RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Important Question Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Sonalika and Kalyan sona are varieties of:
(a) wheat
(b) rice
(c) millef
(d) tobacco
Answer:
(a) wheat

Question 2.
Which one of the following is a marine fish?
(a) Rohu
(b) Hilsa
(c) Catla
(d) Common Carp
Answer:
(b) Hilsa
Question 3.
More than 70 percent of livestock population is in:
(a) Denmark
(b) India
(c) China
(d) India and China
Answer:
(d) India and China
Question 4.
Man - made crop Triticale is a hybrid between:
(a) wheat and rye
(b) rice and barley
(c) maize and barley
(d) rice and maize
Answer:
(a) wheat and rye
Question 5.
Zoological name of Indian buffalos is:
(a) Bubafus bubalus
(b) Bos indicus
(c) Bos taurus
(d) Gallus gallus
Answer:
(a) Bubafus bubalus
Question 6.
Murrah is the productive breed of:
(a) chick
(b) goat
(c) cow
(d) buffalo
Answer:
(d) buffalo
Question 7.
Which one is correctly matched?
(a) Apiculture: Honey bee
(b) Psciculture: Silk Moth
(c) Sericulture: Fish
(d) Acquaculture: Mosquitoes
Answer:
(a) Apiculture: Honey bee
Question 8.
Bombay duck is a:
(a) hen
(b) fish
(c) honeybee
(d) cow
Answer:
(b) fish
Question 9.
Rinderpest disease is the disease of:
(a) honey bee
(b) fishes
(c) poultry
(d) cattle
Answer:
(d) cattle

Question 10.
Aseel and Brhma are breeds of:
(a) paultry
(b) fish
(c) cattle
(d) pigs
Answer:
(a) paultry
Question 11.
Which one of the following is the indegenous breed of chickens?
(a) plymouth rock
(b) white legharn
(c) aseel
(d) rhode island red
Answer:
(c) aseel
Question 12.
Exotic breed of honey bee is:
(a) Apis darsata
(b) A. indica
(c) A. florae
(d) A. mellifera
Answer:
(d) A. mellifera
Question 13.
Which one of the following is a viral disease of chickens?
(a) Pullorum disease
(b) Ranikhet
(c) Mycotic disease
(d) Fowl spirochaetosis
Answer:
(b) Ranikhet
Question 14.
Somaclonal variation is seen in:
(a) tissue culture grown plants
(b) apomictics
(c) polyploids
(d) vegetatively propagative plants
Answer:
(a) tissue culture grown plants
Question 15.
Dual breed vareity of cattle is:
(a) jersey
(b) ayrshine
(c) brown swiss
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) ayrshine
Question 16.
Pebrine is a disease of:
(a) cattle
(b) silk worm
(c) hen
(d) fish
Answer:
(b) silk worm
Question 17.
Mule is produced by:
(a) selection
(b) interspecific hybridization
(c) inbreeding
(d) cross - breeding
Answer:
(b) interspecific hybridization
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define animal husbandry.
Answer:
The science of rearing, feeding, caring, breeding and management of domesticated animals is called animal husbandry.
Question 2.
Give one example of each of Indigenous and exotic milch breeds of cows.
Answer:
Indigenous breed: Sahiwal.
Exotic breed: Brown swiss.

Question 3.
How do roughage and concentrate differ from each other?
Answer:
Roughage contains fibres but less nutrients e.g., folder, while concentrate is rich in nutrients, e.g., cereal grains.
Question 4.
Define artificial insemination.
Answer:
Introducing the collected seemen of a good bull into vagina of a healthy cow is called artificial insemination.
Question 5.
What do you mean by posturage?
Answer:
All those flowering plants which provide necter and pollens to the honey bee are called posturage.
Question 6.
Give the nutritive importance of honey.
Answer:
Honey contains sugars like levulose, dextrose and maltose, enzymes, pigments, minerals, vitamins and water.
Question 7.
Name two Indian breeds of buffalo.
Answer:
- Nagpuri
- Murrah.
Question 8.
Name two exotic breeds of cow.
Answer:
- Brown swiss
- Ayrshire.
Question 9.
What is plant tissue culture?
Answer:
Plant tisb culture is a technique of growing plant cells, tissues, organs in an artificial nutrient medium under aseptic conditions.
Question 10.
What is hybrid?
Answer:
Offspring produced by crossing the parents with different characters is called hybrid.
Question 11.
What are two methods of fisheries?
Answer:
Fishery is done in two ways:
- Capture Fisheries which involve catching them from the natural sources.
- Culture fisheries which involve rearing of fishes in the artificial sources.
Question 12.
Name two types of selection.
Answer:
- Natural selection and
- Artificial selection.
Question 13.
Name the variety of wheat which is resistant to leaf stripe rust and hill bunt.
Answer:
Himgiri.

Question 14.
Name the varieties of a cauliflower which are resistant to black rot and curl blight black rot.
Answer:
- Pusa Shubhra
- Pusa Snowball.
Question 15.
Name the variety of cow pea which is resistant to bacterial blight.
Answer:
Pusa komal.
Question 16.
Where is the international centre for wheat and maize situated?
Answer:
International centre for wheat and maize is located in Mexico.
Question 17.
Mention the economic value of Apis indica.
Answer:
Apis indica is a common source of honey and wax. Honey is used as nutritive, and medicines while wax is used in cosmetics and polish industry.
Question 18.
What is blue - revolution.
Answer:
Increasement in production of fish and other aquatic animals is known as blue revolution.
Question 19.
Mention the importance of blue - revolution.
Answer:
Blue - revolution is related to fish production. Fisheries hold an important position in Indian economy. It provide income and employment to fishermen and farmers particularly living in coastal areas.

Question 20.
Select two disease resistant crop varieties from the list of crop varieties given below:
Himgiri, Pusa Gaurab, Pusa Komal, Pusa A - 4.
Answer:
Himgiri and Pusa Komal.
Short Answer Type Questions - I
Question 1.
Which method is commonly used for improving the cattle breed and why?
Answer:
Best method of improving the cattle breed is artificial insemination because of following reasons:
- Several cows (about 300) can be inseminated by the semen of a single bull of good quality.
- Avoid the transportation of animals.
- Semen can be stored at freezing temperature for a long period.
- It gives high rate of successful fertilization.
Question 2.
What is difference between broilers and layers and their management?
Answer:
- Broilers are the poultry birds grown to provide meat while layers are the poultry birds which are grown to provide more egg.
- Management of the layers involves providing enough space, proper light intensity and duration and nutritive feed, while the ration for the broilers is protein rich and with adequate fat and higher amount of vitamins A and K.
Question 3.
Write advantages of bee keeping.
Answer:
Advantages of the bee keeping:
- It provides honey having both nutritional and medicinal importance.
- It provides bee wax which is used in cosmetics, paints, polish etc.
- It provides bee venom which is used to cure gout and arthritis.
- It provides royal jelly which is used as tonic by heart patient and growing children.
Question 4.
Write two examples of each indigenous and exotic breeds of poultry.
Answer:
Indigenous breeds of Poultry: Aseel, Brahma.
Exotic Breeds of Poultry: Plymouth rock and White leghorn.
Question 5.
What do you understand by composite fish culture (poly culture)?
Answer:
Composite fish culture or polyculture is a novel method of fisli farming in which many types of fishes are cultured together into a pond or water body. In India, it is a very old practice in which Catla, Labio and Cirrhinus are cultured in same water body.

Question 6.
Write the name of common diseases of fishes.
Answer:
Common diseases of fishes:
- Viral Haemorrhagic Septicema (VHS).
- Bacterial Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis (IPN)
- Gill rot (Blackning of gills).
- Dropsy (Swollen belly).
Question 7.
Write four objectives of plant breeding.
Answer:
Objectives of plant breeding:
- Higher yield from crops.
- Better quality of plants.
- Disease, insect and pest resistance.
- New varieties adaptive for particular environment.
Question 8.
Write the name of four high yielding varieties of wheat.
Answer:
- Lerma
- Rojo - 64A
- Pusa Lerma
- Sharbati Sonara.
Question 9.
Write the name of four high yielding varieties of maize.
Answer:
- Ganga - 5
- Vikram
- Sabarmati
- Shakti.

Question 10.
As a student of Biology, how will you explain to farmers that Bee-keeping is simple and economically beneficial for them?
Answer:
Beekeeping or apiculture is the rearing, care and management of honey bees for obtaining honey, wax and other substances. It is the practice of maintaining honeybee colonies, usually in hives. Also, beekeeping requires very low investment and can be an additional income for farmers. Wax which is obtained from it has several medicinal uses.
Question 11.
Differentiate between outbreeding and out crossing.
Answer:
Outbreeding: It is the breeding of unrelated animals, either of same breed or of different breed or even different species.
Out crossing: It refers to mating of animals within the same breed, but common ancestors on either sides of their pedigree up to 4 - 6 generation.
Question 12.
Write down the objectives of plant breeding. Mention the main steps in breeding any new genetic crop.
Answer:
Objectives of plant breeding:
- To increase the crop yield.
- To raise plants with desired characteristics.
- To develop a disease - resistant crop.
- To develop plants that can tolerate extreme environmental stress.
The main steps in breeding a new genetic crop are:
- Collection of variability.
- Evolution and selection of parents.
- Cross hybridization among the selected parents.
- Selection and testing of superior recombinants.
- Testing, release and commercialization of new cultivars.
Question 13.
Suggest four important steps to produce a disease resistant plant through conventional plant breeding technology.
Answer:
The four important steps to produce a disease resistant plant through conventional plant breeding technology are:
- Screening of germplasm from resistant sources.
- Hybridization of selected parents.
- Selection and evaluation of the hybrids.
- Testing of new variety.
Question 14.
“Large scale cultivation of Spirullina is highly advantageous for human population”. Explain giving two reasons.
Or
How does culturing of Spirullina solve the food problems of the growing population.
Answer:
- Spirullina is a very fast, easily growing alga that can produce huge quantity of protein even in a small area of land.
- These microbes grow on material like waste water from potato processing plants, straw, molasses, animal mannure and even sewage. Utilisation of these may reduce environmental pollution.

Question 15.
Write down in sequence in the main steps of plant breeding. What is its importance?
Answer:
Objectives of plant breeding:
- To increase the crop yield.
- To raise plants with desired characteristics.
- To develop a disease - resistant crop.
- To develop plants that can tolerate extreme environmental stress.
The main steps in breeding a new genetic crop are:
- Collection of variability.
- Evolution and selection of parents.
- Cross hybridization among the selected parents.
- Selection and testing of superior recombinants.
- Testing, release and commercialization of new cultivars.
Question 16.
You have obtained a high yielding variety of tomato. Name and explain the procedure that ensures retention of the desired characteristics repeatedly in large populations of future generations of the tomato crop.
Answer:
The procedure that ensures retention of the desired characteristics repeatedly in large populations of future generations of the tomato crop is:
Micropropagation: Healthy explants are taken from the tomato plants and grown in sterile conditions in special nutrient medium. The tomato plants produced from tissue culture are genetically identical to the original plant from which they are grown, so they are called somaclones. Also, through micropropagation more number of tomato plants can be produced in a short time period.
Question 17.
How is ‘somatic hybridization’ carried out? Mention one example of a somatic hybrid.
Answer:
Somatic hybridization is the process of fusion of protoplast of different varieties or species of plant on a suitable nutrient medium in vitro to develop a somatic hybrid.
Procedure:
- Single cells from selected plants are isolated.
- Cell walls of these cells are digested by the enzymes cellulase and pactinase to expose the marked protoplast.
- Naked protoplast are isolated from plasma membrane.
- Isolated protoplasts fused to obtain hybrid protoplasts under sterile condition in special culture medium.
- Hybrid protoplasts obtained are cultured in a suitable medium to form new plant.
- Example of Somatic Hybridization: Pamato, produced by fusion of protoplast of tomato and potato plants.

Question 18.
State what is out crossing type of breeding. Mention on what type of cattle this is practicised.
Answer:
Out crossing is the technique of crossing between different breeds. This is the practice of introducing unrelated genetic material into a breeding line with recessive traits. Outcrossing allows for the recessive traits to migrate across a population. The cattles practised this are below average in milk production and growth rate in beef cattle. It overcomes the problems of inbreeding depression.
Question 19.
How is the MOET programme carried out for herd improvement? Explain.
Answer:
Multiple Ovulation - Embryo Transfer Technology (MOET): To overcome the low success rate of natural cross breeding practices, a number of new procedures have been developed to improve the chances of successful production of hybrids. MOET is most important of such producers. MOET involves following steps:
A cow with disirable characters is administrated with FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone). It induces follicular maturation'and superovulation. A number of follicles undergo maturation producing 6 - 8 eggs. As the eggs are mature i.e., ready for fertilization, the female is inseminated with the selected male either naturally or by its semen. The fertilized eggs of 8 - 32 cells stage are recovered non - surgically and transferred to surrogate mothers. The genetic mother is again induced by harmone for further superovulation. This technology is being used to improve breeds of cows, buffaloes, horses, mares, sheeps, rabbits etc. High milk yielding breeds of females and high quality (lean meat with less fat) meat - yielding bull have been obtained with success to increase hard size in a short time by MOET.
Short Answer Type Questions - II
Question 1.
What do you understand by animal husbandry? Explain two main role of animal husbandry in human welfare.
Answer:
The science of rearing, feeding, caring, breeding and disease control of animals is called animal husbandry.
Animal husbandry is a vital skill for farmers and it is a much science as is art. This animal based farming includes cattle, buffalo, goat, sheep, camel, pig etc., that are useful to humans. Extended it includes poultry farming and fisheries. Fisheries include rearing, cata- ching, selling etc., of fish, molluscs (shell fish) and crustaceans (pawwns, crabs etc.). Since time immemorial, animals like bees, silk worms, prawns, crabs, fishes, birds, pigs, cattle, sheep and camel have been used by humans for products like milk, eggs, meat, wool, silk, honey etc.
According to one estimate more than 70% of the world livestock population is in India and China. But the total contribution of these two countries to the world farm produce is only 25% because of very low productivity. Therefore, newer technologies have to be applied to achieve quality and quantity in addition to conventional practices of animal breeding and care.
Role of Animal Husbandry in Human Welfare:
Animal husbandry is a source of livlihood for a great part of population. It is concerned with providing milk, meat, eggs, honey, hide and fibres.
- Milk: Cattle, buffaloes and goats provide us milk. Milk is the best source of animal protein for vegetarians. Milk is also known as ‘complete food’. There are many products produced from milk such as curd, paneer, cheese, ghee, butter and yoghurt. Sheep, camel and yak are also other milk producing animals.
- Meat: It is a protein rich food for non - vegetarians. Meat is obtained from Ducks, Fowl, Sheep, Pigp and Fishes. Consumption of meat is low in India due to its high cost and a large vegetarian population.
- Eggs: Like milk, egg is also a complete food. Fowl and ducks are two major sources of eggs.
- Honey and Wax: These are obtained from the hives of honeybees.
- Fibres: Wool is mainly prepared from the hair of sheep but the hair of certain other mammals like goats, alpacas, rabbit and camel also provide wool.
- Hides: The skin of many animals is used as hide and leather.
- Manure: Dropping and urine of farm animals are used to enrich soil fertility.
- Draught and Working Animals: Horses, camels, bullocks, buffaloes, ass, mules and elephants are used for transport, agriculture and other jobs.
- Bone - meals: Crushed bones of cattle are used to prepare bone - meal for poultry and fertilizer.
- Other Products: Prawn meal, glue, gelatin, pearl etc., are also useful animal products.

Question 2.
(a) Explain how to overcome inbreeding depression in cattle.
(b) List three advantages of inbreeding in cattle.
(c) Name an improved breed of cattle.
Answer:
(a) In order to overcome the cattle from inbreeding depression, selected animals of the breeding population should be mated with unrelated superior animals of the same breed. This helps in restoring the fertility and yield in the cattle.
(b)
- Pure line can be obtained.
- Harmful recessive genes are exposed that are eliminated by selection.
- Superior genes can be accumulated by inbreeding, by eliminating undesirable gene.
(c) Jersey cow.
Question 3.
Write the significance of inbreeding.
Answer:
Mating of good quality animals to produce highly productive and suitable animals for enhancement of overall performance in the subsequent generations and to increase production and profitability is termed animal breeding. In other words controlled mating followed by selection to obtain good quality of domesticated animals is known as animal breeding.
Main aims of animal breeding are:
- Increased yield and better quality of "animal products like milk, eggs, meat and wool.
- Longer productive life and higher reproductive rate.
- Higher growth rate.
- Resistance to various diseases.
Types of Animal Breeding:
On the basis of type of breeds being employed in animal breeding practices, animal breeding is of two types:
Inbreeding and
outbreeding.
Question 4.
Give one example of each indigenous fresh water fishes and marine fishes with their area of avalability.
Answer:
|
Name of Fishes |
Area of Availability |
|
1. Fresh water Fishes |
|
|
(a)Rohu (Labeo rohita) |
North, East and South India |
|
(b) Catla (Catla catla) |
North and South India |
|
(c) Calabasu (Labeo calabasu) |
North and South India |
|
(d) Mirgal (Cirrhinus mrigala) |
All over India |
|
(e) Singhara (Mystuas singhala) |
All over India |
|
(f) Malli (Wallago attu) |
North, East and South India |
|
(g) Singhi (Heteropneustes) |
All over India |
|
(h) Mangur (Clarias batrachus) |
All over India |
|
2. Marine Fishes |
|
|
(a) Bombay duck (Harpodon) |
Coastal Maharashtra |
|
(b) Sardine (Sardinella) |
West and South Coast |
|
(c) Salmon (Aluitheronema) |
East and West Coast |
|
(d) Eel (Angilla) |
Castal India |
|
(e) Hilsa (Hilsa) |
Castal India |
|
(f) Pomfrot (Stromateus) |
Indo-pacific coast |
Question 5.
Differentiate between callus culture and suspension culture.
Answer:
|
Callus Culture |
Suspension Culture |
|
1. In this culture, cell division in explants form callus which is an irregular, unorganised mass of actively dividing cells. |
1. It consists of single cell or small group of cells suspended in a liquid medium. |
|
2. It is maintained on agar medium. |
2. It is maintained in liquid medium. |
|
3. Medium contains growth hormone like auxin and cytokinin (BAP). |
3. It contain only auxin. |
|
4. Callus is obtained with 2 - 3 weeks. |
4. It grows faster than callus culture. |
|
5. It does require to be agitated. |
5. It is to be constantly agitated of 100 - 150 rpm. |
Question 6.
Write three important points to remember on poultry farming.
Answer:
Important point to remember in poultry farming:
- To develop improved poultry breeds to produce good egg layers and good broilers for meat especially by cross breeding programme.
- Good poultry care through maintenance of proper temperature and lightning and hygenic conditions in housing, poultry feeds etc.
- Prevention and control of their diseases and pests.

Question 7.
(a) Write the two limitations of traditional breeding technique that led to promotion of micro propagation.
(b) Mention two advantages of micro propagation.
(c) Give two examples where it is commercially adopted.
Answer:
(a) Limited of traditional breeding technique:
- The traditional breeding for developing disease resistance varieties is limited by the presence of small number of disease resistant genes in pre - existing varieties.
- It is a time - taking process to develop a disease resistant variety via traditional breeding. It may take several years to develop a new improved variety.
(b) Advantage of Micropropagation:
- Micropropagation allows to produce large number of plants in short duration of time.
- Each of the plant produced has the same genetic make up.
(c) This technique is commercially adopted to produce banana and apple.
Question 8.
(i) Write the desirable characters a farmer looks for in his sugarcane crop.
(ii) How did plant breeding techniques help North Indian farmers to developing cane with desired characters.
Answer:
(i) The desirable characters a farmer looks for in his sugar cane crop are:
- High sugar content.
- High yield.
- Thick stem.
- Ability to grow all over India.
- Disease resistance.
(ii) For breeding technique: Crop plants grown in tropical climates are attacked by many pathogens such as virus, bacteria, fungi etc. Crop losses caused by these pathogens are substantial reaching up to 20 - 30 percent and sometimes even total. If the crops are made disease resistant, food production is increased and use of fungicides and bactericides would be reduced. Ability of host plant to prevent the pathogen from causing disease is known as resistance. Resistance of the plant is due to its genetic constitution. If the plant lack this ability the desired change can be brought by plant breeding. Before breeding it is require to know the pathogen and the mode of transmission of important diseases.
Some diseases of crops are:
- Fungal Diseases: Brown / black rust of wheaf red rot of sugarcane late blight of potato etc.
- Bacterial Diseases: Citrus cancer, rust of rice, black rot of crucifers etc.
- Viral Diseases: Tobacco mosaic, Turnip mosaic etc.
Method of Breeding for Disease Resistance:
Comprise of disease resistance in the only means of preventing disease like wheat rust, red rot of sugarcane etc. Disease resistance is the ability of the plant to remain unaffected even when attacked by the pathogens. When the host genotypes do not allow the pathogens to grow and florish over them, they form resistant host lines.
Some methods used for developing disease resistance are as follows:
Conventional Breeding Techniques: This method breeding for disease resistance consists of hybridization and selection. This includes:
- Screening germplasm.
- Hybridization of selected parents.
- Selection and evolution of the hybrids.
- Testing and release of new varieties.
Question 9.
Explain out breeding, out crossing and cross breeding practices in animal husbandry.
Answer:
The breeding of the unrelated animals which may belongs to same breed but having different ancestories; or between different breeds, or between different species, is called out breeding. Outbreeding is of following types:
- Out - crossing: In this type of breeding, the animals of same breed, but not having common oncestory on either side of their pedigree up to 4 - 6 generations are intercrossed. It has following advantages:
- Out - crossing is the best breeding method for animals that are below average in milk production and growth rate in beef cattle.
- It overcomes the problem of inbreeding depression.
- Cross - breeding: It involves interbreeding of superior males of one breed with superior females of another breed. It allows the desirable qualities of two different breeds to be combined. This strategy is used either to develop new superior breeds or to improve the local breeds. A number of animal breeds have been developed by this approach.

Question 10.
(a) Differentiate between inbreeding and out - breeding.
(b) List any three advantages and one important disadvantage of inbreeding practice in animal husbandry.
Answer:
(a) Difference between inbreeding and outbreeding
|
Inbreeding |
Outbreeding |
|
It refers to the mating of closely related individuals within the same breed for 4 - 6 generations. |
It refers to breeding of unrelated animals either of the same breed with no common ancestor or between different breeds or different species. |
(b) Advantage of Inbreeding:
- It increase homozygosity to evolve a pure line.
- Recessive genes are exposed by inbreeding, which are then eliminated by selection.
- Superior gene can be accumulated by inbreeding and thereby eliminating undesirable genes.
Disadvantage: Close inbreeding leads to the reduction of fertility and productivity. This is due to inbreeding depression.
Question 11.
Study the table given below and identify a, b, c, d, e and f:
|
Crops |
Variety |
Resistance to disease |
|
a |
Pusa sadabahar |
b |
|
c |
d |
White rust |
|
e |
Himgiri |
f |
Answer:
(a) Chilli
(b) Leaf curl
(c) Brassica
(d) Pusa Swarnim
(e) Wheat
(f) Hill bunt.
Question 12.
What is plant breeding? Explain the two steps involved in classical plant breeding.
Answer:
Plant breeding is the purposeful manipulation of plant species in order to develop desired plant types that are better suited for cultivation, give high quality and better yields and are disease resistant. Recorded evidences indicate that plant breeding began with the domestication of wild plants 9000-1100 years ago. Almost all our present day crops are derived from ancient domesticated varieties through plant breeding. Classical plant breeding involves crossing of pure lines with desired characters, their hybridization followed by artificial selection to give rise plants with disirable characters of higher yield and resistance to pathogens. With advancements in genetics, molecular biology and tissue culture, plant breeding is now increasingly being carried out by using molecular genetic tools.
Classical plant breeding involves:
- Hybridisation of pure lines.
- Artificial selection for producing plant with desired characters of higher yield or resistance to diseases.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the breeds of cattle.
Answer:
Our country possesses about 26 breeds of cattle and about 10 breeds of buffaloes. They differ in colour, general body build, form of hairs, forehead and geographical distribution. Depending upon the utility, the cattle have been kept in three groups:
- Milch or Dairy Breeds: The cows (Bos indicus) of dairy breeds are high milk - yielding varieties. However, their bullocks are not very useful as draught animals. Examples: Red sindhi, Sahiwal (Punjab and Haryana), Gir (Gujarat) and Deoni. Sahiwal breed of cow is superior to other dairy cows.
- Draught Breeds: Their males are very strong and browny and used in ploughing of fields, transport of goods and pulling carts. Their females provide little amount of milk. Example: Malir, Nageri and Hallikar.
- Dual Purpose Breeds: These breed of cows are intermediate between the above two breeds. Their cows provide moderate milk yield and bullocks are good for drought purpose and ploughing. Example: Sahiwal, Tharparkar, Kankerj, Dangi and Deoni.
- Indigenous Breeds (Indian or Deshi Cows): These include Sahiwal, Red Sindhi, Deoni, Nageri, Hallikar, Kankrej and Tharparkar cow breeds.
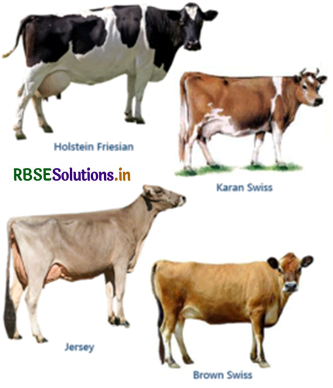
- Exotic Breeds (Introduced to India from other Countries): These include, Halstein - Friesien, Jersey, Ayrshire, Brown Swiss and Red Done.
Breeds of Buffaloes: The best known breeds of Indian buffaloes are Nagpuri, Mehsana (Gujrat). Jaffarabadi, Surti, Bhadawari, Nili Ravi and Murrah (Punjab and Haryana). Of the above breeds, Murrah breeds gives 1800 - 2500 litres of milk, Mehsana gives 1200 - 2500 litres of milk and Surti gives 1600 - 1800 litres of milk per year.
Question 2.
How can be maintan of dairy farm? Write atleast 5 points.
Answer:
Though milk yield of dairy animals depends on the selection of animal breeds, but many other precautions to be taken in order to increase the yield and quality of milk. These precautions are as follows:
1. Shed or Shelter: A good animal shelter is an important aspect of animal husbandry. It should provide protection to the animals from extreme weather conditions and other animals. A shelter should be dry, clean specious and well ventilated. Rigorous cleanliness and hygien (both the cattle and the handlers) are of grand importance. Their shelter should have adequate water and must be maintained disease free. The floor of shelter should be sloping for the drainage of urine and dung removal. Different cattle should be kept separately.
2. Feed: Feeding of dairy animal is most important and directly related with milk yield, therefore, it should be carried out in scientific manner. A balanced feed consists of 15 - 20 kg of fodder as roughage, 4 - 5 kg of grain mixture as concentrate and 30 - 35 litres of water per day. A balanced feed contains appropriate nutrients such as carbohydrates, protein, fats, minerals and vitamins.
3. Water: There should be permanent drinking water supply. The water should be clean and free of germs. The dairy cattle and buffaloes should be provided with water at least three times in summer and two times in winter. The animals should bath regularly.
4. Cleanliness and Hygiene: Proper sanitation to be maintained in the cattle shelter. Hygiene of cattle and milkman is essential particularly during milking, storage and transport. Udders and teats of cattle should be cleaned properly before and after milking. Mechanisation has improved the hygenic condition of the dairy farm.
5. Control of Disease: Transmission of several diseases can be controlled by proper preventive and sanitary measures:
- Several animal diseases affect the health of animal as well as milk producing capacity. Some common animal diseases are: Anthrax, tuberculosis, mastitis (bacterial), foot and mouth disease, rinderpest or cattle plague and blue tongue (viral), coccidysis, trypanosomiasis (protozoan) and ringworm (fungal) disease. These disease can be considerably reduced by vaccination and use of antibiotics.
- Regular visits by veterinary doctor are mandatory for a good dairy farm.
- External parasites such as lice and flies can be controlled by aplying dilute solution of insecticide like lindane.
- Calf losses can be prevented by taking care of the newborn calf.
Question 3.
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Poultry form Management
(b) Poultry breeds.
Answer:
(a) Poultry form Management:
Paultry is the rearing, breeding and caring of poultry birds like chickens, fowls and ducks. Geese and Turkeys are also included in poultry. Egg laying birds are called layers while meat yielding birds are called broilers. More than 90% of poultry farming is based on chicken or domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus).
Poultry in India: In India, annual production of eggs is about 47 billion and 1.5 billion broilers. India ranks third in the world in poultry production. Andhra Pradesh is the largest egg producing state of India.
(b) Poultry Breeds: Aseel, Busra, Brahma and Cochin are pure breeds of India. Of these assel is one of the best table birds with plenty of flavoured flesh. The deshi birds generally have poor egg laying capacity. Some of the exotic breeds utilised for the improvement of egg production are White Leghorn, Rhode Island Red, Plymouth Rock, New Hampshire, Australorp, Orpington, Sussex and Minorca. Some of them are good for meat producing while others are excellent egg layers.
Question 4.
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Artificial Insemination
(b) MOET.
Answer:
(a) Artificial Insemination:
The introduction of semen (sperms) of a high quality bull in the vagina of healthy female by artificial means during heat or oestrous period, is called artificial insemination. For this practice, the semen of a bull of good breed is already collected and stored at freezing temperature. There are more than 600 artificial insemination centres in different parts of our country. Most important of these is located of Veterinary Research Institute of India (IVRI), Izatnagar (U.P.).
Advantages of Artificial insemination: Artificial insamination helps to overcome several problems of normal matiny. It has several advantages:
- Several cows or buffaloes (up to 300) can be inseminated by semen of a single bull.
- It ensure progeny of good quality and also avoid the transportation of animals.
- Sperms can be stored for long period at freezing temperature.
- Contagious diseases do not spread by artificial insemination.
(b) Multiple Ovulation - Embryo Transfer Technology:
To overcome the low success rate of natural cross breeding practices, a number of new procedures have been developed to improve the chances of successful production of hybrids. MOET is most important of such producers. MOET involves following steps:
A cow with disirable characters is administrated with FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone). It induces follicular maturation and superovulation. A number of follicles undergo maturation producing 6 - 8 eggs. As the eggs are mature i.e., ready for fertilization, the female is inseminated with the selected male either naturally or by its semen. The fertilized eggs of 8 - 32 cells stage are recovered non - surgically and transferred to surrogate mothers. The genetic mother is again induced by harmone for further superovulation. This technology is being used to improve breeds of cows, buffaloes, horses, mares, sheeps, rabbits etc. High milk yielding breeds of females and high quality (lean meat with less fat) meat - yielding bull have been obtained with success to increase hard size in a short time by MOET.

Question 5.
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Poultry disease
(b) Bee diseases.
Answer:
(a) Common poultry diseases are as follows:
- Ranikhet disease, fowl pox, Morck’s disease, Bird flu and Hepatitis are viral diseases of poultry.
- Fowl cholera, Salmonallosis, coryza and fowl typhoid are bacterial diseases of poultry.
- Aspergillosis is Fungal disease.
Bird flu is avian influenza which may also attack human beings. It is caused by H5N1 strain of influenza virus. In 1918,, it took the epidemic form and killed millions of people. The disease appeared in 2007 in Maharashtra and in 2008 in Beagal. Bar - headed geese (a migratory bird) is the resevoir of birdflue. Since bird flu undergoes repeated mutation, no safer vaccine or medicine is available. The pathogen of bird flue is airborne. The infected birds are killed and buried under the soil. Raw meat and eggs may contain virus but when cooked they are free from the virus.
Isolation of Sick Birds: In case infection spreads, the sick birds should be isolated and killed.
(b) Bee diseases:
- Nosema disease: It is a protozoan disease caused by Nosema apis.
- Septicema: It is a bacterial disease caused by Bacillus apisepticus.
- Acorine disease: It is caused by a parasite mite Acarapis.
- Fungal disease: It is caused by Aspergillus sp.
Question 6.
How plant breeding can be practicised for developing resistance to insect pest.
Answer:
Insect and pest infection is major cause of large scale destruction of crop plants and their products. Biochemical, morphological or physiological characteristics are used for insect pest resistance in host crop plants are:
- Hairy leaves in several plants are associated with resistance to insect pests. e.g., resistance against jassids in cotton and cereal leaf beetle in wheat.
- In wheat, solid stems lead to non - preference by the stem sawfly.
- Smooth leaved and nector - less cotton varieties do not attract boll worms.
- High aspartic acid, low nitrogen and sugar content in maize lead to resistance to maize stem borers.
Breeding methods for insect pest resistance involve the same steps as those for any other agronomic trait like yield or quality and are discussed earlier. Sources of resistance genes may be cultivated varieties, germplasm collections of the crop or wild relatives. Some insect pest resistance varieties produced by hybridisation and selection.
Question 7.
(a) What is micropropagation?
(b) Briefly explain anther culture, ovule culture and ovary culture.
Answer:
(a) Micropropagation:
It is rapid vegetative multiplication of plant material for agriculture, horticulture and forestry. This process is very fast and highly reproductive. Micropropagation has great advantages because:
- Tissue culture provides rapid multiplication. A small plant bearing 5 - 6 leaves is produced within a few weekly Under favourable condition while under normal conditions may need several months.
- By tissue culture method, large number of offspring on plantlets can be obtained every year.
- The progeny of those plants can be obtained in millions which multiply with difficulty by conventional methods.
- The plantlets obtained by tissue culture (meristem culture) are disease free.
- Cloning can be done through out the year in a very small space under controlled conditions.
- Offspring can be obtained of sterile plants or of rare hybrids of extraordinary characters.
Micropropagation is done by following methods:
- Multiple Shootlet Production: Shoot tips are used for tissue culture and raising mini - plants, shoot tips produce multiple buds in culture medium and bud grows into a shoot. By using rooting hormone the shoot is induced to produce roots. Micropropagation is done in cardamom, potato, almond, orchids, banana, gerberas, Chrysanthemum, Begonia etc.
- Somatic Embryogenesis: The embryos developed from a single somatic cell by tissue culture are known as somatic embryoids. It can be done in carrot, alfa - alfa, Celery etc.
(b) Anther Culture:
By another culture, androgenic haploid embryos or plantlets are produced from the microspores or pollen grains. Guha and Maheswari (1964) obtained androgenic haploid plants by anther culture of Datura innoxia, in culture medium containing kinetin, coconut milk or grape juice.
Ovule and Ovary Culture:
Ovules are excised from the ovary and cultured on the basal medium. By ovule culture, the loss of a hybrid embryo due to premature abscission of fruit may be prevented by ovule culture. Ovary culture has helped in raising interspecific hybrid between sexually incompatible species. Brassica campestris and B. oleracea. Ovaries are excised from the flowers and cultured at the zygote or two - celled proembryo stage for obtaining normal development on culture medium. Coconut milk when used as supplement to the medium promotes formation of fruits that are larger than those formed in vivao.
