RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 4 Sorting Materials into Groups
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 4 Sorting Materials into Groups Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Important Questions Sorting Materials into Groups
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Select the transparent material from the following:
(a) iron
(b) steel
(c) paper
(d) glass
Answer:
(d) glass

Question 2.
Select the opaque material from the following:
(a) glass
(b) water
(c) lemon juice
(d) iron
Answer:
(d) iron
Question 3.
Which one of the following is soft?
(a) Sugar
(b) Mud
(c) Gold
(d) Sponge
Answer:
(d) Sponge
Question 4.
Which one of the following is hard?
(a) Cotton
(b) Sponge
(c) Iron
(d) Dough
Answer:
(c) Iron
Question 5.
Which of the following materials is not lustrous?
(a) Wood
(b) Gold .
(c) Silver
(d) Steel
Answer:
(a) Wood
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1.
Sugar and salt are ................ in water.
Answer:
soluble
Question 2.
The object whose density is more than water will ................ in water.
Answer:
sink
Question 3.
utter paper passes little light to pass through it so it is ................ in nature.
Answer:
translucent
Question 4.
The leaf will ................on oil/water.
Answer:
float
Question 5.
Diamond is ................ in nature.
Answer:
hard.
State whether True or False
Question 1.
Lock and glass are made up of plastics.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
Oil is soluble in water and sugar is insoluble.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
We can see clearly from translucent material.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Oil floats on water because its density is higher than water.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
All gases are soluble in water.
Answer:
False

Match the followings
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Metal |
(a) mixes well with water |
|
2. Plastic |
(b) copper |
|
3. Soluble |
(c) light cannot pass through it |
|
4. Saturate |
(d) sugar |
|
5. Transparent |
(e) shiny |
|
6. Opaque |
(f) bad conductor of heat |
|
7. Translucent |
(g) universal solvent |
|
8. Lemon |
(h) light can pass through it |
|
9. Water |
(i) cannot see the object clearly |
|
10. Silver |
(j) cannot dissolve more substance |
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
1. Metal |
(d) sugar |
|
2. Plastic |
(f) bad conductor of heat |
|
3. Soluble |
(d) sugar |
|
4. Saturate |
(i) cannot see the object clearly |
|
5. Transparent |
(h) light can pass through it |
|
6. Opaque |
(c) light cannot pass through it |
|
7. Translucent |
(i) cannot see the object clearly |
|
8. Lemon |
(a) mixes well with water |
|
9. Water |
(g) universal solvent |
|
10. Silver |
(e) shiny |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why do we group the materials?
Answer:
Grouping of materials is done for our convenience to study their properties and to make the best use of them.
Question 2.
How shine of metal can be regained?
Answer:
We can regain the shine of the metal by rubbing it with the sandpaper or by cutting its outer surface.
Question 3. What is solvent?
Answer:
It is a substance in which other substances are dissolved. It is large in quantity. For example, water.
Question 4.
What is solute?
Answer:
It is a substance which dissolves in solvent. It is generally lesser in quantity. For example, sugar, salt.
Question 5.
What is solution?
Answer:
It is the combination of solute and solvent. For example, Salt + Water = Solution Question 6. If we see the Sun from the glass of water, are we able to view the Sun? Answer: Yes, we are able to see the Sun from a glass of water because the water is transparent in nature.
Question 7.
Why wires are made of copper, silver or aluminium?
Answer:
Wires are made of copper, silver or aluminium because metals are good conductors of electricity.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Can we make different objects from same materials?
Answer:
Yes, we can make different objects from same materials. For example, with the help of plastics, we can make switches, mugs, baskets, buckets, balls, polythene, vehicle parts, etc. With wood, we can make furniture like - chairs, tables, cupboards, etc.

Question 2.
Why tumbler should not be made with cloth?
Answer:
Tumblers should not be made with cloth because we use tumblers to keep liquids, a piece of cloth cannot hold the liquid, therefore, tumblers should be made of glass, mud or metal, etc. in order to hold liquids.
Question 3.
What will happen to chalk powder or sand when we put them in water?
Answer:
Chalk powder and sand will not dissolve in water as they are insoluble substances. Sand will settle at the bottom and chalk powder will suspend in water.
Question 4.
Why some objects float on liquid whereas others sink?
Answer:
Floating and sinking depend on the weight or density of objects and liquid. If density of an object is less than liquid, it will float on water whereas if density of an object is more than liquid, it will sink.
Question 5.
The nature of cooking utensils and its handle are opposite to each other, comment on it.
Answer:
Cooking materials are generally made from materials such as aluminium because it is a good conductor of heat whereas we use the handles of the utensils made of wood or plastics because they are bad conductors of heat.
Question 6.
Among wax, oil, wood, iron, paper, vegetable ghee, thermocol and coin which will float and which will sink in water?
Answer:
|
Substances |
Float/sink |
|
Wax |
Float |
|
Oil |
Float |
|
Wood |
Float |
|
Iron |
Sink |
|
Paper |
Float |
|
Thermocol |
Float |
|
Vegetable g/tee |
Float |
|
Coin |
Sink |
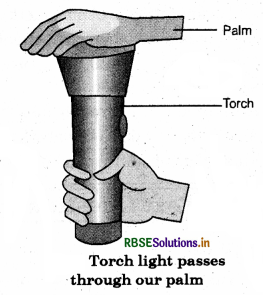
Question 7.
Write an activity to prove that our palm is translucent.
Answer:
Take a torch and switch off the light of the room. Now, cover the glass of torch with your palm and switch on the torch. You will observe that the light passes through other side, of the palm but not clearly. This proves that our palm is translucent in nature.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the difference between hard material and soft material.
Answer:
Difference between Hard Material and Soft Material
|
Hard materials |
Soft materials |
|
The materials which cannot be pressed or scratched easily are known as hard materials. |
The materials which can be pressed or scratched easily are known as soft materials. |
|
For example, iron, steel, wood, etc. |
For example, cotton, sponge, etc. |

Question 2.
Write the difference between soluble and insoluble materials.
Answer:
Difference between Soluble and Insoluble Materials
|
Soluble materials |
Insoluble materials |
|
The materials which easily dissolve in water are called soluble materials. |
The materials which do not mix with water even after stirring them well are known as insoluble materials. |
|
For example, salt, lemon, sugar, alum, etc. |
For example, sand, oil, etc. |
