RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 11 Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 11 Biotechnology : Principles and Processes Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Important Question Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Firstly biotechnology word used by:
(a) Karl Mullis
(b) Karl Erkey
(c) Watson and Crick
(d) Alec Jeffery
Answer:
(a) Karl Mullis

Question 2.
Covid - 19 vaccine is a type of:
(a) t - RNA
(b) m - RNA
(c) S - RNA
(d) r - RNA
Answer:
(b) m - RNA
Question 3.
In vitro studies are performed in:
(a) nature
(b) human body
(c) lab
(d) plant body
Answer:
(c) lab
Question 4.
In vivo studies are performed in:
(a) lab
(b) living cell
(c) out of cell
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) living cell
Question 5.
First foqd enzyme produced using recombinant DNA technology:
(a) trypsin
(b) chymosin
(c) insulin
(d) lypase
Answer:
(b) chymosin
Question 6.
A relaxed ptasmid means:
(a) Have only single copy per cell
(b) can’t be purified
(c) does not exist in bacteria
(d) have multipile copies per cell
Answer:
(d) have multipile copies per cell
Question 7.
First recombinant DNA made by:
(a) Paul berg
(b) Alec Jeffery
(c) Herry Mullis
(d) Herbert Boyer
Answer:
(a) Paul berg
Question 8.
The component only present in Ti plasmid:
(a) Gus gene
(b) Opine gene
(c) a and b both
(d) RB factor
Answer:
(b) Opine gene
Question 9.
Which purine is found in RNA?
(a) Cytosine
(b) Thymine
(c) Guanine
(d) Uracil
Answer:
(d) Uracil

Question 10.
First artificial gene was synthesized by:
(a) Mendel
(b) Morgen
(c) Knorana
(d) Nirenberg
Answer:
(c) Knorana
Question 11.
Genetic engineering is:
(a) addition of gene
(b) removal of gene
(c) a and b both
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) a and b both
Question 12.
Given below in a sample what you can find to special?
5' ............... GAATTC ............... 3'
3' ............... CTTAAG ............... 5'
(a) Deletion of mutation
(b) repeated sequence
(c) Sticky ends
(d) palindromic sequence
Answer:
(d) palindromic sequence
Question 13.
Which one is known as 'molecular scissor'?
(a) Lygase
(b) Electrophoresis
(c) Restriction enzymes
(d) Cloning
Answer:
(c) Restriction enzymes
Question 14.
One, of the following process involves southern blotting techniques:
(a) r - DNA technology
(b) cutting of genes
(c) DNA finger printing
(d) production of transgenic species
Answer:
(c) DNA finger printing
Question 15.
Palindromic sequence found in E. coli at restriction site is:
(a) GTTAAC
(b) GAATTC
(c) CAATTG
(d) TTAAGC
Answer:
(b) GAATTC
Question 16.
Restriction enzyme cut the nucleotide between:
(a) G ↓GAATTC
(b) GT ↓ TAAC
(c) GTT↓AAC
(d) GTTAA↓C
Answer:
(a) G ↓GAATTC
Question 17.
In pseudo palindromic DNA recognition sequence letter W represent to - (CC WGG):
(a) W = U and T
(b) W = T & C
(c) W = A or T
(d) W = C & G
Answer:
(c) W = A or T
Question 18.
Which of the following enzyme produce blunt ends of DNA:
(a) Hind III
(b) Smal
(c) EcoRI
(d) BamHI
Answer:
(b) Smal
Question 19.
Arrange the following sequences in correct manner:
1. Isolation of the gene
2. Amplification of gene
3. Cutting of DNA at specific location
4. Insertion of recombinant DNA into host cell The correct sequence will be
(a) 1, 2, 3, 4
(b) 4,1, 3, 2
(c) 2, 3, 1, 4
(d) 1, 3, 2, 4
Answer:
(d) 1, 3, 2, 4
Question 20.
Shorting of DNA molecule performed by:
(a) DNA finger printing
(b) gel electrophoresis
(c) Bioreactors
(d) PCR
Answer:
(b) gel electrophoresis
Question 21.
The chemical used for visualizing RNA in an agarose gel is:
(a) SDS
(b) DMSO
(c) Ethidium bromide
(d) PMSF
Answer:
(c) Ethidium bromide
Question 22.
Poly acrylamide is used in
(a) PCR
(b) cell proliferation
(c) gel electrophoresis
(d) cell defence
Answer:
(c) gel electrophoresis

Question 23.
Buffer solution provide in gel electrophoresis for:
(a) providing plenty of ions
(b) movement of DNA
(c) rvisualisation of DNA
(d) gene therapy
Answer:
(a) providing plenty of ions
Question 24.
............... is used as a vector for cloning into higher organism.
(a) Baculovirus
(b) Salmonella
(c) Rhizopus
(d) Retrovirus
Answer:
(d) Retrovirus
Question 25.
Which bacterium is used in the production of insulin?
(a) Salmonella
(b) Saccharomyces
(c) Escherichia
(d) Rhizobium
Answer:
(c) Escherichia
Question 26.
One of the earliest commonly used plasmid:
(a) pBR322
(b) pCEV
(c) pVR12
(d) pCW - LIC
Answer:
(a) pBR322
Question 27.
Which one is not selectable marker?
(a) Ampicillin antibiotic resistance gene
(b) Chlorampheniol antibiotic resistance gene
(c) Tetracycline antibiotic resistance gene
(d) Tetramide antibiotic resistance gene
Anwer:
(d) Tetramide antibiotic resistance gene
Question 28.
Which of the following is a genetic vector?
(a) Plasmid
(b) Phage
(c) Cosmid
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 29.
Why cells are treated with CaCl2 in GE?
(a) To make cell competent
(b) Isolation of DNA
(c) Separation of Protein
(d) Joining of two different DNA
Answer:
(a) To make cell competent
Question 30.
Spooling is related to:
(a) extraction of DNA
(b) cutting of DNA
(c) gene expression
(d) breakdown of DNA
Answer:
(a) extraction of DNA
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is biotechnology?
Answer:
The application of scientific and engineering principles to processing of genetic material (i.e. DNA) by biological agents such as bacteria.
Question 2.
What is genetic engineering?
Answer:
In this process several techniques done with the genetic material (DNA, RNA) to alters its original chemical structure into desire structure.
Question 3.
Define recombinant DNA.
Answer:
After the insertion of foreign gene, the newly formed DNA having new genes on it is called recombinant DNA.
Question 4.
Which is the largest vaccine maker institute in the world?
Answer:
The largest vaccine maker institute in the world, by volum. Serum Institute of India in Pune.
Question 5.
Who made the recombinant DNA first time?
Answer:
First recombinant DNA made by Paul berg in 1972, combining DNA from monkey virus with lamba virus.

Question 6.
Who inserted recombinant DNA into host first time?
Answer:
The insertion of recombinant DNA so that the foreign DNA will replicate naturally, as pioneered by Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen.
Question 7.
Give any two uses of genetic engineering.
Answer:
- Producing a new kind of useful proteins
- Produce Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) having advance characters.
Question 8.
Basic difference between plasmid and chromosome.
Answer:
Plasmids are circular extra chromosomal DNA while chromosomes are the type of genomic DNA having important factors for growth, reproduction etc.
Question 9.
What is sonification? How can you break DNA into smaller fragments using other than restriction enzymes?
Answer:
Sonification is another method used of generate small DNA fragments by using mechanical shearing. It is done with the help of ultrasound blenders.
Question 10.
What are cosmids?
Answer:
Cosmids are plasmids having the lambda and cos sequence, they are also used as a cloning vector in genetic engineering.
Question 11.
Can you define why plasmids autonomously replicate in host cell?
Answer:
Plasmids are autonomously replicate in host cell because they have a specific site which is called ‘origin of replication’ (Ori).
Question 12.
What are the features of a plamids to be cloned in cell?
Answer:
A plasmid should have following characters:
- It should have origin of replication.
- It should have restriction sites.
- It should have a selectable marker.
Question 13.
Why it is necessary to incorporate alien DNA into vector DNA.
Answer:
Vector or plasmid DNA have origin of replication site, which is not found in alien DNA, so as we know ori is necessary for the replication, so we have to incorporate alien DNA with vector DNA.
Question 14.
What is cloning?
Answer:
The process in which one molecule of DNA produce population of cells with identical DNA molecule is called cloning.
Quetion 15.
What are the principles of biotechnology?
Answer:
Modern biotechnology follow mainly two crucial technologies:
- genetic engineering
- chemical engineering.
Question 16.
What is the first enzyme that was isolated?
Answer:
The first enzyme was isolated from bacteriophage in 1970 by Hamilton smith and named Hind II. (Type II)
Question 17.
Can you derive the named EcoRI.
Answer:
E’ means Escherichia - a genus
co means coli - a species
R means Ry13 - strain of bacteria
I reletes - firstly identified
Question 18.
Name the first restriction endonuclease
Answer:
Hind II, isolated from coli
Question 19.
Give some examples of exonuclease.
Answer:
Exonuclease I, exonuclease II and snake venom.
Question 20.
Give some example of endonuclease
Answer:
EcoRI, BamHI, Hind II, SI nuclease.
Question 21.
Give some examples of endonuclease produce Blunt ends and sticky ends.
Answer:
Blunt ends produced by Alu I, Hae III, EcoRV sticky ends produced by EcoRI, Hind III, BamHI.
Question 22.
Does Hind 2 produce blunt ends?
Answer:
Hind 2 generate fragments with blunt ends and they are ligated only with blunt ends. Enzymes Smal and EcoRV also produce blunt ends.
Question 23.
How restriction cut the ds DNA?
Answer:
restriction enzyme binds on their specific sequences and cut the DNA by hydrolysing the sugar - phosphate backbone of DNA.
Question 24.
How does EcoRI specifically act on DNA molecule? define EcoRI
Answer:
EcoRI is a type - 2 restriction enzyme found in E.coli It reads usually a palindromic site. That is GAATTC, where the enzyme cut G↓AATTC to create 4 nucleotide overhang of AATT with 5' end. EcoRI cut compliantly sequence of CTTAA↓G to create overhangs or sticky ends.
Question 25.
Which technique is used to separate and isolate of DNA fragments?
Answer:
A technique used to separate DNA fragments. according to their size is gel electrophoresis. Which enables the shorting of DNA based on their size and form DNA bonds.
Question 26.
Write the name of tech to make lacs of copies of DNA from a single copy in very limited , time.
Answer:
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Question 27.
What is the purpose using ethidium bromide in gel electrophoresis?
Answer:
Very small fragments of DNA molecules are not visible in normal medium. There fragments arfe stained with ethidium bromide, so they can illuminate when put under UV light, so the DNA bonding pattern can be vissualised.
Question 28.
Name the selectable marker in PBR322.
Or
Name of two antibiotic resistant genes found in plasmid pBR22.
Answer:
Ampieillin and tetracycline resistance genes are present as selectable marker.
Question 29.
Draw the diagram of PBR322/ or draw the diagram of cloning vector.
Answer:
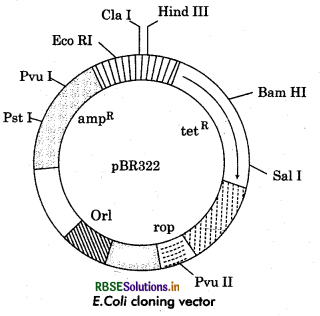
Question 30.
What is the role of selectable marker in a cloning vector?
Answer:
Selectable markers allow the positive selection of transformants over non transformants. Antibiotic resistance genes are often used as selectable marker example ampieillin, ß - galactosidase.
Question 31.
ß - galctodase considered a better selectable marker. Justify your answer.
Or
How does ß - galactosidase coding sequence act as a selectable marker?
Answer:
ß - galactosidase is used as a antibiotic resistance this make whole process less complicated. When the foreign gene inserted the enzyme gets inactivate, called intentional inactivation. When the bacteria grown on chromogenic substrate non-recombinant produce blue colour colonies which transformant produce colourless colonies. This helps in the selection of recombinants.

Question 32.
What is the product of lac Z gene?
Answer:
ß - galactosidase is the product of lac Z gene.
Question 33.
Which bacteria is responsible for the crown gall disease in plant?
Answer:
Agrobacterium tumifaciens case crown gall disease in plant which is responsible for the tumor formation in plant ells at nodules. Plasmid is called Ti plasmid.
Question 34.
Which is first artificial cloning vector?
Answer:
pBR322
Question 35.
Why do we use competent cell?
Answer:
Cell wall is made up of hydrophobic lipid and DNA is a hydrophyllic molecule and it can not pass cell wall easily, so competent cells are designed to take up foreign DNA after same special treatments.
Question 36.
Name any natural competent cell.
Answer:
Agrobacterium species.
Question 37.
Why we need to kept the competent cell on ice?
Answer:
Competent cells are very resistive, keeping then on low temperature help to avoid cell death during processing.
Question 38.
Why it is necessary to use thermostable DNA inPCR?
Answer:
Thermostable DNA isolated from Thermus aquaticus, which can tolerate the high temperature used during the denaturing or DNA at high temp.
Question 39.
Which type of bioreactors are used in biotechnology?
Answer:
The most commonly used bioreactors are stirring type.
Question 40.
Name bioreactor molecules function in our body.
Answer:
Streptokinase produced by Streptococcus.
Question 41.
What are recombinant proteins? Write the name of two recombinant proteins.
Answer:
Recombinant proteins are the product of recombinant DNA. Insulin (Humulin) was the first recombinant protein grown in 1982
- Insulin
- Human growth Hormones
- Follicle - stimulating hormones
- Interferon
- Proteases.
Question 42.
Name the commonly used vector for cloning gene into higher organism.
Answer:
Retrovirus / Adenoviruses / Papilloma virus / Tobacco mosaic virus.
Question 43.
Stage the role of ‘biolistic gun’ in biotechnology experiments.
Answer:
To introducing alien DNA into host cell, DNA molecules coated with gold / tungsten are bombarded with high velocity on the host cell.
Question 44.
What is down stream process?
Answer:
Down stream processing is the recovery of biological product from bioreactor, which includes the extraction, separation and purification of biotechnological products.
Question 45.
What is the full name of‘GMO’?
Answer:
Genetically modified organism.
Question 46.
Define recombinant DNA.
Answer:
The process of inserting new genes or information into existing DNA - RNA through host in order to modify a specific, novel organism with desired character, technique called recombinant DNA technique and newly formed DNA having new genes on it, called recombinant DNA.
Short Answer Type Questions - I
Question 1.
What is the role of plasmid in DNA technology?
Or
Why plasmid is selected as a vector?
Answer:
Plasmid are small, circular, extrachromosomal, double stranded DNA, present in bacterial cell. They are low molecular weight and carry ‘origin of replication’ restriction sites and selectable markers, as they are ideal vectors to inserted into host cell because they can easily incorporate with the host DNA to form recombinant DNA.

Question 2.
Why E. coli is most frequently use in genetic engineering?
Answer:
Because it can grow and cultivate easily in vitro → it is not expensive to use.
E.coli adapted itself very easily in laboratory and grown at high rate of replication.
Plasmid of E.coli can well replicate by using host’s DNA polymerase enzyme.
Question 3.
Explain the role of restriction endonuclease in the formation of recombinant DNA. Draw a labelled diagram of E. coli cloning vector pBR322. Name the enzymes that helps in the formation of recombinant DNA technology?
Answer:
Restriction Enzyme: Restriction Enzymes are bacterial enzyme followed by protective machenism to viral DNA and such enzymes are not found in eukaryotic cells. Restriction enzymes was postulated for the first time by W. Arber in late 1960. He noticed that when DNA of bacteriophage virus entered in host bacterium (E. coll) the host DNA cut virus DNA into smaller pieces.
"First restriction endonculease isolated from bacteriophage by Halmilton and named Hind II. According to there functions restriction enzymes are classified into two kinds.
- Exonuclease: Cleave DNA nucleotide from the ends, usually they are non - specific.
- Endonuclease: Cleave DNA between nucleotide at specific sequences. They are highly specific in different species.
Type I endonuclease are first identified but Type II endonuclease are first isolated from E. coli. Restriction enzymes produce both sticky and blunt ends of DNA. They cut same, sequences in both foreign DNA and vector DNA so they can early ligated. Usually they follow palindromic sequences.
Name of enzymes that help in the formation of r - DNA are:
- Restriction endonuclease
- Ligases
- Proteases
- DNA ploymerase
- Chitinase
- Lysozymes
- Cellulase
Question 4.
What are restriction site? Name of any two restriction site.
Answer:
Restriction site are 6 - 8 nucleotide sequences present on DNA, which are out by the action of restriction enzyme. Which are very specific for their action. Name of some restriction sites are:
1. 5' .................. GAATTC .................. 3' in EcoRI
3' .................. CTTAAG .................. 5'
2. 5' .................. AAGCTT .................. 3' in Hind II
3' .................. TTCGAA .................. 5'
Question 5.
Explain the significance of palindromic nucleotide sequences in r - DNA technology.
Or
What is the relation between restriction endonuclease and palindromic nucleotide sequence?
Answer:
Palindromic nucleotide sequences on DNA read same either we read from 5' to 3' or 3' to 5' direction. This means restriction enzymes read them from both sides which increase the chance of action of restriction enzyme to cut DNA strand. The recognition site of restriction endonuclease is a far away from the center of palindromic sites, but they cut b/w the same base/pairs of DNA strand and leaves stricky overhang end for the action of DNA ligase so presence of palindromic site promote the action of restriction endo - nucleas for the formation of r - DNA.
Question 6.
Write the palindromic sequence recognised by EcoRI
Answer:
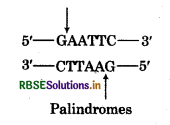
Question 7.
What are sticky ends state the significance in recombinant DNA technology?
Or
Describe the formation of recombinant DNA by the action of EcoRI.
Answer:
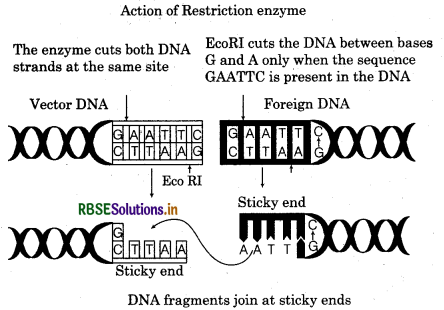
ECORI is most commonly used restriction enzyme act on palindromic sequence (GAATTC) of 6 nucleotide. The enzyme cuts the DNA strand at a specific point, slightly away from the centre of palindromic sequence b/w the some 2 pair on different strands.
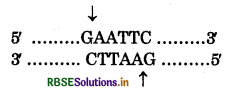
This results in the formation of 5' overhangs portions, called sticky ends. This cut makes 4 nucleotide free on each strand.
(5' .................. AATT .................. 3' ) and
(3' .................. TTAA .................. 5' )on complementary strands.
These 4 nucleotide sticky ends are free to bind another nucleotide sticky ends of foreign DNA Restriction endonuclease treat the foreign DNA as same to produce same to same sticky ends.
Question 8.
Describe the role of DNA ligase in r - DNA technology.
Answer:
Role of DNA ligase
- DNA ligase leads the formation of phosphodiester bond between two DNA fragments.
- Joining of two sticky or blunt ends by th formation of hydrogen bonds.
- Ligation of all purine and pyrimidine bases.
Question 9.
List the key tools used in recombinant DNA technology.
Answer:
The key tools used in recombinant DNA technology are -
- Enzymes
- Restriction Enzymes: Hind II, EcoRI, EcoRI I, Smal, EcoR V are most commonly used restriction enzymes. That cut the DNA at specific sit.
- Ligase: Responsible for the joining of cut ends.
- Protease: Degrade the proteins present along with DNA eg. Histone.
- Cloning Vectors: Plasmids and bacteriophages are used as cloning vector because they have ability to replicate.
- Competent Host: Competent host cells are able to take up foreign DNA it.
Question 10.
Explain the technique that helps in the separation of DNA fragments, formed by the use of restriction endonuclease.
Or
Explain gel electrophoresis.
Or
Principle behind the working of gel electrophoresis.
Answer:
A technique use to separate DNA fragments according to their size is gel electrophoresis. “It is a process which enables the shorting of molecules bases on size using an electric field through 6 gel (agarose) medium.”
Principle - “The principle behind this technique is that the negatively charged molecules of DNA moves towards the Anode and get separated. They arranged on gel in the form of bonds according to their size.
Question 11.
Draw a schematic sketch of PBR322 plasmid.
Answer:
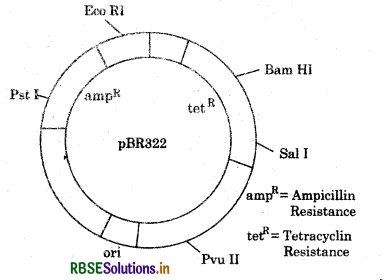
Question 12.
Why must a ceil he made competent in biotechnology experiments? How does calcium ion help in doing so?
Answer:
Competent is the ability to being able to take up the recombinant DNA in it. Recombinant DNA can’t pass the cell membrane directly so first we need to break the cell wall and then cells are trated with cations such as calcium of soaked in CaCl2, which open the channels on the cell membfane and allow the entry of recombinant DNA into cell.

Question 13.
Describe selectable marker.
Or
All Cloning vectors do have a selectable marker. Describe its role in r - DNA - technology.
Answer:
Antibiotic resistance give present In vector acts a selectable marker. Selectable marker identified transformant from non-transformants. The genes encoding resistance to antibiotic such "as ampicillin, chloramphenicol, tetracycline are serves as selectable marker."
Addition of selectable marker or antibiotic resistance allow the host organism to survive antibiotic selection. Generally, ampicillin, tetramycin etc are the useful selectable marker in E. coli.
Question 14.
Describe the process of amplification of gene of interest PCR technique.
Or
Describe the roll and applications of PCR.
Answer:
The method which is used in r - DNA technology for the amplification of gene is polymerase chain reaction. By using sevral products such as DNA sample, primers, nucleotide, Taq polymerase, PCR manipulate the gene of interest as well as vector DNA also. Application of PCR:
- Diagnosis of genetic disease,
- used in medical diagnostics,
- DNA fingerprinting,
- Forensic analysis of DNA,
- Manipulation of piece of DNA.
Question 15.
What are most commonly used bioreactors in biotechnology labs. Write the most essential components this bioreactor have.
Answer:
The most commonly used bioreactor are stirring type. They are biologically active and can grow cells, tissue in optimised condition when the raw material added and they performs bio - process engineering.
The most essential biological agents which used as a raw material are cells, enzymes and antibodies and some other specific products also, at the optimum growth conditions, most essential components of this bioreactor are:
- Agitator system,
- Oxygen delivery system,
- Foam control system,
- Temperature control system,
- pH control system.
Question 16.
Name any two natural cloning vector. Give reasons that make them act as cloning vector. Write two characteristics the engineered vectors are made to possess.
Answer:
Plasmids derived from the environment directly are called natural plasmids. Two natural cloning vectors.
- Plasmid (e.g. Ti Plasmid)
- Bacteriophage
They act as a cloning vector because they have ability to replicate it self in to the host cell very fast and make their protein independently in host cell.
Characters of the engineered vectors:
- Easy to link with foreign DNA,
- They have selectable markers,
- Must have restriction site for endonuclease activity,
- They can self - replicate in host cell.
Short Answer Type Questions - II
Question 1.
Describe the roll of following microorganism in Biotechnology.
(a) Escherichia coli
(b) Salmonella typhimurium
(c) Agrobacterium tumifaciens
(d) Thermuk aquaticus
(e) Retroviruses.
Answer:
(a) Escherichia Coli: E. coli plasmids vectors are most commonly use vectors in any also use as a host to the number of recombinant DNA. E. coli is a model organism in genetic engineering because of its high growth rate and ability to express its protein at very high level.
(b) Salmonella typhinmurium: Stanely Cohen and Herbert Boyer first produced a recombinant DNA in 1972 by combining an antibiotic resistance gene with the nature "plasmid of bacterium Salmonella typhimurium. Most of the recombinant Salmonella based HIV/AIDS vaccines develops so far have only been tested in mainly mice.
(c) Agrobacterium tumifaciens: A.tumifaciens is a bacteria act as a pathogen of several dicot plant and cause crown gall disease. Which is responsible for tumor in plant cells, plasmid is called tumor inducing plasmid or Ti plasmid. When the tumor inducing gene is replace with the desirable gene them use this as a vector and transform into host cell, which develops a plant with new trait.
(d) Thermus aquaticus: Thermus aquaticus (Taq) is a main agent of PCR. It pocesses a heat - resistant enzyme Taq DNA polymerase. Which can tolerate a wide range of temperatures during the denaturing of DNA and other proteins.
(e) Retroviruses: Retroviruses are a type of virus that have a special enzyme called reverse transcriptase, that transform their single stranded RNA into double stranded DNA. Retroviruses can cause cancer in animal Cells. They use as a vector in biotechnology, where the viral gene replace with desirable gene and incorporate into host cell and produce own useful proteins.
Question 2.
Match the following:
|
(1) ß - galactosidase |
(i) Restriction site |
|
(2) Sal I |
(ii) Natural competent |
|
(3) Agrobacterium |
(iii) PCR |
|
(4) Precipitation of DNA |
(iv) Lac - Z |
|
(5) Primers |
(v) spooling |
Answer:
|
(1) ß - galactosidase |
(iv) Lac - Z |
|
(2) Sal I |
(i) Restriction site |
|
(3) Agrobacterium |
(ii) Natural competent |
|
(4) Precipitation of DNA |
(v) spooling |
|
(5) Primers |
(iii) PCR |
Question 3.
Given below is the diagram representing a typical gel electrophoresis technique. Observe the illustration answer the following question that follow.
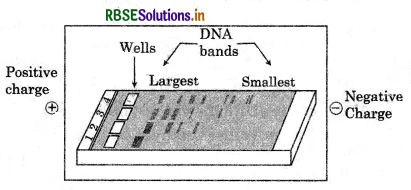
(a) What will be the direction of movement of DNA fragments? and why?
(b) What will be the sites of largest and smallest molecules of DNA and why?
(c) Which medium is used to separate DNA fragments?
Answer:
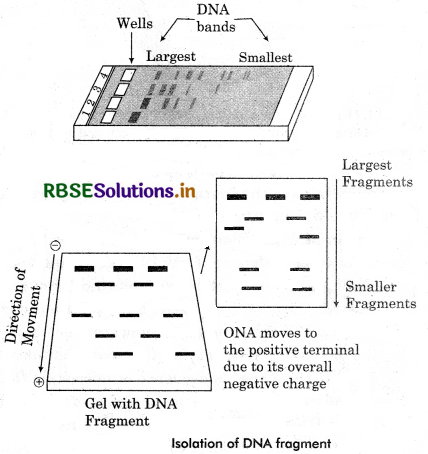
(a) The direction of movements of DNA fragments will be Anode (A) to negative charge (B). Because DNA have overall negative charge and so they move at B site from A site.
(b) Largest molecules can be seen toward, A site or positively charge Anode site and smallest size of molecules of DNA found at the negatively charge B site because they move faster then large molecules.
(c) Agarose gel or polyacrylamide (see weed) medium is used to separate DNA fragments.

Question 4.
Give the reason, if Hind II enzyme was first isolate than Hind I, then why it named so?
Answer:
There are some specific reasons:
- Well Ilind I was firstly discover enzyme but then, it was not isolated, Hind II was the first isolated enzyme.
- Hind I was exonuclease, so the first discovered endonuclease enzyme was Hind II.
- There are many type of restriction enzyme Hind II was the type 2 enzyme, that why it named so.
Question 5.
Arrange the following in the correct sequence based on processes of r - DNA technology:
(1) Amplified DNA
(2) Denaturing of ds DNA
(3) Taq Polymerase
(4) Recombinant Protein
(5) Chitinase
(6) Competent cell.
Answer:
The correct sequence will be
(1) Chitinase
(2) Denaturing of ds - DNA
(3) Taq polynerase
(4) Amplified DNA
(5) Competent cell
(6) Recombinant protein
Question 6.
A ligation of alien DNA at restriction site BamHI in vector pBR322, will not allow the growth of vector in tetracycline medium hut in ampicillin medium they can grow. Give the reason in your own words.
Answer:
In vector pBR322, it has two restriction site BamHI and Pst I, which are responsible for tetracycline and ampicillin antibiotic resistance respectively. Ligation of alien DNA at BamHI in vector, inactivate tetracycline antibiotic resistance gene but ampicillin resistance gene still actual. When we grow that vector in tetracycline medium, the cell will no longer survive due to the absence of tetracycline resistance gene.
Question 7.
What is insertional inactivation?
Or
Why is the coding sequence of an enzyme ß - galactosidase a preferred selectable marker in comparison to the other.
Answer:
For the selection of recombinants from non recombinants another method is used called insertion inactivation. It this process a recombinant DNA is inserted in specific coding sequence. Which encoded an enzyme that is ß - galactosidase is used as a antibiotic resistance gene as a selectable marker and this makes whole process less complicated compare to other markers. When the foreign gene is inserted with in the ß - galactosidase gene, the enzyme inactivated which is called insertional inactivation. Non recombinant bacteria (active ß - galactosidase) produce blue coloured colonies, white recombinant produce colourless colonies.
Question 8.
Study the given diagram and answer the following questions.
(a) Name the enzyme P and Q.
(b) Role of P and Q enzymes.
(c) Location of Ori.
(d) The name of next step after the formation of r - DNA, S.
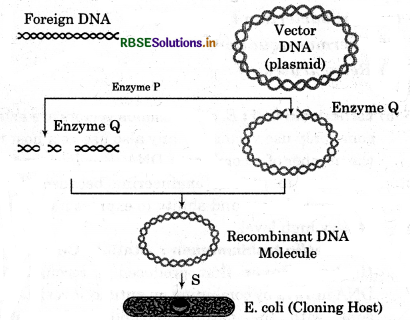
Answer:
(a) Enzyme P = Restriction endonuclease
Enzyme Q = Ligase
(b) Role of P (Restriction endonuclease). Enzyme cut the DNA at specific sequence into small fragments. Role of Q (Ligase) - Enzymes join foreign DNA with the plasmid DNA to form r - DNA.
(c) Ori (origin of replication) located into the vector DNA.
(d) The name of step 5 → Transformation (insertion of r - DNA into host cell).
Question 9.
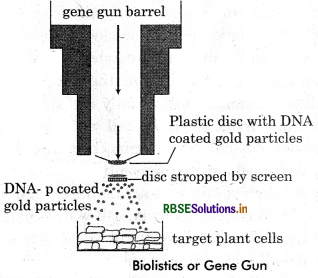
Role of biolistics or gene gun in biotechnology.
Answer:
Biolistics or Gene Gun: This is the technique of shooting the foreign gene or DNA into plant cell. It can also use in animal cell but mostly it is used for plant cells.
Helium gas filled in the chamber of gum to treat pressure. RNA or DNA are coated with heavy metal such as gold, sliver or tungsten that make DNA stable for long time, target cell is prepare in Dish under the gun. When DNA gun fire it hits the cell with DNA coated with gold particles. There particles propelled through the screen into target cell. Hence the gum fire at the clusture of cell and recombinant DNA enter the cell.
Now we have well known about the tools, enzymes and different techniques used in recombinant DNA biotechnology which will make easy understanding to know about processes of recombinant DNA. Technology and discuss from the isolation of gene to get the useful product at the end.
Question 10.
Why must bacterial cells be first made ‘Competent in r - DNA technology’?
Or
How the insertion of recombinant DNA has to be done in host cell?
Answer:
Competent is the ability to being capable to take up the recombinant DNA in it. Many types of cells are not able to take up foreing DNA, untill they have been treated with some special chamical treatments to be competent. Most probably the cells are treated with cations such as calcium or socked in CaCl2 solution which makes the channel open for the entry of recombinant DNA. Micro injection and gene, gum are the other methods for the insertion of recombinant DNA into the host cell.
Question 11.
What is primer and why it is used in biotechnology?
Answer:
Primer are short oigonucliotids used in polymerase chain reaction (PCR) after the denaturing of ds - DNA, 2 Primers are added on each strand at 3 position temperature is decreased to 50° - 70°C for 30° - 40° sec this allow the annealing of primer on each strands. They are joined to amplified the DNA molecules as they are named so, they do priming on each DNA strand and later elongation takes place to form complete ds - DNA direction of priming always 5' to 3'.

Question 12.
How bioreactor molecule function in our body.
Or
What are bioactive proteins name any bioactive molecule produce by trichoder polysporum and monecious purpureus.
Answer:
Bioreactor molecules are bioactive molecules modified by genetic engineering. They used for the treatment of several disease some of important bioactive molecules and this roles are:
- Cyclosporin A: Cyclosporin A is a bioactive molecule produced by fungus trichodema polysporum in our body. It suppress the immune system when any organ and tissue (foreign) transplant to the body so they can be successfully transplanted.
- Monascus Purpureus is a yeast is used to lowering the blood cholesterol level. Product produced from it is called statins.
- Streptokinase: It is produced by the bacterium streptococcus, it is genetically modified bioactive molecule which is used to remove clots from blood vessels and lower the chance of heart attack.
Question 13.
What is recombinant DNA technique? Explain the role of any three enzyme used in this technique.
Answer:
The process of inserting new genes or information into existing DNA - RNA through host in order to modify a specific, novel organism with desired character, technique called recombinant DNA technique and newly formed DNA having new genes on it, called recombinant DNA.
The key tools used in recombinant DNA technology are -
- Enzymes
- Restriction Enzymes: Hind II, EcoRI, EcoRI I, Smal, EcoR V are most commonly used restriction enzymes. That cut the DNA at specific sit.
- Ligase: Responsible for the joining of cut ends.
- Protease: Degrade the proteins present along with DNA eg. Histone.
- Cloning Vectors: Plasmids and bacteriophages are used as cloning vector because they have ability to replicate.
- Competent Host: Competent host cells are able to take up foreign DNA it.
Question 14.
Write two advantages of cloning.
Answer:
Clones are novel organism used to produces healthier off spring having great advantages:
- It contain superior characters no barrier of infertility.
- Cloning allows in vitro for the commercial purpose to make medicines, hormones or enzymes etc.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the role of restriction enzymes in biotechnology.
Or
Write the types of restriction endonuclease enzymes. Justify your answer that synthesis of recombinant DNA molecule is possible only when the vector and source DNA is cut by the same restriction enzyme. Explain.
Answer:
Restriction endonucleases is a bacterial enzymes that can cut double stranded DNA into smaller pieces by recognizing specific nucleotide sequences on DNA. First postulated by W, Arber in late 1960. He found that when viral gene attack on bacterial cell they restricted the entry of viral gen DNA by breaking it into smaller peices do resist viral attach. Hence, they named molecular scissors:
The first restriction enzyme was isolated from bacteriophage in 1970 by Halminth Smith and named - II. Restriction enzymes are belong to the large class of enzymes that is nuclease, they are known to be restriction endonuclease because they act on the nuclic acid of cell.
According the the action on DNA molecules. They are classified in two types.
Exonuclease RE and Endonculease RE.
Restriction Enzymes: Restriction Enzymes are bacterial enzyme followed by protective machenism to viral DNA and such enzymes are not found in eukaryotic cells. Restriction enzymes was postulated for the first time by W. Arber in late 1960. He noticed that when DNA of bacteriophage virus entered in host bacterium (E. coll) the host DNA cut virus DNA into smaller pieces.
"First restriction endonculease isolated from bacteriophage by Halmilton and named Hind II. According to there functions restriction enzymes are classified into two kinds.
- Exonuclease: Cleave DNA nucleotide from the ends, usually they are non - specific.
- Endonuclease: Cleave DNA between nucleotide at specific sequences. They are highly specific in different species.
Type I endonuclease are first identified but Type II endonuclease are first isolated from E. coli. Restriction enzymes produce both sticky and blunt ends of DNA. They cut same, sequences in both foreign DNA and vector DNA so they can early ligated. Usually they follow palindromic sequences.For the synthesis of recombinant DNA molecules possible only. When the vector and source DNA is cut by the same restriction enzyme because restriction enzyme are very specific in their action. For the formation of recombinant DNA cut ends of vector DNA should be complementary to the foreign DNA only when the nucleotides will join together by hydrogen bonds. Because the use same endonuclease enzyme are got some free sticky ends on both vector DNA and foreign DNA and the free sticky ends are joined together (end to end) with the help of DNA ligase enzyme. That form the combination of both foreign and vector DNA and so called recombinant DNA. The diagrammatic representation for the formation of recombinant DNA as shown in figure.

Question 2.
What is genetic engineering? Explain separation and isolation of DNA fragments.
Or
What are the steps in specific sequences of recombinant DNA technology? describe the method of isolation of genetic material.
Answer:
Genetic Engineering: In this process technique done with the genetic material (DNA, RNA) to altering its original chemical structure into its desired structure.
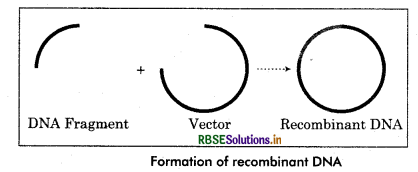
It is a process of genetic manipulation or modification in gene’s using biotechnology, to produce DNA with different new genes to produce improved or novel organism. That newly encoded DNA introduce into host cell/ organism to change its phenotypic characters. We can say that “The process of inserting new genes or information into existing DNA or host in order to modify a specific, novel organism with desired characteristics” is called genetic engineering.
- This newly formed DNA having new genes on it, is called recombinant DNA.
- After insertion of Recombinant DNA into host cell/or DNA developed organism called genetically modified organism (GMO.)

How does Genetic Engineering Work?
- Genetic engineering used to enhance the character of individual organism.
- It is done by extracting DNA from another animal having gene of useful characters or genome, and combine it with the host DNA.
- Genetic engineering can be applied on virus, bacteria plants and animals.
- Normally insulin is produced in the pancreas but are can produce insulin in lab with the help of genetic engineering.
- Genetically modified insulin is known as ‘Humulin’.
There are four main steps in DNA technology:
Step 1: The desirable or useful piece of gene or DNA is ‘cut’ from the source organism using a 'molecular scissors’. Which is an enzyme called restriction enzyme there are different restriction enzyme act on different sequences of DNA.
Step 2: The cut piece of DNA is ‘pasted’ into a plasmid or also called,vector and the end (3' and Rends) of DNA are joined with the vector DNA by ligation. Ligation isr an enzyme which paste or joint the ends of DNA in to the vector DNA.
Step 3: The vector which is now a recombinant DNA plasmid introduced into a host cell. Often a bacterium or yeast by a process called transformation.
The host cell now start replication or making DNA copies along with the vector DNA. Creating multiple copies of the inserted DNA vector could use all the replication enzyme of host cell for the replication process. Thus we can say that recombinant DNA technology is another suitable name for DNA cloning. On the basis of above concept all the virus and bacteria transmitted their infection into other organisms.
Separation and isolation of DNA Fragments: A technique used to separate DNA fragment according to their size is gel electrophoresis.
“Electrophoresis, is a process which enables the shorting of molecules based on size. Using an electric field, molecules (such as DNA) can be made move through a gel made up of agarose or polyacrylamide. The Principle behind technique is that as we know DNA or DNA fragments are made up of nucleic acid and phosphate at free ends. So DNA fragments are excluding negatively enarged molecules. When a charged molecule is placed under the electric field they moves towards the positively charged anode, through matrix or gel and get separated. The apparatus used for the separation is gel electrophoresis. It has negatively charge terminal and a positively charged anode at for end.
The gel is filled in an electrophoresis chamber and connected to electricity most commonly used gel as a medium are agarose gel. Which obtained from sea weeds and a natural polymer. Agarose gels are easily to cast and handled and give samples more easily. The agarose gels are conveniently stored in a plastic bag in refrigerators. A buffer solution also provide to gel electrophoresis with the planty of ions that can carry current. Amplified DNA added to the gel wall and when the current passes, the DNA fragments got separated according to their size in the form of DNA Bands. When the process completed these bands are stained through gel and arranged according to their size by sieving effect.
Hence, the smaller and shorter molecules move faster to the anode then longer piece of DNA and arranged in a line. When the electrophoresis is complete the molecules in the gel are not visualise. These molecules has to be stained to make them visible using ethidium bromide and also expose to the UV light. When the bands are visualised they are physically cut with the gel and extracted from the gel piece. This process is known as elution and we have the pure DNA fragment with desired gene to construct recombinant DNA.
Question 3.
Describe the role of heat, primer and the bacterium Thermus aquaticus in the process of PCR.
Or
Explain PCR, mention its role and applications in biotechnology with diagram.
Or
Describe the process of amplification of gene of interest using PCR technology.
Answer:
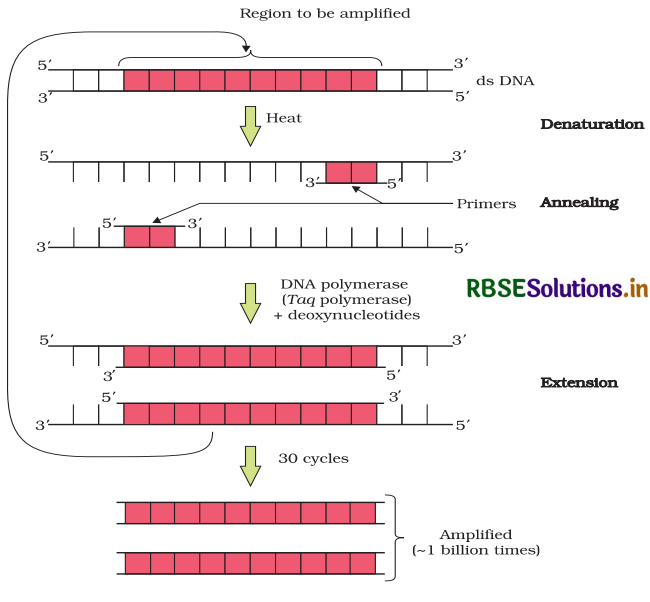
Amplification of Gene of Interest using PCR:
Because we want large scale production we need billions of copied of DNA or gene of interest and vector that will carry gene. For this a process used to manipulate genes In vitro conditions using several components and reagents. Basically it needs those components which are used in DNA replication such as primers (2 sets) of each stand, DNA polymerasse buffer solution and thermocycling. This process is carried by polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Steps of PCR:
Each cycle of PCR has three steps:
- Denaturation: Temperature maintained around 94 - 98° C for 20 - 30 sec. This cause DNA melting of double strand DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds, we yield 2 single strands of DNA.
- Annealing : Temperature is decreased to 50 - 70°C for 30 - 40 sec, this allowing annealing of primers on each single strand of DNA.
- Elongation or Extension : Temperature settel down for the activation of DNA polymerase enzyme at 70 - 80°Q Now DNA polymerase add new nucleotide following primer to 5’ to 3’ direction.
At last we got two molecules of DNA piece or gene of interest. We can say polymerase chain reaction is a kind of replication process in vitro condition. Following steps are performed respectively, because multiple cycles of these steps are required to produce large amount of gene. Same process is done with the vector DNA to amplify the number of vector, in this process Thermostable DNA used. Isolated from bacterium Thermus aquaticus, which can tolerate the hightemperature used during the denaturing and other steps.
Now, the desired gene can be ligated or 'pasted' with the vector DNA further cloned when vector transformed into the host cell.
Role of heat (Thermocyclin) Thermus aquaticus and primer in PCR.
(a) Heat (Thermocyclin): The process of thermocyclin the temperature of PCR maintained according to requirements, in the step of denaturing of ds - DNA is heated to separate it into two single strands at 94° - 98°C temp. The next step annealing is done when the temperature is lower at 50° - 70°. Which allow the activity of Taq polymerase enzyme, in the next step raising of temperature is necessary for the addition of new nucleotide for the extension of DNA molecule.
(b) Primer: Primer are short oigonucliotids used in polymerase chain reaction (PCR) after the denaturing of ds - DNA, 2 Primers are added on each strand at 3 position temperature is decreased to 50° - 70°C for 30° - 40° sec this allow the annealing of primer on each strands. They are joined to amplified the DNA molecules as they are named so, they do priming on each DNA strand and later elongation takes place to form complete ds - DNA direction of priming always 5' to 3'.
(c) Thermus aquaticus: Thermus aquaticus (Taq) is a main agent of PCR. It pocesses a heat - resistant enzyme Taq DNA polymerase. Which can tolerate a wide range of temperatures during the denaturing of DNA and other proteins.
Application of PCR in biotechnology:
PCR is useful in basic researches and also in applied researches.
|
Basic Researches |
Applied Researches |
|
1. Mutation screening |
1. DNA fingerprinting |
|
2. Drugs Discovery |
2. Gene therapy |
|
3. Bioinformatics |
3. Study of pathogens |
|
4. Gene cloning |
4. Genetic matching |
|
5. Gene expression studies |
5. Recombinant proteins |
|
6. Molecular ecology |
|
|
7. Classification of organism |
|
Question 4.
Describe the ideal vector and write four characters, Draw labelled diagram of pBR322 and describe the structure.
Or
Define the importance of cloning vector in biotechnology. What features would have in ideal cloning vector name the commonly used vector in r - DNA technology.
Answer:
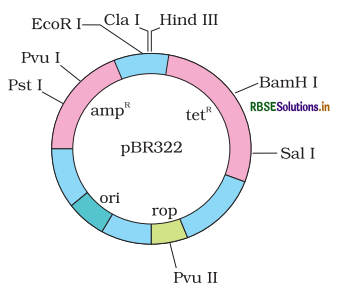
Cloning Vectors:
As we have already told you about plasmid or vector, that they carry desired gene on it and theen transfer to the bacterial or host cell. The plasmid and bacteriophage have aleicty to relicate in host cell other the chromosomal DNA. Because they have 'orgin of replication' process called cloning. Bacteriophage as a host can grow very high number of copies in cell.
Plasmids are standard and most commonly used. They are autonomously relicate. Plasmid can produce a high number of clones from 2 to 100 or more then it per cell one of the earliest commonly used plasmid is pBR322. Cloning vectors are allow for the insertion or removal of gene convenniently by treating the vector with rrestiriction enzymes. Hence, produce DNA fragments with blunt ends or ovberhangs known as sticky ends and joined by ligation. Then recombinant DNA has been further cloned for specigfic uses.
The following are the features that are required to facilitate cloning into a vector.
1. Origin of Replicatiion (ori): As you know for the replication or cloning of any DNA there must be a cloning site from where the replication start in plasmid is called 'origin of replication' or 'ori' it is the necessary elememnt for the mainpulation of gene. Ori is a special sequence of nucleotide that control the number of copies ort clones in the cfell of linked DNA. So we can say origin of rreplication maintain the number of copies in the presence of
DNA polymerase enzyme.
2. Selectable Marker: Selectable markers identified transformed cells. Transformation is a process through which a piece of DNA introduce in a hosst vell. Antibiotic resistance genes serves as selecyable marker. NOrmally, E.coli cell do not contain antibiotic resistance against any of these antibiotics such as ampicillin, chlorampheniol, tetracycline or kanamcycin etc. They genes are known as useful selectable marker for E.coli vector contain one to two selectable markers, at a time selectable marker use for the artificfal selections.
Adding a selectable marker or antibiotiv resistance allow the host organism to survive antibiotic selection. These genes also help in the selction of transformant and non - transformants. Because the non transformant cells do not processes these antibiotic resistance genes so they can't grow in medium, this is how we can eliminate unuseffull, non treansformants, from the medium and now we have purely transformants cells having recombinant DNA. Tranformants are bacterial cells which incorporate plasmid DNA into their genome, non transformants do not incvorporate plasmid into their genome. Among all the selectable marker ampicillin (amp.) is most commonly used selectrable marker.
3. Cloning Site: In addition to link alien DNA, vectors allow a gene to be conveniently added or removal from it cloning site are best for the insertion of foreign DNA to cut the vector at specific site it have recognition site where the restriction enzymes work. Most commonly a vector contain single recognition site that cut the vector onces at one position but some DNA or vector have more than one recognition site that can leaves fragments of DNA. This is called multiple cloning site (MCS). These fragments are amplified with PCR (polymerase chain reaction and ligated into vector. The ligation of desirable gene or DNA with the host DNA is done near the antibiotic resistance genes. For example, we can join the foreign DNA at Bam HI site of tetracycline resistance. When the target gene is incorporated into the plasmid at BamHI site of tetracycline resistance gene. This will inactive that plasmid transformed into the host cell.
When this host cell grown in medium contain ampicillip or tetracycline, depending on which gene is still active in this case ampicillin resistance gene is active. This type of vectors are recombinant vectors in which ampicillin resistance gene is active but not tetracycline. When these transformants grown on ampicillin medium they grow successfully but they these recombinant vectors are grown in tetracycline medium they do not grow, because they lose tetracycline resistance due to insertion of gene at BamHI site. But the non - recombinant DNA vector have both ampicillin and tetracycline resistance gene so they growth in both ampicillin and tetracycline medium. By this experiment we can proof that this is now antibiotic resistance gene helps in the positive selection of transformants and other antibiotic resistance gene which inactivated due to the insertion of foreign DNA helps in the selection of recombinant.
There are also other alternative selectable markers which help to differentiate recombinant and non-recombinant DNA. Which provide more versatility. For the selection of recombinants from non - recombinants a another method is used called insertion inactivation. In this process a recombinant DNA is inserted is specific coding sequence which encoded an enzyme that is ß - galactosidase it is an enzyme that converts galactose into lactose. ß - galactosidase is used as antibiotic resistance gene as a selectable marker this make whole process less complicated and use as a alternative selectable marker. When the foreign gene is inserted within the (kgalactosidase gene, the enzyme inactivated. Which is called insertional inactivation. Then the bacteria are grown on a chromogenic substrate. Non recombinant will produce blue coloured colonies, while recombinants will produce colours colonies.
4. Vectors for Cloning genes in Plants and Animals: At this point now you have understand about the mechanism or transferring genes into any host from bacteria or virus. Several viruses and bacteria attack on plant and avium and harm them, you will surprised to know that what actually do after entering in Eukaryotic cell. Whenever any virus and bacteria attack on Eukaryotic cell, they inject their DNA or RNA into host cell and hack the whole machinery of the Eukaryotic cell by incorporate its own genetic material into host DNA.

Question 5.
What is vector - less direct gene transfer? Write name of its main four methods. Describe with labelled diagram gene gun method.
Or
Explain any two methods of introducing alien DNA into host cell.
Answer:
Vector less gene transfer is a type of direct gene transfer into the host cell without using any vector DNA. It is a stable method of gene transfer, the host cell have to be treated. with different chemical and physical treatments of faciliate, the entry of DNA into plant cell these methods are very easy to handle and High efficient at low toxicity.
The name of four methods using vector less gene transfer are:
- Micro - injection
- Gene - Gun (Biolistics)
- Lipo fection
- PEG
Most useful and highly efficient two methods of gene transfer into host organism are -
Micro - Injection: It is very popular and easy method to inject recombinant DNA into cell. This method is mostly use to deliver foreign DNA into living cellš such as egg, oocytes emboyo etc, the process perform at micro level by using microscope. As a syringes a glass micro-pipette is use to inject recombinant DNA directly to the nucleus of cell micro-pipette is filled with vector DNA. Micro-injections are mostly use as pronuclear inject to create transgenic organism.
Blolistics or Gene Gun: This is the technique of shooting the foreign gene or DNA into plant cell. It can also use in animal cell but mostly it is used for plant cells. Helium gas filled in the chamber of gum to treat pressure. RNA or DNA are coated with heavy metal such as gold. sliver or tungsten that make DNA stable for long time, target cell is prepare in Dish under the gun. When DNA gun fire it hits the cell with DNA coated with gold particles. There particles propelled through the screen into target cell. Hence the gum fire at the clusture of cell and recombinant DNA enter the cell.
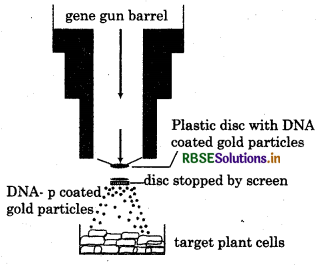
Question 6.
What are bioreactors?
Or
Define downstream processing and name the bioactive molecule produced by Trichnodema Polysp run and Monascus purpureus.
Or
How has the development of bioreactor helped in biotechnology?
Or
Name the most commonly used bioreactors in biotechnology lab. Mention the most essential components. Result in the production of large volume of desirable protein.
Or
Draw a well labelled diagram of commonly used bioreactor.
Answer:
Bioreactors: Bioreactors can refers to any device or machine that are biologically active and can grow cell, tissue in optimised. Conditions where the large volume upto (100 - 1000) litres can cultured. When the raw material have to be added and it performs bioprocess engineering. Processing done with biological agents such as cells, enzymes and antibodies, with the optimum growth conditions such as temperature, pH, nutrients concentration, oxygen level are also required at last we get products at large scale, which can also withdraw in small amount time to time.
Down streaming Process: This is the final stage where the biotransformants or biosynthesised products has to be pour out and converted into more useful form. This include the separation aryl purification of product like liquid - liquid extraction, distillation, drying and must be added preservatives. If the product has to be go for the drugs formation. Then it has to face many clinical trials for its validity. After many kinds of testing finally our product is ready for marketing. Most commonly used bioreactors are stirring type. They are biological active and have 100 to 1000 leters of volume at a time.
Continuous Culture System: The continuous culture system carry material as a flowing stream. Bioreactors can produce large amount of product continuously because they are designed like that where the used medium is drained out from one side while the fresh raw materials can be added continuously from the another side so we get larger biomass leading high yield of product.
Question 7.
What is recombinant DNA? Explain the process of separation and isolation of DNA fragment by gel electrophoresis techniques.
Answer:
The process of inserting new genes or information into existing DNA - RNA through host in order to modify a specific, novel organism with desired character, technique called recombinant DNA technique and newly formed DNA having new genes on it, called recombinant DNA.
The key tools used in recombinant DNA technology are -
- Enzymes
- Restriction Enzymes: Hind II, EcoRI, EcoRI I, Smal, EcoR V are most commonly used restriction enzymes. That cut the DNA at specific sit.
- Ligase: Responsible for the joining of cut ends.
- Protease: Degrade the proteins present along with DNA eg. Histone.
- Cloning Vectors: Plasmids and bacteriophages are used as cloning vector because they have ability to replicate.
- Competent Host: Competent host cells are able to take up foreign DNA it.
For gel electrophoresis technique: The gel is filled in an electrophoresis chamber and connected to electricity most commonly used gel as a medium are agarose gel. Which obtained from sea weeds and a natural polymer. Agarose gels are easily to cast and handled and give samples more easily. The agarose gels are conveniently stored in a plastic bag in refrigerators. A buffer solution also provide to gel electrophoresis with the planty of ions that can carry current. Amplified DNA added to the gel wall and when the current passes, the DNA fragments got separated according to their size in the form of DNA Bands. When the process completed these bands are stained through gel and arranged according to their size by sieving effect.
Hence, the smaller and shorter molecules move faster to the anode then longer piece of DNA and arranged in a line. When the electrophoresis is complete the molecules in the gel are not visualise. These molecules has to be stained to make them visible using ethidium bromide and also expose to the UV light. When the bands are visualised they are physically cut with the gel and extracted from the gel piece. This process is known as elution and we have the pure DNA fragment with desired gene to construct recombinant DNA.
Question 8.
Define biotechnology? Mentioning all steps and explain only first two steps of recombinant DNA technology in detail. Give diagrammatic representation of recombinant DNA technology.
Answer:
Biology and technology combine together to form biotechnology so it is technology that make our life comfortable and easy. “The application of scientific and engineering principles to processing of genetic material (i.e. DNA) by biological agents (i.e. Bacteria).” More simply it is using living organisms to make useful products for the welfare of human beings.
Biotechnology programs combine multiple areas of science and technology with the research and development of numerous type of living organism or enzymes to produce useful products in wide variety of fields, including but not limited to agriculture, engineering virology, tissue culture, bio medicine, forensics, food productions etc.
Basically two techniques are used to alters and manipulate genes used in Morden biotechnology are:
- Genetic Engineering: Which is done with the genetic material to alters is original chemical structure into its desire structure.
- Bioprocess Engineering: Which create a atmosphere which allow to grow microorganism in large quantities to produce vaccines, enzymes, hormones etc.
Steps of Recombinant DNA technology are:
- Isolation of the genetic material.
- Cutting of DNA at specific location.
- Amplification of gene of interest using PCR.
- Insertion of recombinant DNA into the Host cell.
- Obtaining the foreign gene product.
- Downstream processing.
1. Isolation of the genetic material: We know all organism contain, nucleic acid as a genetic material. In majority of cases there is genetic material is DNA and some viruses are found in it as RNA genetic material in addition to DNA. Whenever we prepared for recombinant DNA for that we first have to take that DNA out of cell, taking out from the cell to DNA is called isolation of DNA. For that we have to break the cell wall or membrane of cell in which genetic material enclosed along with the genetic material other macromolecules such RNA, protein, lipids also come out from the cell.
Cell wall or membrane are usually digested by certain enzymes, that break down the cell wall from which we want to take desired gene. Virus, bacteria, fungi and plants cells have different composition of cell membrane. So different type of enzymes act on different organism, for example, in case of bacteria, cell wall is made up of peptidoglycon. They are digested or break by lysozymes. Fungi cell wall is made up of chitine which digested by chitinase. Similarly plant cell wall are digested by cellulase enzyme.
2. Cutting of DNA at specific location: Now we have the long strands isolated from desired organism , but we have to cut out desirable gene from DNA strand. This is done by restriction enzyme. That enzyme have dual role, firstly it cut DNA into small segments near the cloning site and álso create sticky ends. Still we don’t have our ckt irable gene, for that we have to separate all DNA fragments by the gel electrophororis.
That we have already discuss about its mechanism, due to the negatively charged DNA, it moves towares the positive electrode and from the bonds creates in this process, we separate our desired gene treatment of restriction enzyme also he done with the vector DNA to make a cut where desired gene has to be inverted or paste and we got circular DNA in the form of linear DNA molecules with sticky ends where desirable gene pasted with the keep of ligase enzyme. As we have already discussed that DNA ligase fill the gaps b/w two nucleotide on a strand of DNA and this is how get a molecule of recombinant DNA.
