RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 4 Reproductive Health
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Important Questions and Answers
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Important Question Reproductive Health
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
A national level approach to build up a reproductively healthy society was taken up in our country in:
(a) 1951
(b) 1961
(c) 1971
(d) 1981
Answer:
(a) 1951

Question 2.
Increased IMR and decreased MMR in a population will:
(a) cause rapid increase in growth rate
(b) result in decline in growth rate
(c) not cause significant change in growth
(d) result in an explosive population
Answer:
(c) not cause significant change in growth
Question 3.
Sterilization techniques are generally fool proof methods of contraception with least side effects. Yet, this is the last option for the couples because:
I. It is almost irreversible.
II. Of the miscenception that it will reduce sexual drive/urge.
III. It is a surgical procedure.
IV. Of lack of sufficient facilities in many parts of the country.
Choose the correct option:
(a) I and III
(b) II and III
(c) II and IV
(d) I, II, III and IV
Answer:
(d) I, II, III and IV
Question 4.
Emergency contraceptives are effective if used within:
(a) 72 hrs of coitus
(b) 72 hrs of ovulation
(c) 72 hrs of menstruation
(d) 72 hrs of implantation
Answer:
(a) 72 hrs of coitus
Question 5.
‘Saheli’ an oral contraceptive for the females was developed by the scientists of which institute?
(a) I.I.Sc., Bangalore
(b) C.D.R.I., Lucknow
(c) LC.M.R., New Delhi
(d) C.S.I.R. New Delhi
Answer:
(b) C.D.R.I., Lucknow
Question 6.
The function of copper - T is:
(a) to prevent mutation
(b) to prevent gametogenesis
(c) to prevent fertilization
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) to prevent fertilization
Question 7.
Test tube baby means when the baby:
(a) develops in test tube
(b) develops from unfertilized Ovum
(c) develops by tissue culture technique
(d) ovum is externally fertilized and implanted in the uterus
Answer:
(d) ovum is externally fertilized and implanted in the uterus
Question 8.
Mala - D is a:
(a) pain killer
(b) contraceptive
(c) narcotics
(d) antibiotic
Answer:
(b) contraceptive
Question 9.
Which is related to males?
(a) aral pills
(b) Tubectomy
(c) Vasectomy
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Vasectomy
Question 10.
Which of the following is the component of oral pills?
(a) Progesterone
(b) Oxytocin
(c) Relaxin
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Progesterone
Question 11.
Amniocentesis is usually done of:
(a) 10 - 12 weeks of gestation
(b) 15 - 16 weeks of gestation
(c) 16 - 20 weeks of gestation
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) 15 - 16 weeks of gestation
Question 12.
Which one of the following is natural contraceptive method?
(a) Use of male condom
(b) Use of ‘Saheli’ pills
(c) Coitus interruptus
(d) Abortion
Answer:
(c) Coitus interruptus
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Expand MMR and IMR.
Answer:
MMR: Maternal Mortality Rate.
IMR: Infant Mortality Rate.
Question 2.
Name the most recent and improved programme in operation in India in reproduction related areas.
Answer:
Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH) Programme.
Question 3.
Define population explosion.
Answer:
At present, human population is raising at the rate of 2 persons per second or 20,000 persons everyday. This high rate of human population growth called population explosion.

Question 4.
Give two examples of natural methods of contraceptions.
Answer:
- Periodic abstinence.
- Coitus interruptus.
Question 5.
Name the surgical methods of contraceptions.
Answer:
Vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females.
Question 6.
What is meant by artificial insemination?
Answer:
It is a technique by which semen collected from the donor (husband) is artificially introduced either into the vagina or into the uterus of the female.
Question 7.
What general term is given to the method in which the male partner withdraws his penis from the vagina just before ejaculation so as to avoid insemination?
Answer:
Coitus interruptus.
Question 8.
Name any copper releasing IUD.
Answer:
Copper T.
Question 9.
Define medical termination of pregnancy (MTP).
Answer:
Intentional or voluntary termination of pregnancy before the foetus becomes viable is called medical termination of pregnancy.
Question 10.
List two most common STDs.
Answer:
- AIDS and
- Gonorrhoea.
Question 11.
Name an IUD that you would recommend to promote the cervix hostility to sperms.
Answer:
The hormone releasing IUDs, e.g., progestasert and LNG - 20 are recommended to promote the cervix hostility to sperms.
Question 12.
Mention the application of invitro fertilization.
Answer:
In vitro fertilization is used in test tube baby method to produce child in case of infertility.
Question 13.
Write down the name of any one natural method of contraceptive.
Answer:
Coitus interruptus.
Question 14.
Write the full form of IVF.
Answer:
The full form of IVF is: In vitro Fertilization.
Question 15.
Name any one intra - uterine device.
Answer:
Multiload - 375.

Question 16.
Our government has intentionally imposed strict conditions for MTP in our country. Justify giving a reason.
Answer:
MTP or induced abortion is the termination of pregnancy due to certain medical issues. Government of India legalised MTP in 1971 with strict conditions to check its misuse, i. e. , to check indiscriminate and illegal female foeticides.
Question 17.
Name any two assisted reproductive techniques that help infertile couples to have children.
Answer:
The assisted reproductive techniques that can help infertile couple to have children are:
- Zygote Intra - Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT).
- Artificial insemination technique.
Question 18.
Mention one positive and one negative application of amniocentesis.
Answer:
Positive Application: Amniocentesis can used to diagnose any genetic disorder in foetus.
Negative Application: It can be used to determine the sex of the foetus and lead to female foeticide.
Question 19.
Why is tubectomy considered as a contraceptive method?
Answer:
In tubectomy, a small part of fallopian tube is cut and tied up to block the passage of ova from ovary to the site of fertilization in fallopian tube. It prevents fertilization so, it is considered as a contraceptive method.
Question 20.
Name the causative agents of the following STDs:
(a) AIDS
(b) Gonorrhoea.
Answer:
(a) Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
(b) Neisseria genorrhoeae.
Short Answer Type Questions - I
Question 1.
Write four problems related to reproductive health.
Answer:
Problems related to Reproductive Health:
- There is little knowledge of personal hygiene and hygiene of reproductive organs. This causes sexually transmitted diseases.
- Early marriage lead to high maternal and infant mortality rate.
- Due to lack of awareness, there has been a rapid increase in population size.
- People encourage beliefs in myth and misconceptions about sex - related issues.
Question 2.
Write four reasons of high population growth.
Answer:
Reasons of high population growth:
- Rapid decline in death rate.
- Decline in maternal mortaiity rate (MMR).
- Decline in infant mortality rate (IMR).
- Increase in number of people in reproductive age.
Question 3.
Expand IUD, MTP, ZIFT and RTI.
Answer:
IUD : IntraUterine Device.
MTP : Medical Termination of pregnancy.
ZIFT: Zygote Intra - Fallopian transfer.
RTI : Reproductive Tract Infection.
Question 4.
Mention any four characteristics that an ideal contraceptive should have.
Answer:
An ideal contraceptive should:
- be easily available,
- be effective and have no side effects.
- not interfere with the sexual derive/desire or the sexual act of the user.
- be user - friendly.
Question 5.
A woman has certain queries as listed below, before starting with contraceptive pills. Answer them.
(a) What do contraceptive pills contain and how do they act as contraceptives?
(b) What schedule should be followed for taking these pills?
Answer:
(a) Contraceptive pills contain progesterone or progesterone - oestrogen combination. They act by either of the following ways:
- inhibit ovulation.
- inhibit implantation.
- After quality of cervical mucus to prevent or retard entry of sperms.
(b) Contraceptive pills should be taken daily for a period of 21 days starting within first five days of menstrual cycle.
Question 6.
Why is the term test tube baby a misnomer?
Answer:
The term test tube baby is a misnomer because the baby is not developed in the test tube; only fertilization is carried out in such devices in the laboatory conditions (in vitro). The fertilized egg (zygote) or early embryo is then transferred into the fallopian tube or uterus of the
mother where it develops and a normal baby is born.
Question 7.
Within what age group sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are reported to bery high. Mention three practices to avoid them.
Answer:
In the age group of 15 - 24 years, STDs are reported to be very high. Following are the three practices to avoid them:
- Always use condom during sexual intercourse.
- Avoid coitus with unknown partners or multiple partners.
- In case of any doubt, medical help should be taken for early detection.
Question 8.
Write the rate of hormones in contraception.
Answer:
In contraception, the hormones - progesterons or progesteron - oestrogen combinations play an important role. They are used in the form of tablets or pills. They inhibit ovulation and hence implantation. They are also used by females as injections or implants under the skin. Their mode of action is similar to that of pills but their effective periods are longer.
Question 9.
List some common sexually transmitted disease and name their causal organisms.
Answer:
Some common sexually transmitted diseases and their causal organisms are listed below:
|
STDs |
Casual Organism |
|
1. AIDS |
1. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) |
|
2. Genetal Herpes |
2. Herpes simplex virus |
|
3. Genital Warts |
3. Human papilloma virus |
|
4.Syphilis |
4. Treponema pallidum |
|
5. Chalmydia |
5. Chalmydia trachomatics |
|
6. Gonorrhoea |
6. Nissaria gonorrhea |
|
7. Trichomoniasis |
7. Trichomonas vaginalis |
Question 10.
Differentiate between in - vitro and in - vivo fertilization.
Answer:
The fertilization of ovum outside the body of female almost in the similar conditions as those in the body is known as in - vitro fertilization.
in - vivo fertilization is the method of sexual reproduction where the fusion of sperm and egg takes place inside the body of the female.
Question 11.
Describe the technique by which chromosomal disorder in a developing foetus can be detected.
Answer:
Amniocentesis is a technique by which chromosomal or genetic disorder in a developing foetus can be detected. This is based on the chromosomalíkaryotype pattern in the cells found the amniotic fluid surrounding the developing foetus. Amniotic fluid contains cells and molecules shed by the foetus. The chromosomes of foetal cells can also be used to find out the sex of the foetus and abnormalities if any.
So, if an abnormality is found, the mother can start the treatment or get the foetus aborted.
Question 12.
What suggestions will you give to infertile couple to produce children?
Answerw:
The inability of a couple to produce a baby inspite of unprotected sexual intercourse is termed as infertility which can arise due to congenital disease, physical, physiological and immunological causes. The corrective and the diagnoestic measures of few of these disorders can be carried out in specialized health care centres. Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ARTs) are the special techniques that can assist infertil techniques that can assist infertile couple to bear children.
Some methods assisting infertile couples to have children are listed below:
- In vitro fertilization: Embryo transfer (IVF - ET).
- In vitro fertilization: Surrogacy.
- Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT).
- Artificial insemination (AI).
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Question 13.
After a brief medical examination a healthy couple came to know that both of them are unable to produce functional gametes and should look for an ‘ART’ (Assisted Reproduction Technique). Name the ‘ART’ and the procedure involve that you can suggest to them to help them bear a child.
Answer:
The Assisted Reproduction Technique (ART) that would assist the couple to bear a child is in vitro fertilization or test tube baby programme. In this process, ova from wife and sperms from the husband are collected and fused to form zygote in the laboratory under same conditions as in the uterus. This is called in vitro fertilization.
Zygote or early embryo is then transferred into fallopian tube or uterus for further development. This process is called zygote or embryo transfer. It can be Zygote Intra - Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) or Intra Uterine Transfer (IUT).

Question 14.
An infertile couple is advised to adopt test tube baby programme. Describe two principal procedure adopted for such technologies.
Or
Explain the Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer Technique (ZIFT). How is Intra Uterine Transfer (TUT) Technique different from it.
Answer:
Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZTFT) is the technique in which zygote or early embryo (produced by in vitro fertilization) with up to 8 blastomere is transferred into the fallopian tube of female. On the other hand in Intra Uterine Transfer (lUT), embryo with more than S blastomeres is transferred into the uterus. These are two principal procedure adopted for test tube baby programme.
Question 15.
A childless couple has agreed for a test tube baby programme. List only the basic steps the procedure would envolve to conceive the baby.
Or
(i) Give any two reasons for infertility among young couple.
(ii) Test tube baby programme is a boon to such couples. Explain the steps followed in the procedure.
Answer:
(i) The reasons of infertility in young couples can be physical, congenital disease, use of drugs, immunological or even psychological factors.
(ii) In test tube baby programme:
- Ova from wife or donor female and sperms from husband or donor male are taken.
- Sperm and ovum are allow to fuse under simulated condition in the laboratory. (called in vitro fertilization).
- Zygote or embryo up to 8 - celled stage is transferred into fallopian tube (called ZIFT).
- Embry with more than 8 - celled stage is transferred into uterus (called IUT).
Question 16.
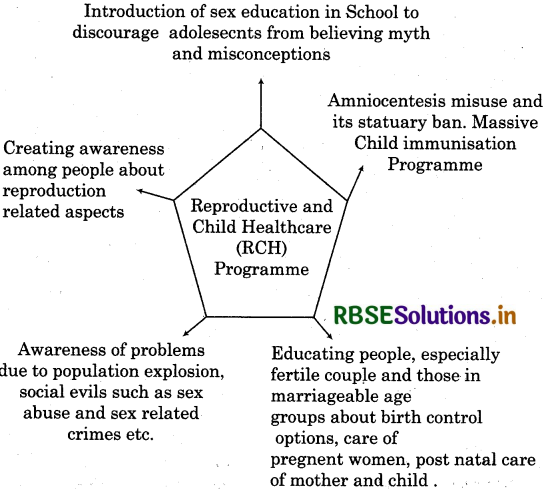
Mention the problems that are taken care of by reproduction and child health care programme.
Answer:
Reproduction and child healthcare (RCH) programme cover wide range of reproduction related areas. They include:
- Creating awareness among people about various reproduction related aspects.
- Support for building up a reproductively healthy society by providing increased medical facilities, better postnatal care, better detection and cure of disease like STDs, etc.
Question 17.
Name an oral pill used as a contraceptive by human females. Explain how does it prevent pregnancy?
Or
Why is ‘Saheli’ a well - accepted contraceptive pill?
Answer:
‘Saheli’ is a non - steroidal contraceptive pill used by most of the females to space children. Saheli inhibits ovulation and implantation. It alters the quality of cervical mucus to prevent the entry of sperms into cervix.
Question 18.
(a) Expand IUD.
(b) Why is hormone releasing IUD considered a good contraceptive to space children?
Answer:
(a) IUD: Intra Uterine Device.
(b) IUDs are considered a good contraceptives because:
- They make the uterus unsuitable for implantation.
- They increase the phagocytosis of sperms within uterus and the Cu ions released suppress sperm motility and the fertilising capacity of sperms.
Short Answer Type Questions -II
Question 1.
Describe three manners in which fertilization of human ovum by a sperm can be prevented.
Answer:
Fertilization of human ovum by a sperm can be prevented by the following methods:
- Spermicidal creams, jellies and foams are introduce in vagina to kill the sperms.
- Condoms act as barriers made of thin rubber or latex sheath. They are used to cover the penis in the male or vagina and cervix in females.
- Diaphragm, cervical caps, and vaults are the barriers made of rubber that are introduced in the female reproductive tract to cover cervix.
Question 2.
What cause infertility in men and women?
Answer:
Causes of infertility in Men: The most common male infertility causes include azoospermia (no sperm cells are produced) and oligospermia (few sperm cells are produced). Sometimes, sperm cells are malformed or they die before they can reach the egg. These reasons for infertility could be physical, congenital, diseases, drugs, immunological or even psychological.
Causes of Infertility In Women: The most common female infertility factor is an ovulation disorder. Other causes of female infertility include blocked fallopian tubes, which can occur when a woman has pelvic inflamatory disease. Congenital anomolies involving the structure of the uterus and uterine fibroids are associated with repeated miscarriage. Aging is also an important factor in female infertility. The ability for
ovaries to produce eggs declines with age, especially after age 35.
Question 3.
Write about various problems related to reproductive health.
Answer:
Problems Related to Reproductive Health:
1. Prohibitions: In our India religions, traditions and society set up do not permit dissemination of knowledge about family planning and reproductive health to children.
2. Early Marriage: Children are married as soon as they attain puberty in many parts of our country. Child marriage results in having children even when the parents themselves are in their early adulthood.
3. Career: Early marriage may not allow the young couple especially the women to pursue studies. This result in arrest of career of the husband and more particularly of the woman due to household work.
4. Teen - age Mother: The teen - age mother may not be physically fit to give birth, bear child and nourish infants properly. The children born to parents married early may have various deformities.
5. Maternal Mortalhy Rate (MMR) and Infant Mortality Rate (IMR): Due to married early the chances of maternal and infant mortality rates rise. Complications of pregnancy, child birth and abortions are major reasons of female’s mortality between 15 and 19 years of age.
6. Personal Hygiene: Couples married early and uneducated couples hardly have any knowledge of personal hygiene and hygiene of reproductive organs. The incidence of infection of sexually transmitted diseases is maximum in young people of 15 - 24 years of age.
7. Health of Woman: Due to poor diet and lack of care, woman in our society isually remain weak, anaemic and are prone to several diseases.
8. Population Growth: There is a surge or explosion in population growth due to lack of knowledge and also no measures to check the growing population.
Question 4.
Write about our government efforts to solve reproductive health problems.
Answer:
Government Efforts to Solve Reproductive Health Problems:
Our government has framed and iniplemented various action plans, to develop anti establish reprtaluctively healthy society. These action plans are as follows:
- Maternity and Child health (MCH) and family planning.
- Family planning programme.
- Universal 1m munisation Program me.
- Indian government has established more than 5000 community development blocks since 1958. Each block has a primary health care centre and then subcentres which provide basic healthcare to persons of its centre.
Question 5.
Write a short note on population explosion.
Answer:
Population Explosion:
The increased health facilities along with improved quality of human life in the last over hundred years, had an explosive impact on the growth of human population. Consequently, human population started increasing of a striking rate. At present human population is increasing at a rate over two persons every second or about 2,00,000 persons every day or 8 million persons every month or over 70 million persons every year. This high rate of human population growth is termed as population explosion. The world population was about 2 billion (2,000 million) in 1900 AD, increased to about 6 billion (6,000 million) by 2001 and 7 billion (7,000 million) on 2011.
A similar trend was observed in India too. In 1901 the population of India Was 238 million, which increased to 350 million at the time of our independence in 1947, crossed 1,000 million in 2000 and now in 2011 it stands at above 1.2 billion (1200 million). It means every 6th person in the world isan Indian. India’s population grew five times in last 100 years. Projections are that India will have 1,613.8 million persons by 2050. While during the last century. World population raise by slightly more than three times. Today India has 18% of the world population with only 2.4% of the land area.

Question 6.
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Periodic abstinance
(b) Coitus interruption
Answer:
(a) Safe Period (Rhythm Method or Periodic Abstinance Method): In this method couples of reproductive age are advised to avoid or abstain from coitus from day 10th to 17th of the menstrual cycle a few days before and after ovulation. Since the chance of fertilization are very high during this period, it is called the fertile period. Conception could be prevented by abstaining from coitus during this priod. Rhythm method is based on the following facts:
- Ovulation occurs on about the 14th day of menstruation in a 28 days menstrual cycle.
- Ovum remain alive for 1 - 2 days only.
- Sperms survive for about 3 days in the female genital tract.
Since only a few women have regular menstrual cycle and the actual time of ovulation can not be predicted, the effectiveness of this method is limited though it does not have any side effects.
(b) Coitus Interruption or Withdrawal Method: This is the oldest method of birth control. In this male partner withdraws his penis from the vagina just before ejaculation to avoid insemination in the females vagina. This method being used over 2000 years. This method is also not fully effective since there is every possibility of some sperms passing into the vagina.
Question 7.
Write about gonorrhoea diseases on the basis of following points :
(i) Causative organism
(ii) Symptoms
(iii) Transmission
(iv) Treatment.
Answer:
(i) Causative Organism: It is caused by diplococcus bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoea.
(ii) Symptoms: The bacterium lives in genital tract producing a pus containing discharge, pain over genetalia and burning during urination. It may lead to arthritis, and eye infections.
(iii) Transmission: The bacterium transmitted through sexual contact, common toilets and undergarments.
(iv) Treatment: For this penicillin and Ampicillin are effective drugs.
Question 8.
(i) List any four characteristics of an ideal contraceptive.
(ii) Name any two intrauterine contraceptive devices that affect the motility of sperms.
Answer:
(i) An ideal contraceptive must have the following four characteristics:
- It must be easily available.
- It must be reversible with little or no side effects.
- It must no interfere with the sexual derive/desire or sexual act of the user.
- It must be safe and user friendly.
(ii) Cu - T and Cu - 7 are two examples of IUDs that affect the motility of sperms.
Question 9.
Name and explain the surgical method advised to human males and females as a mean of birth control. Mention its one advantage and one
disadvantage.
Answer:
The surgical methods advised to human males and females are vasectomy and tubectomy respectively.
Surgical Method or Permanent Methods: Surgical methods are also called sterilisation. It provides a permanent and sure method of birth control. It is called vasectomy in man and tubectomy in woman.
1. Vasectomy: It is the surgical removal of a part of vas deferens in miles. For this, a small incision is made in the side of the scrotum and a portion of vas deferens is removed and then both cut ends are ligated. This prevents the sperms to reach urethra, hence the semen of such a man does not have sperms.
2. Tubectomy: It is also the surgical removal of a small portion of fallopian tubes in a female. For this a small incision is made in the abdomen or this process is done through vagina. The cut ends are ligated. This prevents the ovulated egg from entering the fallopian tube.
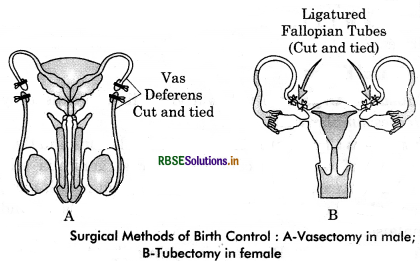
The operations for both vasectomy and tubectomy are minor, usually performed under, local anesthesia, give very little discomfort, and do not affect the sexual life. Both vasectomy and tubectomy are very effective but their reversibility is very poor.
Question 10.
Awoman has certain queries as listed below, before starting with contraceptive pills. Answer them.
(i) What do contraceptive pills contain and how do they act as contraceptives.
(ii) What schedule should be followed for taking these pills?
Answer:
(i) Oral contraceptive pills contain either progesterone or progesterone - oestrogen combinations.
- Inhibiting ovulation.
- Altering the quality of cervical mucus to prevent the motility of sperms in female genital tract.
(ii) The oral contraceptive pills are to be taken daily for 21 days, preferably within the first five days of menstrual cycle. After the onset of menstruation cycle i.e., 5 - 7 days, this process is to be repeated in the same pattern (again for 21 days). This schedule is to be followed till the women wants to avoid conception.
Question 11.
What do you understand by medical termination of pregnancy? Explain the safe period to MTP.
Answer:
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP):
Intentional or voluntary termination of pregnancy before the foetus becomes viable is known as Medical Termination of pregnancy or Induced abortion.
Incidence: MTP is one of the most widely used measure of birth control in the world. Nearly, 45 to 50 million induced abortions are done every year. This accounts for about 1/5th of the total number of conceived pregnancies in a year.
Period of Safe time for MTP: Abortion is safe during first trimester of pregnancy (i.e., up to 12 weeks of pregnancy). Induced abortion is riskier in 2nd trimester of pregnancy because foetus becomes intimately associated with the maternal tissue. Medical termination of pregnancy is done to avoid birth of unwanted child concieved due to:
- Casual unprotected intercourse.
- Pregnancy due to rape cases.
- Failure of contraceptive during intercourse.
- In such cases where continuation of pregnancy may pose threat to the foetus, mother or both.
Indian government legalised MTP by an act (amendment). The medical termination of pregnancy Act, 1971 to prevent unnatural maternal deaths due to unsafe abortions by untrained persons (about 9% of total meternal deaths. MTP is usually performed after the testing the sex of the foetus by amniocentesis or sonography. It leads a large scale female focticide and complications. To prevent this malpractice of female foeticide, government enacted a law, Prenatal Diagnostic Techniques (Regulation and prevention of misuse) Act, 1994, with amendments in 2003. It prohibits prenatal sex determination. Violation or contravention of this act is punishable with imprisonment of 5 years and a fine of 50.000 to 1.00.000 Rs. along with cancellation of registration.
Question 12.
What is infertility? What are the reasons of infertility in males and females?
Answer:
Infertility is the inability to conceive or produce children in spite of unprotected sexul cohabitation. The term infertility is not synonym of sterility which means complete inability to produce children.
Reason of Infertility: There are a number of causes of infertility in the human beings. These can be categorized as physical, congenital, drugs, immunological and psychological.
Infertility In Males: A fertile male deposite about 3 - 4 ml semen per ejaculation containing over 200 million normal, motile sperm. A male human is infertile if the semen has low sperm count or abnormal sperm structure or poor sperm motility. The causes of male infertility may mclude Cryptorchidism (Failure of testes to descend into scrotum), hyperthermia (higher temperature in scrotal sac due to tight undergarments), blockage of vas deferens, alcoholism which inhibits spermatogenesis), infection with mumps virus after puberty, deficiency of genadotropin, ejaculation defect, exposure to radiation etc.
Infertility in Female: In females infertility may be due to irregular ovulation or no ovulation or defect in the genital tract like impared motility of fallopian tube, defective uterine endometrium, defect in the cervix, defective vaginal of deficiency of sex hormones.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write down strategies related to reproductive health.
Answer:
The various strategies of reproductive health in human beings are as follows:
1. General Awareness about Reproduction: With the help of audio - visual aids, print media (e.g., newspaper and Magazine) and primary health centres, both government and non - government agencies are engaged in creating awareness among people about various aspects of reproduction. Parents, other close relatives. friends, teachers can play important role in dissemination of 8uch information.
2. Sex Education: Appropriate sex education in schools can help in removing myths and misconceptions about sex related aspects. It should also provide education about various sex - related problems, reproductive organs, changes during adolescence, harm of early sex and hygienic sex practices.
3. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD’s): Awareness programmes about sexually transmitted diseases such as AIDS, Gonorrhoea, Gential herpes etc., would help people, especially adolescents, to lead a reproductively healthy life.
4. FanillyPlanrdng : Through audio, video and other media, the young people should be provided knowledge about benefits of a small family. The family planning centres can play an important role in maintaining reproductive health.
5. Birth Control Devices and Care of Mother and Child: Couples in the reproductive age and youth in marriageable age group should be communicated about available birth control devices, care of pregnant mothers, postnatal care of the mother and child, importance of breast feeding etc.
6. Information about Reproduction Related Problems: Effective action plans to attain reproductive health require better infrastructural facilities, professional experts advise and material support. These are required to solve problems of infertility, pregnancy, contraception, abortion and sexually transmitted diseases.
7. Pregnancy : Premarital sexual intercourse without using any contraceptive measure is on the increase among adolescence. This rešults in unwanted pregnancy. Unmarried pragnent girls face humiliation, disrespect and suffer from loss of self - esteem. They give up their studies or their career. They visit illegal abortion clinics and risk their life. The adolescence require to be well informed about abstinence from unprotected intercourse, use of contraceptives and family planning.
8. Bon on Foetal Sex Determination: Amniocentesis is a foetal sex determination and disorder diagnostic test based on the chromosomal pattern in the amniotic fluid surrounding the developing embryo. Amniotic fluid contains cells from the skin of the foetus and other sources. These cells can be used to determine the sex of infant, to identify some abnormalities in the number of chromosomes and to detect certain biochemical and enzymatic defects.
It is established that the foetus is likely to suffer form a serious incurable congenital defect, the mother should get the foetus aborted. But now a days amniocentesis is being misused. It is being used to kill the normal female foetus. It is legally
banned the determination of sex to avoid female foeticide.
9. Populalon Explosion: Awareneiw require to be created about problems due to uncontrolled population growth. social evils like sex - abuse and sex - related crimes enabling people to take up necessary steps to check them.
10. Knowledge of Social Evils relaeed to Sex: Awareness about harmful social, physiological and behavioral effects of sex - abuses and sex - related crimes and drugs, alcohol and tobacco etc., is also needed.
11. Marriageable Age: Early marriage have been legally banned in India. The minimum marriageable age for girls and boys is 18 years and
21 years respectively.
12. Research: Researches in reproductive health area should be encouraged and supported to find out new method. ‘Saheli’ a new oral contraceptive for the flrnales was developed by scientists at Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI) in Lucknow, India.

Question 2.
MCH and family planning is one of the main an important programmes of health centres. What are the aspects of child and mothers health taken care by these health centres.
Or
Write a detail note on Maternity and child Health (MCH) programme and family planning.
Answer:MCH and family planning is one of the main and importgant programmes of health centres. Under this programme, the primary health centres and their subcentres take care of following aspects of child and mother's health:
1. Health centres provide necessary information, guidance and assistance to the mothers before and after delivery so that they may properly look after themselves and the infants. Pregnant women reequire more nutritious food than the other because some part of the food they take is ussed by their foetus to grow. They specifically require minerals (calcium, iron etc.) and vitamins. They should avoid the use of tobacco, alcohol and frugs as these substances may cause abnormalities of form or function in the infants.
Women should keep themselves happy all the time and normally continue moderate activitu during pregnancy. Medicines should be taken under strict supervision of doctor or should be generally avoided as far as possible because some of them may be teratogenic (abnormality causing).
2. Health centres ensure safe dillivery and postnatal care of infant. They have trained midwives (Dais) and qualified doctores for this aim. The women shjould prefer delivery in the hospitals having qualified doctors and nurses and proper facilities. Selivery by untrained midwives may be of serious conswquences.
3. The health centres ara also responsible for immunisation of infants and prophylaxis against anaemia and vitamin deficiency.
4. Abnormal conditions and pregnancy related diseases are detected early and pregnancy related health centres.
5. Health centres take up such programmes such as immunisation of infants against smallpox, tuberculosis and inoculation against diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough etc. World Health Organisation (WHO) launched Universal Immunisation Programme for immunising infants and children world over. In our country this programme was launched in 1985.
6. Health centres arrange for milk - feeding programmes. Mother's milk provides food and more importantly antibodies to the infant for fighting infection. The infant do not have antibodies of their own. It has been found that the breast feeding infants are less prone to certain allergies later in life than the bottle fed infants.
7. Health centres also provide information and knowledge to the new couple about the advantage of small families and gapping between successive birth to have a pregnancy when the reproductive system is fully mature physically as well as functionally is better for the mother and her baby.
Question 3.
Write the reason for high population growth in India.
Answer:
Reasons for the increase in human population in India are:
1. Decline in Death Rate: Due to better healthcare facilities, reduced Maternal Mortalily Rate (MMR) and reduced Infant Mortality Rate (IMR), there has been a steady decline in death rate. In our country the death rate has declined from 44.1/1000 in 1901 to 8.7/1000 in 2001.
2. Slower Decline in Birth Rate: The birth rate is decreasing at a much slower rate as compared to decrease in death rate. The population growth rate in our country is about 17/1000 or 1.7% at present. At this growth rate, India’s population will again double in next 33 years.
3. Increase In Longevity: Longevity (longer lifespan) is also a cause of population growth in our country. In longer life span, the chances of reproduction increase result increase in population. Life expectancy was 34 years in 1901, which has increased to 65 years in 2001.
4. Control of Diseases: Control of communicable diseases e.g., plague, cholera etc., as well as decline in the incidence of dreaded diseases such as malaria, tuberculosis etc., have reduced the death rate and increased the average human life span.
5. Religious Beliefs: In many communities in our country, traditional beliefs do not permit adoption of small family norm. Some communities believe that the big families are better than that of small one.
6. Lack of Eduction: Literacy in women has brought awareness about the benifits of a small family. Educated persons understand the importance of spacing children, 2 - children norm, their proper education and uobringing.
7. Early Marriages: Despite the ban on child marriages, it is a common arrangement in villages. This results in the birth of more but unhealthy children. Such children not only add to the population but are a liability to the community.
8. Advancement In Agriculture: Improve agricultural techniques as well as development of high yielding, disease resistant varieties have increased food production for the rising human population. Advancement in the techniques of animal breeding have also increased food production of animal origin (such as milk, meat, egg). These means have resulted in generation of surplus food for emergency situation thereby decreasing death rate.
9. Protection from Natural Risks: Advancement in scientific resources has led people to live better and protected life. Living in houses in villages and cities with better hygienic conditions has protected people from adverse changes in climatic conditions, diseases as well as from wild animal. This has decreased death rate.
10. Government Efforts: To ensure food supply to all by introducing public distribution system, checking harding and maintenance of reserve stocks has helped poors to have healthy stomachful meal.
11. Poor Access to Contraceptive Services: In rural areas, por availability of contraceptive services results in unwanted birth.
12. Medical FacIlities: Improvements in medical facilities have also helped in reducing death rate.

Question 4.
Write the consequences of over population.
Answer:
Over population has resulted in serious problems like depletion in natural resources, various socio - economic problems, food and energy crisis and ecodegradation. Over population also leads to individual family problems as well. These all types of problems are discussed below:
(A) Socio - economic Problems: Over population, creates many socio - economic problems, these are as follows:
- Food Supply: Over population has resulted in large families. These large families with limited means are unable to provide balanced diet to their children. As a result, the latter suffer from malnutrition and grow into less fit members of the society.
- Pressure on Land: Increasing population increases demand for more food, industries, more clothing and more housing. All these activities require more land which comes through deforestation. This results in ecodegradation and desertification of land.
- Unemployment: Unemployment increases with the increase in human population for lack of poor educational facilities and job opportunities. Over population has resulted in lowering of education standards, imability of afford higher education to all the children. This leads to crimes and lawlessness among the unemployed youths.
- Standard of Living: Over population leads to shortage of essential things, thereby resulting in shortage and price rise. Large families with single earner after remain poor since they can neither maintain decent standard of living nor provide well education and medical facilities to the children.
- Slum Area: Increasing population results in the expanding of slum area in big cities.
- Infrastructure: All the resources of the country are consumed in meeting the extra requirements of increasing human population. These including drinking water, housing, transport, educational institution, hospitals and essential things. As a consequence, very little is left for the development of infrastructure.
(B) Energy Crisis: Increasing population has created greater demand of energy - fossil fuel (petroleum, natural gas and coal), firewood and electricity. Rapid industrialisation and urbanisation have added to the problem. Alternative sources of energy like solar energy, muscle power, nuclear energy, wind energy etc., may solve this problem.
(C) Ecodegradation: Over population causes ecodegrad ation in more than one way:
1. Pollution: Rise in population has caused environmental pollution - water, air and land. This is seriously affecting the human health.
2. Sanitation: It is not possible to maintain sanitation in congested areas as is evident from urban slums.
3. Deforerntion: Because at large - scale deforstation soil erosion has increased, and floods and droughts cause erosion of fertile lands.
4. Natural Resources: There is excessive pressure on natural resources in order to meet the demands of the increasing population. Thus over population may cause mental tension, rise in heart diseases, ill health and misery.
Question 5.
What are the measure to be used population control.
Answer:
Over population is the barrier in the development and progress of any country. Natural resources are suffered by the over population. Presently, human population is doubling every 35 years. If this continues, soon the earth will be over - crowded with human beings. Human has started realising his fate and has initiated plans to stop this rate of increase by adopting following measures:
Planned Control of Population: Decline in birth rate is the only practicable and direct method to check over population in the world. It can be done in the following three ways:
1. Education: People, especially those are in the reproductive age group, should be educated about disadvantage of over population and advantages of small family. Educational institutes and mass media (e.g., te1evision, . radio, newspapers, magazines etc.) are the means by which people can be educated in this compaign. The awareness in the people will certainly help to check population growth.
2. Increasing Marriageable Age: To raise the age of marriage is a much effective way to control the population. At present, marriageable age for
female and males are 18 years and 21 years respectively. If the marriageable age is reasonably increased, it can definitely help to check population growth.
3. Family Planning: Indian government, in an attempt to check high birth rate, started voluntary approach towards birth control programmes. This programmes initially failed in a view of people’s traditional resistance to birth control measures. In 1976, Indian government started tentative programme of compulsory sterilization which required one parent to undergo sterilization after a couple had produced two children. This programme was later again replaced by voluntary approach alongwith steps to educate people regarding benefits of family planning programmes.
Question 6.
Name the methods/devices to be used for birth control. Give any two natural methods used to birth control.
Answer:
The regulation of conception by preventive measures or devices to limit the number of children is known as birth control. Family planning is a programme aimed at limiting the size of the family by spacing the birth of children and prevention of some conceptions. The main aim of birth control measures to check the population growth rate.
1. Contraceptions: It is a permanent or temporary measure to prevent pregnancy. Government is motivating young couples through education and mass media.
2. Contraceptives : These are the devices that prevent conception without interfering with the reproductive health of the individuals. The characteristics of an ideal contraceptive device are:
- It should be comfortable and easy to use.
- It should not have any side effects.
- It should in no way interfere with sexual drive, desire or the sexual act of the user.
There are various methods of contraception. These are Natural/traditional methods, Barrier methods, IUDs, Oral contraceptive, Injactables, Implants and Surgical methods.
1. Natural/Traditional Methods: These methods work on the principle of avoiding chances of sperms and ovum meeting. These methods do not have any device, medicine or religious sanction. These includes safe period, coitus interruption and lactation amenorrhea.
- Safe Period (Rhythm Method or Periodic Abstinance Method)
- Coitus Interruption or Withdrawal Method
- Lactation Amenorrhoea
2. Barrier Methods: These are mechanical methods by which sperms and ovum are prevented to come in physical contact. So that fertilization does not takes place. The common barrier methods are condom, fem shield, diaphragm, cervical cap and vault cap.
- Condom
- Fern Shield
- Diaphragm
- Cervical cap
- Vault cap
3. Chemical Methods: These methods include use of contraceptive, available in the form of creams, paste, jelly, foam, tablets, aerosol foam etc. They have spermicides (sperm killing agents) such as citric acid, lactic acid, potassium permaganate and zinc sulphate. Application of cream or tablets in the vagina of female before intercourse kills the ejaculated sperms.
4. Intrauterine Devices (IUDS): These devices are made of plastic, netal or a combination of the two which are inserted into the uterus of the female by a doctor. Different types of IUDs are available now a days. These may be grouped as non - medicated IUDs (i.e., Lippes loop), copper releasing IUDs and the Hormone releasing TUDs.
- Non - Medicated or Inert IUDs
- Copper Ts (Copper Releasing IUDs)
- Hormone Releasing IUDs
5. Oral Contraceptives (Oral Pills): These are used in the form of tablets by women and, therefore commonly called ‘oral contraceptive pills’. These pills contain small amount of either progesterons or a combination of progesteron - oestrogen. This is the most common contraceptive method used by women. Birth control pills check ovulation in female by inhibiting the secretion of fallicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and lutening hormone (LH) that are necessary for ovulation. Hence, no eggs are released in a woman taking the pills and conception can not occur.
Pills are normally taken daily for a period of 21 days starting preferably within the first five day of menstrual cycle. Its intake has to be repeated a gap of 7 days (period ot menstruation) in the same pattern till the women desire. The birth control pills have some side effects such as nausea, brest tenderness, weight gain and break - through bleeding (slight blood loss between mentrual period) and high blood pressure. On the other hand, the oral contraceptive pills reduces the chances of certain types of cancer occur in their users.
Question 7.
Your school has been selected by the Department of Education to organise and host an interschool seminar on “Reproductive Health problems and Practices.” However, many parents are reluctant to permit their wards to attend it. Their argument is that the topic is too embarrassing. Put forth four arguments with appropriate reasons and expanation to justify the topic to be very essential and timely.
Answer:
The parents should encourage their children to attend such seminar as they will get right informations regarding myth and misconceptions about sex related aspects. Parents to justify this topic to be essential are given below:
- Large group of school students comprises of adolescence who have attained puberty. Therefore this seminar is necessary to provide medical help and care for reproduction related problems like menstrual problems, infertility, pregnancy, delivery, contraception, abortions etc.
- Awareness of problems due to uncontrolled population growth, social evils like sex abuse and sex related crimes etc., need to be created so that children should thînk and take up necessary steps to prevent them and thereby build up a reproductively healthy society.
- Increasing population is a major problem of India which is directly related with reproductive health.
- Knowledge about sexually transmitted dieses (STDs) is essential as children should be aware that unprotected sex with multiple partners results in the transmission of sex related problems. Children should be aware of family planning programmes such as reproductive and child healthcare (RCH) programme.

Question 8.
(i) Explain one application of each one of the following:
(a) Amniocentesis
(b) Lactational amenorrhoes
(c) ZIFT
(ii) Prepare a poster for the school programme depicting the objectives of ‘Reproductive and Child Healthcare Programme’.
Answer:
(a) The application of amniocentesis include the diagnosis of chromosomal disorders and developmental disorders of foetus.
(b) Lactation amenorrhoea is natural contraceptive measure. Ovulation does not occurs during the period when mother fully feeds her baby.
(c) ZIFT is related to embryo transfer in the test tube baby programme. In this, the zygote or embyro up to 8 - celled is transferred into fallopian tube.
(ii)