RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 1 The Solid State
These comprehensive RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 1 The Solid State will give a brief overview of all the concepts.
RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Notes The Solid State
→ Solid: They have definite mass, volume and shape. The position of constituent particles are fixed because of strong intermolecular force of attraction.
→ Crystalline solid: Those solids, in which the constituent particles have a regular orderly arrangement throughout and it gets repeated again and again resulting in a definite pattern, knovvn as crystalline solids.
→ Amorphous solid: Those solids in which the constituent particles are not arranged in any regular arrangement are called amorphous solids.
→ Crystal lattice or space lattice: Space lattice is a regular three-dimensional arrangement of identical points in space.
→ Lattice point: The point at which constituent particles are arranged is known as lattice point.
→ Bravais lattice: 14 different types of lattices are called Bravais lattice.
→ Unit cell: A unit cell is a three-dimensional group of lattice point that generates the whole lattice by translation or stacking.
→ Packing efficiency: The percentage of the total space filled by the particles is called packing efficiency or the fraction of the total space filled is called packing fraction.

→ Interstitial spaces or voids : The vacant spaces present in between the spheres is called hole or interstitial spaces or voids.
→ Tetrahedral void: The vacant space among four spheres having tetrahedral arrangement is called tetrahedral void.
→ Octahedral void: The empty space created at the cer \e of six spheres which are placed octahedrally is known as octahedral void.
→ Radius ratio: The ratio of radius of cation to the radius of anion is known as radius ratio of the ionic solid.
→ Defect or imperfection: The deviation in perfectly arrangement of constituent particles in a crystal is known as defect or imperfection.
→ Line defects: These defects are the irregularities or deviations from ideal arrangement in entire rows of lattice points. These irregularities are also called crystal defects or lattice imperfections. When this defect arises at whole plane then it is called plane defect. These defects are collectively known as dislocations.
→ Point defects: The defects which arise due to the irregularity in the arrangement of atoms or ions are called atomic imperfections. The atomic defects caused by missing of ions from the lattice point are called point defects.
→ Vacancy defect: When some lattice sites are left vacant then such type of defect is called vacancy defect.
→ Interstitial defect: The defect in which constituent particles occupy an interstitial sites or voids. Such defect is called interstitial defect.
→ Schottky defect: When equal number of cations and anions are missing from their lattice site then such defect is called Schottky defect.
→ Frenkel defect: When smaller ion (usually cation) lefts its lattice site and occupies the interstitial site then such defect is known as Frenkel defect.
→ Non-stoichiometric compounds : The compounds, in which the number of cations and anions are not in the same ratio as indicated by their chemical formula, known as non-stoichiometric compounds.
→ F-centres: The holes occupied by electrons are called F-centres. This centre is resposible for colour.
→ Impurity defect: When foreign atoms occupy the lattice site and create defect then such defect is known as impurity defect.
→ Band: The energies of molecular orbitals are so close that they appear to be a continuum, it is called bond or quasi- continuous energy band.
→ Non-conduction band: The completely filled band is called non-conduction band.
→ Valence band: The band, which is formed by lower energy valence orbital or the highest occupied band is known as valence band.

→ Conduction bond: The band, which is formed by the atomic orbitals having slightly higher energy than valence orbital or the lowest unoccupied band is known as conduction band.
→ Energy gap or forbidden zone: Two bands are separated from each other by empty places. These empty places between two bands are known as energy gap or forbidden zone.
→ Diamagnetic substances : The substances, which are weakly repelled by the external magnetic field are called diamagnetic substances.
→ Paramagnetic substances : The substances, which are attracted* by the external magnetic field, are known as paramagnetic substances.
→ Ferromagnetic substances: The substanfeg, which have permanent magnetism even in the absence of the magnetic field, are called ferromagnetic substances.
→ Anti-ferromagnetic substances: The substances, which are expected to possess paramagnetism or ferromagnetism on the basis of the magnetic moments of the domains but actually thair net magnetic moment is equal to zero, are called antiferromagnetic susbtances.
→ Ferrimagnetic susbtances: Substances which are expexted to possess large magnetism on the basis of the magnetic moments of the domains but actually they have small net magnetic moment are called ferrimagnetic substances.
→ Density (d) = \(\frac{\mathrm{ZM}}{(a)^3 \cdot \mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{A}}}\)
Where Z = number of atoms, M = molar mass, NA = Avogadro's Number, a = edge length
→ Various parameters of unit cell and some iirtportant formulae
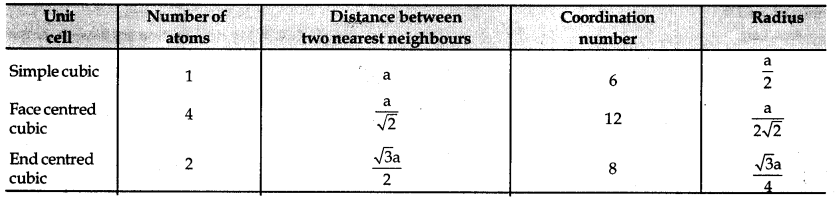 → Packing efficiency = \(\frac{\text { Volume of one sphere }}{\text { Total volume of cubic unitcell }}\) × 100
→ Packing efficiency = \(\frac{\text { Volume of one sphere }}{\text { Total volume of cubic unitcell }}\) × 100
|
Crystal syste |
Packing efficiency |
|
Simple cubic |
52.4% |
|
Body centred cubic |
68% |
|
Face centred cubic |
74% |
|
Hexagonal close packing |
74% |
|
Cubic close packing |
74% |

→ Radius ratio = \(\frac{r^{+}(\text {radius of cation })}{r^{-}(\text {radius of anion })}\)
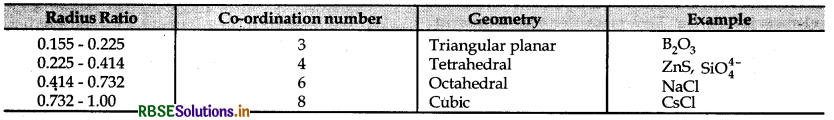 → Tetrahedral void \(\frac{r_{\text {void }}}{r_{\text {sphere }}}\) = 0.225
→ Tetrahedral void \(\frac{r_{\text {void }}}{r_{\text {sphere }}}\) = 0.225
→ Octahedral void \(\frac{r_{\text {void }}}{r_{\text {sphere }}}\) = 0.414
