RBSE Class 6 Maths Important Questions Chapter 14 Practical Geometry
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Maths Important Questions Chapter 14 Practical Geometry Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 14 Important Questions Practical Geometry
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Name the geometrical instrument having a semicircular device graduated into 180 degree parts :
(a) Divider
(b) Compasses
(c) Set squares
(d) Protractor
Answer:
(d) Protractor
Question 2.
Which geometrical instrument used to mark of equal lengths but not to measure them and draw arcs and circles :
(a) Compasses
(b) Set squares
(c) Divider
(d) Protractor
Answer:
(a) Compasses

Question 3.
A ....................... is a simple closed curve all of whose points are at the same distance from a fixed point.
(a) Diameter
(b) Radius
(c) Triangle
(d) Circle
Answer:
(d) Circle
Question 4.
Using ruler and compasses, we cannot draw an angle of measure :
(a) 45°
(b) 75°
(c) 90°
(d) 80°
Answer:
(d) 80°
Question 5.
The number of lines of symmetry in a compasses is :
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer:
(a) 0

Question 6.
Number of set squares in the geometry box is:
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer:
(c) 2
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1.
A 30° - 60° - 90° set square has ___________ line/lines of symmetry.
Answer:
no
Question 2.
Circles having same centre but different radius are called ___________ circles.
Answer:
concentric circles
Question 3.
The number of scales in a protractor for measuring the angle is ___________ .
Answer:
180°
Question 4.
Axis of symmetry of a line segment is the ___________ bisector of line segment.
Answer:
perpendicular
Question 5.
A protractor has ___________ line/lines of symmetry.
Answer:
one.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Draw a line segment of length 6.6 cm. Bisect it and measure the length of each part.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
1. Draw a line segment AB of length 6.6 cm.
2. With A as centre and radius more than half of AB, draw arcs; one on each side of AB.
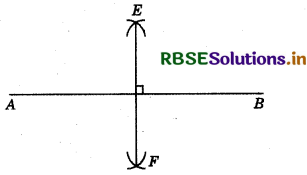
3. With B as centre and radius more than half of AB, draw arcs, cuting the arcs in previous step at E and F respectively.
4. Join EF.
5. Thus, EF is the required perpendicular bisector of AS.

Question 2.
Draw an angle and label it as ∠BAC. Construct an angle ∠DEF such that ∠DEF = 2 ∠BAC.
Answer:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw a ray ED.
(ii) With A as centre and suitable radius draw an arc intersecting AB and AC at P and Q respecti-vely.
(iii) With E as centre and the same radius as the ne used in step (ii), draw an arc to intersect ED at R.
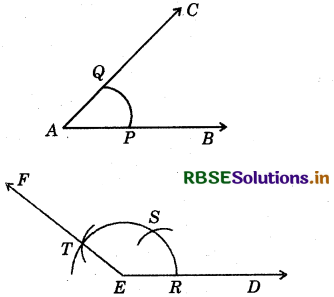
(iv) With R as centre and radius equal to PQ, draw an arc to intersect the arc; from EatS.
(v) With S as centre and radius equal to
PQ, draw an arc to intersect the arc; draw from E at T. Join E and T and produce it to any point F. .
Thus, ∠DEF so obtained is the required angle.
