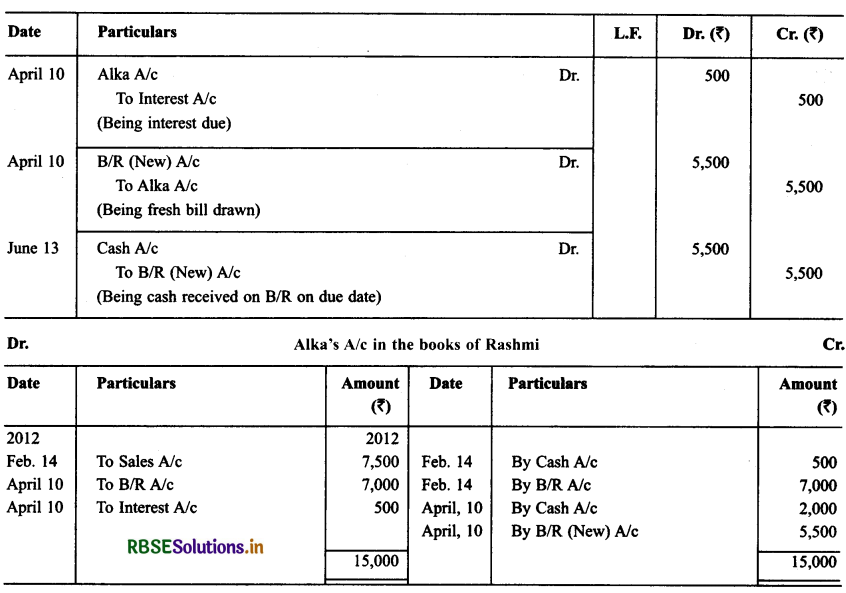
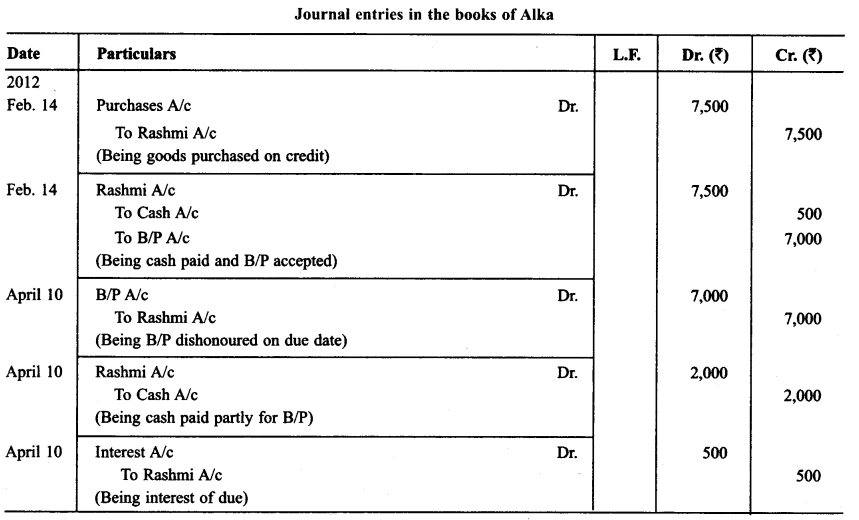
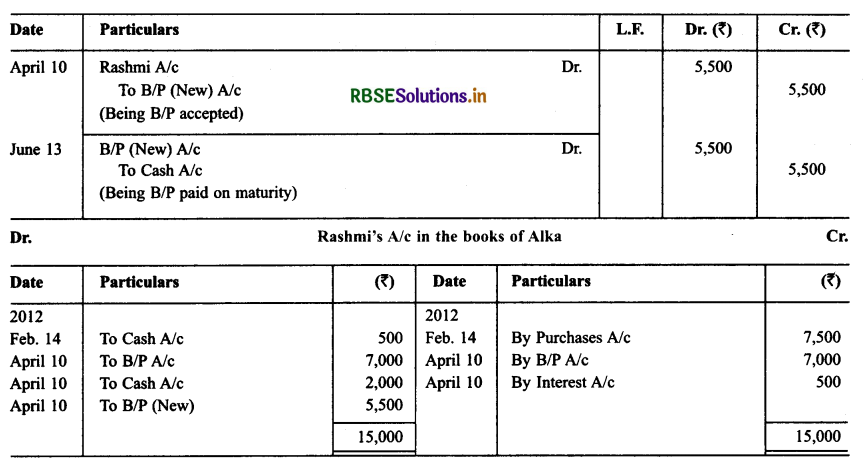
On Feb. 14, 2012 Rashmi sold goods for ₹ 7,500 to Alka. Alka paid ₹ 500 in cash and for the balance accepted a bill of exchange drawn upon her by Rashmi payable after two months. On Apr. 10, 2012 Alka approached Rashmi to cancel the bill since she was short of funds. She further requested Rashmi to accept ₹ 2,000 in cash and draw a new bill for the balance including interest ₹ 500.
Rashmi accepted Alka’s request and drew a new bill for the amount due payable after 2 months. The bill was accepted by Alka. The new bill was duly met by Alka on maturity. Record the necessary journal entries in the books of Rashmi and Alka and prepared Alka’s account in the books of Rashmi and Rashmi’s account in the books of Alka.
Solution:

Question 20.
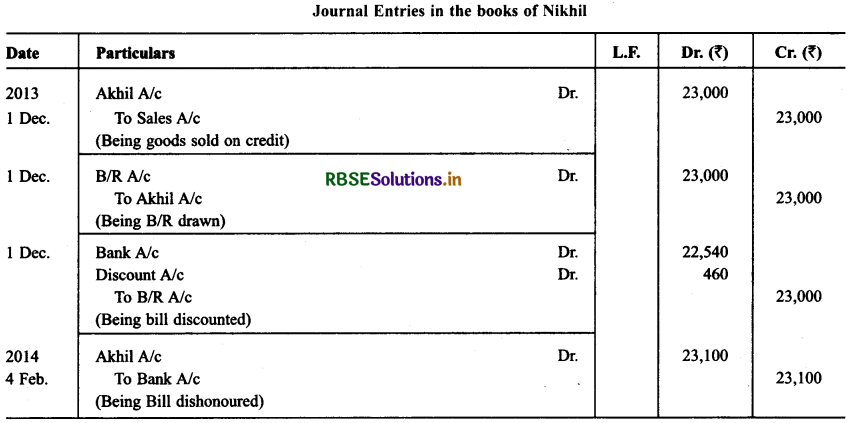
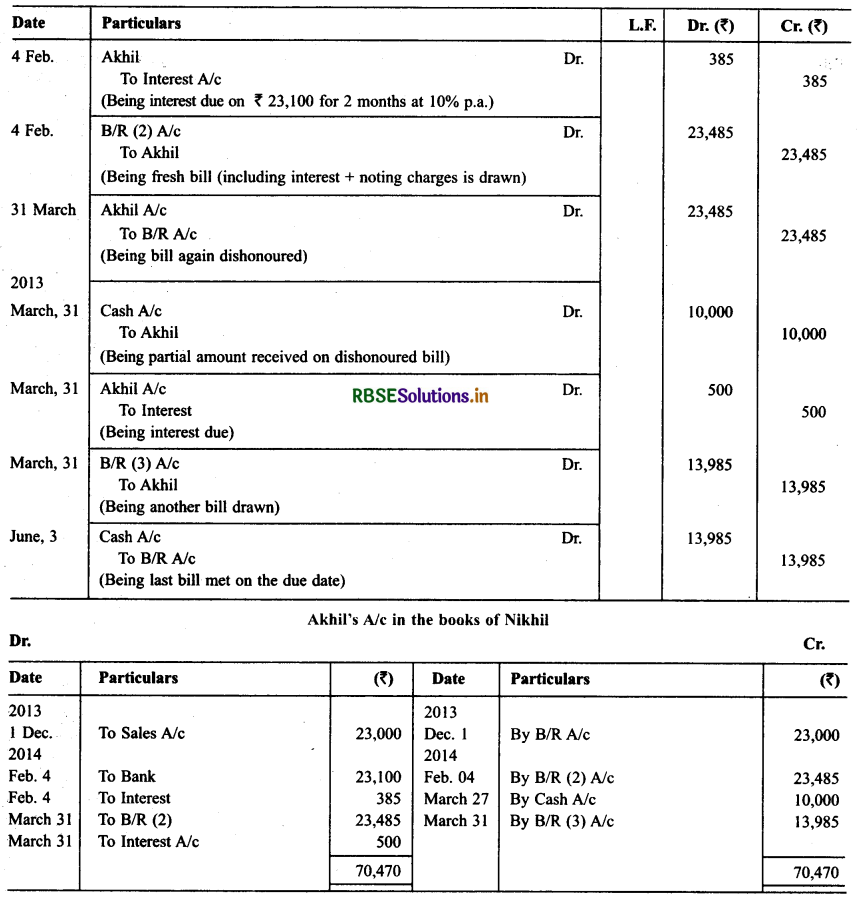
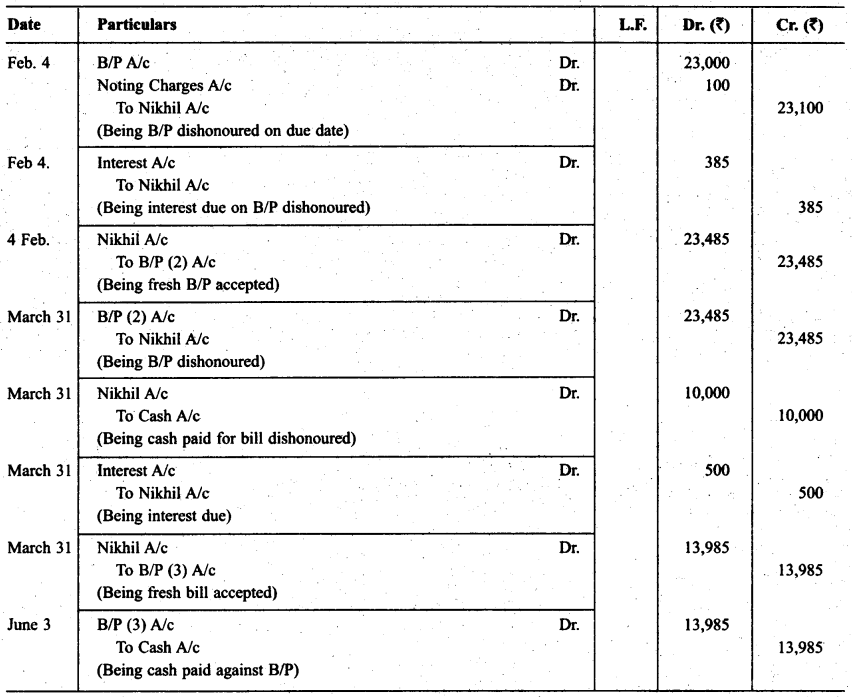
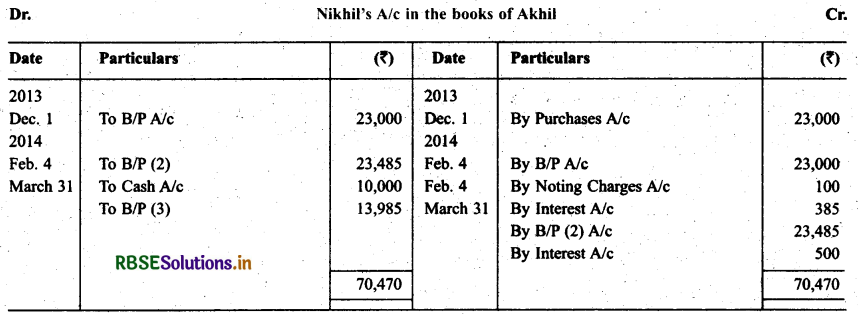
Nikhil sold goods for ₹ 23,000 to Akhil on Dec. 01,2013. He drew upon Akhil a bill of exchange for the same amount payable after 2 months. Akhil accepted the bill and sent it back to Nikhil. Nikhil discounted the bill immediately with his bank @ 12 p.a. On the due date Akhil dishonored the bill of exchange and the bank paid ₹ 100 as noting charges. Akhil requested Nikhil to draw a new bill upon him with interest @ 10% p.a. which he agreed.
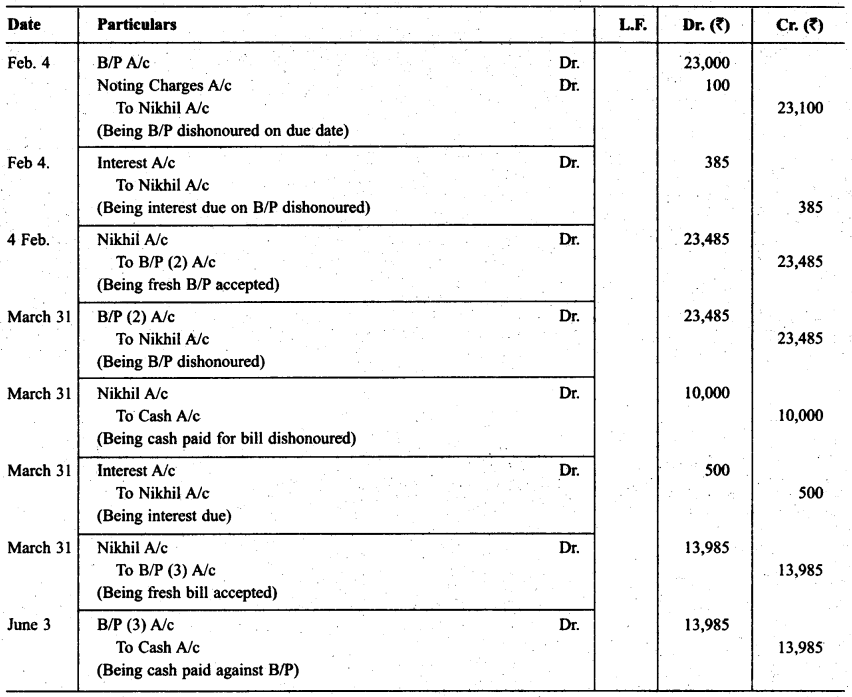
The new bill was payable after two months. A week before the maturity of the second bill Akhil requested Nikhil to cancel the second bill. He further requested to accept ₹ 10,000 in cash immediately and drew a third bill upon him including interest of 7 500. Nikhil agreed to Akhil’s request. The third bill was payable after one month. Akhil met the third bill on its maturity. Record the necessary journal entries in the books of Nikhil and Akhil and also prepare Akhil’s account in the books of Nikhil and Nikhil’s account in the books of Akhil.
Solution:


Question 21.
On Jan. 01, 2013 Vibha sold goods worth ₹ 18,000 to Sudha and drew upon the later a bill of exchange for the same amount payable after two months. Sudha accepted Vibha’s draft and returned the same to Vibha after acceptance. Vibha endorsed the bill immediately in favour of her creditor Geeta. Five days before the maturity of the bill Sudha requested Vibha to cancel the bill since she was short of funds.
She further requested to draw a new bill upon her including interest of ₹ 200. Vibha accepted Sudha’s request and took the bill from Geeta by making the payment to her in cash and cancelled the same. Then she drew a new bill upon Sudha as agreed. The new bill was payable after one month. The new bill was duly met by Sudha on maturity. Record the necessary journal entries in the books of Vibha.
Solution:
Question 22.
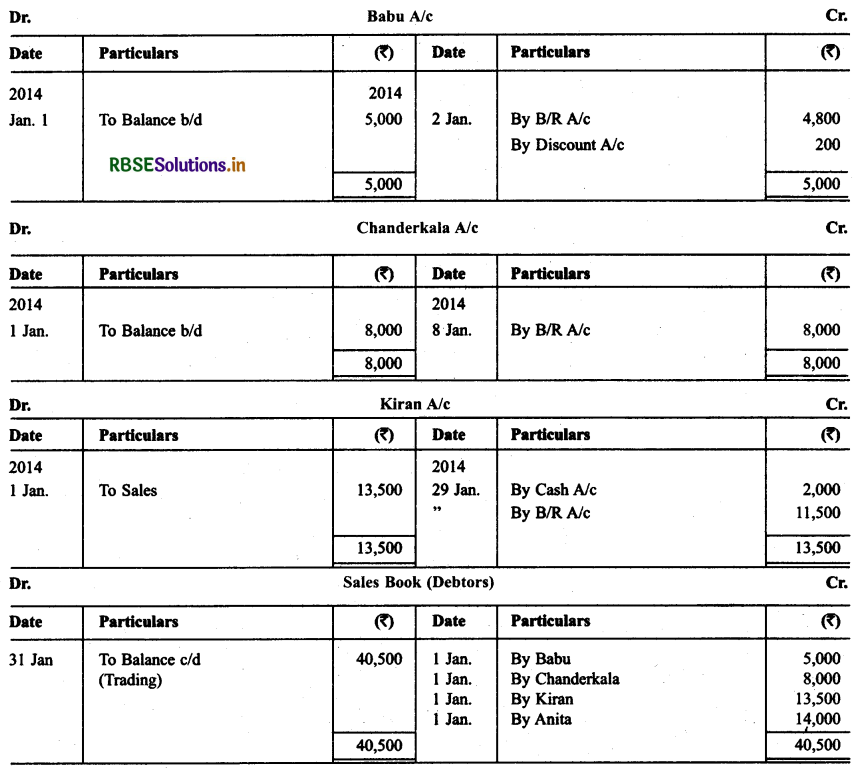
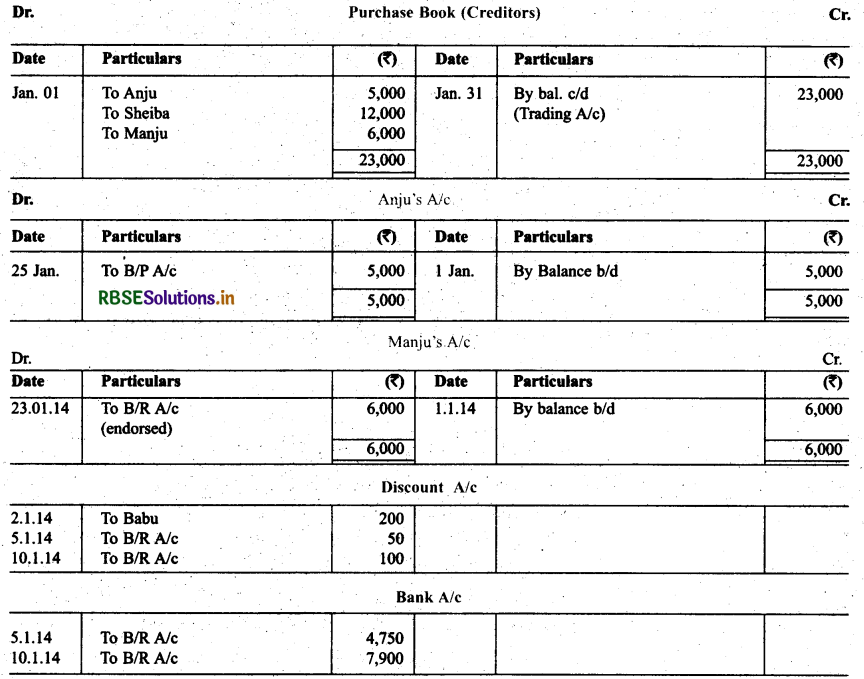
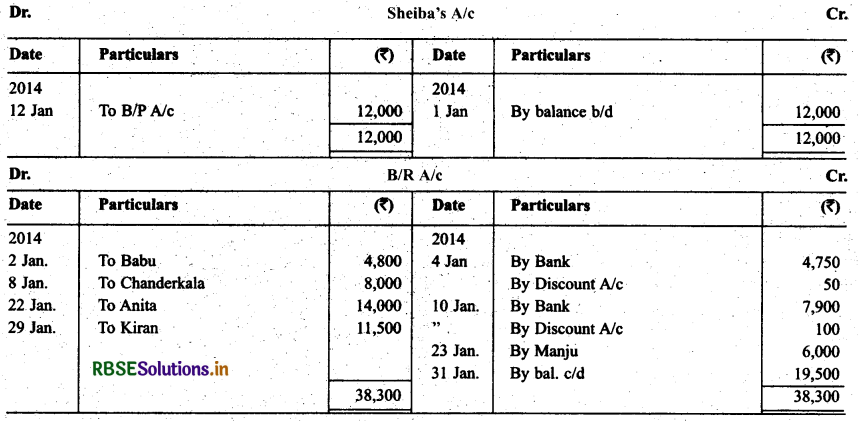
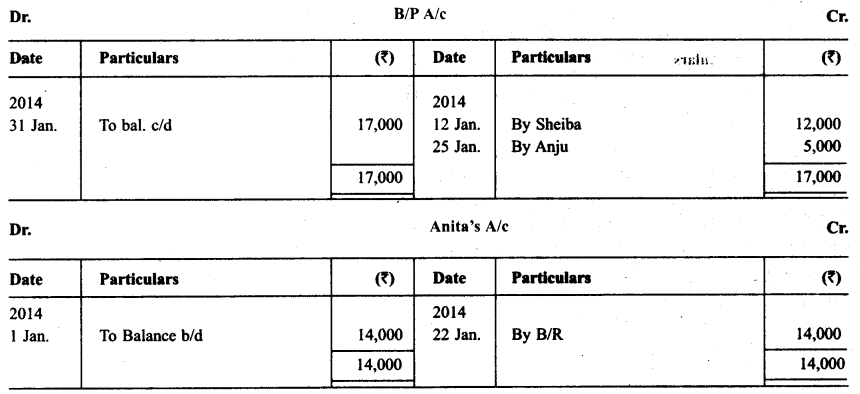
Following were the position of debtors and creditors of Gautam as on 1.1.2014.

The following transactions took place in the month of Jan. 2014:
Jan. 2 Drew on Babu at two months after date in full settlement of ₹ 4,800.
K Babu accepted the bill and returned it on 5.1.2014.
Jan. 5 Babu’s bill discounted for ₹ 4,750.
Jan. 8 Chanderkala sent a promissory note for ₹ 8,000 payable three months after date.
Jan. 10 Promissory note received from Chanderkala discounted for ₹ 7,900.
Jan. 12 Accepted Sheiba draft for the amount due payable two months after date.
Jan. 22 Anita sent his promissory note payable after two months.
Jan. 23 Anita’s promissory note endorsed in favour of Manju.
Jan. 25 Accepted Anju’s draft payable after three months.
Jan. 29 Kiran sent ₹ 2,000 in cash and a promissory note for the balance payable after three months.
Record the above transactions in the proper subsidiary books.
Solution:

Question 23.
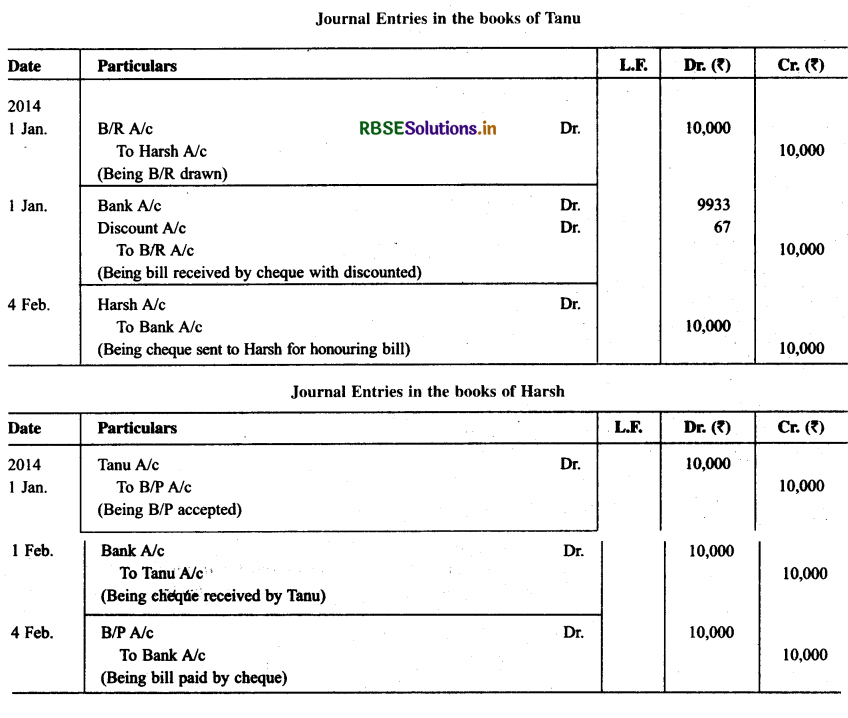
On Jan. 01, 2014 Harsh accepted one months bill for ₹ 10,000 drawn on him by Tanu for later’s benefit. Tanu discounted the bill on same day @ 8% p.a. On the due date Tanu sent a cheque to Harsh for honour the bill. Harsh duly honoured his acceptance. Record the journal entries in the Books of Tanu and Harsh.
Solution:
Question 24.
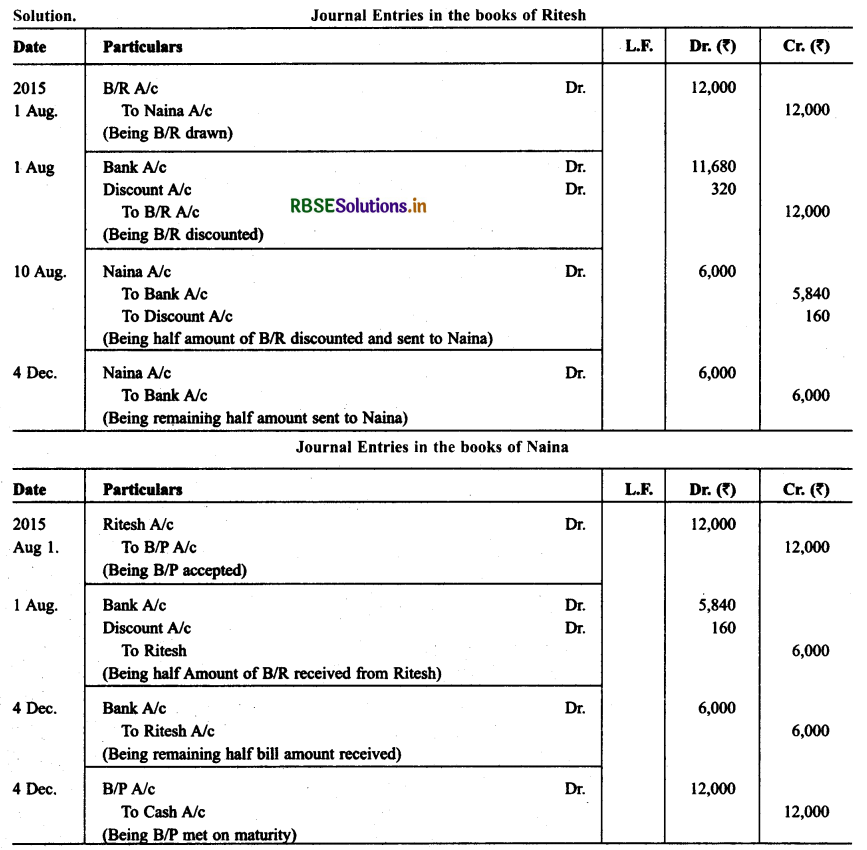
Ritesh and Naina were in need of funds temporarily. On August 01,2015 Ritesh drew upon Naina a bill for ₹ 12,000 for 4 months. Naina Accepted the bill and returned to Ritesh. Ritesh discounted the bill @ 8% p.a. Half amount of the discounted bill remitted to Naina. On due date, Ritesh sent the required sum to Naina, who met the bill. Journalise the transaction in the books of both the parties.
Solution:

Question 25.
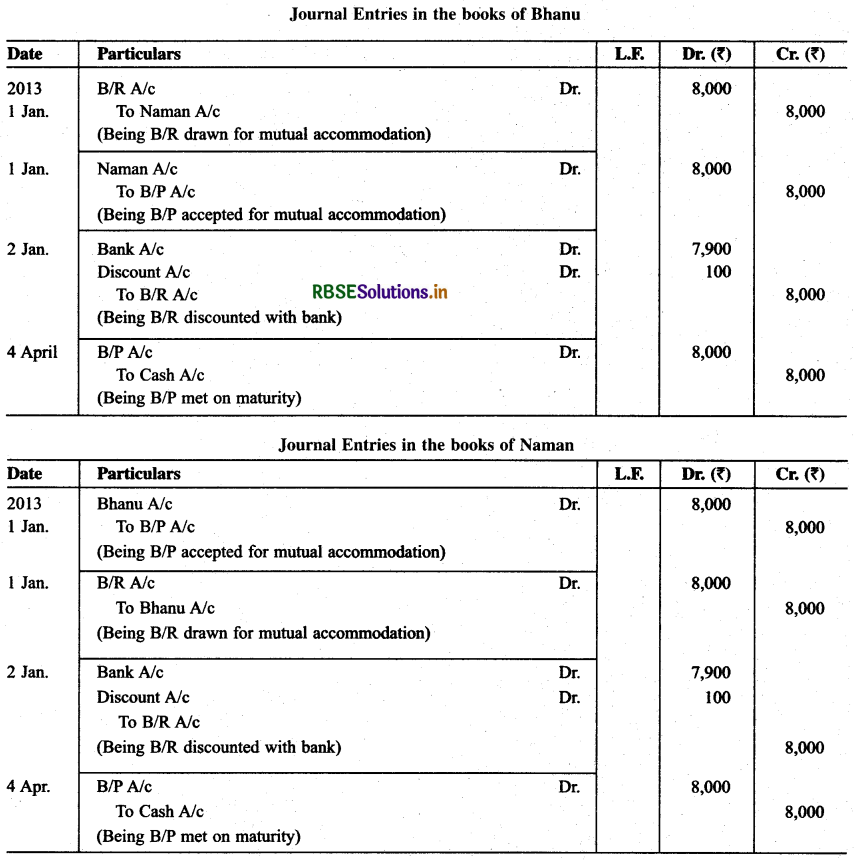
On Jan. 01, 2013 Bhanu and Naman drew on each other a bill for ₹ 8,000 payable 3 months after the due date for their Mutual benefit. On 2nd January they discounted with their bank each other’s bill at 5% p.a. on the due date each met his own’s acceptance. Give journal entry in the books of Bhanu and Naman.
Solution:
Question 26.
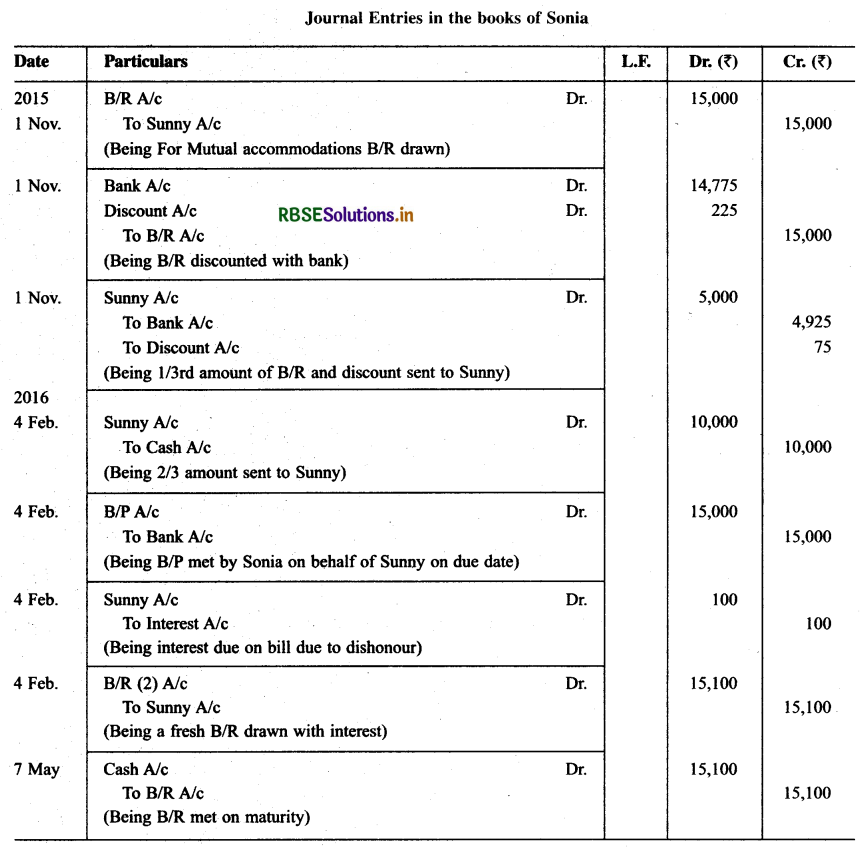
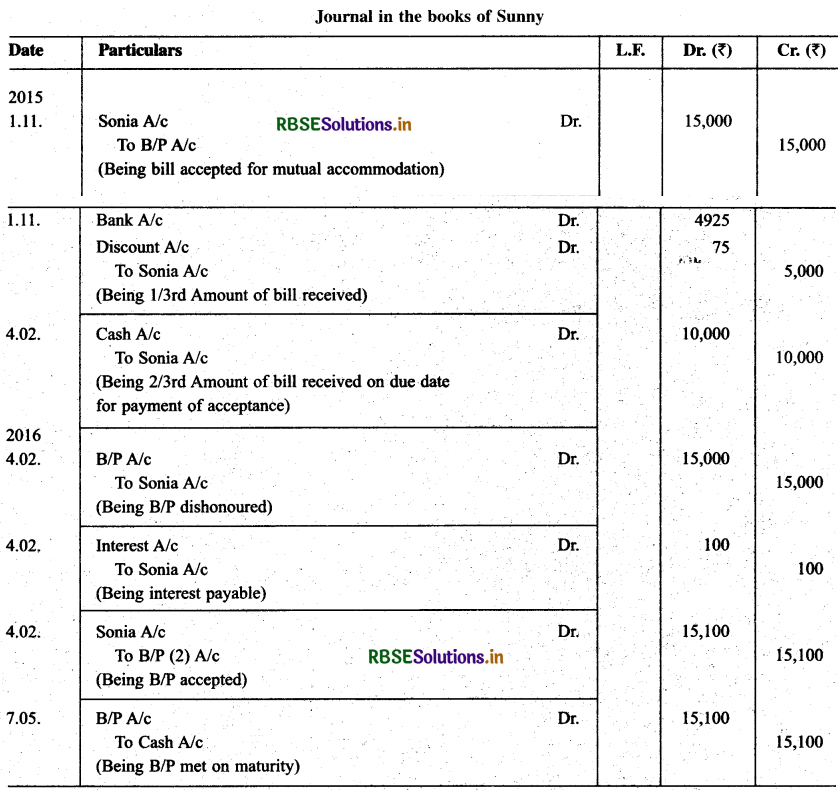
On Nov. 01, 2015 Sonia drawn a bill on Sunny for ₹ 15,000 for 3 months for mutual accommodation. Sunny accepts the bill and return it to Sonia. Sonia discounted the same with his bankers @ 6% p.a. The proceeds are shared between Sonia and Sunny in proportion of 2/3rd, 1/3rd respectively. On the due date Sonia remits his proportion to Sunny who fails to met the bill and as a result Sonia has to meet it. Sunny give a fresh acceptance for the amount due to Sonia plus interest of₹ 100. Sunny meet his second acceptance on due date. Record the necessary journal entries in the books of Sonia and Sunny.
Solution: